Open Chest Maze Procedure
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW:
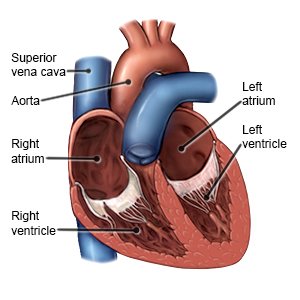
An open chest maze procedure is heart surgery done to treat atrial fibrillation.
 |
HOW TO PREPARE:
The week before your surgery:
- Arrange to have someone drive you home after surgery.
- Tell your surgeon about all medicines you currently take. He or she will tell you if you need to stop any medicine for surgery, and when to stop. He or she will tell you which medicines to take or not take on the day of surgery.
- You may need to have an EKG, electrophysiologic studies (EPS), and blood tests.
The night before your surgery:
You may be told not to eat or drink anything after midnight.
The day of your surgery:
- You or a close family member will be asked to sign a legal document called a consent form. It gives healthcare providers permission to do the procedure or surgery. It also explains the problems that may happen, and your choices. Make sure all your questions are answered before you sign this form.
- Take only the medicines your surgeon told you to take.
- An IV will be put into a vein. You may get medicine or liquids through the IV.
- An anesthesiologist will talk to you before your surgery. You may need medicine to keep you asleep or numb an area of your body during surgery. Tell healthcare providers if you or anyone in your family has had a problem with anesthesia in the past.
WHAT WILL HAPPEN:
What will happen:
- A tube will be used to keep your airway open and help you breathe. An incision will be made in the center of your breastbone or in your chest wall. You will be connected to a heart-lung bypass machine that does the work of your heart and lungs during surgery.
- Your surgeon will work on your heart to make a new heartbeat pathway that is shaped like a maze. You will be taken off of the heart-lung bypass machine, allowing your heart and lungs to work on their own.
- Wires may be put into your chest that improve your heartbeat. The incision in your chest will be closed with wire and stitches.
After your surgery:
You will be taken to a room to rest until you are fully awake. Healthcare providers will monitor you closely for any problems. Do not get out of bed until your healthcare provider says it is okay. When your healthcare provider sees that you are okay, you may be able to go home or be taken to your hospital room.
CONTACT YOUR HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IF:
- You have a fever.
- You get a cold or the flu.
- You have questions or concerns about your surgery.
Seek Care Immediately if
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
- You have any of the following signs of a stroke:
- Numbness or drooping on one side of your face
- Weakness in an arm or leg
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Dizziness, a severe headache, or vision loss
Risks
You may bleed more than expected and need more surgery. Your body may hold onto too much fluid, or your kidneys may fail. You may have swelling of your heart or other tissues. Your heart may not work as it should after surgery. You may need a permanent pacemaker. You may continue to have atrial fibrillation for several months after your surgery. You may develop a life-threatening blood clot.
Related medications
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
