Macular Edema
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Macular edema
is swelling from fluid buildup in the macula. The macula is the central part of the retina (thin membrane lining the inside of the back of the eye). The macula helps you see objects clearly and in full detail and color.
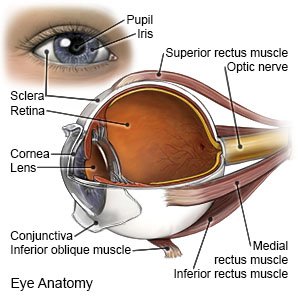 |
Common signs and symptoms of macular edema:
- Blurred or wavy vision
- Vision that gets worse over time
- Objects look different sizes when you look at them with each eye
- Seeing colors as faded or not as bright as before
- Loss of vision in the center of the eye that causes problems with reading or other activities
Seek care immediately if:
- You suddenly lose vision in one or both eyes.
Related medications
Call your doctor or ophthalmologist if:
- You have new or increased vision problems.
- You have new or increased eye pain when you are in bright light, such as sunlight.
- Your symptoms prevent you from doing your daily activities.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment
depends on the cause of your macular edema. You may need any of the following:
- Medicines may be injected to lower the swelling or reverse the effects of the swelling.
- Eye drops that contain NSAIDs or steroids help lower the swelling.
- Laser treatment is used for edema caused by a condition such as diabetes.
- Surgery may be used to remove fluid from part of your eye.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Protect your vision:
- Get an eye exam as often as directed. Adults age 40 to 64 should have an eye exam every 2 to 4 years. Adults age 65 and older should get an eye exam every 1 to 2 years. You may need more regular eye exams if you have diabetic retinopathy. Early diagnosis and treatment of eye problems may prevent permanent vision damage.
- Manage health conditions that can cause vision problems. Common examples include diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. Follow up with healthcare providers who manage these conditions.
- Wear sunglasses with UVA and UVB protection. Ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun can damage your eyes and increase your risk for vision loss.
- Eat foods that contain eye-healthy nutrients. Healthy nutrients include vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, omega-3 fatty acids, lutein, and zeaxanthin. They can be found in foods such as spinach, peanuts, salmon, collard greens, avocados, squash, eggs, and blueberries. Ask your healthcare provider for a full list of foods that contain eye-healthy nutrients. You may also need to take a vitamin or supplement to help you get enough of these nutrients.
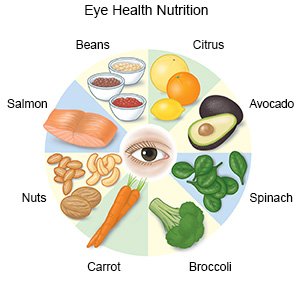
- Do not smoke. Nicotine can damage blood vessels in your eyes. Do not use e-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco in place of cigarettes or to help you quit. They still contain nicotine. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit.
Follow up with your doctor or ophthalmologist as directed:
You may need ongoing tests or treatment, depending on the cause of your macular edema. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
