How to Use A Metered-Dose Inhaler
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
A metered-dose inhaler
is a handheld device that gives you a dose of medicine as a mist. You breathe the medicine deep into your lungs to open your airways.
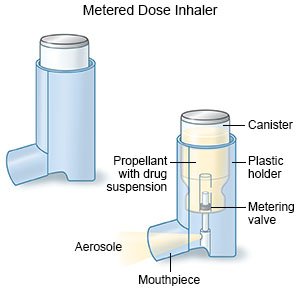 |
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US), or have someone call if:
- Your lips or nails turn blue or gray.
Seek immediate care if:
- You cough up blood.
- The skin between your ribs or around your neck pulls in with every breath.
- You feel short of breath, even after you use your inhaler.
Related medications
Call your doctor if:
- You feel the medicine spray on your tongue or throat, rather than going into your lungs.
- You have to take more puffs from the inhaler than directed, in order to get relief.
- You run out of medicine before your next refill is due.
- You feel like your medicine is not making your symptoms better.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
How to use a metered-dose inhaler:
Follow the instructions that come with your inhaler. Your medicine will work best if you use the inhaler correctly. The following steps will help you use your inhaler correctly:
- Remove the cap. Check to make sure nothing is in the mouthpiece that could block the medicine from coming out.
- Shake the inhaler to mix the medicine. Hold the inhaler upright. Prime the inhaler as directed.
- Breathe out fully. Do not breathe out into the mouthpiece.
- Place the mouthpiece between your lips. Close your lips tightly around the mouthpiece to form a seal and prevent a medicine leak.
- Breathe in slowly through your mouth as you press down on the canister. Breathe in for 5 seconds.
- Hold your breath for at least 5 seconds. This helps the medicine get deep into your lungs.
- Remove the mouthpiece from your mouth. Breathe out slowly.
- Repeat puffs of medicine as directed by your healthcare provider. Wait 1 minute between puffs.
- Rinse your mouth with water or saline. Do not swallow the water or saline.
Care for your inhaler properly:
Put the cap back on the inhaler after each use to keep the mouthpiece clean. Clean the inhaler at least 1 time each week, or as directed. Read and follow the cleaning instructions that come with your inhaler.
Follow up with your doctor or specialist as directed:
Bring your inhaler to all of your visits. You may be asked to use your inhaler at these visits so your doctor or specialist can make sure you are using it correctly. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
