How to Change A Catheter Drainage Bag
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What do I need to know about a Foley catheter drainage bag?
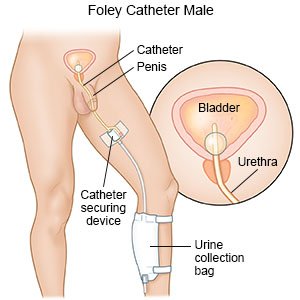
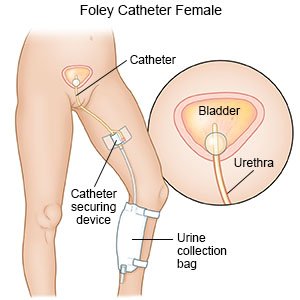
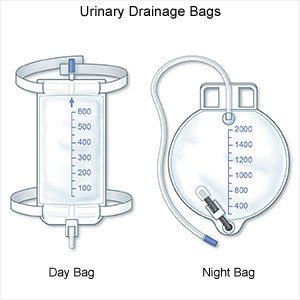
A Foley catheter is a sterile tube that is inserted into your bladder to drain urine. It is also called an indwelling urinary catheter. The tip of the catheter has a small balloon filled with solution that holds the catheter in your bladder. The catheter is attached to a drainage bag that holds the urine. A large drainage bag is usually used during the night. A leg bag can be worn under your clothes during the day. The leg bag is worn around your calf or thigh. It allows you to be in public without anyone knowing you have a catheter.
 |
 |
How can I attach or remove the drainage bag?
You use the same steps to attach or remove a large drainage bag and a leg bag.
- Gather supplies:
- Large drainage bag
- Clean leg bag
- A clean towel
- Alcohol pads
-
- Wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.

- Empty the drainage bag. Do not touch the tip against the container or the toilet as you empty the urine.
- Place the clean towel under the connection between the catheter tube and the drainage bag tubing. The towel will catch urine that may leak out of the tubing.
- Pinch and hold the catheter tubing. Disconnect the tubing from the bag by using a twisting motion. Be careful not to pull on the catheter. Place the disconnected bag on the towel.
- Clean the tip of the tubing on the bag to be connected. Use an alcohol pad. Start at the tip and clean towards the bag. You may have to hold the bag tubing in the same hand as the pinched catheter tubing while you are cleaning the tip. Do not allow the tip to touch the catheter tubing.
- Connect the bag tubing to the catheter tubing. Place the tip into the catheter tubing with a twisting motion until it is securely connected.
- Use straps to fasten the bag to your calf if you are attaching a leg bag. You may need to tape the catheter tubing to your thigh. Be careful not to pull the catheter tubing tight. Damage can be done to your urethra and bladder.
- Wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
What else do I need to know about drainage bags?
- Wash your hands with soap and water before and after emptying the drainage bag.
- Empty your drainage bag when it is half full throughout the day. The bag may leak if it gets too full. Also, empty the large drainage bag when you wake in the morning or from a nap.
- Make sure to clamp or twist the drainage bag closed after emptying.
- Put a cap on the end of the connection tubing to prevent germs in the tubing.
How can I prevent problems with my catheter and drainage bag?
- Drink liquids as directed. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you. Liquids will help flush your kidneys and bladder to help prevent infection.
- Check for kinks in the tubing and straighten them out.
- Check the tape or strap used to secure the catheter tube to your skin. Make sure it is not blocking the tube.
- Make sure you are not sitting or lying on the tubing.
- Make sure the urine bag is hanging below the level of your waist.
Related medications
When should I call my doctor?
- Your catheter comes out.
- You have a fever.
- You have material that looks like sand in the tubing or drainage bag.
- You see blood in the tubing or drainage bag.
- You see a layer of crystals inside the tubing.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
