Erythroblastosis Fetalis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is erythroblastosis fetalis?
Erythroblastosis fetalis is a condition that causes your unborn baby's red blood cells (RBCs) to break down. This may cause severe anemia (low RBC count). Anemia makes it difficult for the RBCs in your baby's blood to carry enough oxygen to his or her body. This condition is also called hemolytic disease of the newborn. Hemolysis means breaking down RBCs.
What causes erythroblastosis fetalis?
Certain differences in blood type can cause this condition. One type happens because you are Rh negative (Rh-) and your baby is Rh positive (Rh+). Another type happens because you and your baby have different major blood types. A, B, and O are the 3 major blood types. Erythroblastosis fetalis is most common when the mother's blood type is O and the baby's blood type is A or B. The differences in blood type causes your immune system to react by making antibodies. The antibodies can cross over to your baby through the placenta. They attack your baby's RBCs, causing them to break down.
What are the signs and symptoms of erythroblastosis fetalis?
- Before your baby is born:
- Fast heart rate
- Larger than normal organs, such as the heart, liver, or spleen
- Swelling of your baby's body
- After your baby is born:
- Pale skin caused by anemia
- Jaundice (yellowing of your baby's skin or the whites of his or her eyes)
- Small red or brown spots, or purple patches on your baby's skin
- Swelling of your baby's body
- Trouble breathing
How is erythroblastosis fetalis diagnosed?
Healthcare providers will need to know if you have past pregnancies, abortions, miscarriages, or any blood transfusions. You or your baby may need any of the following tests:
- Blood tests are used to check your blood type and Rh type, and to look for antibodies. Providers may want to test the blood of the baby's father for ABO and Rh type. Your baby's blood type, RBCs, Rh type, and bilirubin levels may also be checked. Bilirubin is made when RBCs break down. It is usually removed from the body through bowel movements. A high bilirubin level in your baby can be a sign of erythroblastosis fetalis. Your baby may need more blood tests after he or she is born.
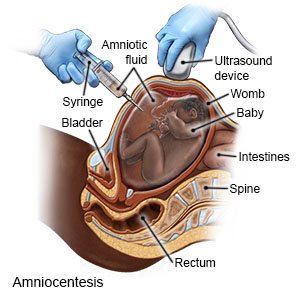
- Amniocentesis is a procedure done during pregnancy. It is used to check for problems in your amniotic fluid (fluid around your baby), such as increased bilirubin level. Healthcare providers take a fluid sample by putting a needle through your skin into your uterus (womb). The sample will then be sent to a lab for tests. This test may be repeated to monitor your baby's risk of anemia.
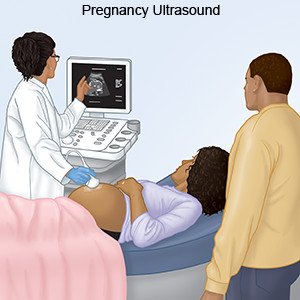
- Ultrasound uses sound waves to show pictures of your baby inside your uterus. Healthcare providers can learn the age of your baby and see how fast he or she is growing. The ultrasound shows your baby's movement, heart rate, and organs. Your placenta and amniotic fluid may be checked. A Doppler ultrasound may be used to see the blood flow. Providers may use this test to check if your baby has anemia.
How is erythroblastosis fetalis treated?
- Before your baby is born:
- Blood transfusions may be given to your baby through the umbilical cord.
- Preterm delivery means your baby may need to be born earlier than expected.
- After your baby is born:
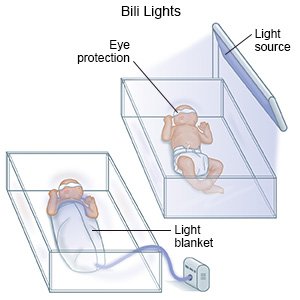
- Phototherapy uses light to turn bilirubin into a form that your newborn's body can remove. One or more lights will be placed above your baby. He or she will be placed on his or her back to absorb the most light. Your baby may also lie on a flexible light pad. His or her healthcare provider may wrap him or her in the light pad. Eye covers are used to protect your baby's eyes from the light.
- Immune globulin is medicine to help keep your baby's RBCs from being damaged by your antibodies. This treatment may help prevent the need for an exchange transfusion.
- An exchange transfusion is a procedure that removes the antibodies that are attacking RBCs and some of the bilirubin. Small portions of your baby's blood will be removed and replaced with donor blood. This procedure may need to be done more than 1 time.
- Phototherapy uses light to turn bilirubin into a form that your newborn's body can remove. One or more lights will be placed above your baby. He or she will be placed on his or her back to absorb the most light. Your baby may also lie on a flexible light pad. His or her healthcare provider may wrap him or her in the light pad. Eye covers are used to protect your baby's eyes from the light.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can erythroblastosis fetalis be prevented?
- Get your blood type checked before you get pregnant. You can also have it checked during your first prenatal visit. You may need more tests if you have been pregnant before or had blood transfusions. Healthcare providers may screen your blood for antibodies to other blood types. Providers may also want to test the baby's father's blood. Healthcare providers may also do a test to see if your blood reacts to your baby's blood.
- You may be given Rh factor immune globulin if you and your baby have different Rh blood types. This medicine is given to prevent erythroblastosis fetalis. This medicine may be given while you are pregnant and after you give birth.
Related medications
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- Your baby is having a seizure.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your baby has jaundice that does not go away or gets worse.
- Your baby has shortness of breath.
- Your baby is very irritable, fussy, and has a high-pitched cry.
- Your baby looks very tired or weak, or sleeps more than usual.
When should I call a doctor?
- Before your baby is born:
- You feel your baby is moving less or is not moving at all.
- You develop a fever.
- After your baby is born:
- Your baby develops a fever.
- Your baby develops jaundice.
- Your baby is not feeding well or is urinating less than before.
- You have breastfeeding problems.
- By his or her fourth day of life, your breastfeeding baby has either of the following:
- Fewer than 4 to 6 wet diapers in a period of 24 hours.
- Fewer than 3 to 4 bowel movements in a period of 24 hours.
- You have questions or concerns about your baby's condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your baby's care. Learn about your baby's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your baby's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your baby. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
