Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
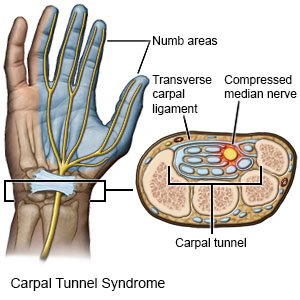
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a condition that causes pressure to build in the carpal tunnel. The carpal tunnel is a small area between bones and tissues in your wrist. Swelling in this area puts pressure on the median nerve. The median nerve controls muscles and feeling in the hand.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Seek care immediately if:
- You suddenly lose feeling in your hand or fingers and you cannot move them.
- Your hand suddenly changes color.
Call your doctor if:
- Your symptoms get worse.
- Your hand and fingers are so weak that you cannot grab, squeeze, or lift items.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Medicines:
- NSAIDs help decrease swelling and pain or fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Manage CTS:
- Apply ice to your wrist. Ice helps decrease swelling and pain in your wrist. Ice may also help prevent tissue damage. Use an ice pack, or put crushed ice in a plastic bag. Cover the ice pack with a towel. Place it on your wrist for 15 to 20 minutes every hour, or as directed.
- Rest your hands. Let your hands rest for a short time between repetitive motions, such as typing. If you feel pain, stop what you are doing and gently massage your wrist and hand.
- Go to physical and occupational therapy, if directed. Physical therapists will show you ways to exercise and strengthen your wrist. Occupational therapists will show you safe ways to use your wrist while you do your usual activities.
- Use a wrist splint as directed. A splint will keep your wrist straight or in a slightly bent position. A wrist splint decreases pressure on the median nerve by letting your wrist rest. You may need to wear the splint for up to 8 weeks. You may need to wear it at night.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
