Cardiac Stress Test
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
What you need to know about a cardiac stress test:
A cardiac stress test shows how healthy your heart is and how well your heart works during stress. Your heart may be placed under stress with medicine or exercise. This test may also be called an exercise stress test or a cardiac exercise test. Plan for up to 90 minutes for prep time and the test.
How to prepare for a cardiac stress test:
- Your healthcare provider will talk to you about how to prepare for your test. Your provider may tell you not to eat, drink, or smoke for up to 4 hours before the test.
- Tell your provider about all your current medicines. Your provider will tell you if you need to stop any medicine for the test, and when to stop. Your provider will tell you which medicines to take or not take on the day of your test.
- Wear comfortable shoes and clothes that you can exercise in to your test.
- Bring an inhaler with you if you normally use one during exercise.
What will happen during a cardiac stress test:
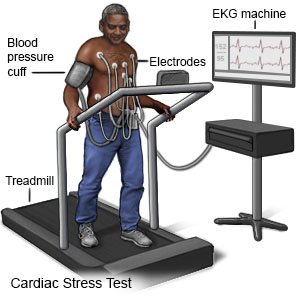
A healthcare provider will place electrodes (sticky patches) on your chest. Hair may be shaved to help them stick. Wires connect the electrodes to a computer. The computer records your heart's electrical activity. You may have a blood pressure cuff on your arm to monitor your blood pressure. Providers may also measure your blood oxygen level. You may be asked to breathe into a tube during the test. This will show how well you are able to breathe during exercise. If you are going to get medicine during the test, a provider will insert an IV. A provider will monitor your heart rate, heart rhythm, and blood pressure during the test.
- During a cardiac stress test with exercise, you will be asked to walk on a treadmill or pedal on a stationary bicycle. The exercise will get harder during the test. You will exercise until your heart rate has reached a certain level, or you start to have certain signs and symptoms. These include shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, or an abnormal blood pressure or heart rhythm.
- During a cardiac stress test with medicine, your provider will inject medicine through your IV. This medicine will make your heart beat faster and work harder. You may have the same symptoms as with the exercise test. These symptoms should stop when your provider stops giving you medicine. Tell your provider if you have severe chest pain or dizziness. Other medicine may be given to treat severe chest pain or dizziness.
What to expect after a cardiac stress test:
You will sit or lie down. Your breathing, blood pressure, and heart rate will be monitored for several minutes. Your IV will be removed if you had one. You can return to your usual activities after the test, or as directed.
Risks of a cardiac stress test:
You may have low blood pressure during or right after the test. This can cause you to feel dizzy or faint. You may have an abnormal heart rhythm. These risks usually go away after the test is complete. A heart attack is possible but rare.
Related medications
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US), or have someone call if:
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
Seek care immediately if:
- You feel weak, dizzy, or faint.
Call your doctor if:
- You have nausea or are vomiting.
- Your skin is itchy, swollen, or you have a rash.
- You have pain, redness, or swelling in the area where the medicine was injected.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Heart-healthy tips:
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause heart and lung damage. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your provider before you use these products.
- Create an exercise plan with your healthcare provider. Do not begin an exercise plan before you talk to your provider. Exercise helps to lower high cholesterol, blood sugar, and high blood pressure. It can also help you maintain a healthy weight.

- Maintain a healthy weight. Ask your provider what a healthy weight is for you. Your provider can help you create a weight loss plan, if needed. A weight loss of 10% can improve your heart health.
- Eat heart-healthy foods. Include fresh fruits and vegetables in your meal plan. Choose low-fat foods, such as skim or 1% fat milk, low-fat cheese and yogurt, fish, chicken (without skin), and lean meats. Eat two 4-ounce servings of fish high in omega-3 fats each week, such as salmon, fresh tuna, and herring. Do not eat foods that are high in sodium, such as canned foods, potato chips, salty snacks, and cold cuts. Put less table salt on your food.

- Limit or do not drink alcohol. Ask your provider if it is okay for you to drink alcohol and how much is okay to drink. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
