Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
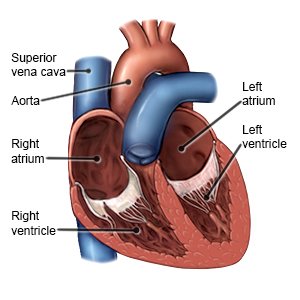
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is a procedure used to treat problems with how your heart beats. CRT is also called biventricular pacing. The 2 upper chambers of the heart are called atria. The 2 lower chambers are called ventricles. Your heartbeat is synchronized when all areas of your heart beat together properly. When the areas of your heart do not beat as they should, your heart cannot pump enough blood and oxygen to your body. You may have trouble breathing, tire easily, and have swelling in your legs and feet.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have any of the following signs of a heart attack:
- Squeezing, pressure, or pain in your chest
- You may also have any of the following:
- Discomfort or pain in your back, neck, jaw, stomach, or arm
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lightheadedness or a sudden cold sweat
- You feel like your heart is fluttering or jumping.
Call your doctor or cardiologist if:
- You have new or increased swelling in your legs or feet.
- You feel more tired than usual.
- You have trouble breathing during activity.
- Your procedure area is red, warm, swollen, or draining pus.
- You have a fever.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Related medications
Medicines:
- Heart medicine may be given to help your heart beat strongly and regularly. Ask your healthcare provider for more information about heart medicines.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Device safety:
Some electrical devices may interfere with how your pacemaker works. Some examples are cell phones, security systems, power cables, and electric monitors. Ask your healthcare provider how long you can be near these devices, and which devices to avoid. Tell healthcare providers you have a pacemaker before you have a procedure or surgery.
Procedure area care:
Care for the area as directed. You may need to wash the area with soap and water. Dry the area and put on new, clean bandages as directed. Change your bandages when they get wet or dirty.
Follow up with your doctor or cardiologist as directed:
You will need to return to have your pacemaker checked. You may also need tests to check the leads in your heart. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
