Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
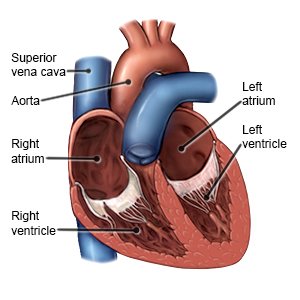
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is a procedure used to treat problems with how your heart beats. CRT is also called biventricular pacing. The 2 upper chambers of the heart are called atria. The 2 lower chambers are called ventricles. Your heartbeat is synchronized when all areas of your heart beat together properly. When the areas of your heart do not beat as they should, your heart cannot pump enough blood and oxygen to your body. You may have trouble breathing, tire easily, and have swelling in your legs and feet.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Before your procedure:
- Informed consent is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
- An IV is a small tube placed in your vein that is used to give you medicine or liquids.
- General anesthesia will keep you asleep and free from pain during the procedure. You may get anesthesia through your IV. You may breathe it in through a mask or a tube placed down your throat. The tube may cause you to have a sore throat when you wake up.
During your procedure:
- A small incision will be made over a vein near your neck. An x-ray may be used to help guide your healthcare provider during the procedure. An electrode catheter holding 3 leads will be inserted through the incision. The catheter and leads are guided into your heart. The catheter records the activity of your heart to help your provider decide where to place the leads.
- If any of the leads cannot be placed through your vein, they may be placed through your chest. Your provider will make 3 or 4 small cuts on your left side, between your ribs. The leads will be placed directly on your heart. After the leads are placed, a pacemaker will be secured under the skin on your chest. The pacemaker will help your heart beat correctly. Your incisions will be closed with stitches or medical glue.
Related medications
After your procedure:
You will be taken to a room to rest until you are fully awake. Healthcare providers will monitor you closely for any problems. Do not get out of bed until your healthcare provider says it is okay. You will then be taken to your hospital room.
RISKS:
- You may need a large chest incision if the leads cannot be placed through your vein or small cuts. The activity of the pacemaker may make it hard for you to breathe at times. Your heart, blood vessels, and the area around them may be damaged. You may have abnormal heartbeats, and your heart may stop beating. Blood may collect around your heart, making it hard for your heart to beat. This can be life-threatening.
- You may get an infection around the pacemaker implant. The leads in your heart may move out of place. The leads may not be in the right position to synchronize your heartbeats. The pacemaker may not work properly.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
