Vinorelbine: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: vinorelbine tartrate
Dosage form: injection, solution
Drug class: Mitotic inhibitors
J Code (medical billing code): J9390 (Per 10 mg, injection)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 21, 2024.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- References
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
VINORELBINE injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1994
Indications and Usage for Vinorelbine
Vinorelbine Dosage and Administration
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Vinorelbine Injection: 10 mg per 1 mL and 50 mg per 5 mL in single-dose vial (3)
Contraindications
None (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hepatic Toxicity: Monitor hepatic function prior to initiation and during treatment (5.2)
- Severe constipation and bowel obstruction, including necrosis and perforation, occur. Institute a prophylactic bowel regimen to mitigate potential constipation, bowel obstruction and/or paralytic ileus (5.3)
- Extravasation can result in severe tissue injury, local tissue necrosis and/or thrombophlebitis. Immediately stop vinorelbine and institute recommended management procedures (5.4)
- Neurologic Toxicity: Severe sensory and motor neuropathies occur. Monitor patients for new or worsening signs and symptoms of neuropathy. Discontinue for Grade 2 or greater neuropathy (5.5)
- Pulmonary toxicity and respiratory failure occur. Interrupt vinorelbine in patients who develop unexplained dyspnea or have any evidence of pulmonary toxicity. Permanently discontinue for confirmed interstitial pneumonitis or ARDS (5.6)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of potential risk to the fetus and to use effective contraception (5.7, 8.1, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 20%) are leukopenia, neutropenia, anemia, increased aspartate aminotransferase, nausea, vomiting, constipation, asthenia, injection site reaction and peripheral neuropathy (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sagent Pharmaceuticals at 1-866-625-1618 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Inhibitors of CYP3A4: May cause earlier onset and/or increased severity of adverse reactions (7.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 9/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Vinorelbine
Vinorelbine Injection is indicated:
- In combination with cisplatin for first-line treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
- As a single agent for the treatment of patients with metastatic NSCLC
2. Vinorelbine Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
In Combination with Cisplatin 100 mg/m2
- The recommended dosage of Vinorelbine Injection is 25 mg/m2 administered as an intravenous injection or infusion over 6 to 10 minutes on Days 1, 8, 15 and 22 of a 28-day cycle in combination with cisplatin 100 mg/m2 on Day 1 only of each 28-day cycle.
2.2 Dosage Modifications
Myelosuppression
Hold or decrease the dose of Vinorelbine Injection in patients with decreased neutrophil counts according to the following schema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]:
| Neutrophils on Day of Treatment (cells/mm3) | Percentage of Starting Dose of Vinorelbine Injection |
| ≥ 1,500 | 100% |
| 1,000 to 1,499 | 50% |
| < 1,000 | Do not administer Vinorelbine Injection. Repeat neutrophil count in one week. If three consecutive weekly doses are held because neutrophil count is < 1,000 cells/mm3, discontinue Vinorelbine Injection |
| Note: For patients who experience fever and/or sepsis while neutrophil count is < 1,500 cells/mm3 or had 2 consecutive weekly doses held due to neutropenia, subsequent doses of Vinorelbine Injection should be: | |
| > 1,500 | 75% |
| 1,000 to 1,499 | 37.5% |
| < 1,000 | Do not administer Vinorelbine Injection. Repeat neutrophil count in one week. |
Hepatic Impairment/Toxicity
Reduce Vinorelbine Injection dose in patients with elevated serum total bilirubin concentration according to the following schema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]:
| Serum Total Bilirubin Concentration (mg/dl) | Percentage of Starting Dose of
Vinorelbine Injection |
| ≤ 2.0 | 100% |
| 2.1 to 3.0 | 50% |
| > 3.0 | 25% |
Concurrent Myelosuppression and Hepatic Impairment/Toxicity
In patients with both myelosuppression and hepatic impairment/toxicity, administer the lower of the doses based on the corresponding starting dose of Vinorelbine Injection determined from the above schemas.
Neurologic Toxicity
Discontinue Vinorelbine Injection for Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Grade 2 or higher peripheral neuropathy or autonomic neuropathy causing constipation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
2.3 Preparation and Administration
Preparation
Dilute Vinorelbine Injection in an intravenous bag to a concentration between 0.5 mg/mL and 2 mg/mL. Use one of the following recommended solutions for dilution:
- 5% Dextrose Injection, USP
- 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
- 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
- 5% Dextrose and 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP
- Ringer's Injection, USP
- Lactated Ringer's Injection, USP
Stability and Storage Conditions of Diluted Solutions
Diluted Vinorelbine Injection may be used for up to 24 hours under normal room light when stored in polyvinyl chloride bags at 5° to 30°C (41° to 86°F).
Administration
Administer diluted Vinorelbine Injection over 6 to 10 minutes into the side port of a free-flowing intravenous line followed by flushing with at least 75 to 125 mL of one of the solutions.
Vinorelbine Injection must only be administered intravenously. It is extremely important that the intravenous needle or catheter be properly positioned before any Vinorelbine Injection is injected.
Parenteral drug products should be visually inspected for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. If particulate matter is seen, Vinorelbine Injection should not be administered.
Management of Suspected Extravasation
- If Vinorelbine Injection leakage into surrounding tissue occurs or is suspected, immediately stop administration of Vinorelbine Injection and initiate appropriate management measures in accordance with institutional policies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
2.4 Procedures for Proper Handling and Disposal
Vinorelbine Injection is a cytotoxic drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures1.
Exercise caution in handling and preparing the solution of Vinorelbine Injection. The use of gloves is recommended. If the solution of Vinorelbine Injection contacts the skin or mucosa, immediately wash the skin or mucosa thoroughly with soap and water.
Avoid contamination of the eye with Vinorelbine Injection. If exposure occurs, flush the eyes with water immediately and thoroughly.
Discard unused portion.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Vinorelbine Injection, USP: 1 mL (10 mg per 1 mL) and 5 mL (50 mg per 5 mL) clear colorless to pale yellow solution in single-dose vial.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Myelosuppression
Myelosuppression, manifested by neutropenia, anemia and thrombocytopenia, occur in patients receiving vinorelbine as a single agent and in combination with cisplatin [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)]. Neutropenia is the major dose-limiting toxicity with vinorelbine. Grade 3-4 neutropenia occurred in 53% of patients treated with vinorelbine at 30 mg/m2 per week. Dose adjustment due to myelosuppression occurred in 51% of patients (Study 2). In clinical trials with vinorelbine administered at 30 mg/m2 per week, neutropenia resulted in hospitalizations for pyrexia and/or sepsis in 8% of patients. Death due to sepsis occurred in 1% of patients. Neutropenia nadirs occur between 7 and 10 days after dosing with neutropenia count recovery usually occurring within the following 7 to 14 days.
Monitor complete blood counts prior to each dose of vinorelbine. Do not administer vinorelbine to patients with neutrophil counts <1,000 cells/mm3. Adjustments in the dosage of vinorelbine should be based on neutrophil counts obtained on the day of treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.2 Hepatic Toxicity
Drug-induced liver injury manifest by elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and bilirubin occur in patients receiving vinorelbine as a single agent and in combination with cytotoxic agents. Assess hepatic function prior to initiation of vinorelbine and periodically during treatment. Reduce the dose of vinorelbine for patients who develop elevations in total bilirubin ≥ 2 times upper limit of normal [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
5.3 Severe Constipation and Bowel Obstruction
Severe and fatal paralytic ileus, constipation, intestinal obstruction, necrosis, and perforation occur in patients receiving vinorelbine. Institute a prophylactic bowel regimen to mitigate potential constipation, bowel obstruction and/or paralytic ileus, considering adequate dietary fiber intake, hydration and routine use of stool softeners.
5.4 Extravasation and Tissue Injury
Extravasation of vinorelbine can result in severe irritation, local tissue necrosis and/or thrombophlebitis. If signs or symptoms of extravasation occur, immediately stop administration of vinorelbine and institute recommended management procedures [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.5 Neurologic Toxicity
Sensory and motor neuropathies, including severe neuropathies, occur in patients receiving vinorelbine. Monitor patients for new or worsening signs and symptoms of neuropathy, such as paresthesia, hyperesthesia, hyporeflexia and muscle weakness while receiving vinorelbine. Discontinue vinorelbine for CTCAE Grade 2 or greater neuropathy [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.6 Pulmonary Toxicity and Respiratory Failure
Pulmonary toxicity, including severe acute bronchospasm, interstitial pneumonitis, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) occur in patients receiving vinorelbine. Interstitial pneumonitis and ARDS included fatalities. The mean time to onset of interstitial pneumonitis and ARDS after vinorelbine administration was one week (range 3 to 8 days) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Interrupt vinorelbine in patients who develop unexplained dyspnea or have any evidence of pulmonary toxicity. Permanently discontinue vinorelbine for confirmed interstitial pneumonitis or ARDS.
5.7 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, vinorelbine can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies in mice and rabbits, embryo and fetal toxicity were observed with administration of vinorelbine at doses approximately 0.33 and 0.18 times the human therapeutic dose, respectively.
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with vinorelbine and for 6 months after the final dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with vinorelbine and for 3 months after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hepatic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Severe Constipation and Bowel Obstruction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Extravasation and Tissue Injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Neurologic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Pulmonary Toxicity and Respiratory Failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under varying designs and in different patient populations, the adverse reaction rates reported in one clinical trial may not be easily compared to those rates reported in another clinical trial and may not reflect the rates actually observed in clinical practice.
Single Agent
The data below reflect exposure to vinorelbine as a single agent administered at a dose of 30 mg/m2 on a weekly basis to 365 patients enrolled in 3 controlled studies for metastatic NSCLC and advanced breast cancer. The population included 143 patients with previously untreated metastatic NSCLC (Study 3) who received a median of 8 doses of vinorelbine. The patients were aged 32 to 79 (median 61 years), 71% were male, 91% White, 48% had adenocarcinoma histology. The data also reflect exposure to vinorelbine in 222 patients with previously treated advanced breast cancer who received a median of 10 doses of vinorelbine. Vinorelbine is not indicated for the treatment of breast cancer.
Selected adverse reactions reported in these studies are provided in Tables 1 and 2. The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) of single agent vinorelbine were leukopenia, neutropenia, anemia, increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST), nausea, vomiting, constipation, asthenia, injection site reaction and peripheral neuropathy. The most common (≥ 5%) Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions were neutropenia, leukopenia, anemia, increased total bilirubin, increased AST, injection site reaction and asthenia.
Approximately 49% of patients with NSCLC who were treated with vinorelbine experienced at least one dose reduction due to an adverse reaction.
Thirteen percent of patients discontinued vinorelbine due to adverse reactions. The most frequent adverse reactions leading to vinorelbine discontinuation were asthenia, dyspnea, nausea, constipation, anorexia, myasthenia and fever.
|
*Grade based on modified criteria from the National Cancer Institute version 1. |
|||
|
†Patients with NSCLC had not received prior chemotherapy. The majority of the remaining patients had received prior chemotherapy. |
|||
| All Patients
(N=365) (%) | NSCLC
(N=143) (%) |
||
| Laboratory | |||
| Hematologic | |||
| Neutropenia | < 2,000 cells/mm3 | 90 | 80 |
| < 500 cells/mm3 | 36 | 29 | |
| Leukopenia | < 4,000 cells/mm3 | 92 | 81 |
| < 1,000 cells/mm3 | 15 | 12 | |
| Thrombocytopenia | < 100,000 cells/mm3 | 5 | 4 |
| Anemia | < 11 g/dl | 83 | 77 |
| < 8 g/dl | 9 | 1 | |
| Hospitalizations due to neutropenic complications | 9 | 8 | |
|
*Grade based on modified criteria from the National Cancer Institute version 1. |
||||
|
†Patients with NSCLC had not received prior chemotherapy. The majority of the remaining patients had received prior chemotherapy. |
||||
|
‡ Incidence of paresthesia plus hypesthesia. |
||||
| All Grades | Grade 3-4 | |||
| All Patients
(%) | NSCLC
(%) | All Patients
(%) | NSCLC
(%) |
|
| Laboratory | ||||
| Hepatic | ||||
| AST increased (N=346) | 67 | 54 | 6 | 3 |
| Bilirubin increased (N=351) | 13 | 9 | 7 | 5 |
| Clinical | ||||
| Nausea | 44 | 34 | 2 | 1 |
| Asthenia | 36 | 27 | 7 | 5 |
| Constipation | 35 | 29 | 3 | 2 |
| Injection site reaction | 28 | 38 | 2 | 5 |
| Injection site pain | 16 | 13 | 2 | 1 |
| Neuropathy peripheral‡ | 25 | 20 | <2 | 1 |
| Vomiting | 20 | 15 | 2 | 1 |
| Diarrhea | 17 | 13 | 1 | 1 |
| Alopecia | 12 | 12 | ≤1 | 1 |
| Phlebitis | 7 | 10 | <1 | 1 |
| Dyspnea | 7 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
Myelosuppression: In clinical trials, Grade 3-4 neutropenia, anemia and thrombocytopenia occurred in 69%, 9% and 1%, respectively of patients receiving single agent vinorelbine. Neutropenia is the major dose-limiting toxicity.
Neurotoxicity: Neurotoxicity was most commonly manifested as constipation, paresthesia, hyperesthesia and hyporeflexia. Grade 3 and 4 neuropathy was observed in 1% of the patients receiving single agent vinorelbine.
Injection Site Reactions: Injection site reactions, including erythema, pain at injection site and vein discoloration, occurred in approximately one third of patients; 5% were severe. Phlebitis (chemical phlebitis) along the vein proximal to the site of injection was reported in 10% of patients.
Cardiovascular Toxicity: Chest pain occurred in 5% of patients; myocardial infarction occurred in ˂0.1% of patients.
Pulmonary Toxicity and Respiratory Failure: Dyspnea (shortness of breath) was reported in 3% of patients; it was severe in 2%. Interstitial pulmonary changes were documented.
Other: Hemorrhagic cystitis and the syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion were each reported in <1% of patients.
In Combination with Cisplatin
Table 3 presents the incidence of selected adverse reactions, occurring in ≥10% of vinorelbine treated patients reported in a randomized trial comparing the combination of vinorelbine 25 mg/m2 administered every week of each 28-day cycle and cisplatin 100 mg/m2 administered on day 1 of each 28-day cycle versus cisplatin alone at the same dose and schedule in patients with previously untreated NSCLC (Study 1).
Patients randomized to vinorelbine plus cisplatin received a median of 3 cycles of treatment and those randomized to cisplatin alone received a median of 2 cycles of treatment. The incidence of Grade 3 and 4 neutropenia was significantly higher in the vinorelbine plus cisplatin arm (82%) compared to the cisplatin alone arm (5%).
Thirty-five percent of the eligible patients in the combination arm required treatment discontinuation due to an adverse reaction compared to 19% in the cisplatin alone arm.
Four patients in the vinorelbine plus cisplatin arm died of neutropenic sepsis. Seven additional deaths were reported in the combination arm: 2 from cardiac ischemia, 1 cerebrovascular accident, 1 multisystem failure due to an overdose of vinorelbine and 3 from febrile neutropenia.
|
*Graded according to the standard SWOG criteria version 1. |
||||
|
†Categorical toxicity grade not specified |
||||
| Vinorelbine 25mg/m2
plus
Cisplatin 100 mg/m2 (N=212) | Cisplatin 100 mg/m2
(N=210) |
|||
| All Grades
(%) | Grades 3-4
(%) | All Grades
(%) | Grades 3-4
(%) |
|
| Laboratory | ||||
| Hematologic | ||||
| Neutropenia | 89 | 82 | 26 | 5 |
| Anemia | 89 | 24 | 72 | <8 |
| Leukopenia | 88 | 58 | 31 | <1 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 29 | 5 | 21 | <2 |
| Febrile neutropenia† | N/A | 11 | N/A | 0 |
| Renal | ||||
| Blood creatinine increased | 37 | 4 | 28 | <5 |
| Clinical | ||||
| Malaise/Fatigue/Lethargy | 67 | 12 | 49 | 8 |
| Vomiting | 60 | 13 | 60 | 14 |
| Nausea | 58 | 14 | 57 | 12 |
| Decreased appetite | 46 | 0 | 37 | 0 |
| Constipation | 35 | 3 | 16 | 1 |
| Alopecia | 34 | 0 | 14 | 0 |
| Weight decreased | 34 | 1 | 21 | <1 |
| Fever without infection | 20 | 2 | 4 | 0 |
| Hearing impaired | 18 | 4 | 18 | <4 |
| Injection site reaction | 17 | <1 | 1 | 0 |
| Diarrhea | 17 | <3 | 11 | <2 |
| Paraesthesia | 17 | <1 | 10 | <1 |
| Taste alterations | 17 | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| Peripheral numbness | 11 | 2 | 7 | <1 |
| Myalgia/Arthralgia | 12 | <1 | 3 | <1 |
| Phlebitis/Thrombosis/Embolism | 10 | 3 | <1 | <1 |
| Weakness | 12 | <3 | 7 | 2 |
| Infection | 11 | <6 | <1 | <1 |
| Respiratory tract infection | 10 | <5 | 3 | 3 |
Table 4 presents the incidence of selected adverse reactions, occurring in ≥10% of vinorelbine treated patients reported in a randomized trial of vinorelbine plus cisplatin, vindesine plus cisplatin and vinorelbine as a single agent in patients with stage III or IV NSCLC who had not received prior chemotherapy. A total of 604 patients received either vinorelbine 30 mg/m2 every week plus cisplatin 120 mg/m2 on Day 1 and Day 29, then every 6 weeks thereafter (N=207), vindesine 3 mg/m2 for 6 weeks, then every other week thereafter plus cisplatin 120 mg/m2 on Days 1 and Day 29, then every 6 weeks thereafter (N=193) or vinorelbine 30mg/m2 every week (N=204).
Patients randomized to vinorelbine plus cisplatin received a median of 15 weeks of treatment, vindesine plus cisplatin 12 weeks and vinorelbine received 13 weeks. Grade 3 and 4 neutropenia was significantly greater in the vinorelbine plus cisplatin arm (78%) compared to vindesine plus cisplatin (48%) and vinorelbine as a single agent (53%). Neurotoxicity, including peripheral neuropathy and constipation, was reported in 44% (Grade 3-4, 7%) of the patients receiving vinorelbine plus cisplatin, 58% (Grade 3-4, 17%) of the patients receiving vindesine and cisplatin and 44% (Grade 3-4, 8.5%) of the patients receiving vinorelbine as a single agent.
Study discontinuation due to an adverse reaction was required in 27, 22 and 10% of the patients randomized to vinorelbine plus cisplatin, vindesine plus cisplatin and cisplatin alone arms, respectively.
|
* Grade based on criteria from the World Health Organization (WHO). |
||||||
|
† N=194 to 207; all patients receiving vinorelbine/cisplatin with laboratory and non-laboratory data. |
||||||
|
‡ N=173 to 192; all patients receiving vindesine/cisplatin with laboratory and non-laboratory data. |
||||||
|
§ N=165 to 201; all patients receiving vinorelbine with laboratory and non-laboratory data. |
||||||
|
¦ Categorical toxicity grade not specified. |
||||||
|
¶ Neurotoxicity includes peripheral neuropathy and constipation. |
||||||
| Vinorelbine/Cisplatin† | Vindesine/Cisplatin‡ | Vinorelbine§ | ||||
| All Grades
(%) | Grades 3-4
(%) | All Grades
(%) | Grades 3-4
(%) | All Grades
(%) | Grades 3-4
(%) |
|
| Laboratory | ||||||
| Hematologic | ||||||
| Neutropenia | 95 | 78 | 79 | 48 | 85 | 53 |
| Leukopenia | 94 | 57 | 82 | 27 | 83 | 32 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 15 | 4 | 10 | 3.5 | 3 | 0 |
| Renal | ||||||
| Blood creatinine increased¦ | 46 | N/A | 37 | N/A | 13 | N/A |
| Clinical | ||||||
| Nausea/Vomiting | 74 | 30 | 72 | 25 | 31 | 2 |
| Alopecia | 51 | 7.5 | 56 | 14 | 30 | 2 |
| Neurotoxicity¶ | 44 | 7 | 58 | 17 | 44 | 8.5 |
| Diarrhea | 25 | 1.5 | 24 | 1 | 12 | 0.5 |
| Injection site reaction | 17 | 2.5 | 7 | 0 | 22 | 2 |
| Ototoxicity | 10 | 2 | 14 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of vinorelbine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Infections: pneumonia
Immune system disorders: anaphylactic reaction, pruritus, urticaria, angioedema
Nervous system disorders: loss of deep tendon reflexes, muscular weakness, gait disturbance, headache
Ear and labyrinth disorders: vestibular disorder, hearing impaired
Cardiac disorders: tachycardia
Respiratory disorders: pulmonary edema
Vascular disorders: pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, hypertension, hypotension, flushing, vasodilatation
Gastrointestinal disorders: mucosal inflammation, dysphagia, pancreatitis
Skin disorders: generalized cutaneous reactions (rash), palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: jaw pain, myalgia, arthralgia
General disorders and administration site conditions: injection site rash, urticaria, blistering, sloughing of skin
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications: radiation recall phenomenon, dermatitis, esophagitis
Laboratory abnormalities: electrolyte imbalance including hyponatremia
Other: tumor pain, back pain, abdominal pain
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], vinorelbine can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Available human data are insufficient to inform the drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal reproduction studies in mice and rabbits, embryo and fetal toxicity were observed with administration of vinorelbine at doses approximately 0.33 and 0.18 times the human therapeutic dose, respectively (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies are 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In a mouse embryo-fetal development study, administration of a single dose of vinorelbine at a dose level of 9 mg/m2 or greater (approximately 0.33 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area) was embryotoxic and fetotoxic. Vinorelbine was embryotoxic and fetotoxic to pregnant rabbits when administered every 6 days during the period of organogenesis at doses of 5.5 mg/m2 (approximately 0.18 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area) or greater. At doses that did not cause maternal toxicity in either species, vinorelbine administration resulted in reduced fetal weight and delayed ossification.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of vinorelbine in human milk or its effects on the breastfed infant or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from vinorelbine, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with vinorelbine and for 9 days after the final dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating vinorelbine [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Females
Vinorelbine can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with vinorelbine and for 6 months after the final dose.
Males
Vinorelbine may damage spermatozoa [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. Advise males with female sexual partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with vinorelbine and for 3 months after the final dose.
Males
Based on animal findings, vinorelbine may impair fertility in males [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of vinorelbine in pediatric patients have not been established.
Results from a single-arm study of vinorelbine administered at the dose of 33.75 mg/m2 (for 35 patients) or at the dose of 30 mg/m2 (for 11 patients) every week for 6 weeks followed by 2 weeks of rest were evaluated (courses of 8 weeks). Forty-six patients age 1 to 25 (median 11 years) with recurrent solid malignant tumors, including rhabdomyosarcoma or undifferentiated sarcoma (N=21 patients), neuroblastoma (N= 4 patients) and central nervous system (CNS) tumors (N=21 patients), were enrolled. The most significant grade 3 or 4 hematological adverse reactions were neutropenia (70%) and anemia (33%). The most significant grade 3 or 4 non-hematological adverse reactions were motor (15%) or cranial (13%) neuropathy, hypoxia (13%) and dyspnea (11%). Objective tumor response was observed in 2 out of 21 patients with rhabdomyosarcoma or undifferentiated sarcoma. No objective tumor response was observed in patients with CNS tumors (N=21) or neuroblastoma (N=4).
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 769 number of patients who received vinorelbine as a single agent and in combination with cisplatin in studies 1, 2 and 3, 247 patients were 65 years of age or older. No overall differences in safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetic parameters were observed between these patients and younger patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
The influence of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of vinorelbine has not been evaluated, but the liver plays an important role in the metabolism of vinorelbine. Elevated AST occurs in >60% of the patients receiving vinorelbine as a single agent (6% Grade 3-4). Therefore, exercise caution in patients with hepatic impairment. Reduce the dose of vinorelbine for patients with elevated serum total bilirubin concentrations [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
10. Overdosage
There is no known antidote for overdoses of vinorelbine. Overdoses involving quantities up to 10 times the recommended dose (30 mg/m2) have been reported. The adverse reactions described were consistent with those listed in the ADVERSE REACTIONS section, including paralytic ileus, stomatitis and esophagitis. Bone marrow aplasia, sepsis and paresis have also been reported. Fatalities have occurred following overdose of vinorelbine. If overdosage occurs, general supportive measures together with appropriate blood transfusions, growth factors and antibiotics should be instituted as deemed necessary by the physician.
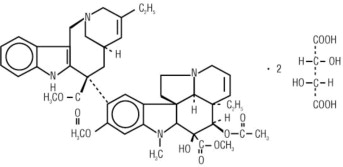
11. Vinorelbine Description
Vinorelbine Injection, USP contains vinorelbine, a semi-synthetic vinca alkaloid. The molecular formula for vinorelbine tartrate is C45H54N4O8•2C4H6O6. It has a molecular weight of 1079.11. The structural formula is as follows:
Vinorelbine tartrate is a white to light yellow amorphous powder. It is easily soluble in water, very soluble in methanol and practically insoluble in hexane.
Vinorelbine Injection, USP is a sterile nonpyrogenic aqueous solution for intravenous use. Each milliliter of solution contains 10 mg vinorelbine (equivalent to 13.85 mg vinorelbine tartrate) in Water for Injection, USP. The pH of Vinorelbine Injection, USP is approximately 3.5.
12. Vinorelbine - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Vinorelbine is a vinca alkaloid that interferes with microtubule assembly. The antitumor activity of vinorelbine is thought to be due primarily to inhibition of mitosis at metaphase through its interaction with tubulin. Vinorelbine may also interfere with: 1) amino acid, cyclic AMP and glutathione metabolism, 2) calmodulin-dependent Ca++-transport ATPase activity, 3) cellular respiration, and 4) nucleic acid and lipid biosynthesis. Vinorelbine inhibited mitotic microtubule formation in intact mouse embryo tectal plates at a concentration of 2 μM inducing a blockade of cells at metaphase, but produced depolymerization of axonal microtubules at a concentration 40 μM, suggesting a modest selectivity of vinorelbine for mitotic microtubules.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of vinorelbine were studied in 49 patients who received doses of 30 mg/m2 administered as 15- to 20-minute constant-rate infusions. Vinorelbine concentrations in plasma decay in a triphasic manner.
Distribution
Steady-state volume of distribution (VSS) values range from 25.4 to 40.1 L/kg. Vinorelbine demonstrated high binding to human platelets and lymphocytes. The free fraction was approximately 0.11 in human plasma over a concentration range of 234 to 1169 ng/mL. The binding to plasma constituents in cancer patients ranged from 79.6% to 91.2%. Vinorelbine binding was not altered in the presence of cisplatin, fluorouracil, or doxorubicin.
Elimination
The terminal phase half-life averages 27.7 to 43.6 hours and the mean plasma clearance ranges from 0.97 to 1.26 L/hr/kg.
Metabolism
Vinorelbine undergoes substantial hepatic elimination in humans, with large amounts recovered in feces. Two metabolites of vinorelbine have been identified in human blood, plasma and urine; vinorelbine N-oxide and deacetylvinorelbine. Deacetylvinorelbine has been demonstrated to be the primary metabolite of vinorelbine in humans and has been shown to possess antitumor activity similar to vinorelbine. Therapeutic doses of vinorelbine (30 mg/m2) yield very small, if any, quantifiable levels of either metabolite in blood or urine. The metabolism of vinorelbine is mediated by hepatic CYP3A.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The carcinogenic potential of vinorelbine has not been studied. Vinorelbine has been shown to affect chromosome number and possibly structure in vivo (polyploidy in bone marrow cells from Chinese hamsters and a positive micronucleus test in mice). It was not mutagenic in the Ames test and gave inconclusive results in the mouse lymphoma TK Locus assay.
Vinorelbine did not affect fertility to a statistically significant extent when administered to rats on either a once-weekly (9 mg/m2, approximately one third the human dose) or alternate-day schedule (4.2 mg/m2, approximately 0.14 times the human recommended dose) prior to and during mating. In male rats, administration of vinorelbine twice weekly for 13 or 26 weeks at dose levels of 2.1 and 7.2 mg/m2 (approximately 0.07 and 0.24 times the recommended human dose), respectively, resulted in decreased spermatogenesis and prostate/seminal vesicle secretion.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Combination Use with Cisplatin
The safety and efficacy of vinorelbine in combination with cisplatin was evaluated in two randomized, multicenter trials.
Cisplatin 100mg/m2
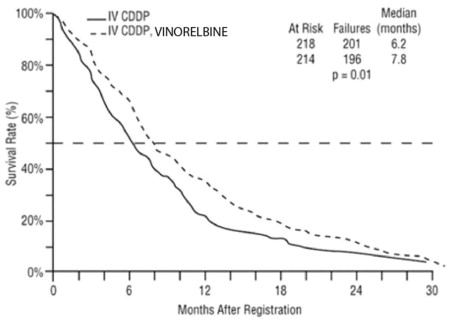
Study 1 was a randomized, multicenter, open-label trial of vinorelbine plus cisplatin and cisplatin alone for the treatment of stage IV or stage IIIb NSCLC in patients with malignant pleural effusion or multiple lesions in more than one lobe of the ipsilateral lung who had not received prior chemotherapy. A total of 432 patients were randomized 1:1 to receive either vinorelbine 25 mg/m2 on Day 1 then every week of each 28-day cycle plus cisplatin 100 mg/m2 administered on Day 1 of each 28-day cycle (N=214) or single agent cisplatin 100 mg/m2 on Day 1 of each 28-day cycle (N=218).
Patient demographics and disease characteristics were similar between arms. Of the overall study population, the median age was 64 (range 33 to 84), 66% were male, 80% were White, 92% had stage IV disease and 8% stage IIIB, 53% had adenocarcinoma, 21% squamous cell, 14% large cell histology. The major efficacy outcome measure was overall survival. The efficacy results are presented in Table 7 and Figure 1.
| Vinorelbine plus Cisplatin (N=214) | Cisplatin (N=218) |
|
| Overall Survival | ||
| Median Survival in months (95% CI) | 7.8 (6.9, 9.6) | 6.2 (5.4, 7.7) |
| Unstratified log-rank p-value | 0.01 | |
| Overall Response rate (ORR) | ||
| Evaluable patients ORR (95% CI) | N=206 19% (14%, 25%) | N=209 8% (5%, 13%) |
| Chi-square test p-value | <0.001 | |
Figure 1: Overall Survival Vinorelbine / Cisplatin versus Single Agent Cisplatin
Cisplatin 120mg/m2
Study 2 was a randomized, 3-arm, open-label, multicenter trial of vinorelbine plus cisplatin, vindesine plus cisplatin and vinorelbine as a single agent for the treatment of patients with stage III or IV NSCLC who had not received prior chemotherapy. The study was conducted in Europe. A total of 612 patients were randomized 1:1:1 to receive vinorelbine 30 mg/m2 every week of a 6-week cycle plus cisplatin 120 mg/m2 on Day 1 and Day 29, then every 6 weeks thereafter (N=206); and vindesine 3 mg/m2 for 6 weeks, then every other week thereafter plus cisplatin 120 mg/m2 on Days 1 and Day 29, then every 6 weeks thereafter (N=200) or vinorelbine 30mg/m2 every week of a 6-week cycle (N=206). The main efficacy outcome measure was to compare overall survival between vinorelbine plus cisplatin and vindesine plus cisplatin. The other efficacy outcome measure was to compare overall survival in the better of the two combination regimens to that of vinorelbine as a single agent.
Patient demographics were in general similar between arms: the median age of the overall population was 60 years (range 30 to 75), 90% were male, 78% had WHO performance status of 0 or 1. Tumor characteristics were in general similar with the exception of histologic subtype of NSCLC. Adenocarcinoma was the histologic subtype in 32% of patients in the vinorelbine plus cisplatin arm, 40% of patients in vindesine plus cisplatin arm and 28% of patients on the vinorelbine arm. Ten percent of the patients had stage IIIA disease, 28% stage IIIB and 50% stage IV. Twelve percent of the patients had received prior surgery or radiotherapy.
The efficacy results of Study 2 are presented in Table 8.
|
1n/a = not applicable |
|||
| Vinorelbine (N=206) | Vinorelbine plus cisplatin (N=206) | Vindesine plus cisplatin (N=200) |
|
| Median survival in
months (99.5% CI) | 7.2 (5.4, 9.1) | 9.2 (7.4, 11.1) | 7.4 (6.1, 9.1) |
| Unstratified log-rank p-value | n/a1 | 0.087 | |
| 0.05 | n/a | ||
| Overall Response (ORR) Evaluable Patients ORR (95% CI) |
N=205 14% (10%, 20%) |
N=203 28% (22%, 35%) |
N=198 19% (14%, 25%) |
| Chi-square test p-value | n/a | 0.03 | |
| < 0.001 | n/a | ||
14.2 Single Agent
The safety and efficacy of vinorelbine as a single agent was evaluated in one randomized multicenter trial. Study 3 was a randomized, open-label clinical trial of vinorelbine or fluorouracil (FU) plus leucovorin (LV) in patients with Stage IV NSCLC who had not received prior chemotherapy. A total of 211 patients were randomized 2:1 to receive vinorelbine 30 mg/m2 weekly of an 8-week cycle (N=143) or FU 425 mg/m2 bolus intravenously plus LV 20 mg/m2 bolus intravenously daily for 5 days of a 4-weeks cycle (N=68).
Patient demographics and disease characteristics were in general similar between arms. In the overall population, the median age was 61 years (range 32 to 83), 74% were male, 88% were White, 46% had adenocarcinoma histology. Fifty percent of the patients had Karnofsky performance status ≥ 90 in the vinorelbine arm compared to 38% in the FU/LV arm.
The primary efficacy outcome of the study was overall survival. The median survival time was 30 weeks versus 22 weeks for patients receiving vinorelbine versus FU/LV, respectively (p=0.06). Partial objective responses were observed in 11.1% (95% CI=6.2%, 17.9%) and 3.5% (95% CI=0.4%, 11.9%) of patients who received vinorelbine and FU/LV, respectively.
16. How is Vinorelbine supplied
Vinorelbine Injection, USP is supplied as follows:
| Vinorelbine Injection, USP | ||
| NDC | (10 mg per mL) | Package Factor |
| 25021-204-01 | 10 mg per mL Single-Dose Vial | 1 vial per carton |
| 25021-204-05 | 50 mg per 5 mL Single-Dose Vial | 1 vial per carton |
Vinorelbine Injection, USP is a clear, colorless to pale yellow aqueous solution.
Storage Conditions
Store refrigerated between 2° and 8°C (36° and 46°F).
Do not freeze.
Protect from light. Retain in carton until time of use.
Discard unused portion.
Unopened vials of Vinorelbine Injection, USP are stable at 25°C (77°F) for up to 72 hours. Store diluted solutions of Vinorelbine Injection, USP at 5° to 30°C (41° to 86°F) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Vinorelbine Injection, USP is a cytotoxic drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures.1
Sterile, Nonpyrogenic, Preservative-free.
The container closure is not made with natural rubber latex.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Myelosuppression
Advise patients to contact a healthcare provider for new onset fever, or symptoms of infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Constipation and Bowel Obstruction
Advise patients to follow a diet rich in fibers, drink fluids to stay well hydrated and use stool softeners to avoid constipation. Contact a health care provider for severe constipation, new onset abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Neurologic Toxicity
Advise patients to contact a health care provider for new onset or worsening of numbness, tingling, decrease sensation or muscle weakness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Pulmonary Toxicity
Advise patients to contact a healthcare provider for new onset or worsening of shortness of breath, cough, wheezing or other new pulmonary symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
- Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Vinorelbine Injection and for 6 months after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Vinorelbine Injection and for 3 months after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3) and Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with Vinorelbine Injection and for 9 days after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Advise males of reproductive potential that Vinorelbine Injection may impair fertility [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
SAGENT®
Mfd. for SAGENT Pharmaceuticals
Schaumburg, IL 60195 (USA)
Made in China
©2023 Sagent Pharmaceuticals
Revised: September 2023
SAGENT Pharmaceuticals®
| VINORELBINE
vinorelbine injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Sagent Pharmaceuticals (080579617) |
More about vinorelbine
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Latest FDA alerts (1)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: mitotic inhibitors
- Breastfeeding
- En español