Kyxata: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: carboplatin
Dosage form: injection
Drug class: Alkylating agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 16, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- References
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
KYXATATM (carboplatin) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2003
WARNING: HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS, INCLUDING ANAPHYLAXIS
- Serious and life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, can occur with KYXATA within minutes of administration during any cycle. (5.1)
- Immediately withhold KYXATA for severe hypersensitivity reactions and administer appropriate treatment for management of the hypersensitivity reaction. (5.1)
Indications and Usage for Kyxata
Kyxata Dosage and Administration
- Initial Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Carcinoma:
- KYXATA 300 mg/m2-OR-AUC of 4 mg/mL∙min to 6 mg/mL∙min intravenously in combination with cyclophosphamide on Day 1 every 4 weeks for each cycle. (2.2)
- Administer up to six cycles or until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs. (2.2)
- Recurrent Advanced Ovarian Carcinoma as a Single Agent:
KYXATA 360 mg/m2-OR- AUC of 4 mg/mL∙min to 6 mg/mL∙min intravenously on Day 1 every 4 weeks for each cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs. (2.2)
- Avoid contact of carboplatin with aluminum parts. (2.5)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Injection: 20 mg/2 mL (10 mg/mL), 80 mg/8 mL (10 mg/mL), and 500 mg/50 mL (10 mg/mL) in multiple-dose vial. (3)
Contraindications
- None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Myelosuppression: Myelosuppression (leukopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia) can cause severe or fatal infections or hemorrhage. Monitor complete blood counts prior to each treatment cycle, and as clinically indicated. If myelosuppression occurs, modify KYXATA dosage. (5.2)
- Nausea and Vomiting: Administer pre-treatment and post-treatment antiemetics as clinically indicated. (5.3)
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Peripheral neuropathy, including paresthesia, can occur in patients treated with KYXATA. Monitor for signs and symptoms of peripheral neuropathy and modify the dosage of KYXATA based on severity. (5.4)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.5, 8.1, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Most common adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, in patients with advanced ovarian cancer who received KYXATA in combination with cyclophosphamide (≥30%) are leukopenia, neutropenia, nausea and vomiting, anemia, thrombocytopenia, hypomagnesemia, other gastrointestinal adverse reactions, alopecia, asthenia, and pain. (6.1)
- Most common adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, in patients with recurrent ovarian cancer who received KYXATA as a single agent (≥30%) are nausea and vomiting, anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, hyponatremia, hypomagnesemia, hyperphosphatasemia, and hypocalcemia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Avyxa Pharma, LLC at 1-888-520-0954 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Aminoglycosides: Avoid concomitant use with aminoglycosides. (7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 9/2025
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS, INCLUDING ANAPHYLAXIS
- Serious and life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, can occur with KYXATA within minutes of administration during any cycle.
- Immediately discontinue KYXATA for severe hypersensitivity reactions and administer appropriate treatment for management of the hypersensitivity reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Kyxata
2. Kyxata Dosage and Administration
2.1 Premedication and Supportive Medications
Administer KYXATA in a setting where cardiopulmonary resuscitation medication and equipment are available [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Premedicate patients with antiemetics prior to each infusion of KYXATA for the prevention of nausea and vomiting. Continue antiemetics following infusion as needed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage
Initial Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Carcinoma with Cyclophosphamide
- KYXATA 300 mg/m2-OR-AUC of 4 mg/mL∙min to 6 mg/mL∙min* intravenously in combination with cyclophosphamide 600 mg/m2intravenously on Day 1 every 4 weeks for each cycle.
*Carboplatin Dose (mg) = Target Area Under the Curve (AUC) (mg/mL/min) x (GFR + 25). Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is commonly calculated as estimated creatinine clearance (CLcr) using the Cockroft-Gault formula.
- Administer up to six cycles or until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
Refer to cyclophosphamide prescribing information for additional information.
For older adults, calculate the dose based on AUC to reduce risk of severe adverse reactions.
Individualize the dose and dosing schedule of KYXATA based on the specific regimen administered, response to treatment, and patient risk factors [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)].
Secondary Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Carcinoma as a Single Agent
- KYXATA 360 mg/m2-OR- AUC of 4 mg/mL∙min to 6 mg/mL∙min* intravenously on Day 1 every 4 weeks for each cycle until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs.
* Carboplatin Dose (mg) = Target AUC (mg/mL/min) x (GFR + 25). GFR is commonly calculated as estimated creatinine clearance (CLcr) using the Cockroft-Gault formula.
For older adults, calculate the dose based on AUC to reduce risk of severe adverse reactions.
Individualize the dose and dosing schedule of KYXATA based on response to treatment and patient risk factors [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)].
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
For a patients administered a dose based on body surface area as a single agent or combination, dosage modifications are shown in Table 1.
Monitor complete blood counts prior to treatment, weekly during treatment, and as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
| Adverse Reaction
| Severity
| Dosage Modification
|
| Neutropenia
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | Grade ≥ 4 ANC ≤ 0.5 x 109 / L | ● Interrupt KYXATA until ≤ Grade 1. ● Reduce dose by 25% |
| Thrombocytopenia
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | Grade ≥ 3 Platelet count ≤ 50 x 109 / L | ● Interrupt KYXATA until ≤ Grade 1. ● Reduce dose by 25% |
2.4 Dosage Recommendations for Patients with Renal Impairment
For patients administered a dose based on AUC, no dose modification is recommended for renal impairment.
For patients administered a dose based on body surface area, the recommended doses for renal impairment are described in Table 2 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. A recommended dose has not been established for patients with creatinine clearance <16 mL/min.
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min)
| Recommended Dose on Day 1
|
| 60 to 89 | No dose reduction |
| 41 to 59 | 250 mg/m2
|
| 16 to 40 | 200 mg/m2
|
2.5 Preparation and Administration
KYXATA is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable handling and disposal procedures.1
Do not use needles or intravenous infusion sets containing aluminum; aluminum reacts with carboplatin causing precipitate formation and a loss of potency.
Visually inspect KYXATA vials prior to use. Discard solution if particulate matter or discoloration are observed.
KYXATA is supplied as a multiple-dose vial. After first use, store the partially used vial in the original carton at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) and then discard after 28 days.
- Withdraw the calculated dose of KYXATA from the vial.
- Prior to administration, KYXATA can be further diluted to concentrations as low as 0.5 mg/mL with 5% Dextrose Injection, USP or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Diluted carboplatin solution for infusion when prepared as directed in an infusion bag should be used immediately, but may be stored at room temperature (20°C to 25°C) for a maximum of 8 hours. Discard KYXATA infusion solution 8 hours after dilution.
Administer KYXATA by intravenous infusion over 30 to 60 minutes.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 20 mg/2 mL (10 mg/mL), 80 mg/8 mL (10 mg/mL), and 500 mg/50 mL (10 mg/mL) available as clear to pale yellow solution in multiple-dose vials.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity, including anaphylaxis, can occur in patients treated with KYXATA. Hypersensitivity reactions occurred in 2% of patients treated with carboplatin and included rash, urticaria, erythema, pruritus, bronchospasm, and hypotension. These adverse reactions may occur within minutes of administration and during any cycle. There is an increased risk of allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, in patients previously exposed to platinum-based therapy or after 6 cycles of carboplatin [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor patients receiving KYXATA for hypersensitivity reactions. Ensure supportive equipment and medications are available to treat severe hypersensitivity reactions. Severe hypersensitivity reactions may require immediate discontinuation of KYXATA.
5.2 Myelosuppression
Myelosuppression (leukopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia) is dose-dependent may be severe, and can cause fatal infections or hemorrhage in patients treated with KYXATA.
Grade 3–4 neutropenia occurred in 16% of the patients treated with carboplatin as a single agent. Grade 3-4 thrombocytopenia occurred in 25% of patients with ovarian cancer. Febrile neutropenia may occur. Blood product transfusions were required in 26% (44% of pretreated) of patients with ovarian cancer treated with carboplatin as a single agent. Infectious and hemorrhagic complications each occurred in 5% of the patients treated with carboplatin as a single agent. Fatal adverse reactions occurred in less than 1% of patients treated with carboplatin as a single agent.
Patients with impaired kidney function are at increased risk of severe myelosuppression and may require dosage modifications [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Monitor complete blood counts prior to each cycle and as clinically indicated. If myelosuppression occurs, modify KYXATA dosage when required [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Nausea and Vomiting
KYXATA can induce emesis, which can be more severe in patients previously receiving emetogenic therapy, and is dose-dependent. Administer pre-treatment and post-treatment antiemetics as clinically indicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Monitor and manage patients with antiemetics, or fluid replacement, as clinically indicated. Consider withholding or delaying KYXATA if nausea or vomiting is severe or intolerable and is not responsive to antiemetics.
5.4 Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, including paresthesia, can occur in patients treated with KYXATA.
Peripheral neuropathy occurred in 4% of patients receiving carboplatin as a single agent (6% of pretreated patients with ovarian cancer). Peripheral neuropathy occurred in 10% of patients older than 65 who were previously treated with carboplatin.
Prolonged treatment, treatment with other platinum-containing therapies, or use in combination with other drugs that cause peripheral neuropathy may increase the incidence or severity of peripheral neuropathy.
Monitor for signs and symptoms of peripheral neuropathy. Withhold, reduce, or discontinue KYXATA depending on the severity and persistence of peripheral neuropathy as clinically indicated.
5.5 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings in animals and its mechanism of action, KYXATA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. Administration of carboplatin to pregnant rats caused adverse developmental outcomes, including embryo-fetal lethality and structural abnormalities.
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with KYXATA and for 6 months after the last dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with KYXATA and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1,8.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Nausea and Vomiting [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Peripheral Neuropathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Initial Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Cancer
The safety of KYXATA in combination with cyclophosphamide for initial treatment of advanced ovarian cancer was evaluated in two randomized controlled studies conducted by NCIC and SWOG [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Patients in the carboplatin arm received carboplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide and patients in the active-comparator arm received cisplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide.
Tables 3 and 4 summarize the adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities in the NCIC study, respectively.
|
* Values are in percent of evaluable patients. |
||
| Adverse Reaction
| Carboplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide (N=224)
(%)* | Cisplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide (N=223)
(%)* |
| Gastrointestinal (GI)
|
||
| Nausea and vomiting | 93 | 98 |
| Vomiting | 84 | 97 |
| Other GI adverse reactions | 50 | 62 |
| Mucositis | 10 | 9 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue
|
||
| Alopecia | 50 | 62 |
| General
|
||
| Asthenia | 40 | 33 |
| Pain | 36 | 37 |
| Cardiovascular | 15 | 19 |
| Infection | 14 | 12 |
| Hypersensitivity | 12 | 9 |
| Hemorrhage | 10 | 4 |
| Genitourinary | 10 | 10 |
| Respiratory | 8 | 9 |
| Neurologic
|
||
| Central neurotoxicity | 28 | 40 |
| Peripheral neuropathies | 16 | 42 |
| Ototoxicity | 13 | 33 |
| Other sensory disorders | 6 | 10 |
|
* Values are in percent of evaluable patients. |
||
| Laboratory Abnormality
| Carboplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide (N=224)*
| Cisplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide
(N=223)* |
| (%)
| (%)
|
|
| Hematology
|
||
| Decreased neutrophils <2000 cells/mm3
| 97 | 96 |
| Decreased neutrophils <1000 cells/mm3
| 81 | 79 |
| Decreased hemoglobin <11 g/dL | 91 | 91 |
| Decreased hemoglobin <8 g/dL | 18 | 12 |
| Decreased platelets <100,000/mm3
| 70 | 29 |
| Decreased platelets <50,000/mm3
| 41 | 6 |
| Chemistry
|
||
| Decreased magnesium | 63 | 88 |
| Increased blood urea nitrogen | 17 | 31 |
| Increased AST | 17 | 13 |
| Decreased potassium | 16 | 22 |
| Decreased calcium | 16 | 19 |
| Decreased sodium | 10 | 20 |
| Increased serum creatinine | 5 | 13 |
| Increased bilirubin | 5 | 3 |
Tables 5 and 6 summarize the adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities in the SWOG study, respectively.
|
* Values are in percent of evaluable patients. |
||
| Adverse Reaction
| Carboplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide (N=171)
(%)* | Cisplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide (N=171)
(%)* |
| Gastrointestinal (GI)
|
||
| Nausea and vomiting | 94 | 96 |
| Vomiting | 82 | 91 |
| Other GI side effects | 40 | 48 |
| General
|
||
| Pain | 54 | 52 |
| Alopecia | 43 | 57 |
| Asthenia | 43 | 46 |
| Cardiovascular | 23 | 30 |
| Respiratory | 12 | 11 |
| Genitourinary | 11 | 13 |
| Hypersensitivity | 10 | 11 |
| Mucositis | 6 | 11 |
| Neurologic
|
||
| Central neurotoxicity | 23 | 29 |
| Peripheral neuropathies | 13 | 28 |
| Ototoxicity | 12 | 30 |
| Other sensory side effects | - | 6 |
|
* Values are in percent of evaluable patients. |
||
| Laboratory Abnormality
| Carboplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide (N=171)
(%)* | Cisplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide (N=171)
(%)* |
| Hematology
|
||
| Decreased neutrophils <2000 cells/mm3
| 95 | 97 |
| Decreased neutrophils <1000 cells/mm3
| 84 | 78 |
| Decreased hemoglobin <11 g/dL | 88 | 87 |
| Decreased hemoglobin <8 g/dL | 8 | 24 |
| Decreased platelets <100,000/mm3
| 59 | 35 |
| Decreased platelets <50,000/mm3
| 22 | 11 |
| Chemistry
|
||
| Decreased magnesium | 58 | 77 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 29 | 20 |
| Increased AST | 23 | 16 |
| Increased serum creatinine | 7 | 38 |
| Increased bilirubin | 5 | - |
The safety of carboplatin as a single agent for patients with ovarian carcinoma recurrent after prior chemotherapy was evaluated in two prospective, randomized controlled studies [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Tables 7 and 8 summarize the adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities from these studies, respectively
| Adverse Reaction
| Carboplatin as a Second Line
Single-Agent Therapy N=553 (%) |
| Gastrointestinal (GI)
|
|
| Nausea and vomiting | 92 |
| Vomiting | 81 |
| Other GI side effects | 21 |
| Neurologic
| |
| Pain | 23 |
| Asthenia | 11 |
| Peripheral neuropathies | 6 |
| Central neurotoxicity | 5 |
| General
|
|
| Cardiovascular | 6 |
| Respiratory | 6 |
| Infections | 5 |
| Bleeding | 5 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 5% of patients who received carboplatin included allergic reactions, alopecia, mucositis, ototoxicity, and sensory disorders.
| Laboratory Abnormality
| Carboplatin as a Second Line
Single-Agent Therapy N=553 (%) |
| Hematology
|
|
| Decreased hemoglobin <11 g/dL | 90 |
| Decreased hemoglobin <8 g/dL | 21 |
| Decreased neutrophils <2000 cells/mm3
| 67 |
| Decreased neutrophils <1000 cells/mm3
| 21 |
| Decreased platelets <100,000/mm3
| 62 |
| Decreased platelets <50,000/mm3
| 35 |
| Chemistry
|
|
| Decreased sodium | 47 |
| Decreased magnesium | 43 |
| Increased alkaline phosphatase | 37 |
| Decreased calcium | 31 |
| Decreased potassium | 28 |
| Increased blood urea | 22 |
| Increased AST | 19 |
| Increased serum creatinine | 10 |
| Increased bilirubin | 5 |
Other Clinical Trials Experience
The following adverse reactions occurred in patients treated with carboplatin for ovarian cancer as a single agent or in combination with chemotherapy in clinical trials:
The following adverse reactions occurred in patients (n=1893) with solid tumors or hematological malignancies treated with single agent carboplatin in clinical trials:
Gastrointestinal Disorders: diarrhea (6%), constipation (6%), dysgeusia (1%)
Ocular Disorders: visual disturbances (1%).
The following adverse reactions occurred in patients treated with carboplatin for ovarian cancer in combination with chemotherapy in clinical trials:
Cardiovascular: arterial thromboembolic event, venous thromboembolic event
General: fatigue, febrile neutropenia
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: fistula, wound-healing complication
Renal and Urinary Disorders: proteinuria
Respiratory: dyspnea
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of carboplatin. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Allergic reactions: anaphylaxis, bronchospasm, erythema, hypotension, pruritus, rash, urticaria
- Blood and Lymphatic System:hemolytic uremic syndrome, secondary acute myeloid leukemia
- Cardiovascular: cardiac failure, cerebrovascular accident, embolism, hemorrhage, hypertension
- Gastrointestinal:stomatitis
- General disorders:anorexia, dehydration, injection site reactions (including redness, pain, swelling, extravasation, and necrosis), malaise
- Infection:sepsis/septic shock
- Renal and Urinary Disorders: acute kidney injury
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Based on findings from animals and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], KYXATA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Available data from case reports with carboplatin use in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk. Administration of carboplatin to pregnant rats caused adverse developmental outcomes, including embryo-lethality and structural abnormalities (see Data). Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Carboplatin administered to pregnant rats was embryo-lethal and teratogenic.
8.2 Lactation
There are limited data on the presence of carboplatin or its metabolites in human milk, its effects on a breastfed child, or its effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with KYXATA and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
KYXATA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating KYXATA.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with KYXATA and for 6 months after the last dose.
Males
Based on genotoxicity findings, advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with KYXATA and for 3 months after the last dose [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of KYXATA in pediatric patients have not been established.
Pediatric patients may be at risk of hearing loss if KYXATA is administered at higher than recommended dosages or in combination with other ototoxic agents.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 395 patients treated with carboplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide, 141 (36%) were over 65 years of age, and 22 (6%) were 75 years and older [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients.
Elderly patients treated with carboplatin were more likely to develop severe thrombocytopenia or peripheral neuropathy than younger patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4)]
Of the 1,942 patients with solid tumors or hematological malignancies from pooled clinical trials that received single-agent carboplatin, 414 (21%) were 65 years of age and older, and a similar incidence of other adverse reactions was seen in these older patients compared to patients less than 65 years of age.
Consider renal function when selecting the KYXATA dose for older adults since they often have decreased renal function. To minimize the risk of toxicity in older adults, calculate the dose based on AUC [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
For patients administered a dose based on AUC, no dose modification is recommended for renal impairment.
For patients administered a dose based on body surface area, reduce the dose if creatinine clearance (CLcr) is 16 to 59 mL/min [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. A recommended dose of KYXATA has not been established for patients with CLcr <16 mL/min.
Patients with impaired renal function are at increased risk of myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
10. Overdosage
There is no known antidote for KYXATA overdosage. The anticipated complications of overdosage would be secondary to bone marrow suppression and/or hepatic toxicity. Patients receiving overdosages of carboplatin experienced severe liver function test abnormalities. Loss of vision, which can be complete for light and colors, has been reported after the use of carboplatin at doses higher than the recommended approved dosage for KYXATA. Vision recovers totally or to a significant extent after discontinuation of carboplatin. Clinically significant hearing loss has been reported to occur in pediatric patients when carboplatin was administered at higher than approved recommended doses for KYXATA and in combination with other ototoxic agents [see Drug Interactions (7)]. KYXATA is removed by dialysis.
Closely monitor patients suspected of receiving an overdose, including for the adverse reactions described above, and administer appropriate supportive treatment.
11. Kyxata Description
KYXATA is a platinum-based drug. The chemical name for carboplatin is platinum, diammine [1,1- cyclobutane-dicarboxylato(2-)-0,0']-,(SP-4-2) and carboplatin has the following structural formula:
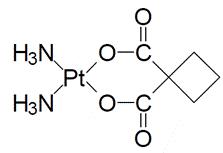
Carboplatin is a white crystalline powder with the molecular formula of C6H12N2O4Pt and a molecular weight of 371.26 g/mol. It is sparingly soluble in water and very slightly soluble in acetone and in alcohol. The pH of a 1% carboplatin solution in water is 5 to 7.
KYXATA (carboplatin) injection is supplied as a sterile, clear to pale yellow solution as 20 mg/2 mL, 80 mg/8mL, 500 mg/50 mL in multiple-dose vials for administration by intravenous infusion. Each mL contains 10 mg carboplatin.
12. Kyxata - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Carboplatin is a platinum-based drug that binds to DNA and forms DNA cross-links. These crosslinks inhibit DNA replication and transcription and trigger cytotoxic processes that lead to cell death.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Carboplatin exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic response have not been fully characterized.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Carboplatin pharmacokinetics were observed in patients with creatinine clearance (CLcr) of about 60 mL/min or greater following a dose of 300 mg/m2 to 500 mg/m2as an intravenous infusion over 30-minutes. The Cmax and AUC0-INF increase linearly with dose, although the increase was slightly more than dose proportional.
Distribution
The volume of distribution is 16 L.
Carboplatin is not bound to plasma proteins. No significant quantities of protein-free, ultrafilterable platinum-containing species other than carboplatin are present in plasma. However, platinum from carboplatin becomes irreversibly bound to plasma proteins.
Elimination
The elimination half-life is 2.6 to 5.9 hours and the total body clearance is 4.4 L/hour.
The elimination half-life of platinum from carboplatin bound to plasma proteins is a minimum of 5 days.
Excretion
The major route of elimination of carboplatin is renal excretion with 65% of the dose excreted in the urine within 12 hours and 71% within 24 hours. All of the platinum in the 24-hour urine is present as carboplatin.
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment: In patients with CLcr below 60 mL/min, the total body and renal clearances of carboplatin decrease as renal function decreases.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Use with Cyclophosphamide for Initial Treatment of Ovarian Cancer
The efficacy of carboplatin was evaluated in additional two randomized, controlled studies conducted by the National Cancer Institute of Canada, Clinical Trials Group (NCIC) and the Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) in patients with advanced ovarian cancer.
| Overview of Pivotal Trials
|
||
|
| NCIC
| SWOG
|
| Number of patients | 447 | 342 |
| Median age (years) | 60 | 62 |
| Dose of cisplatin | 75 mg/m2
| 100 mg/m2
|
| Dose of carboplatin | 300 mg/m2
| 300 mg/m2
|
| Dose of cyclophosphamide | 600 mg/m2
| 600 mg/m2
|
| Residual tumor <2 cm (number of patients) | 39% (174/447) | 14% (49/342) |
The efficacy results from the NCIC Trial are shown below in Table 10.
|
a Kaplan-Meier Estimates |
||
|
b 114 carboplatin and 109 cisplatin patients did not undergo second look surgery in NCIC study. |
||
|
| Carboplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide
| Cisplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide
|
| Overall Survival
|
||
| Median OS in months | 25.3 | 22.8 |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 0.98 (0.78, 1.23) |
|
| 2-year Survivala
| 51.9% | 40.2% |
| 3-year Survivala
| 34.6% | 33.1% |
| Progression-free Survival
|
||
| Median PFS in months | 13.6 | 14 |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 1.10 (0.89, 1.35) |
|
| 2-year PFSa
| 31% | 31% |
| 3-year PFSa
| 19% | 23% |
| Response Rates
|
||
| Pathologic Complete Response, n (%)b
| 24/224 (11%) | 33/223 (15%) |
| Clinical Response in Measurable Patients (%) | 60% | 58% |
The efficacy results from the SWOG trial are shown below in Table 11.
|
a Kaplan-Meier Estimates |
||
|
b 90 carboplatin and 106 cisplatin patients did not undergo second look surgery in SWOG study. |
||
|
| Carboplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide
| Cisplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide
|
| Overall Survival
|
||
| Median OS in months | 19.8 | 18.2 |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 1.01 (0.78, 1.30) |
|
| 2-year Survivala
| 40.2% | 39.0% |
| 3-year Survivala
| 18.3% | 24.9% |
| Progression-free Survival
|
||
| Median PFS in months | 11.3 | 10.8 |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 1.02 (0.81, 1.29) |
|
| 2-year PFSa
| 21% | 21% |
| 3-year PFSa
| 8% | 14% |
| Response Rates
|
||
| Pathologic Complete Response, n (%)b
| 17/171 (10%) | 17/171 (10%) |
| Clinical Response in Measurable Patients (%) | 58% | 43% |
14.2 Use as a Single Agent for Secondary Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Cancer
In two prospective, randomized controlled studies in 47 patients with advanced ovarian cancer previously treated with chemotherapy who were treated with carboplatin as a single agent, 13% (6/47) of patients had clinical complete responses. The duration of these responses ranged from 45 to 71+ weeks. Within the group of patients previously treated with cisplatin, those who have developed progressive disease while receiving cisplatin therapy may have a decreased response rate.
16. How is Kyxata supplied
KYXATATM (carboplatin) injection is supplied as clear to pale yellow solution in the following presentations:
| Unit of Sale
| Strength
|
| NDC 83831-140-02
Carton containing 1 multiple-dose vial (Light Blue flip-off seals) | 20 mg/2 mL (10 mg/mL) |
| NDC 83831-141-08
Carton containing 1 multiple-dose vial (Green flip-off seals) | 80 mg/8 mL (10 mg/mL) |
| NDC 83831-142-50
Carton containing 1 multiple-dose vial (Grey flip-off seals) | 500 mg/50 mL (10 mg/mL) |
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted from 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light.
KYXATA is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures.1
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Hypersensitivity
Inform patients that KYXATA can cause hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. and to immediately report signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions to their healthcare provider. Advise patients to seek medical attention immediately if they experience severe symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Myelosuppression
Inform patients that KYXATA can cause myelosuppression to immediately report signs or symptoms such as bleeding, easy bruising, symptoms of infection (fever, chills, cough, pain, or burning during urination), fatigue, or shortness of breath to their healthcare provider. Advise patients that complete blood counts will be monitored at baseline, during treatment, and as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Nausea and Vomiting
Advise patients about the use of antiemetics to prevent nausea and vomiting and to report persistent or severe symptoms to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Peripheral Neuropathy
Advise patients to report any new paresthesia to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with KYXATA and for 6 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with KYXATA and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with KYXATA and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Manufactured for:
Avyxa Pharma, LLC
New Jersey 07054, USA
Made in Switzerland

SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
|
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: 09/2025 |
||
| Patient Information
KYXATATM (Kix-ZAT-ah) (carboplatin) injection for intravenous use |
||
| What is the most important information I should know about KYXATA?
KYXATA can cause allergic reactions, including serious allergic reactions that can be life-threatening. KYXATA is a platinum-based medicine. Serious allergic reactions can happen in people who take KYXATA and who have had a previous allergic reaction to platinum-based medicines. Serious allergic reactions can happen within a few minutes of your KYXATA infusion or any time during your treatment with KYXATA. Tell your healthcare provider or get emergency medical help right away if you: ● have trouble breathing ● feel like your throat is closing up Call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following signs or symptoms of an allergic reaction: |
||
| ● rash ● flushed face ● hives ● itching ● swelling of your lips or tongue | ● sudden cough ● dizziness or feel faint ● sweating ● chest pain |
|
| See "What are the possible side effects of KYXATA?" for more information about side effects. |
||
| What is KYXATA?
KYXATA is a prescription medicine used to treat adults: ● in combination with another chemotherapy medicine, for your first treatment of advanced ovarian cancer. ● alone when your ovarian cancer has come back (recurrent) after you have been treated with prior chemotherapy medicines. It is not known if KYXATA is safe and effective in children. |
||
| Before you receive KYXATA tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
● have kidney problems ● are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. KYXATA can harm your unborn baby. Females who are able to become pregnant: ○ Your healthcare provider will check to see if you are pregnant before you start treatment with KYXATA. ○ Use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment with KYXATA and for 6 months after your last dose. ○ Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you may be pregnant during treatment with KYXATA. Males with female partners who are able to become pregnant: ○ Use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment with KYXATA and for 3 months after your last dose. ○ Tell your healthcare provider right away if your female partner becomes pregnant or thinks she may be pregnant during your treatment with KYXATA. ● are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if KYXATA passes into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment with KYXATA and for 1 week after your last dose of KYXATA. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during this time. Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take , including prescription and over‑the‑counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. |
||
| How will I receive KYXATA?
● Your healthcare provider will give you KYXATA into your vein as an intravenous (IV) infusion over 30 to 60 minutes. ● Your healthcare provider will give you medicines before each KYXATA infusion to help prevent nausea and vomiting and may continue these medicines after your infusion as needed. ● For advanced ovarian cancer, KYXATA may be given in combination with another chemotherapy medicine on Day 1 of each cycle. Your healthcare provider will decide how often KYXATA is given based on the other chemotherapy medicine used with KYXATA. ● For recurrent ovarian cancer, KYXATA may be given alone on Day 1 every 4 weeks (1 cycle). ● Your healthcare provider will decide how many treatments you need. ● Your healthcare provider may change your dose of KYXATA, or tell you to stop KYXATA for a short period of time or permanently if you have certain side effects. |
||
| What are the possible side effects of KYXATA?
KYXATA can cause serious side effects, including: See "What is the most important information about KYXATA?" above. ● Low blood cell counts . Decreased red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are common with KYXATA, but can also be severe and lead to bleeding or infections that can cause death. Some people have needed blood transfusions. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests before you start and during treatment with KYXATA to check your blood cell counts. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop a fever of 100.5°F or greater or get any of the following signs or symptoms: |
||
| ○ chills or shivering ○ cough ○ pain ○ burning or pain on urination | ○ feeling tired ○ shortness of breath ○ unusual bruising or bleeding ○ black tarry stools ○ blood in your urine |
|
| ● Nausea and vomiting. Nausea and vomiting are common during treatment with KYXATA but can also be severe. Before each infusion of KYXATA, you will receive medicines to help prevent nausea and vomiting. You may receive medicines after your infusion if needed. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have severe nausea or vomiting that does not stop. ● Peripheral neuropathy. Tell your healthcare provider if you develop tingling, numbness, or burning (feel like "pins and needles") in your hands or feet. The most common side effects in adults with advanced ovarian cancer who received KYXATA in combination with another chemotherapy medicine include: |
||
| ● decreased white blood cells ● nausea and vomiting ● decreased red blood cells (anemia) ● decreased platelets ● decreased magnesium | ● diarrhea ● constipation ● hair loss ● weakness ● pain |
|
|
The most common side effects in adults with recurrent ovarian cancer who received KYXATA alone include: |
||
| ● nausea and vomiting ● decreased red blood cells (anemia) ● decreased white blood cells ● decreased platelets | ● decreased sodium ● decreased magnesium ● increased alkaline phosphatase ● decreased calcium |
|
| These are not all the possible side effects of KYXATA. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||
| General information about the safe and effective use of KYXATA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information about KYXATA that is written for health professionals. |
||
| What are the ingredients in KYXATA?
Active ingredient: carboplatin |
||
| Manufactured for:
Avyxa Pharma, LLC New Jersey 07054, USA Made in Switzerland For more information, call 1-888-520-0954. |
 |
|
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
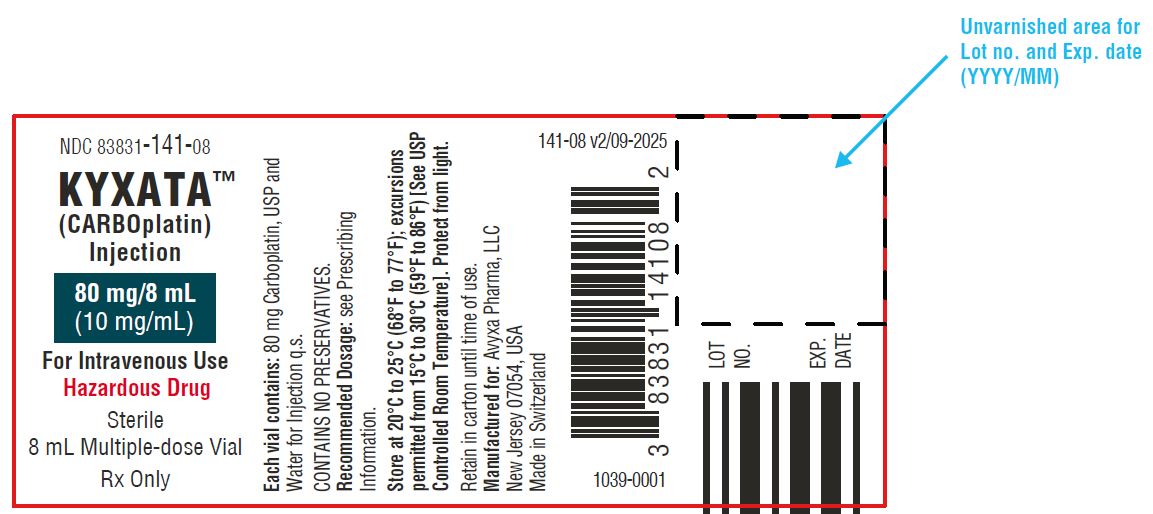
KYXATA (CARBOplatin) Injection, 80 mg/8 mL (10 mg/mL) -Vial Label
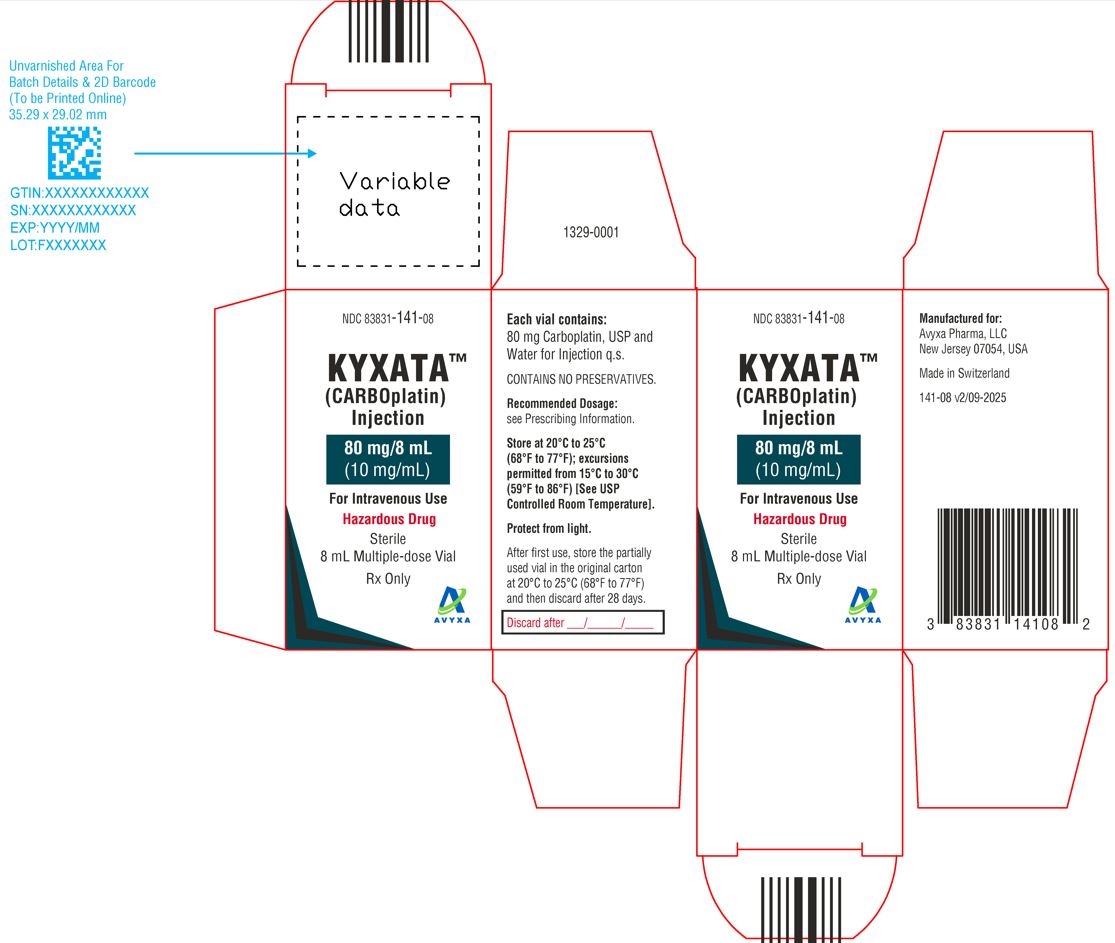
KYXATA (CARBOplatin) Injection, 80 mg/8 mL (10 mg/mL) -Carton Label

KYXATA (CARBOplatin) Injection, 500 mg/50 mL (10 mg/mL) -Vial Label

KYXATA (CARBOplatin) Injection, 500 mg/50 mL (10 mg/mL) -Carton Label
| KYXATA
carboplatin injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| KYXATA
carboplatin injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| KYXATA
carboplatin injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Avyxa Pharma, LLC (128918748) |
| Registrant - Avyxa Holdings, LLC. (119187191) |
Frequently asked questions
- Why give Taxol (Paxel) before carboplatin?
- How soon can you start chemo after port placement?
- Radiation vs. Chemo: Which cancer treatment is right for you?
- What is chemo brain and how long does it last?
- What is TCHP chemotherapy and how is it used?
- How does carboplatin stop cancer?
- Does carboplatin cause neuropathy?
More about Kyxata (carboplatin)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: alkylating agents
- Breastfeeding
