Axicabtagene Ciloleucel
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Oct 2, 2024.
Pronunciation
(ax i CAB tay jeen sye LO loo sel)
Index Terms
- Anti-CD19/CD28/CD3zeta CAR Gammaretroviral Vector-transduced Autologous T Lymphocytes KTE-C19
- Autologous Anti-CD19 CAR-positive T lymphocytes KTE-C19
- Axi-Cel
- Axicel
- KTE-C19
- KTE-C19 CAR
Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Suspension, Intravenous [preservative free]:
Yescarta: (1 ea) [contains albumin human, dimethyl sulfoxide]
Brand Names: U.S.
- Yescarta
Pharmacologic Category
- Antineoplastic Agent, Anti-CD19
- Antineoplastic Agent, CAR-T Immunotherapy
- CAR-T Cell Immunotherapy
- Cellular Immunotherapy, Autologous
- Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Immunotherapy
Pharmacology
Axicabtagene ciloleucel is a CD19-directed genetically modified autologous T cell immunotherapy in which a patient's T cells are reprogrammed with a transgene encoding a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) to identify and eliminate CD19-expressing malignant and normal cells. The CAR is comprised of a murine single-chain antibody fragment which recognizes CD19 and is fused to CD28 and CD3 zeta. CD3 zeta is a critical component for initiating T-cell activation and antitumor activity. After binding to CD19-expressing cells, the CD28 and CD3-zeta co-stimulatory domains activate downstream signaling cascades, which results in T cell activation, proliferation, acquisition of effector functions, and secretion of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, leading to destruction of CD19-expressing cells. Axicabtagene ciloleucel is prepared from the patient's peripheral blood cells obtained via leukapheresis.
Onset of Action
Median time to response: 1 month (range: 0.8 to 6 months) (Neelapu 2017)
Time to Peak
Peak levels of anti-CD19 CAR T cells occurred within the first 7 to 14 days after infusion
Duration of Action
Anti-CD19 CAR T cells displayed an initial rapid expansion followed by a decline to near baseline levels by 3 months post axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion
Use: Labeled Indications
Large B-cell lymphoma, relapsed or refractory: Treatment of relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma after 2 or more lines of systemic therapy, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, high grade B-cell lymphoma, and DLBCL arising from follicular lymphoma
Limitations of use: Not indicated for the treatment of patients with primary CNS lymphoma
Contraindications
There are no contraindications listed in the manufacturer's labeling.
Dosing: Adult
For autologous use only; confirm patient identity matches cassette and infusion bag prior to infusion.
Large B-cell lymphoma (relapsed or refractory): Note: A treatment course consists of lymphodepleting chemotherapy (with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide) on the fifth, fourth, and third day prior to axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion (confirm availability of autogolous axicabtagene ciloleucel prior to initiating lymphodepleting chemotherapy). Ensure tocilizumab and emergency equipment are available prior to axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion and during recovery period.
Premedicate with acetaminophen 650 mg orally and diphenhydramine 12.5 mg IV or orally ~60 minutes prior to axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion. Avoid prophylactic systemic corticosteroids because they may interfere with the axicabtagene ciloleucel activity.
IV: Target dose: 2 × 106 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-positive viable T cells per kg body weight (Locke 2019; Neelapu 2017); maximum dose: 2 × 108 CAR-positive viable T cells.
Dosage adjustment for concomitant therapy: Significant drug interactions exist, requiring dose/frequency adjustment or avoidance. Consult drug interactions database for more information.
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Dosing: Adjustment for Toxicity
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS): Note: Patients with ≥ grade 2 CRS should be monitored with continuous cardiac telemetry and pulse oximetry. Consider obtaining an echocardiogram in patients with severe CRS; severe or life-threatening CRS may require intensive care supportive therapy.
Grade 1 (fever, nausea, fatigue, headache, myalgia, malaise): Treat symptoms as appropriate; tocilizumab and/or corticosteroids are not indicated.
Grade 2 (oxygen requirement <40% FiO2 or hypotension responsive to fluids or low-dose of one vasopressor or grade 2 organ toxicity): Administer tocilizumab 8 mg/kg IV; maximum: 800 mg/dose (see Tocilizumab monograph); may repeat every 8 hours as needed (maximum: 3 doses in a 24-hour period, maximum total of 4 doses). If no improvement within 24 hours after initiating tocilizumab, administer methylprednisolone 1 mg/kg IV twice daily or equivalent dexamethasone (eg, 10 mg IV every 6 hours); continue corticosteroid until toxicity is ≤ grade 1, then taper over 3 days.
Grade 3 (oxygen requirement ≥40% FiO2 or hypotension requiring high-dose or multiple vasopressors or grade 3 organ toxicity or grade 4 transaminitis): Administer tocilizumab 8 mg/kg IV; maximum: 800 mg/dose (see Tocilizumab monograph); may repeat every 8 hours as needed (maximum: 3 doses in a 24-hour period, maximum total of 4 doses). In addition to tocilizumab, administer methylprednisolone 1 mg/kg IV twice daily or equivalent dexamethasone (eg, 10 mg IV every 6 hours); continue corticosteroid until toxicity is ≤ grade 1, then taper over 3 days.
Grade 4 (life-threatening; requirements for ventilator support, continuous veno-venous hemodialysis [CVVHD] or grade 4 organ toxicity [excluding transaminitis]): Administer tocilizumab 8 mg/kg IV; maximum: 800 mg/dose (see Tocilizumab monograph); may repeat every 8 hours as needed (maximum: 3 doses in a 24-hour period, maximum total of 4 doses). In addition to tocilizumab, administer methylprednisolone 1,000 mg IV daily for 3 days; if improves, then manage corticosteroid therapy as above.
Neurologic toxicity: Note: Patients with ≥ grade 2 neurologic toxicity should be monitored with continuous cardiac telemetry and pulse oximetry. Severe or life-threatening neurologic toxicity may require intensive care supportive therapy. Consider non-sedating anti-seizure medication (eg, levetiracetam) for seizure prophylaxis for any ≥ grade 2 neurologic toxicity.
Neurologic toxicity with concurrent CRS:
Grade 2: Administer tocilizumab 8 mg/kg IV; maximum: 800 mg/dose (see Tocilizumab monograph); may repeat every 8 hours as needed (maximum: 3 doses in a 24-hour period, maximum total of 4 doses). If no improvement within 24 hours after initiating tocilizumab, administer dexamethasone 10 mg IV every 6 hours (if not already receiving other corticosteroids); continue corticosteroid until toxicity is ≤ grade 1, then taper over 3 days.
Grade 3: Administer tocilizumab 8 mg/kg IV; maximum: 800 mg/dose (see Tocilizumab monograph); may repeat every 8 hours as needed (maximum: 3 doses in a 24-hour period, maximum total of 4 doses). In addition to tocilizumab, administer dexamethasone 10 mg IV every 6 hours (administer the first dose with the first dose of tocilizumab); continue corticosteroid until toxicity is ≤ grade 1, then taper over 3 days.
Grade 4: Administer tocilizumab 8 mg/kg IV; maximum: 800 mg/dose (see Tocilizumab monograph); may repeat every 8 hours as needed (maximum: 3 doses in a 24-hour period, maximum total of 4 doses). In addition to tocilizumab, administer methylprednisolone 1,000 mg IV daily for 3 days (administer the first dose with the first dose of tocilizumab); if improves, then manage corticosteroid therapy as above.
Neurologic toxicity without concurrent CRS:
Grade 2 or grade 3: Administer dexamethasone 10 mg IV every 6 hours; continue corticosteroid until toxicity is ≤ grade 1, then taper over 3 days.
Grade 4: Administer methylprednisolone 1,000 mg IV daily for 3 days; if improves, then manage corticosteroid therapy as above.
Reconstitution
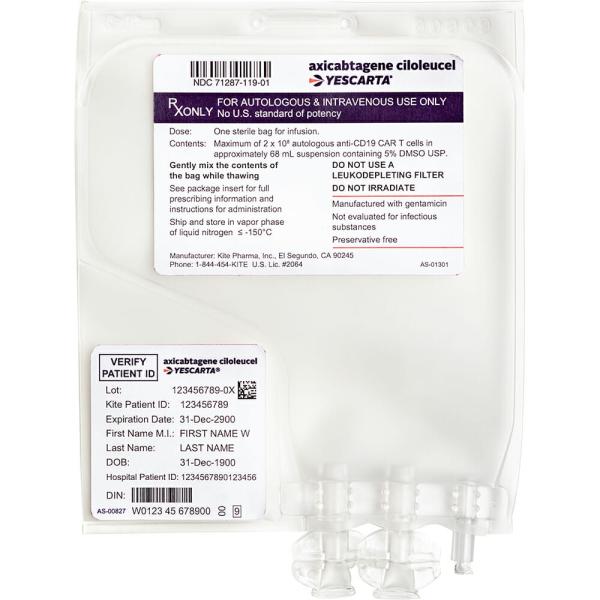
Do not remove the product bag from the cassette if the information on the patient-specific label does not match the intended patient. Inspect patient-specific infusion bag for breaks or cracks prior to thawing (if bag is compromised, contact manufacturer). Place infusion bag inside a second sterile bag in case of leaks and to protect ports from contamination. Thaw at 37°C using a water bath or dry thaw method until there is no visible ice in the infusion bag. Do not wash, spin down, and/or re-suspend axicabtagene ciloleucel in new media prior to infusion. Gently mix contents of the thawed infusion bag to disperse cellular material clumps; inspect for visible cell clumps; if visible cell clumps remain, gently mix the contents of the bag (small clumps of cellular material should disperse with gentle manual mixing). Do not infuse if clumps are not dispersed, if the infusion bag is damaged or leaking, or if it otherwise appears to be compromised (contact manufacturer). Axicabtagene ciloleucel contains human blood cells that are genetically modified with replication incompetent retroviral vector. Follow universal precautions and local biosafety guidelines for handling and disposal.
Administration
IV: For IV use only. Administer in a health care facility. Coordinate the timing of administration with thawing (may be stored for up to 3 hours at room temperature after thawing); infusion start time may need to be adjusted based on thawing.
Prime the tubing with NS prior to infusion. Infuse entire contents of bag within 30 minutes either by gravity or a peristaltic pump (infusion bag volume is ~68 mL). A central line is preferred for infusion. Gently agitate the bag during infusion to prevent cell clumping. After completion of the infusion, rinse the tubing with NS at the same infusion rate to ensure cell product delivery. Do not use a lymphocyte depleting filter.
Prior to administration: Ensure tocilizumab and emergency equipment are available prior to infusion and during recovery period. Premedicate with acetaminophen 650 mg orally and diphenhydramine 12.5 mg IV or orally ~60 minutes prior to axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion. Avoid prophylactic systemic corticosteroids, as they may interfere with the axicabtagene ciloleucel activity. Confirm patient identity and match to patient identifiers on the infusion cassette and bag. Inspect the contents of the thawed infusion bag for visible cell clumps; if visible cell clumps remain, gently mix the contents of the bag (small clumps of cellular material should disperse with gentle manual mixing). Do not infuse if clumps are not dispersed, if the infusion bag is damaged or leaking, or if it otherwise appears to be compromised. Apply universal precautions for product handling.
Storage
Store frozen suspension in the vapor phase of liquid nitrogen (≤ -150°C). After thawing, may be stored for up to 3 hours at room temperature of 20°C to 25°C.
Drug Interactions
Baricitinib: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Baricitinib. Management: Use of baricitinib in combination with potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine or cyclosporine is not recommended. Concurrent use with antirheumatic doses of methotrexate or nonbiologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) is permitted. Consider therapy modification
BCG (Intravesical): Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of BCG (Intravesical). Avoid combination
Cladribine: May enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Immunosuppressants. Avoid combination
Coccidioides immitis Skin Test: Immunosuppressants may diminish the diagnostic effect of Coccidioides immitis Skin Test. Monitor therapy
Corticosteroids (Systemic): May diminish the therapeutic effect of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel. Management: Avoid use of corticosteroids as premedication before axicabtagene ciloleucel. Corticosteroids may, however, be required for treatment of cytokine release syndrome or neurologic toxicity. Consider therapy modification
Denosumab: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Immunosuppressants. Specifically, the risk for serious infections may be increased. Monitor therapy
Echinacea: May diminish the therapeutic effect of Immunosuppressants. Management: Consider avoiding Echinacea in patients receiving therapeutic immunosuppressants. If coadministered, monitor for reduced efficacy of the immunosuppressant during concomitant use. Consider therapy modification
Fingolimod: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Fingolimod. Management: Avoid the concomitant use of fingolimod and other immunosuppressants when possible. If combined, monitor patients closely for additive immunosuppressant effects (eg, infections). Consider therapy modification
Inebilizumab: May enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Immunosuppressants. Monitor therapy
Leflunomide: Immunosuppressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Leflunomide. Specifically, the risk for hematologic toxicity such as pancytopenia, agranulocytosis, and/or thrombocytopenia may be increased. Management: Consider not using a leflunomide loading dose in patients receiving other immunosuppressants. Patients receiving both leflunomide and another immunosuppressant should be monitored for bone marrow suppression at least monthly. Consider therapy modification
Natalizumab: Immunosuppressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Natalizumab. Specifically, the risk of concurrent infection may be increased. Avoid combination
Nivolumab: Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Nivolumab. Management: Avoid use of immunosuppressants (including systemic corticosteroids) prior to initiation of nivolumab. Use of immunosuppressants after administration of nivolumab (eg, for immune-related toxicity) is unlikely to affect nivolumab efficacy. Consider therapy modification
Ocrelizumab: May enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Immunosuppressants. Monitor therapy
Ozanimod: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Ozanimod. Monitor therapy
Pidotimod: Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Pidotimod. Monitor therapy
Pimecrolimus: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Immunosuppressants. Avoid combination
Roflumilast: May enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Immunosuppressants. Management: Consider avoiding concomitant use of roflumilast and immunosuppressants as recommended by the Canadian product monograph. Inhaled or short-term corticosteroids are unlikely to be problematic. Consider therapy modification
Siponimod: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Siponimod. Monitor therapy
Sipuleucel-T: Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Sipuleucel-T. Management: Evaluate patients to see if it is medically appropriate to reduce or discontinue therapy with immunosuppressants prior to initiating sipuleucel-T therapy. Consider therapy modification
Tacrolimus (Topical): May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Immunosuppressants. Avoid combination
Talimogene Laherparepvec: Immunosuppressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Talimogene Laherparepvec. Specifically, the risk for disseminated herpetic infection may be increased. Avoid combination
Tertomotide: Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Tertomotide. Monitor therapy
Tofacitinib: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Tofacitinib. Management: Concurrent use with antirheumatic doses of methotrexate or nonbiologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) is permitted, and this warning seems particularly focused on more potent immunosuppressants. Consider therapy modification
Upadacitinib: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Upadacitinib. Management: Concomitant use of upadacitinib with potent immunosuppressants is not recommended. Avoid combination
Vaccines (Inactivated): Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Vaccines (Inactivated). Management: Complete all age-appropriate vaccinations at least 2 weeks prior to starting an immunosuppressant. If vaccinated less than 2 weeks before starting or during immunosuppressant therapy, revaccinate at least 3 months after immunosuppressant discontinuation. Consider therapy modification
Vaccines (Live): Immunosuppressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Vaccines (Live). Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Vaccines (Live). Management: Avoid use of live organism vaccines with immunosuppressants; live-attenuated vaccines should not be given for at least 3 months after immunosuppressants. Avoid combination
Vaccines (Live): Axicabtagene Ciloleucel may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Vaccines (Live). Specifically, the risk of infection may be increased. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel may diminish the therapeutic effect of Vaccines (Live). Management: Avoid live virus vaccines for at least 6 weeks prior to initiation of lymphodepleting therapy, during axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion, and after treatment until full immune recovery is achieved. Consider therapy modification
Adverse Reactions
The following adverse drug reactions and incidences are derived from product labeling unless otherwise specified.
>10%:
Cardiovascular: Cardiac arrhythmia (23%), edema (19%), hypertension (15%), hypotension (57%), tachycardia (57%)
Endocrine & metabolic: Dehydration (11%), hyponatremia (grades 3/4: 19%), hypophosphatemia (grades 3/4: 50%), increased uric acid (grades 3/4: 13%), weight loss (16%)
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal pain (14%), constipation (23%), decreased appetite (44%), diarrhea (38%), nausea (34%), vomiting (26%), xerostomia (11%)
Hematologic & oncologic: Anemia (grades 3/4: 66%), febrile neutropenia (34% to 36%; grade ≥3: 31%), hypogammaglobulinemia (15%), leukopenia (grades 3/4: 96%), lymphocytopenia (grades 3/4: 100%), neutropenia (grades 3/4: 93%), thrombocytopenia (grades 3/4: 58%)
Hepatic: Increased direct serum bilirubin (grades 3/4: 13%)
Hypersensitivity: Cytokine release syndrome (94%)
Infection: Bacterial infection (13%), infection (26% to 38%, including serious infection; fungal infection: 5%), viral infection (16%)
Nervous system: Aphasia (18%), chills (40%), delirium (17%), dizziness (21%), encephalopathy (57%; can last up to 173 days), fatigue (46%), headache (44% to 45%), motor dysfunction (19%)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Back pain (15%), limb pain (17%), myalgia (14%), tremor (31%)
Renal: Renal insufficiency (12%)
Respiratory: Cough (30%), dyspnea (19%), hypoxia (32%), pleural effusion (13%)
Miscellaneous: Fever (86%)
1% to 10%:
Cardiovascular: Capillary leak syndrome (3%), cardiac failure (6%), thrombosis (10%)
Dermatologic: Skin rash (9%)
Endocrine & metabolic: Hypokalemia (grades 3/4: 10%)
Gastrointestinal: Clostridioides difficile associated diarrhea (>2%)
Genitourinary: Urinary tract infection (>2%)
Hematologic & oncologic: Disorder of hemostatic components of blood (2%), natural killer cell count increased (hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis/macrophage activation syndrome: 1%)
Hepatic: Increased serum alanine aminotransferase (grades 3/4: 10%)
Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reaction (1%; including anaphylaxis)
Nervous system: Anxiety (9%), ataxia (6%), cognitive dysfunction (comprehending mathematics: 2%), insomnia (9%), myoclonus (2%), seizure (4%)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Arthralgia (10%)
Respiratory: Pulmonary edema (9%), pulmonary infection (>2%)
Frequency not defined: Nervous system: Brain edema, leukoencephalopathy
Postmarketing:
Gastrointestinal: Dysphagia
Nervous system: Quadriplegia, spinal cord injury (spinal cord edema)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Myelitis
Related/similar drugs
ALERT: U.S. Boxed Warning
Cytokine release syndrome:Cytokine release syndrome (CRS), including fatal or life-threatening reactions, occurred in patients receiving axicabtagene ciloleucel. Do not administer axicabtagene ciloleucel to patients with active infection or inflammatory disorders. Treat severe or life-threatening CRS with tocilizumab or tocilizumab and corticosteroids.
Neurological toxicities:Neurological toxicities, including fatal or life-threatening reactions, occurred in patients receiving axicabtagene ciloleucel, including concurrently with CRS or after CRS resolution. Monitor for neurologic toxicities after treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel. Provide supportive care and/or corticosteroids as needed.
REMS program:Axicabtagene ciloleucel is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the YESCARTA and TECARTUS REMS Program.
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
• Cytokine release syndrome: [US Boxed Warning]: Cytokine release syndrome (CRS), including fatal or life-threatening reactions, occurred in patients receiving axicabtagene ciloleucel. Do not administer axicabtagene ciloleucel to patients with active infection or inflammatory disorders. Treat severe or life-threatening CRS with tocilizumab or tocilizumab and corticosteroids. Grade 3 or 4 CRS reactions have occurred. The median time to onset of CRS was 2 days (range: 1 to 12 days); the median duration of CRS was 7 days (range: 2 to 58 days). Key manifestations of CRS include fever, hypotension, tachycardia, hypoxia, and chills. Cardiac arrhythmias (eg, atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia), cardiac arrest, cardiac failure, renal insufficiency, capillary leak syndrome, and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis/macrophage activation syndrome (HLH/MAS) may be associated with CRS (may be serious). Ensure that tocilizumab is available (a minimum of 2 doses) on site prior to axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion. Monitor for signs or symptoms of CRS for at least 4 weeks after treatment (daily for 7 days following the infusion). Patients should seek immediate medical attention if signs or symptoms of CRS occur at any time. Evaluate patients immediately at the first sign of CRS; hospitalize and begin supportive care, tocilizumab, and/or corticosteroids as indicated.
• Cytopenias: Prolonged cytopenias may occur several weeks after lymphodepleting chemotherapy and axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion. Unresolved (by day 30 following axicabtagene ciloleucel treatment) grade 3 and 4 cytopenias included neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia. Monitor blood counts.
• Hepatitis B virus reactivation: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation (sometimes resulting in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, and death) can occur in patients treated with medications directed against B cells. Screen for HBV, HCV, and HIV in accordance with clinical guidelines prior to collection of cells for manufacturing.
• Hypersensitivity: Allergic reactions may occur with axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion. Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, may occur due to the dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or residual gentamicin in axicabtagene ciloleucel.
• Hypogammaglobulinemia: Hypogammaglobulinemia and B-cell aplasia may occur in patients receiving axicabtagene ciloleucel. Monitor immunoglobulin levels after axicabtagene ciloleucel treatment. Manage hypogammaglobulinemia with infection precautions, antibiotic prophylaxis, and immunoglobulin treatment (per standard replacement guidelines).
• Infection: Serious infections (including life-threatening infections) occurred in patients after axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion, including grades 3 and higher infections in close to one-quarter of patients. Viral and bacterial infections were reported as well as infections due to unknown pathogens. Begin prophylaxis according to local guidelines prior to axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion. Monitor for signs and symptoms of infection before and following treatment and manage appropriately; do not administer to patients with clinically significant active systemic infections. Neutropenic fever has been observed after axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion and may occur concurrently with CRS. If neutropenic fever occurs, evaluate for infection and manage with broad-spectrum antibiotics, fluids, and other supportive care as clinically indicated.
• Neurological toxicities: [US Boxed Warning]: Neurological toxicities, including fatal or life-threatening reactions, occurred in patients receiving axicabtagene ciloleucel, including concurrently with CRS or after CRS resolution. Monitor for neurological toxicities after treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel. Provide supportive care and/or corticosteroids as needed. Most neurological toxicities occurred within 8 weeks following axicabtagene ciloleucel infusion; the median time to onset was 4 days (range: 1 to 43 days). The median duration of neurologic toxicities was 17 days. Grade 3 or higher neurologic toxicities have been observed in close to one-third of patients. The most common neurological toxicities were encephalopathy, headache, tremor, dizziness, aphasia, delirium, insomnia, and anxiety. Prolonged encephalopathy (lasting up to 173 days) was observed. Fatal and serious cases of cerebral edema have occurred; other serious events included leukoencephalopathy and seizures. Monitor for signs or symptoms of neurologic toxicities for at least 4 weeks after treatment (daily for 7 days following the infusion). Treat promptly if neurologic toxicities occur. Due to the potential for neurologic events, including altered mental status or seizures, patients receiving axicabtagene ciloleucel are at risk for altered or decreased consciousness or coordination in the 8 weeks following administration; during this initial period, advise patients to refrain from driving and engaging in hazardous occupations or activities, such as operating heavy or potentially dangerous machinery.
• Secondary malignancy: Patients treated with axicabtagene ciloleucel may develop secondary malignancies or leukemia recurrence. Monitor permanently for secondary malignancies. If a secondary malignancy occurs, contact the manufacturer (1-844-454-KITE) to obtain patient sampling instructions for testing.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
• Immunizations: Vaccination with live virus vaccines is not recommended for at least 6 weeks prior to the start of lymphodepleting chemotherapy, during axicabtagene ciloleucel treatment, and until immune recovery following treatment. The safety of immunization with live viral vaccines during or following axicabtagene ciloleucel treatment has not been studied.
Special populations:
• Elderly: A subgroup analysis found that patients ≥65 years of age experienced a higher incidence of neurologic toxicities (compared to younger patients), although other serious adverse effects, including CRS, occurred at similar rates between the groups (Neelapu 2020).
Other warnings/precautions:
• Appropriate use: For autologous use only. Confirm patient identity and match to patient identifiers on the cassette and infusion bag prior to infusion. Administer in a health care facility; patients should remain within proximity of the facility for at least 4 weeks after infusion.
• REMS program: [US Boxed Warning]: Axicabtagene ciloleucel is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the YESCARTA and TECARTUS REMS Program. Information is available at https://www.YescartaTecartusREMS.com or 1-844-454-5483.
Monitoring Parameters
Screen for hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, and HIV (prior to collection of cells for manufacturing). Monitor immunoglobulin levels and blood counts (after treatment). Evaluate pregnancy status prior to therapy (in females of reproductive potential).
Monitor for signs/symptoms of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurological toxicities for at least 4 weeks after treatment (monitor daily for the first 7 days after infusion at the health care facility; patients with ≥ grade 2 CRS should be monitored with continuous cardiac telemetry and pulse oximetry), monitor for hypersensitivity reactions and for signs/symptoms of infection. Monitor (life-long) for secondary malignancies.
Reproductive Considerations
Evaluate pregnancy status prior to therapy in females of reproductive potential; pregnancy testing is recommended prior to therapy in sexually active women of reproductive potential. Refer to the cyclophosphamide and fludarabine monographs for information related to use of effective contraception in patients using these medications for lymphodepleting chemotherapy. The duration of contraception needed following axicabtagene ciloleucel administration is not known. Potential pregnancies (following treatment) should be discussed with the prescriber.
Pregnancy Considerations
Treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel is not recommended during pregnancy. If placental transfer were to occur, fetal toxicity, including B-cell lymphocytopenia, may occur.
Potential pregnancies (following treatment) should be discussed with the prescriber.
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
• It is used to treat a type of lymphoma
All drugs may cause side effects. However, many people have no side effects or only have minor side effects. Call your doctor or get medical help if any of these side effects or any other side effects bother you or do not go away:
• Lack of appetite
• Nausea
• Vomiting
• Diarrhea
• Constipation
• Abdominal pain
• Dry mouth
• Weight loss
• Loss of strength and energy
• Painful extremities
• Muscle pain
• Joint pain
• Muscle spasm
• Muscle weakness
• Back pain
WARNING/CAUTION: Even though it may be rare, some people may have very bad and sometimes deadly side effects when taking a drug. Tell your doctor or get medical help right away if you have any of the following signs or symptoms that may be related to a very bad side effect:
• Cytokine release syndrome like chills, dizziness, loss of strength and energy, fever, headache, passing out, rash, swelling in your throat, trouble breathing, nausea, vomiting, or wheezing
• Agitation
• Confusion
• Anxiety
• Vision changes
• Dizziness
• Passing out
• Sensing things that seem real but are not
• Headache
• Seizures
• Tremors
• Trouble speaking
• Behavioral changes
• Mood changes
• Infection
• Bleeding like vomiting blood or vomit that looks like coffee grounds; coughing up blood; blood in the urine; black, red, or tarry stools; bleeding from the gums; abnormal vaginal bleeding; bruises without a reason or that get bigger; or any severe or persistent bleeding
• Kidney problems like unable to pass urine, blood in the urine, change in amount of urine passed, or weight gain
• Fluid and electrolyte problems like mood changes, confusion, muscle pain or weakness, abnormal heartbeat, severe dizziness, passing out, fast heartbeat, increased thirst, seizures, loss of strength and energy, lack of appetite, unable to pass urine or change in amount of urine passed, dry mouth, dry eyes, or nausea or vomiting
• Shortness of breath
• Excessive weight gain
• Swelling in arms or legs
• Severe loss of strength and energy
• Fast heartbeat
• Abnormal heartbeat
• Trouble sleeping
• Severe fatigue
• Trouble focusing
• Swelling
• Swelling, warmth, numbness, change of color, or pain in a leg or arm
• Chest pain
• Signs of an allergic reaction, like rash; hives; itching; red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin with or without fever; wheezing; tightness in the chest or throat; trouble breathing, swallowing, or talking; unusual hoarseness; or swelling of the mouth, face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a limited summary of general information about the medicine’s uses from the patient education leaflet and is not intended to be comprehensive. This limited summary does NOT include all information available about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not intended to provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. For a more detailed summary of information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine, please speak with your healthcare provider and review the entire patient education leaflet.
Frequently asked questions
- What is CAR T-cell therapy and how does it work?
- What is the cost of Yescarta?
- How is Yescarta administered?
- What type of drug is Yescarta (axicabtagene ciloleucel)?
More about axicabtagene ciloleucel
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Latest FDA alerts (3)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: miscellaneous antineoplastics
- Breastfeeding
- En español
Patient resources
Other brands
Professional resources
Other brands
Related treatment guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.