Tuberculosis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 23, 2025.
Tuberculosis (TB) is a severe infection caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. TB usually starts in the lungs. The bacteria are easily spread from one person to another through the air. They can live in your body a long time without making you sick. This is called latent TB. Latent means you do not have symptoms, but you may develop them later. Latent TB can develop into active TB if it is not treated.
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Rest with your head elevated:
Keep the head of your bed raised to help you breathe easier. You can also raise your head and shoulders on pillows or rest in a reclining chair. If you feel short of breath, let healthcare providers know right away.
Isolation:
Isolation safety measures are used to protect others from infection. Healthcare providers and visitors will need to wear sealed medical masks to enter your room. You need 3 negative sputum samples to stop isolation.
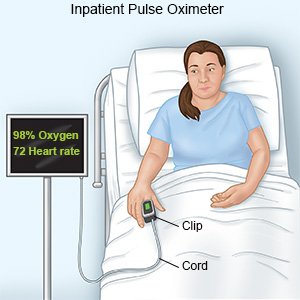
Pulse oximeter:
A pulse oximeter is a device that measures the amount of oxygen in your blood. A cord with a clip or sticky strip is placed on your finger, ear, or toe. The other end of the cord is hooked to a machine that records the oxygen level.
 |
Related medications
Medicines:
- Antibiotics help fight the TB infection.
- Steroid medicine decreases inflammation.
- Antipyretics decrease a fever.
- Expectorant medicine helps thin the mucus from your lungs. When sputum is thin, it may be easier for you to cough it up and spit it out.
Tests:
- A sputum sample may be collected often. This may help healthcare providers choose the best treatment for you. Mucus from your lungs is collected in a cup when you cough. You may need to give 3 samples of your sputum, usually first thing in the morning.
- Arterial blood gases (ABGs) are done to test your blood for the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The results can tell healthcare providers how well your lungs are working.
- Blood tests may show damage to your organs, or that the infection has spread.
- A chest x-ray may show swelling, infection, or lung collapse.
- A CT scan may show tissue damage. You may be given contrast liquid to help tissues show up better. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
Treatment:
- Breathing treatments help open your airways so you can breathe easier. A machine is used to change liquid medicine into a mist. You will breathe the mist into your lungs through tubing and a mouthpiece. Inhaled mist medicines act quickly on your airways and lungs to relieve your symptoms.
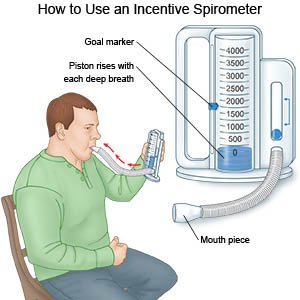
- Deep breathing and coughing will help expand your lungs and prevent more damage. Take a deep breath and hold it for as long as you can. Let the air out and then cough strongly. Deep breaths help open your airway. You may be given an incentive spirometer to help you take deep breaths. Put the plastic piece in your mouth and take a slow, deep breath. Then let the air out and cough. Repeat these steps 10 times every hour.
RISKS:
TB can spread to others and cause infection. Treatment may be more difficult if the infection has spread to other parts of your body. Without treatment, TB can cause long-term lung problems. The infection can spread to your brain, bones, spine, and kidneys. This can be life-threatening.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Tuberculosis
Treatment options
- Medications for Adrenal Tuberculosis
- Medications for CNS Tuberculosis
- Medications for History, Tuberculosis
- Medications for Ocular Tuberculosis
- Medications for Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- Medications for Tuberculosis
- Medications for Tuberculosis, Active
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
