Prevent Infections
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 23, 2025.
What is an infection?
An infection is an illness caused by germs, such as bacteria or a virus. Infections can spread from one person to another. Germs can spread through the air when someone coughs or sneezes. You can also be infected if you touch something an infected person used and then touch your eyes, nose, or mouth. Examples include doorknobs, used tissues, and sometimes dirty laundry.
What can I do to prevent infections?
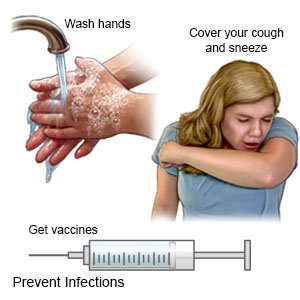
- Wash your hands often. This is the most important thing you can do to prevent infections. Wash your hands several times each day. Wash after you use the bathroom, change a child's diaper, and before you prepare or eat food. Use soap and water every time you wash your hands. Rub your soapy hands together, lacing your fingers. Use the fingers of one hand to scrub under the nails of the other hand. Wash for at least 20 seconds. Rinse with warm, running water for several seconds. Then dry your hands with a clean towel or paper towel. Use hand sanitizer that contains alcohol if soap and water are not available. Do not touch your eyes, nose, or mouth without washing your hands first.

- Cover a sneeze or cough. Use a tissue that covers your mouth and nose. Throw the tissue away immediately. If you do not have a tissue, use the bend of your elbow. Then wash your hands well or use a hand sanitizer.
- Prevent person-to-person spread of germs. If you are sick, stay home as much as possible. Do not have close contact with someone who is sick. Ask friends and family to visit only when they are not sick.
- Ask about vaccines you may need. Vaccines help protect you and others around you from some infections. Talk to your healthcare provider about your vaccine history. For example, you may not have received certain vaccines as a child, or all recommended doses. It is okay if you do not know your vaccine history. Your provider will tell you which vaccines you need, and when to get them. Your provider may recommend these and other vaccines:
- Influenza vaccine helps prevent influenza (flu). Everyone 6 months or older should get a yearly influenza vaccine. Get the vaccine as soon as recommended each year, usually in September or October.
- Get a pneumonia vaccine as directed. The vaccine is recommended for all adults aged 50 or older. Adults aged 19 to 49 years who are at high risk for pneumonia should also receive the vaccine. You may need 1 dose or 2. The number depends on the vaccine used and your risk factors. Children routinely receive 4 doses of the pneumonia vaccine, starting at 2 months.
- Get a COVID-19 vaccine as directed. At least 1 dose of an updated vaccine is recommended for everyone 6 months or older. COVID-19 vaccines are given as a shot in 1 to 3 doses, depending on the age of the person who receives it. COVID-19 vaccines are updated throughout the year. Your healthcare provider can help you schedule all needed doses as updated vaccines become available.
 |
Related medications
What can I do in my home to prevent infections?
- Keep surfaces clean. Use a disinfecting cleaner. You can create a cleaning solution by mixing 1 part bleach to 10 parts water. Clean the toilet, the area around the toilet, the sink, the area around the sink, and faucets. The toilet should be cleaned after each use if someone in the home has infectious diarrhea. Items used often by an infected person should be cleaned daily. These items include phones, doorknobs, and remote controls. Clean the shower or bathtub after each use.
- Wash dishes and silverware in a dishwasher or in hot water. Do not use unwashed dishes or silverware.
- Do not share personal items. Do not use toothbrushes, towels, or washcloths that have been used by others.
Where can I find more information?
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
1600 Clifton Road
Atlanta , GA 30333
Phone: 1- 800 - 232-4636
Web Address: http://www.cdc.gov/
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
