Perineal Prostatectomy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW:
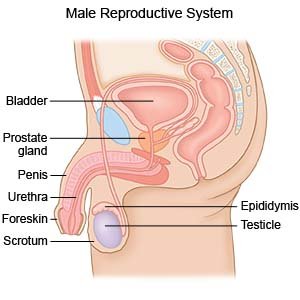
A perineal prostatectomy is surgery to remove your prostate gland.
 |
HOW TO PREPARE:
The week before your surgery:
- Arrange to have someone drive you home after surgery and stay with you for 24 hours.
- Tell your surgeon about all medicines you currently take. He or she will tell you if you need to stop any medicine before surgery, and when to stop. He or she will tell you which medicines to take or not take on the day of surgery.
- You may be given hormone therapy to shrink your prostate gland before surgery.
- Tell your surgeon if you have hip or spine problems. These problems may not allow you to be in the position needed for a perineal prostatectomy.
- You will need to be on a clear liquid diet the day before your surgery. You may drink clear liquids, including water, broth, apple juice, or lemon-lime soft drinks. You may also suck on ice chips or eat gelatin.
- You may need blood or urine tests before your surgery. You may also need an ultrasound or cystoscopy (procedure to look at your bladder and urethra).
The night before your surgery:
You may be told not to eat or drink anything after midnight. You may need to drink medicine that empties your bowel.
The day of your surgery:
- You or a close family member will be asked to sign a legal document called a consent form. It gives healthcare providers permission to do the procedure or surgery. It also explains the problems that may happen, and your choices. Make sure all your questions are answered before you sign this form.
- You may be given an enema (liquid medicine put in your rectum) to help empty your bowel.
- You may be given medicine to help prevent a bacterial infection.
- You may need to wear pressure stockings to help prevent blood clots.
- Healthcare providers may insert an intravenous tube (IV) into your vein. A vein in the arm is usually chosen. You may be given liquids or medicine through the IV.
- An anesthesiologist will talk to you before your surgery. You may need medicine to keep you asleep or numb an area of your body during surgery. Tell healthcare providers if you or anyone in your family has had a problem with anesthesia in the past.
WHAT WILL HAPPEN:
What will happen:
Your surgeon will make an incision between your scrotum and anus. He or she will move layers of skin, tissue, and muscle to get to your prostate. Your surgeon will cut your prostate gland away from your urethra (tube that drains urine from your bladder). He or she will reattach your bladder to your urethra and place a Foley catheter to drain urine. Your surgeon may make another incision in your abdomen and remove lymph nodes. Your incisions will be closed with stitches and covered with a bandage. Your prostate gland will be sent to a lab for testing.
After your surgery:
You will be taken to a room to rest until you are fully awake. You will be monitored closely for any problems. Do not get out of bed until your healthcare provider says it is okay. You will then be taken to your hospital room.
CONTACT YOUR HEALTHCARE PROVIDER IF:
- You cannot make it to your surgery.
- You have a fever.
Seek Care Immediately if
- You are urinating very little or not at all.
- You have new or increased abdominal or pelvic pain.
Risks
Surgery may increase your risk for bleeding or an infection. Nerves, organs, or tissues near your prostate may be injured during surgery. After surgery, you may leak urine and bowel movements. Urine leakage may be short-term or permanent. You may have trouble having an erection or ejaculating. You may get a blood clot in your leg. This may become life-threatening.
Related medications
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Perineal Prostatectomy
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
