Aplastic Anemia
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
Aplastic anemia is when your body stops making new red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are made in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is soft, spongy tissue inside the bone. Red blood cells carry oxygen to all the organs and tissues of your body. White blood cells help your body fight infection by attacking and killing germs. Platelets stop the bleeding when you are cut or injured.
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Activity:
You may need to rest. Your healthcare provider will tell you when it is okay to increase your activities. Call your healthcare provider before getting up for the first time. If you ever feel weak or dizzy, sit or lie down right away. Then call your healthcare provider.
A heart monitor
is also called an ECG or EKG. Sticky pads placed on your skin record your heart's electrical activity.
Reverse isolation
is a safety measure used to protect you from outside germs. You may have a weak immune system or trouble fighting infection. With reverse isolation, you are given a private room. Everyone should wash their hands when entering and leaving your room. Healthcare providers and visitors wear gloves, a mask, and a gown when they enter your room.
You may need extra oxygen
if your blood oxygen level is lower than it should be. You may get oxygen through a mask placed over your nose and mouth or through small tubes placed in your nostrils. Ask your healthcare provider before you take off the mask or oxygen tubing.
Related medications
A pulse oximeter
is a device that measures the amount of oxygen in your blood. A cord with a clip or sticky strip is placed on your finger, ear, or toe. The other end of the cord is hooked to a machine.
Medicines:
- Bone marrow stimulants, or growth factor medicines, help trigger your bone marrow to start making new red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Immunosuppressants help prevent your body from attacking its own bone marrow. This may help the bone marrow make more blood cells.
- Antibiotics are given to prevent or fight a bacterial infection.
- Antifungals help treat or prevent a fungal infection.
- Antinausea medicine may be given to calm your stomach and prevent vomiting.
- Antivirals help treat or prevent a viral infection.
- Antipyretics are used to reduce a fever.
- Pain medicine may be given. Do not wait until the pain is severe before you ask for more medicine.
- Stool softeners help make it easier for you to have a bowel movement. You may need this medicine to treat or prevent constipation.
Tests:
- Blood tests are used to monitor the growth of your blood cells. This will help healthcare providers know what treatment is best for you.
- A bone marrow biopsy may be used to find which types of blood cells are low. A sample of bone marrow is removed and sent to a lab for tests.
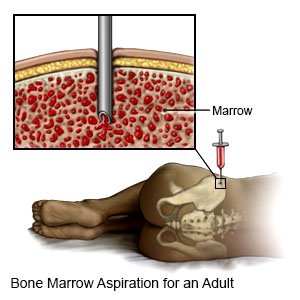
Treatment:
- A blood transfusion may be needed to replace blood you have lost. You may need more than one transfusion.
- A bone marrow or stem cell transplant is a procedure used to replace your stem cells with healthy cells. Stem cells are the part of the bone marrow that make the red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The transplanted stem cells return to the bone marrow, grow, and start producing red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
RISKS:
You are at higher risk for infections. Heavy bleeding may also happen when you are injured. You may need several blood transfusions. Treatments may be slow to work, or may not work at all. This can be life-threatening. Ask your healthcare provider for more information about the risks of aplastic anemia.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Aplastic Anemia
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
