The originating document has been archived. We cannot confirm the completeness, accuracy, or currency of the content.
Orbax Oral Suspension
This treatment applies to the following species: Company: Intervet/Merck Animal Health
Company: Intervet/Merck Animal Health
(orbifloxacin)
For Oral Use in Dogs and Cats Only.
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-305
 |
Federal law prohibits the extralabel use of this drug in food-producing animals. |
 |
CAUTION: Federal law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
Description
Orbifloxacin is a synthetic broad-spectrum antibacterial agent from the class of fluoroquinolone carboxylic acid derivatives. Orbifloxacin is the international nonproprietary name for 1 - cyclopropyl - 5,6,8 - trifluoro - 1,4 - dihydro - 7 - (cis - 3,5 - dimethyl - 1 - piperazinyl) - 4 - oxoquinoline - 3 - carboxylic acid. The chemical formula for orbifloxacin is C19H20F3N3O3 and its molecular weight is 395.38.
The compound is slightly soluble in water; however, solubility increases in both acidic and alkaline conditions. The compound has two dissociation constants (pKa’s): 5.95 and 9.01.
ORBAX® Oral Suspension is a malt flavored antibiotic suspension containing 30 mg/mL of orbifloxacin and sorbic acid as a preservative.
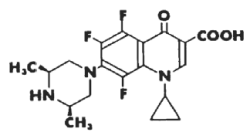
FIGURE 1. Chemical structure of orbifloxacin.
DOGS
Orbax Oral Suspension Indications
ORBAX® Oral Suspension is indicated for the treatment of urinary tract infections (cystitis) in dogs caused by susceptible strains of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius, Proteus mirabilis, Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis. ORBAX® Oral Suspension is also indicated for skin and soft tissue infections (wounds and abscesses) in dogs caused by susceptible strains of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius, Staphylococcus aureus, coagulase positive staphylococci, Pasteurella multocida, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas spp., Klebsiella pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter spp., Citrobacter spp., Enterococcus faecalis, β-hemolytic streptococci (Group G) and Streptococcus equisimilis.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Shake Well Before Use. BEFORE INITIAL USE, remove the cap and insert the syringe adaptor by pressing firmly into top of bottle. Insert the syringe tip into the adaptor opening and invert the bottle. Withdraw the required amount of medication with the calibrated syringe. After use, replace cap, leaving adaptor in the bottle, and rinse the syringe with water.
The dose of ORBAX® Oral Suspension in the dog is 1.1 to 3.4 mg/lb (2.5 to 7.5 mg/kg) of body weight administered once daily (See Drug interactions and Animal Safety). The determination of dosage for any particular patient must take into consideration such factors as the severity and nature of the infection, the susceptibility of the causative organism, and the integrity of the patient’s host-defense mechanisms. Antibiotic susceptibility of the pathogenic organism(s) should be determined prior to use of this preparation. Therapy with ORBAX® Oral Suspension may be initiated before results of these tests are known. Once results become available, continue with appropriate therapy.
For the treatment of skin infections, ORBAX® Oral Suspension should be given for two (2) to three (3) days beyond the cessation of clinical signs to a maximum of 30 days. For the treatment of urinary tract infections, ORBAX® Oral Suspension should be administered for at least 10 consecutive days. If no improvement is seen within five (5) days, the diagnosis should be re-evaluated and a different course of therapy considered.
Contraindications
Orbifloxacin and other quinolones have been shown to cause arthropathy in immature animals of most species tested, the dog being particularly sensitive to this side effect. Orbifloxacin is contraindicated in immature dogs during the rapid growth phase (between 2 and 8 months of age in small and medium-sized breeds, and up to 18 months of age in large and giant breeds).
Orbifloxacin is contraindicated in dogs known to be hypersensitive to quinolones.
HUMAN WARNING: For use in animals only. Keep out of the reach of children.
Individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to quinolones should avoid this product. In humans, there is a risk of user photosensitization within a few hours after excessive exposure to quinolones. If excessive accidental exposure occurs, avoid direct sunlight.
Avoid contact with eyes. In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with copious amounts of water for 15 minutes. In case of dermal contact, wash skin with soap and water. Consult a physician if irritation persists following ocular or dermal exposure.
Precautions
Prescribing antibacterial drugs in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection is unlikely to provide benefit to treated animals and may increase the risk of the development of drug-resistant animal pathogens.Administer orbifloxacin with caution in the presence of hepatic insufficiency/impairment. Please refer to the cat side of the package insert for Precautions related specifically to cats. Quinolones should be used with caution in animals with known or suspected central nervous system (CNS) disorders. In such animals, quinolones have, in rare instances, been associated with CNS stimulation, which may lead to convulsive seizures. Quinolones have been shown to produce erosions of cartilage of weight-bearing joints and other signs of arthropathy in immature animals of various species. The safety of orbifloxacin in animals that are used for breeding or that are pregnant and/or lactating has not been demonstrated.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Compounds (eg, sucralfate, antacids, and multivitamins) containing divalent and trivalent cations (eg, iron, aluminum, calcium, magnesium, and zinc) may substantially interfere with the absorption of quinolones resulting in a decrease in product bioavailability. Therefore, the concomitant oral administration of quinolones with foods, supplements, or other preparations containing these compounds should be avoided.
The dosage of theophylline should be reduced when used concurrently with fluoroquinolones. Cimetidine has been shown to interfere with the metabolism of fluoroquinolones and should be used with care when used concurrently. Concurrent use of fluoroquinolones with oral cyclosporine is contraindicated. Concurrent administration of fluoroquinolones may increase the action of oral anticoagulants.
Adverse Reactions
In a field study, when the tablet formulation of orbifloxacin was administered at 2.5 mg/kg/day, no drug-related adverse reactions were reported. In a foreign field study using the oral suspension at 7.5 mg/kg/day, vomiting was reported for ORBAX® Oral Suspension and the comparator.Post Approval Experience with ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets (Rev. 2010): The following adverse events are based on post-approval adverse drug experience reporting with ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets. Not all adverse reactions are reported to FDA CVM. It is not always possible to reliably estimate the adverse event frequency or establish a causal relationship to product exposure using this data. The following adverse events are listed in decreasing order of reporting frequency:
DOG: Vomiting, convulsions, depression/lethargy, anorexia
For a complete listing of adverse reactions for ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets reported to the CVM see: http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae
For technical assistance or to report a suspected adverse reaction call 1-800-224-5318.
Clinical Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics in healthy, adult Beagle dogs: In fasted animals, orbifloxacin is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract following oral administration. The absolute bioavailability (F) of an oral dose is approximately 100%. The effects of concomitant feeding on the absorption of orbifloxacin have not been studied in the dog. Divalent cations are generally known to diminish the absorption of fluoroquinolones. (See DRUG INTERACTIONS.)
Distribution in the Body: Orbifloxacin penetrates into most tissues and body fluids following oral dosing. A summary of the body fluid and tissue drug levels at 3 and 6 hours following dose administration is presented in Table 1. Particularly high levels of orbifloxacin are found in the prostate, kidneys, liver, bile, lungs, lymph nodes, small intestine, cartilage, muscle, salivary gland and testes.
Table 1: Body Fluid/Tissue Distribution of 14C-Orbifloxacin-derived radioactivity in Dogs following Single and Multiple Oral Dose Administration of 5.0 mg/kg
|
Post-Treatment Levels of 14C-Orbifloxacin Derived Radioactivity (µg equiv/g) |
|||
|
|
Single Dose |
Multiple Dose |
|
|
|
3 hours |
6 hours |
6 hours following the final dose of a once daily for five day regimen (n=1) |
|
Body Fluids |
|
|
|
|
Aqueous humor |
... |
... |
0.526 |
|
Bile |
151 |
63.9 |
280 |
|
Blood |
... |
1.43 |
1.29 |
|
Red Blood Cells |
3.19 |
1.29 |
1.11 |
|
Plasma |
... |
... |
1.56 |
|
Cerebrospinal fluid |
0.203 |
0.300 |
0.548 |
|
Tissues |
|
|
|
|
Bone |
0.231 |
0.258 |
0.152 |
|
Cartilage |
4.67 |
6.62 |
4.72 |
|
Kidneys |
8.89 |
3.83 |
4.28 |
|
Liver |
10.1 |
3.49 |
3.30 |
|
Lungs |
4.10 |
2.03 |
1.81 |
|
Lymph nodes |
6.44 |
2.72 |
2.06 |
|
Muscle |
4.55 |
1.94 |
2.21 |
|
Prostate |
6.00 |
1.91 |
1.35 |
|
Salivary gland |
10.2 |
4.43 |
3.17 |
|
Skin |
1.90 |
1.05 |
1.57 |
|
Small Intestine |
6.00 |
6.31 |
6.91 |
|
Testes |
4.59 |
2.89 |
2.48 |
In a pharmacokinetic study conducted with ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets, within 24 hours of
administration, approximately 40% of an oral dose was excreted into the urine unchanged in dogs with normal renal function (n=12). This supports the effectiveness of orbifloxacin in the treatment of urinary tract infections. Based on the plasma elimination half-life and the dosing interval, negligible drug accumulation is expected with multiple dosing.
Pharmacokinetic parameters estimated in a randomized two-period, two-sequence crossover study using single intravenous and oral doses are summarized in Tables 2 and 3 and Figure 2.
Table 2: Mean Pharmacokinetic Parameters Estimated in 12 Adult Beagle Dogs After a Single IV Bolus of Orbifloxacin at 2.5 mg/kg
|
Pharmacokinetic Parameter |
Estimate (SE) |
|
Total body clearance (mL/min/kg) |
2.9 ± 0.2 |
|
Volume of distribution at steady state, Vss (L/kg) |
1.2 ± 0.2 |
|
AUC0-∞ (µg•h/mL) |
14.3 ± 0.9 |
|
Terminal plasma elimination half-life, T1/2 (hrs) |
5.4 ± 1.1 |
Table 3: Mean Pharmacokinetic Parameters Estimated in 12 Adult Beagle Dogs After a Single Oral Dose of Orbifloxacin Tablets at 2.5 mg/kg
|
Pharmacokinetic Parameter |
Tablets Estimate (SE) |
|
Total body clearance/F (mL/min/kg) |
3.0 ± 0.2 |
|
Maximum concentration Cmax (µg/mL) |
2.3 ± 0.3 |
|
Time of maximum concentration, Tmax (minutes) |
46 ± 27 |
|
AUC0-∞ (µg•h/mL) |
14.3 ± 1.4 |
|
Terminal plasma elimination half-life, T1/2 (hrs) |
5.6 ± 1.1 |
Figure 2: Plasma Concentration of Orbifloxacin (Tablet Formulation) vs. Time in Dogs
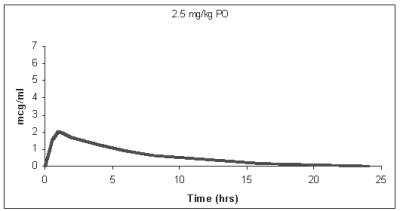
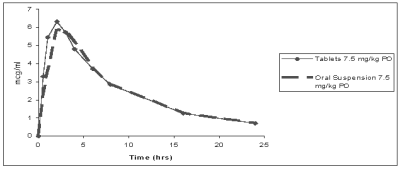
Pharmacokinetic parameters estimated in a randomized, two-period, two-sequence crossover biocomparability study between the orally administered ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets and ORBAX® Oral Suspension are summarized in Table 4 and Figure 3. Results of this study demonstrate that ORBAX® Oral Suspension is bioequivalent to ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets.
Table 4: Mean Pharmacokinetic Parameters Estimated in 24 Adult Beagle Dogs After a Single Oral Dose of Orbifloxacin Tablets or Oral Suspension at 7.5 mg/kg
|
Pharmacokinetic Parameter |
Tablets Estimate (SE) |
Oral Suspension Estimate (SE) |
|
Total body clearance/F (mL/min/kg) |
2.09 ± 0.32 |
2.17 ± 0.54 |
|
Maximum concentration Cmax (µg/mL) |
6.32 ± 0.87 |
5.82 ± 0.87 |
|
Time of maximum concentration, Tmax (hrs) |
2.02 ± 0.94 |
2.29 ± 0.55 |
|
AUC0-∞ (µg•h/mL) |
60.85 ± 9.08 |
60.37 ± 11.50 |
|
Terminal plasma elimination half-life, T1/2 (hrs) |
6.13 ± 0.88 |
6.26 ± 0.84 |
FIGURE 3: Mean plasma concentration of orbifloxacin (tablets and oral suspension) vs. time in dogs (7.5 mg/kg)
MICROBIOLOGY: Orbifloxacin is bactericidal against a wide range of gram-negative and gram-positive organisms and exerts its antibacterial effect through interference with the bacterial enzyme DNA gyrase which is needed for the maintenance and synthesis of bacterial DNA. The time-kill kinetics of orbifloxacin against Staphylococcus spp. has been described by Ganiere et al., 20041.
The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of pathogens isolated in multicentered clinical field studies performed with the oral tablet formulation in the United States were determined using Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines2, and are in Tables 7 and 8.
Table 7: MIC Values* (µg/mL) of Orbifloxacin Against Urinary Pathogens Isolated Between 1994 and 1996 From Clinical Infections During Field Studies in Dogs
|
Bacteria Name |
Number of Isolates |
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
MIC Range |
|
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius |
5 |
** |
** |
0.0975 - 0.39 |
|
Proteus mirabilis |
19 |
0.78 |
1.56 |
0.048 - 1.56 |
|
Escherichia coli |
17 |
0.0975 |
0.39 |
0.024 - ≥25 |
|
Enterococcus faecalis |
5 |
** |
** |
0.003 - 3.12 |
*The correlation between the in vitro susceptibility data (MIC Values) and clinical response has not been determined.
**There were an insufficient number of isolates to calculate the MIC50 or MIC90.
Table 8: MIC Values* (µg/mL) of Orbifloxacin Against Skin Pathogens Isolated Between 1994 and 1996 From Clinical Infections During Field Studies in Dogs
|
Bacteria Name |
Number of Isolates |
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
MIC Range |
|
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius |
51 |
0.195 |
0.39 |
0.003 - 1.56 |
|
Staphylococcus aureus |
8 |
** |
** |
0.195 - ≥25 |
|
coagulase positive staphylococci |
59 |
0.195 |
0.39 |
0.003 - ≥25 |
|
Pasteurella multocida |
5 |
** |
0 |
0.003 - 0.78 |
|
Proteus mirabilis |
7 |
** |
** |
0.39 - 1.56 |
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
14 |
3.125 |
12.5 |
0.39 - ≥25 |
|
Pseudomonas spp. |
18 |
3.125 |
12.5 |
0.02 - ≥25 |
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae |
9 |
** |
** |
0.0975 - 0.195 |
|
Escherichia coli |
28 |
0.0975 |
0.39 |
0.012 - 6.25 |
|
Enterobacter spp. |
24 |
0.0975 |
0.39 |
0.012 - 6.25 |
|
Citrobacter spp. |
4 |
** |
** |
0.024 - 0.0975 |
|
Enterococcus faecalis |
11 |
** |
** |
0.3 - ≥25 |
|
β-hemolytic streptococci (Group G) |
22 |
0.39 |
1.56 |
0.006 - 3.12 |
|
Streptococcus equisimilis |
10 |
** |
** |
0.003 - 0.78 |
*The correlation between the in vitro susceptibility data (MIC values) and clinical response has not been determined.
**There were an insufficient number of isolates to calculate the MIC50 or MIC90.
Effectiveness
Clinical effectiveness for ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets (NADA 141-081) was established for the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections (wounds and abscesses) and urinary tract infections (cystitis) in dogs. Specific bacterial pathogens isolated in the clinical field study are listed in the MICROBIOLOGY section.Effectiveness of the oral suspension in dogs was established in a biocomparability study demonstrating that ORBAX® Oral Suspension is bioequivalent to ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets.
ANIMAL SAFETY:
No mortality occurred when ORBAX® Oral Suspension was administered to young, clinically healthy, adult Beagles at doses of 7.5 mg/kg, 22.5 mg/kg, and 37.5 mg/kg once daily for 30 consecutive days, and at 75 mg/kg/day once daily for 10 consecutive days. Body temperature, respiratory rate and heart rate were not affected by orbifloxacin treatment. Discoloration of the feces (white to yellow) was observed at all dose levels. At 37.5 and 75 mg/kg/day, ORBAX® Oral Suspension caused gastrointestinal signs, including emesis and soft and/or mucoid feces. At doses of 75 mg/kg/day, hypersalivation was observed. Male dogs treated with 75 mg/kg/day had reduced food consumption and mild weight loss. Glucosuria and lower urine pH were also observed in 7 out of 10 dogs treated with orbifloxacin at 75 mg/kg/day. No other changes in clinical chemistry related to these changes in the urinalysis were observed. The mechanism responsible for the glucosuria and lower pH in this group could not be determined. Following 10 days of treatment with 75 mg/kg/day, one male dog developed hepatic perilobular necrosis, bile duct hyperplasia and inflammation associated with serum elevations in bilirubin and hepatic enzymes (ALK, ALT, AST, GGT). The dog completed the study without clinical signs of illness. At necropsy, the liver had a tan discoloration and weighed significantly less than the livers from other dogs in the group and control dogs. No treatment-related pathologic liver changes were noted in any other dogs treated with orbifloxacin during the study. Articular cartilage defects in the head of the humerus in one male dog in the 3X dose group, and in the medial condyle of the distal femur in one male dog in the 5X dose group were observed. Based on microscopic examination of these lesions it was determined that both lesions were long standing and were present prior to treatment with orbifloxacin. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS)
PALATABILITY: In a field palatability study, conducted in 81 dogs, ORBAX® Oral Suspension was accepted by 96.3% of the dogs following oral administration.
CATS
Orbax Oral Suspension Indications
ORBAX® Oral Suspension is indicated for the treatment of skin infections (wounds and abscesses) in cats caused by susceptible strains of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pasteurella multocida.
Dosage and Administration
Shake Well Before Use. BEFORE INITIAL USE, remove the cap and insert the syringe adaptor by pressing firmly into top of bottle. Insert the syringe tip into the adaptor opening and invert the bottle. Withdraw the required amount of medication with the calibrated syringe. After use, replace cap, leaving adaptor in the bottle, and rinse the syringe with water.In the cat, ORBAX® Oral Suspension and ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets are not bioequivalent. On a mg/kg basis, ORBAX® Oral Suspension provides lower and more variable plasma levels of orbifloxacin than ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets (See Clinical Pharmacology and Precautions). The dose of ORBAX® Oral Suspension in the cat is 3.4 mg/lb (7.5 mg/kg) of body weight administered once daily. DO NOT EXCEED 3.4 mg/lb (7.5 mg/kg) BODY WEIGHT PER DAY IN CATS. ORBAX® Oral Suspension should be given for two (2) to three (3) days beyond the cessation of clinical signs.
Antibiotic susceptibility of the pathogenic organism(s) should be determined prior to use of this preparation. Therapy with ORBAX® Oral Suspension may be initiated before results of these tests are known. Once results become available, continue with appropriate therapy. If no improvement is seen within 3 to 4 days, the diagnosis should be re-evaluated and a different course of therapy considered.
Contraindications
Orbifloxacin and other quinolones have been shown to cause arthropathy in immature animals of most species tested, the dog being particularly sensitive to this side effect. Orbifloxacin is contraindicated in immature dogs during the rapid growth phase (between 2 and 8 months of age in small and medium-sized breeds, and up to 18 months of age in large and giant breeds).
Orbifloxacin is contraindicated in cats known to be hypersensitive to quinolones.
HUMAN WARNING: For use in animals only. Keep out of the reach of children.
Individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to quinolones should avoid this product. In humans, there is a risk of user photosensitization within a few hours after excessive exposure to quinolones. If excessive accidental exposure occurs, avoid direct sunlight.
Avoid contact with eyes. In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with copious amounts of water for 15 minutes. In case of dermal contact, wash skin with soap and water. Consult a physician if irritation persists following ocular or dermal exposure.
Precautions
Prescribing antibacterial drugs in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection is unlikely to provide benefit to treated animals and may increase the risk of the development of drug-resistant animal pathogens.The use of fluoroquinolones in cats has been reported to adversely affect the retina. Such products should be used with caution in cats. Blindness has also been reported post-approval in cats. In some cases, blindness has been temporary. DO NOT EXCEED 3.4 mg/lb (7.5 mg/kg) BODY WEIGHT PER DAY IN CATS. If higher blood levels of orbifloxacin are needed, ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets should be used at a dose of 2.3-3.4 mg/lb (5.0-7.5 mg/kg). On a mg/kg basis, ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets provide higher and less variable plasma levels of orbifloxacin than ORBAX® Oral Suspension.
Quinolones should be used with caution in animals with known or suspected central nervous system (CNS) disorders. In such animals, quinolones have, in rare instances, been associated with CNS stimulation, which may lead to convulsive seizures. Quinolones have been shown to produce erosions of cartilage of weight-bearing joints and other signs of arthropathy in immature animals of various species. The safety of orbifloxacin in animals that are used for breeding or that are pregnant and/or lactating has not been demonstrated.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Compounds (eg, sucralfate, antacids, and multivitamins) containing divalent and trivalent cations (eg, iron, aluminum, calcium, magnesium, and zinc) may substantially interfere with the absorption of quinolones resulting in a decrease in product bioavailability. Therefore, the concomitant oral administration of quinolones with foods, supplements, or other preparations containing these compounds should be avoided.
The dosage of theophylline should be reduced when used concurrently with fluoroquinolones.
Cimetidine has been shown to interfere with the metabolism of fluoroquinolones and should be used with care when used concurrently. Concurrent use of fluoroquinolones with oral cyclosporine is contraindicated. Concurrent administration of fluoroquinolones may increase the action of oral anticoagulants.
Adverse Reactions
In a field study, when the tablet formulation of orbifloxacin was administered at 2.5 mg/kg/day, no drug-related adverse reactions were reported. In a foreign field study using the oral suspension at 7.5 mg/kg/day, vomiting was reported for ORBAX® Oral Suspension and the comparator.Post Approval Experience with ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets (Rev. 2010): The following adverse events are based on post-approval adverse drug experience reporting with ORBAX® Tablets. Not all adverse reactions are reported to FDA CVM. It is not always possible to reliably estimate the adverse event frequency or establish a causal relationship to product exposure using this data. The following adverse events are listed in decreasing order of reporting frequency:
CAT: Blindness, mydriasis, anorexia, ataxia, depression/lethargy, vomiting, convulsions, abnormal retina, hypersalivation. In some cases, blindness has been temporary.
For a complete listing of adverse reactions for ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets reported to the CVM see: http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae
For technical assistance or to report a suspected adverse reaction call 1-800-224-5318.
Clinical Pharmacology
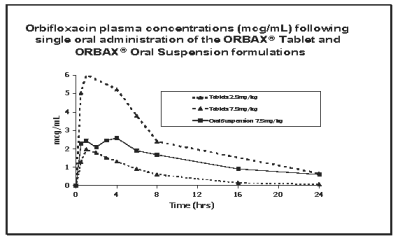
Comparison to ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets: In the cat, ORBAX® Oral Suspension and ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets are not bioequivalent. On a mg/kg basis, ORBAX® Oral Suspension provides lower and more variable plasma levels of orbifloxacin than ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets. When ORBAX® Oral Suspension is dosed at its clinical dose of 7.5 mg/kg, plasma levels of orbifloxacin are consistently higher than those provided by ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets dosed at the low end (2.5 mg/kg) of its clinical dose range of 2.5 - 7.5 mg/kg. See Figure 2.
Figure 2. Plasma Concentration of Orbifloxacin
Based upon the data generated across three separate studies, the pharmacokinetics of orbifloxacin when administered as a 7.5 mg/kg dose of ORBAX® Oral Suspension is provided in Table 1.
Table 1. Pharmacokinetic parameter estimates following a single 7.5 mg/kg dose of ORBAX® Oral Suspension to Fasted Cats (n=42)
|
|
AUC 0-24 (µg*hr /mL) |
Cmax (µg /mL) |
AUC 0-inf (µg*hr /mL) |
T 1/2 (hr) |
|||
|
|
Total |
Unbound |
Total |
Unbound |
Total |
Unbound |
|
|
Mean |
28.49 |
23.36 |
3.01 |
2.47 |
33.98 |
27.86 |
7.57 |
|
Stdev |
9.03 |
|
1.16 |
|
11.37 |
|
3.19 |
|
%CV |
31.70 |
|
38.58 |
|
33.47 |
|
42.12 |
Effect of Food: In the cat, the Cmax and T1/2 of orbifloxacin in plasma is unchanged by concomitant administration of ORBAX® Oral Suspension with food, although the Tmax is delayed and the AUC is increased by an average of 32% (the observed fed/fasted ratios of AUC0-inf values ranged from 0.70 to 1.60).
Plasma Protein-Binding: Orbifloxacin has low protein binding (~18%) in feline plasma.
MICROBIOLOGY: Orbifloxacin is bactericidal against a wide range of gram-negative and gram-positive organisms and exerts its antibacterial effect through interference with the bacterial enzyme DNA gyrase which is needed for the maintenance and synthesis of bacterial DNA. The time-kill kinetics of orbifloxacin against Staphylococcus spp. has been described by Ganiere et al., 2004 1.
The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of pathogens isolated in multicentered clinical field study performed with the oral tablet formulation in the United States were determined using Clinical and laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines 2, and are shown in Table 2.
Table 2: MIC Values* (mcg/mL) of Orbifloxacin Against Skin Pathogens Isolated Between 1994 and 1996 From the ORBAX® Tablet Field Study in Cats
|
Bacteria Name |
Number of Isolates |
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
MIC Range |
|
Staphylococcus aureus |
7 |
** |
** |
0.195-0.39 |
|
Pasteurella multocida |
47 |
0.012 |
0.048 |
0.003-0.195 |
|
Escherichia coli |
17 |
0.048 |
0.195 |
0.024-25 |
*The correlation between the in vitro susceptibility data (MIC values) and clinical response has not been determined.
**There were an insufficient number of isolates to calculate the MIC50 or MIC90.
Effectiveness
Clinical effectiveness for ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets (NADA 141-081) was established for the treatment of skin infections (wounds and abscesses) caused by susceptible strains of Pasteurella multocida, Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus in cats. Specific bacterial pathogens isolated in clinical field study are listed in the MICROBIOLOGY section.Effectiveness of the oral suspension in cats was established through comparison of the plasma pharmacokinetics of the approved product, ORBAX® (orbifloxacin) Tablets (NADA #141-081) to the pharmacokinetics of ORBAX® Oral Suspension. When administered at a dose of 3.4 mg/lb (7.5 mg/kg), ORBAX® Oral Suspension achieves plasma concentrations that exceed those reached following administration of the low end of the approved tablet dose range (2.5 mg/kg). The pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic data indicate that cats treated with ORBAX® Oral Suspension at a dose of 3.4 mg/lb (7.5 mg/kg) would exceed the CLSI2 criterion for clinical success in cats for Pasteurella multocida, Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus with a high degree of certainty on the first and subsequent days of dosing even if it were assumed that all orbifloxacin bound to plasma protein (18%) was biologically unavailable.
ANIMAL SAFETY: Orbifloxacin administered as ORBAX® Oral Suspension to young, clinically healthy, adult cats at doses of 7.5 mg/kg, 15 mg/kg, 45 mg/kg, and 75 mg/kg once daily for 30 consecutive days. At the 45 mg/kg/day and 75 mg/kg/day doses, ORBAX® Oral Suspension caused mild gastrointestinal effects including an increased incidence of emesis, salivation, increased lacrimation and soft, mucoid, and/or watery feces. A mild decrease in food consumption was noted in females that received 45 mg/kg/day and in both sexes that received 75 mg/kg/day.
One cat in the 75 mg/kg/day group had a transient increase in AST (56U/L: normal 14-30) and ALT (642 U/L: normal 42-86) on Day 21 which returned to normal levels by study completion. Additionally at 75 mg/kg/day a decrease in serum alkaline phosphatase was observed in 4 of the 8 cats. Decreased serum albumin was noted in a cat that received 45 mg/kg/day and one cat that received 75 mg/kg/day, with a secondary decrease in serum calcium noted in one cat that received 75 mg/kg/day. Leukocytosis with neutrophilia was seen in one 75 mg/kg/day and two 15 mg/kg/day cats. A marked leukopenia was seen in one cat receiving 15 mg/kg/day.
In cats treated with 45 and 75 mg/kg/day, ophthalmic changes were apparent. Ophthalmologic examinations of multiple cats that received 45 and 75 mg/kg/day revealed tapetal hyperreflectivity, which correlated histopathologically with minimal photoreceptor swelling. Electron microscopy revealed swollen rod cells with disorganized disc material in the outer photoreceptor segments. The ophthalmologic examinations on study Days 24 and 31 revealed test article-related hyperreflectivity (retinal degeneration) in some cats at both 45 and 75 mg/kg/day, although electroretinographic responses at the same time intervals did not indicate any changes in retinal function. Minimal photoreceptor degeneration was noted microscopically in all cats at 45 and 75 mg/kg/day. In the 7.5 mg/kg/day-dose group, two cats had abnormal retinal exams (metallic sheen to tapetum) but no functional or structural pathology was observed.
PALATABILITY: In a field palatability study, conducted in 101 cats, ORBAX® Oral Suspension was accepted by 95% of cats.
STORAGE CONDITIONS: Store between 2°C and 25°C (36°F and 77°F). ORBAX® Oral Suspension does not require refrigeration. Shake well before use. Store upright.
How Supplied
ORBAX® Oral Suspension is supplied in a sealed bottle with a 20 mL deliverable volume.References
1 Ganiere JP, Medaille C, and Etoré F: In vitro antimicrobial activity of orbifloxacin against Staphylococcus intermedius isolates from canine skin and ear infections. Research in Veterinary Science 77:67-71, 2004.
2 CLSI Document M37-A3 Development of In Vitro Susceptibility Testing Criteria and Quality Control Parameters for Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents; Approved Guideline-Third Edition
Formulated in Friesoythe, Germany
Intervet Inc (d/b/a Merck Animal Health)
Rev. 06/20
© 2010, 2015, Intervet Inc., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Madison, NJ 07940
All rights reserved.
386914 R2
CPN: 1047300.3
Intervet Inc.
126 E. LINCOLN AVENUE, PO BOX 2000, Rahway, NJ, 07065
| Customer Service: | 800-521-5767 | |
| Technical Service (Companion Animal): | 800-224-5318 | |
| Technical Service (Livestock): | 800-211-3573 | |
| Website: | www.merck-animal-health-usa.com |
 |
THIS SERVICE AND DATA ARE PROVIDED "AS IS". DVMetrics assumes no liability, and each user assumes full risk, responsibility, and liability, related to its use of the DVMetrics service and data. See the Terms of Use for further details. |

Copyright © 2025 Animalytix LLC. Updated: 2025-08-27
