A180 (Canada)
This treatment applies to the following species: Company: Zoetis
Company: Zoetis
danofloxacin mesylate sterile injectable solution
Veterinary Use Only
DIN 02261200
Description
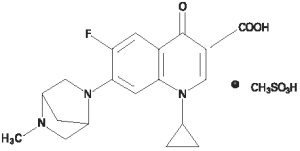
A180® Injectable Solution is a sterile solution containing danofloxacin mesylate, a synthetic fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agent. Danofloxacin mesylate is the non-proprietary designation for (1S)-1cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-7-(5-methyl-2,5-diazabicyclo [2.2.1]hept-2-yl)-4-oxo-3-quinolone carboxylic acid monomethanesulfonate. The empirical formula is C19H20FN3O3•CH3SO3H and molecular weight 453.49.
Figure 1. The chemical structure of danofloxacin mesylate
Each mL contains 180 mg of danofloxacin (as danofloxacin mesylate) and 2.5 mg phenol as the preservative.
A180 Indications
For the treatment of bovine respiratory disease associated with Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida.
Dosage and Administration
Care should be taken to dose accurately. Administered dose volume should not exceed 15 mL per injection site.
Single-Dose Therapy: Administer subcutaneously at 8 mg/kg of body weight (4.4 mL/100 kg) as a one-time injection,
Multi-Day Therapy: Administer subcutaneously at 6 mg/kg of body weight (3.3 mL/100 kg) with this treatment repeated once approximately 48 hours following the first injection
Table 1. A180 Danofloxacin Mesylate Injectable Solution Dosage Table
|
Cattle Weight |
Dose Volume (mL) |
||
|
Lb |
kg |
6 mg/kg given twice 48 hours apart |
8 mg/kg given once |
|
50 |
22 |
0.75 |
1 |
|
100 |
45 |
1.5 |
2 |
|
200 |
91 |
3.0 |
4 |
|
300 |
136 |
4.5 |
6 |
|
400 |
181 |
6.0 |
8 |
|
500 |
227 |
7.5 |
10 |
|
600 |
272 |
9.0 |
12 |
|
700 |
318 |
10.5 |
14 |
|
800 |
363 |
12.0 |
16* |
|
900 |
408 |
13.5 |
18* |
|
1000 |
454 |
15.0 |
20* |
*Administered dose volume should not exceed 15 mL per injection site.
Cautions: Quinolone-class drugs should be used with caution in animals with known or suspected central nervous system (CNS) disorders. In such animals, quinolones have, in rare instances, been associated with CNS stimulation, which may lead to convulsive seizures. Quinolone-class drugs have been shown to produce erosions of cartilage of weight-bearing joints and other signs of arthropathy in immature, rapidly growing animals of various species. Care should be taken to dose accurately. The effects of danofloxacin on bovine reproductive performance, pregnancy, and lactation have not been adequately determined. Subcutaneous injection can cause a local tissue reaction that may result in trim loss of edible tissue at slaughter.
Warnings
Treated animals must not be slaughtered for use as food for at least 7 days after the latest treatment with this drug. Do not use in dairy cattle. Do not use in veal calves. The withdrawal period has not been established in pre-ruminating calves.To limit the development of antimicrobial resistance:
● Fluoroquinolone drugs such as A180 should not be used indiscriminately.
● A180 should not be used as an arrival treatment for feedlot cattle.
● A180 should only be used for treating individual cases of bovine respiratory disease after first choice treatments have failed.
● The choice of A180 as the most appropriate treatment should be confirmed by clinical experience supported where possible, by pathogen culture and drug susceptibility testing.
● Do not use in an extra-label manner in cattle or any other species.
Keep out of reach of children
Note: To reduce the possibility of excess trim at the injection site, it is recommended that cattle not be slaughtered for up to 21 days after the latest treatment with this drug.
Adverse Reactions
A hypersensitivity reaction was noted in two (2) healthy calves treated with A180 Injectable Solution in a laboratory study. No adverse reactions attributable to the treatment were observed during the clinical field trials.Clinical Pharmacology
Danofloxacin distributes extensively throughout the body, as evidenced by a steady state volume of distribution (VDss) exceeding 1L/kg. Danofloxacin concentrations in the lung homogenates markedly exceed those observed in plasma, further suggesting extensive distribution to the indicated site of infection. Danofloxacin is rapidly eliminated from the body (apparent terminal elimination T1/2 ranging from 3 to 6 hours), and therefore negligible accumulation is expected to occur when animals are dosed twice, 48 hours apart. Danofloxacin is rapidly absorbed and is highly bioavailable when administered as a subcutaneous injection in the neck. No statistically significant gender difference was observed in peak or total systemic exposure following subcutaneous administration. Linear pharmacokinetics have been demonstrated when danofloxacin is administered by subcutaneous injection at doses up to 10-mg/kg.
Pharmacokinetic parameter values associated with a 6 mg/kg dose are provided in Table 2.
Table 2: Danofloxacin pharmacokinetic values (6 mg/kg)
|
|
|
Steers |
Heifers |
||
|
Mean |
%CVe |
Mean |
%CVe |
||
|
a AUC0-24 |
µg x hr/mL |
9.4 |
10 |
8.8 |
9 |
|
b F |
|
92 |
5 |
87 |
3 |
|
a Cmax |
µg/mL |
1.25 |
16 |
1.27 |
13 |
|
a,c Tmax |
h |
3.2 |
42 |
1.7 |
31 |
|
d CL |
L/hr |
0.54 |
12 |
0.62 |
9 |
|
d VDss |
L/kg |
2.7 |
7 |
2.6 |
4 |
|
a T |
hr |
4.8 |
18 |
4.2 |
7 |
a Pharmacokinetic estimates based upon a 6 mg/kg subcutaneous injection administered into the lateral neck region. AUC0-24 = area under the plasma concentration versus time curve from hr zero to hr 24 postdose; Cmax = maximum observed concentration. Tmax = time to Cmax.
b F = extent of drug absorption following subcutaneous administration. Within subject F values were determined as the ratio of AUC0-inf values estimated following a 6-mg/kg dose administered as either a subcutaneous or intravenous injection
c Tmax: statistically significant differences were detected between genders. Given the similarity in Cmax values, these differences are not expected to have any clinical significance.
d CL (clearance) and VDss (steady state volume of distribution) were determined from data obtained after intravenous administration of a 6 mg/kg dose.
e Coefficient of variation %
Microbiology: Danofloxacin exerts its activity by inhibiting the bacterial DNA gyrase enzyme, thereby blocking DNA replication. Inhibition of DNA gyrase is lethal to bacteria and danofloxacin has been shown to be bactericidal. Danofloxacin is active in vitro against gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria. The Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (MIC) of danofloxacin were determined for isolates obtained from natural infections in cattle in the United States and Canada, from 1994 to 1997 (Table 3), using the standardized microdilution technique (SENSITITRE/ALAMAR, Accumed International).
Table 3. MIC Values (µg/mL) of Danofloxacin Against Bacterial Isolates from Natural Infections of Cattle
|
Species |
No. Isolates |
MIC90* |
|
Mannheimia haemolytica |
400 |
0.06 |
|
Pasteurella multocida |
318 |
0.03 |
* The minimum inhibitory concentration for 90% or more of the isolates.
Table 4. Danofloxacin minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values* of indicated bacteria isolated from 2013 field studies in the U.S. and Canada
|
Indicated Bacteria |
Number of Isolates |
MIC50** (µg/mL) |
MIC90** (µg/mL) |
MIC Range (µg/mL) |
|
Mannheimia haemolytica |
507 |
0.03 |
0.06 |
≤0.008 to >8 |
|
Pasteurella multocida |
324 |
≤0.008 |
0.12 |
≤0.008 to 1.0 |
*The correlation between in vitro susceptibility data and clinical effectiveness is unknown.
**The lowest MIC to encompass 50% and 90% of the most susceptible isolates, respectively.
Table 5. Danofloxacin minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) 50%, 90% and range values (µg/mL) of Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida isolates from the United States and Canada, 2004-2009*
|
Organism |
Year |
No. Isolates |
MIC50 |
MIC90 |
Range |
|
M. haemolytica |
2004 |
330 |
0.03 |
0.5 |
0.015->2 |
|
2005 |
333 |
0.03 |
0.5 |
≤0.004->2 |
|
|
2006 |
352 |
0.06 |
0.25 |
0.008->2 |
|
|
2007 |
438 |
0.06 |
0.5 |
0.008->2 |
|
|
2008 |
369 |
0.03 |
0.5 |
0.008->2 |
|
|
2009 |
304 |
0.06 |
1 |
0.008->2 |
|
|
P. multocida |
2004 |
364 |
0.03 |
0.5 |
0.008->2 |
|
2005 |
377 |
0.015 |
0.25 |
≤0.004->2 |
|
|
2006 |
392 |
0.015 |
0.5 |
0.008->2 |
|
|
2007 |
508 |
0.015 |
0.5 |
0.008->2 |
|
|
2008 |
397 |
0.015 |
0.5 |
≤0.004->2 |
|
|
2009 |
328 |
0.03 |
0.25 |
0.008->2 |
*MIC50: Drug concentration that inhibits 50% of a bacterial population; MIC90: Drug concentration that inhibits 90% of a bacterial population and was summarized from Portis et al. A ten-year (2000-2009) study of antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria that cause bovine respiratory disease complex - Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida - in the United States and Canada. JVDI, 24(5):932-944. 2012.
Interpretive Standards (Provisional) for Disk Diffusion and Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Susceptibility Testinga
|
Antimicrobial Agent |
Disk Content |
Zone Diameter (mm) |
MIC (µg/mL) |
||||
|
S |
I |
R |
S |
I |
R |
||
|
Danofloxacin (DAN 5) Bovine (Respiratory Disease) - Mannheimia haemolytica - Pasteurella multocida |
5 µg |
≥ 22 |
- a |
- a |
≤ 0.25 |
- a |
- a |
a Insufficient data were available to establish breakpoints for the Intermediate (I) and Resistant (R) categories. Zone sizes smaller than 22 mm or MIC values greater than 0.25 µg/mL suggest a decreased susceptibility compared to susceptible (S) strains.
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals. 3rd edition. CLSI supplement VET01S. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 950 West Valley Road, Suite 2500, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087 USA, 2015.
Safety: Safety studies were conducted in feeder calves using single doses of 10, 20, or 30 mg/kg for six consecutive days and 18, 24, or 60 mg/kg for three consecutive days. No clinical signs of toxicity were observed at doses of 10 and 20 mg/kg when administered for six days nor at doses of 18 and 24 mg/kg when administered for three days. Histologic evidence of fluoroquinolone chondropathy was detected in one of five (1/5) animals in the 18 mg/kg group. Clinical signs of inappetance, transient lameness, ataxia, tremors, nystagmus, and recumbency were observed when a dose of 30 mg/kg had been administered for four consecutive days. Clinical signs of inappetance and recumbency were observed when a dose of 60 mg/kg was administered for three days. Articular cartilage lesions, consistent with fluoroquinolone chondropathy, were also observed after examination of joints from one of six (1/6) and five of six (5/6) animals administered 20 and 30 mg/kg for six days, respectively, and four of four (4/4) animals treated with 60 mg/kg for three days. Swelling at the injection site was noted at each dose level.
Safety was also evaluated in 21-day-old calves. In one group, these immature animals were given injections of 6 mg/kg on study days 0, 2, 3, 5, 6, and 8. A second group of animals received injections of 18 mg/kg for a total of two injections 48 hours apart. The only treatment-related sign was erythema of the sclera and nasal pad in calves that received 18 mg/kg.
No changes in clinical pathology parameters were observed. No articular cartilage lesions were observed in the joints at any dosage. An injection site study conducted in feeder calves demonstrated that the product may induce a reaction in the subcutaneous tissue and the underlying muscle.
Efficacy Confirmation: A180 Injectable Solution has been shown in clinical field trials to be effective in the treatment of bovine respiratory disease associated with Mannheimia haemolytica and Pasteurella multocida. Bacterial pathogens isolated in clinical field studies are provided in the Microbiology section.
Storage
Store between 15 and 30°C. Protect from light and from freezing. The color is yellow to amber. Color does not affect potency.Presentation: A180 Injectable Solution is supplied in 100 mL amber glass sterile multi-dose vials.
Zoetis® and A180 are registered trademarks of Zoetis or its licensors.
Zoetis Canada Inc., Kirkland QC H9H 4M7
40052053
April 2025
CPN: 1198316.6
16,740 TRANS-CANADA HIGHWAY, KIRKLAND, QC, H9H 4M7
| Order Desk: | 800-663-8888 | |
| Technical Services Canada: | 800-461-0917 | |
| Technical Services USA: | 800-366-5288 | |
| Website: | www.zoetis.ca |
 |
THIS SERVICE AND DATA ARE PROVIDED "AS IS". Animalytix assumes no liability, and each user assumes full risk, responsibility, and liability, related to its use of the Animalytix service and data. See the Terms of Use for further details. |

Copyright © 2025 Animalytix LLC. Updated: 2025-08-27
