Tlando: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: testosterone undecanoate
Dosage form: capsule, liquid filled
Drug class: Androgens and anabolic steroids
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 27, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Drug Abuse and Dependence
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
- Medication Guide
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TLANDO (testosterone undecanoate) capsules, for oral use, CIII
Initial U.S. Approval: 1953
Recent Major Changes
| Boxed Warnings, Blood Pressure Increases | Removed 07/2025 |
| Indications and Usage, Limitations of Use (1) | 07/2025 |
| Contraindications, Men with “age related hypogonadism” (4) | Removed 07/2025 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Venous Thromboembolism (5.2) | 07/2025 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Blood Pressure Increases (5.4) | 07/2025 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Cardiovascular Risk (5.4) | Removed 07/2025 |
Indications and Usage for Tlando
TLANDO is an androgen indicated for testosterone replacement therapy in adult males for conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone (1).
Limitations of Use
Tlando Dosage and Administration
- Prior to initiating TLANDO, confirm the diagnosis of hypogonadism by ensuring that serum testosterone concentrations have been measured in the morning on at least two separate days and that these serum testosterone concentrations are below the normal range (2.2).
- Recommended dosage is 225 mg orally twice daily with food (2.3).
- Monitor serum testosterone after initiating TLANDO to determine if TLANDO should be continued or discontinued (2.3).
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Capsules: 112.5 mg (3)
Contraindications
Warnings and Precautions
-
Polycythemia: Monitor hematocrit approximately every 3 months during the first year after beginning TLANDO and then every 6 months thereafter during treatment. Discontinue TLANDO if necessary (5.1).
-
Venous thromboembolism (VTE): VTE, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) have been reported in patients using testosterone products. Discontinue TLANDO if VTE is suspected and initiate appropriate workup and management (5.2).
-
Worsening of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Potential Risk of Prostate Cancer: Monitor patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH. Evaluate patients for prostate cancer, including monitoring prostate specific antigen (PSA) prior to initiating and during treatment with androgens (5.3)
-
Blood Pressure Increases: TLANDO can increase blood pressure, which can increase cardiovascular risk over time. Measure blood pressure periodically. Not recommended for use in men with uncontrolled hypertension (5.4)
-
Abuse of Testosterone and Monitoring of Serum Testosterone: If testosterone use at doses higher than recommended for the approved indication and in combination with other anabolic androgenic steroids is suspected, check serum testosterone concentration (5.5).
-
Potential for Adverse Effects on Spermatogenesis: TLANDO may cause azoospermia (5.7, 8.3).
-
Edema: Edema, with or without congestive heart failure (CHF) may occur in patients with preexisting cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease. Discontinue TLANDO and initiate appropriate workup (5.9).
-
Sleep Apnea: TLANDO may potentiate sleep apnea in those with risk factors (5.10).
-
Lipid Changes: Testosterone may affect serum lipid profile. Monitor patient lipid concentrations; if necessary, adjust dosage of lipid lowering drug(s) or discontinue TLANDO (5.12).
-
Increases in Prolactin: Monitor serum prolactin levels prior to initiation of TLANDO and 3 to 4 months after starting TLANDO. Discontinue TLANDO if serum prolactin levels remain elevated (5.15).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 2%): increased blood prolactin, hypertension, increased hematocrit, upper respiratory tract infection, weight increased, headache, and musculoskeletal pain (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Verity Pharma at 1-844-837-4891 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Insulin: In patients with diabetes, concomitant use with TLANDO may decrease blood glucose and insulin requirements (7.1).
- Oral Anticoagulants: Concomitant use with TLANDO may cause changes in anticoagulant activity. Monitor International Normalized Ratio and prothrombin time frequently (7.2).
- Corticosteroids: Concomitant use with TLANDO may result in increased fluid retention. Use with caution, particularly in patients with cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease (7.3).
- Drugs that May Also Increase Blood Pressure: Concomitant use with TLANDO may lead to additional increases in blood pressure (7.4).
Use In Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients: Geriatric patients treated with androgens may also be at risk for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH and hypertension (8.5).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 7/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Tlando
TLANDO is indicated for testosterone replacement therapy in adult males for conditions associated with a deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone:
- Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): testicular failure due to conditions such as cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testis syndrome, orchiectomy, Klinefelter's syndrome, chemotherapy, or toxic damage from alcohol or heavy metals. These men usually have low serum testosterone concentrations and gonadotropins (follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH)) above the normal range [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired): gonadotropin or luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) deficiency or pituitary-hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation. These men have low testosterone serum concentrations but have gonadotropins in the normal or low range [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Limitations of Use
-
Safety and efficacy of TLANDO in males less than 18 years old have not been established [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
-
Safety and efficacy of TLANDO in men with “age-related hypogonadism” (also referred to as “late-onset hypogonadism”) have not been established [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
2. Tlando Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Dosage Information
TLANDO is not substitutable with other oral testosterone undecanoate products.
2.2 Confirmation of Hypogonadism Before Initiation of TLANDO
Prior to initiating TLANDO, confirm the diagnosis of hypogonadism by ensuring that serum testosterone concentrations have been measured in the morning on at least two separate days and that these serum testosterone concentrations are below the normal range.
2.3 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of TLANDO is 225 mg (taken as two 112.5 mg capsules), orally twice daily, once in the morning and once in the evening. Take with food.
Monitoring for Continued Use or Discontinuation
Monitor serum testosterone (8 to 9 hours after the morning dose) 3 to 4 weeks after initiating TLANDO, and periodically thereafter. Based on serum testosterone measurements, determine if TLANDO should be continued or discontinued:
- Serum testosterone 300 - 1080 ng/dL: continue TLANDO
- Serum testosterone < 300 ng/dL: discontinue TLANDO
- Serum testosterone > 1080 ng/dL: discontinue TLANDO
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Capsules: 112.5 mg, white opaque body imprinted with “112” in black ink and grey opaque cap, banded with a colorless gelatin band.
4. Contraindications
TLANDO is contraindicated in:
- Patients with carcinoma of the breast or known or suspected carcinoma of the prostate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Women who are pregnant. Testosterone can cause virilization of the female fetus when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Known hypersensitivity to testosterone undecanoate or any of TLANDO’s ingredients [see Description (11)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Polycythemia
Increases in hematocrit levels, reflective of increases in red blood cell mass, may require discontinuation of TLANDO. Check hematocrit prior to initiating TLANDO. Evaluate hematocrit approximately every 3 months during the first year of treatment, and then every 6 months thereafter while the patient is taking TLANDO. If hematocrit becomes elevated, stop TLANDO until hematocrit decreases to an acceptable concentration. If TLANDO is restarted and again causes hematocrit to become elevated, stop TLANDO permanently. An increase in red blood cell mass may increase the risk of thromboembolic events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5.2 Venous Thromboembolism
There have been post marketing reports of venous thromboembolic events, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), in patients using testosterone replacement products such as TLANDO.
In the Testosterone Replacement therapy for Assessment of long-term Vascular Events and efficacy ResponSE in hypogonadal men (TRAVERSE) Study, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cardiovascular (CV) outcomes study, compared to placebo, topical testosterone gel was associated with a numerically higher incidence of VTE (1.7% vs 1.2%) which included DVT (0.6% vs 0.5%) and PE events (0.9% vs 0.5%) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Evaluate patients who report symptoms of pain, edema, warmth, and erythema in the lower extremity for DVT and those who present with acute shortness of breath for PE. If a venous thromboembolic event is suspected, discontinue TLANDO and initiate appropriate workup and management [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.3 Worsening of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Potential Risk of Prostate Cancer
- Patients with BPH treated with androgens are at an increased risk for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH. Monitor patients with BPH for worsening signs and symptoms.
- Patients treated with androgens may be at increased risk for prostate cancer. Evaluate patients for prostate cancer, including measurement of prostate specific antigen (PSA), prior to initiating and during treatment with androgens [see Contraindications (4)].
5.4 Blood Pressure Increases
TLANDO can increase blood pressure. Based on ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in Study 18-001, TLANDO increased mean systolic/diastolic BP by 4.3/1.4 mmHg from baseline after 4 months of treatment.In patients with hypertension on antihypertensive therapy, TLANDO increased the mean systolic/diastolic BP by 4.8/1.6 mm Hg from baseline. [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Blood pressure increases can increase cardiovascular (CV) risk over time.
The CV risk associated with topical testosterone gel was evaluated in TRAVERSE, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, CV outcomes study in men with a history of CV disease or multiple CV risk factors. In TRAVERSE, topical testosterone gel increased mean systolic blood pressure by 1.0 mmHg from baseline to 36 months, whereas a mean decrease from baseline of 0.5 mmHg was observed in the placebo group at this timepoint, for a mean between group difference of 1.5 mmHg. However, the incidences of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), including cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction [MI] and non-fatal stroke, were similar between treatment groups (7% for topical testosterone gel vs 7.3% for placebo) [See Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor BP periodically in men using TLANDO, especially men with hypertension. TLANDO is not recommended for use in patients with uncontrolled hypertension.
5.5 Abuse of Testosterone and Monitoring of Serum Testosterone Concentrations
Testosterone has been subject to abuse, typically at doses higher than recommended for the approved indication and in combination with other anabolic androgenic steroids. Anabolic androgenic steroid abuse can lead to serious cardiovascular and psychiatric adverse reactions [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9)].
If testosterone abuse is suspected, check serum testosterone concentrations to ensure they are within therapeutic range. However, testosterone levels may be in the normal or subnormal range in men abusing synthetic testosterone derivatives. Counsel patients concerning the serious adverse reactions associated with abuse of testosterone and anabolic androgenic steroids. Conversely, consider the possibility of testosterone and anabolic androgenic steroid abuse in suspected patients who present with serious cardiovascular or psychiatric adverse events.
5.6 Not for Use in Women
Due to lack of controlled studies in women and the potential for virilizing effects, TLANDO is not indicated for use in women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.2)].
5.7 Potential for Adverse Effects on Spermatogenesis
With large doses of exogenous androgens, including TLANDO, spermatogenesis may be suppressed through feedback inhibition of pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) possibly leading to adverse effects on semen parameters including sperm count [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]. Patients should be informed of this possible risk when deciding whether to use or to continue to use TLANDO.
5.8 Hepatic Adverse Effects
Prolonged use of high doses of orally active 17-alpha-alkyl androgens (e.g., methyltestosterone) has been associated with serious hepatic adverse effects (peliosis hepatis, hepatic neoplasms, cholestatic hepatitis, and jaundice). Peliosis hepatis can be a life-threatening or fatal complication. Long-term therapy with intramuscular testosterone enanthate has produced multiple hepatic adenomas. TLANDO is not a 17 alpha-alkyl androgen and is not known to produce hepatic adverse effects associated with 17-alpha-alkyl androgens.
Nonetheless, patients should be instructed to report any signs or symptoms of hepatic dysfunction (e.g., jaundice). If these occur, promptly discontinue TLANDO while the cause is evaluated.
5.9 Edema
Androgens, including TLANDO, may promote retention of sodium and water. Edema, with or without congestive heart failure, may be a serious complication in patients with preexisting cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. In addition to discontinuation of the drug, appropriate work up and management of edema may be required.
5.10 Sleep Apnea
The treatment of hypogonadal men with testosterone products may potentiate sleep apnea in some patients, especially those with risk factors such as obesity or chronic lung diseases.
5.12 Lipid Changes
Changes in serum lipid profile may require dose adjustment of lipid lowering drugs or discontinuation of testosterone therapy. Monitor the lipid profile periodically after starting testosterone therapy.
5.13 Hypercalcemia
Androgens, including TLANDO, should be used with caution in cancer patients at risk of hypercalcemia (and associated hypercalciuria). Monitor serum calcium concentrations periodically in these patients.
5.14 Decreased Thyroxine-binding Globulin
Androgens, including TLANDO, may decrease concentrations of thyroxin-binding globulins, resulting in decreased total T4 serum concentrations and increased resin uptake of triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). Free thyroid hormone concentrations remain unchanged, however, and there is no clinical evidence of thyroid dysfunction.
5.15 Increases in Prolactin
Increases in serum prolactin have been reported in patients treated with TLANDO in clinical trials. Evaluate serum prolactin levels prior to initiating treatment with TLANDO. Re-evaluate serum prolactin levels 3 to 4 months after starting treatment. If serum prolactin remains elevated, discontinue TLANDO [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
-
Polycythemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Venous Thromboembolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
-
Worsening of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Potential Risk of Prostate Cancer [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
-
Blood Pressure Increases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
-
Hepatic Adverse Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Sleep Apnea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Gynecomastia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Lipid Changes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Hypercalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Decreased Thyroxine-binding Globulin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
- Increases in Prolactin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of TLANDO 225 mg twice daily, without dose titration, was evaluated in 233 hypogonadal males during two clinical studies: Study LPCN 1021-18-001 (18-001) and Study LPCN 1021-16-002 (16-002) [see Clinical Studies (14)].
In Study 18-001, an uncontrolled ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) study, 138 hypogonadal males were treated with TLANDO 225 mg twice daily with morning and evening meals for approximately four months. Patients had a median age of 54 years (range 26-75), 79% were White, 18% were Black, and 2% were Asian. In 138 hypogonadal male patients, 70% (n=96) were obese (BMI≥30 kg/m2), 24% (n=33) reported a history of type 2 diabetes, and 48% (n=66) reported a history of hypertension.
Table 1 summarizes adverse reactions (>2%) reported in patients receiving TLANDO in Study 18-001.
| Adverse Reaction | Overall (N=138)
n (%) |
| Hypertension | 7 (5.1) |
| Hematocrit increased | 6 (4.3) |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 5 (3.6) |
Four of the 138 patients (2.9%) in Study 18-001 reported adverse reactions that led to premature discontinuation from the study, including dizziness (n=1), weight increased (n=1), insomnia (n=1), and hypertension (n=2).
In Study 16-002, 95 hypogonadal males were treated with TLANDO 225 mg twice daily with morning and evening meals for approximately 24 days. The dose of TLANDO was not titrated. Patients had a median age of 56 years (range 29-74), 81% were White, 16% were Black, 2% were mixed race, and 1% were Asian; 26% were Hispanic. In 95 hypogonadal male patients, 70% (n=66) were obese (BMI≥30 kg/m2), 23% (n=22) reported a history of type 2 diabetes, and 50% (n=47) reported a history of hypertension.
Table 2 summarized adverse reactions (>2%) reported during Study 16-002 in patients receiving TLANDO.
| Adverse Reaction | Overall (N=95)
n (%) |
| Blood prolactin increased | 6 (6.3) |
| Weight increased | 2 (2.1) |
| Headache | 2 (2.1) |
| Musculoskeletal pain | 2 (2.1) |
One of the 95 patients (1.1%) in the 24-day study reported an adverse reaction (gastric ulcer hemorrhage) that led to premature discontinuation from the study.
Blood Pressure Increases
In Study 18-001 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) was conducted in 138 male patients, 126 of whom completed the study. ABPM was conducted at 2 distinct 24-hour time periods: at baseline and following approximately 16 weeks of treatment with TLANDO. A total of 123 patients had acceptable 24-hour ABPM recordings at both time periods. In that group, the mean change in systolic BP from Baseline to End of Study was + 4.3 mmHg (95% CI 2.1, 6.5) and the mean change in diastolic BP was 1.4 mmHg (95% CI 0.5, 2.3). In patients with a history of hypertension at baseline, the mean ABPM systolic and diastolic blood pressure increased by 4.8 mmHg (95% CI 1.0, 8.5) and 1.6 mmHg (95% CI 0.1, 3.0), respectively (n=60). In patients with no history of hypertension at baseline systolic and diastolic blood pressure increased by 3.9 mmHg (95% CI 0.9, 6.8) and 1.2 mmHg (95% CI -0.1, 2.5), respectively (n =63).
2 patients (1.4 %) in the TLANDO safety set (n=138) either started new antihypertensive medications (n=2) or had their antihypertensive medication regimen adjusted (n=0) during Study 18-001.
Of the 138 patients in Study 18-001 who used TLANDO, 7 patients (5.1%) were reported to have either an adverse reaction of hypertension (7 patients, 5.1%) or increased blood pressure (0 patients, 0.0%).
Cardiovascular Outcomes
TRAVERSE was a randomized, double-blind, cardiovascular outcomes study to assess the cardiovascular (CV) safety of topical testosterone gel compared to placebo in 5198 hypogonadal men aged 45 to 80 years with a history of CV disease or with multiple CV risk factors. The primary outcome was the incidence of the composite endpoint of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), consisting of CV death, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI), and non-fatal stroke.
The mean duration of therapy was approximately 22 months. The mean duration of follow-up was 33 months. Approximately 61% of all patients discontinued topical testosterone gel or placebo therapy.
The mean patient age (±SD) was 63.3 (7.9) years, with 2452 patients aged 65 years or more (47%), 2847 (about 55%) patients had pre-existing cardiovascular disease, whereas 2357 patients (about 45%) had an elevated cardiovascular risk at baseline, and mean BMI was 35 kg/m2. Approximately 80% of patients were White, 17% were Black, and 3% were of other races or ethnic groups. Approximately 69%, 84%, and 93% had diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension, respectively.
The mean serum testosterone concentration at baseline in patients receiving topical testosterone gel was 220.4 ng/dL (n=2596). The mean serum testosterone concentrations at 12 months, 24 months, 36 months, and 48 months in patients receiving topical testosterone gel were 440.5 ng/dL (n=1683), 420.9 ng/dl (n=1125), 428.7 ng/dL (n=731), and 365.2 ng/dL (n=220), respectively.
For patients treated with topical testosterone gel, the incidence of MACE was 7.0% (n=182 events) and for those receiving placebo, the incidence of MACE was 7.3% (n=190 events). The study demonstrated non-inferiority of topical testosterone gel versus placebo because the upper bound of 95% CI was less than the pre-specified risk margin, of 1.5 for MACE (Hazard Ratio 0.96 [95% CI: 0.78, 1.17]).
Additional Adverse Reactions Reported in TRAVERSE
Additional adverse reactions reported in TRAVERSE at an incidence rate >2% in either treatment group and greater in topical testosterone gel versus placebo included: nonfatal arrythmias warranting intervention (5.2% vs 3.3%), atrial fibrillation (3.5% vs 2.4%), acute kidney injury (2.3% vs 1.5%) and bone fracture (3.5% vs 2.5%). For the adverse reaction of bone fracture, each event was adjudicated by clinical review.
Increases in Hematocrit
Increases in hematocrit were reported in 6 of the 138 patients (4.3%) in Study 18-001. None of these increases led to premature discontinuation of TLANDO.
Increases in Prolactin
Increases in serum prolactin were reported in 6 (6.3%) of the 95 patients in the 24-day clinical study. The mean increase from baseline in serum prolactin was 7.0 ng/mL (n=93). The 4-month clinical study did not assess serum prolactin concentrations after the screening visit.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of testosterone replacement products. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiovascular Disorders: myocardial infarction, stroke
Vascular Disorders: venous thromboembolism
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Insulin
Changes in insulin sensitivity or glycemic control may occur in patients treated with androgens. In diabetic patients, the metabolic effects of androgens may decrease blood glucose and, therefore, insulin requirements.
7.2 Oral Anticoagulants
Changes in anticoagulant activity may be seen with androgens. Frequent monitoring of INR and prothrombin time may be necessary in patients taking anticoagulants, especially at the initiation and termination of androgen therapy.
7.3 Corticosteroids
The concurrent use of testosterone with corticosteroids may result in increased fluid retention and should be monitored cautiously, particularly in patients with cardiac, renal or hepatic disease.
7.4 Drugs that May Also Increase Blood Pressure
Some prescription drugs and nonprescription analgesic and cold medications can increase blood pressure. Concomitant administration of these medications with TLANDO may lead to additional increases in blood pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
TLANDO is contraindicated in pregnant women and not indicated for use in females [see Contraindications (4)]. Testosterone is teratogenic and may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman based on data from animal studies (see Data) and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. Exposure of a female fetus to androgens may result in varying degrees of virilization. In animal developmental studies, exposure to testosterone in utero resulted in hormonal and behavioral changes in offspring and structural impairments of reproductive tissues in female and male offspring. These studies did not meet current standards for nonclinical development toxicity studies.
Data
Animal Data
In developmental studies conducted in rats, rabbits, pigs, sheep and rhesus monkeys, pregnant animals received intramuscular injection of testosterone during the period of organogenesis. Testosterone treatment at doses that were comparable to those used for testosterone replacement therapy resulted in structural impairments in both female and male offspring. Structural impairments observed in females included increased anogenital distance, phallus development, empty scrotum, no external vagina, intrauterine growth retardation, reduced ovarian reserve, and increased ovarian follicular recruitment. Structural impairments seen in male offspring included increased testicular weight, larger seminal tubular lumen diameter, and higher frequency of occluded tubule lumen. Increased pituitary weight was seen in both sexes.
Testosterone exposure in utero also resulted in hormonal and behavioral changes in offspring. Hypertension was observed in pregnant females and offspring in rats exposed to doses approximately twice those used for testosterone replacement therapy.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
Males
During treatment with large doses of exogenous androgens, including TLANDO, spermatogenesis may be suppressed through feedback inhibition of the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. Reduced fertility is observed in some men taking testosterone replacement therapy. The impact on fertility may be irreversible. Testicular atrophy, subfertility, and infertility have also been reported in men who abuse anabolic androgenic steroids [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of TLANDO in pediatric patients less than 18 years old have not been established. Improper use may result in acceleration of bone age and premature closure of epiphyses.
8.5 Geriatric Use
There have not been sufficient numbers of geriatric patients in controlled clinical studies with TLANDO to determine whether efficacy or safety in those over 65 years of age differs from younger subjects. Of the 95 patients enrolled in Study 16-002, the 24-day major safety and effectiveness study utilizing TLANDO, 16 (16.8%) were over 65 years of age. Additionally, there is insufficient long-term safety data in geriatric patients utilizing TLANDO to assess the potentially increased risk of cardiovascular disease and prostate cancer.
Geriatric patients treated with androgens may also be at risk for worsening of signs and symptoms of BPH and hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3 and 5.4)].
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
9.1 Controlled Substance
TLANDO contains testosterone undecanoate, a schedule III controlled substance.
9.2 Abuse
Drug abuse is intentional non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, for its rewarding psychological and physiological effects. Abuse and misuse of testosterone are seen in male and female adults and adolescents. Testosterone, often in combination with other anabolic androgenic steroids (AAS), and not obtained by prescription through a pharmacy, may be abused by athletes and bodybuilders. There have been reports of misuse by men taking higher doses of legally obtained testosterone than prescribed and continuing testosterone despite adverse events or against medical advice.
Abuse-Related Adverse Reactions
Serious adverse reactions have been reported in individuals who abuse anabolic androgenic steroids and include cardiac arrest, myocardial infarction, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, congestive heart failure, cerebrovascular accident, hepatotoxicity, and serious psychiatric manifestations, including major depression, mania, paranoia, psychosis, delusions, hallucinations, hostility and aggression.
The following adverse reactions have also been reported in men: transient ischemic attacks, convulsions, hypomania, irritability, dyslipidemias, testicular atrophy, subfertility, and infertility.
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported in women: hirsutism, virilization, deepening of voice, clitoral enlargement, breast atrophy, male-pattern baldness, and menstrual irregularities.
The following adverse reactions have been reported in male and female adolescents: premature closure of bony epiphyses with termination of growth, and precocious puberty.
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size and may include abuse of other agents, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
9.3 Dependence
Behaviors Associated with Addiction
Continued abuse of testosterone and other anabolic steroids, leading to addiction is characterized by the following behaviors:
- Taking greater dosages than prescribed
- Continued drug use despite medical and social problems due to drug use
- Spending significant time to obtain the drug when supplies of the drug are interrupted
- Giving a higher priority to drug use than other obligations
- Having difficulty in discontinuing the drug despite desires and attempts to do so
- Experiencing withdrawal symptoms upon abrupt discontinuation of use
Physical dependence is characterized by withdrawal symptoms after abrupt drug discontinuation or a significant dose reduction of a drug. Individuals taking supratherapeutic doses of testosterone may experience withdrawal symptoms lasting for weeks or months which include depressed mood, major depression, fatigue, craving, restlessness, irritability, anorexia, insomnia, decreased libido and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.
Drug dependence in individuals using approved doses of testosterone for approved indications has not been documented.
10. Overdosage
There is one report of acute overdosage with use of an approved injectable testosterone product: this subject had serum testosterone levels of up to 11,400 ng/dL with a cerebrovascular accident.
Treatment of overdosage consists of discontinuation of TLANDO and appropriate symptomatic and supportive care.
11. Tlando Description
TLANDO (testosterone undecanoate) capsules contain 112.5 mg testosterone undecanoate, an ester of testosterone, for oral administration. Testosterone, an androgen, is formed by cleavage of the ester side chain of testosterone undecanoate.
The chemical name of testosterone undecanoate is 17β-undecanoyloxy-4-androsten-3-one. It has an empirical formula of C30H48O3 and a molecular weight of 456.7. The structural formula is:
Testosterone undecanoate is a white to off-white crystalline substance.
The inactive ingredients in TLANDO capsules are ascorbyl palmitate, glyceryl monolinoleate, polyethylene glycol 8000, and polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil. The capsule shell contains black iron oxide, gelatin, and titanium dioxide. The capsule is imprinted with black ink that contains ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, propylene glycol, and shellac.
12. Tlando - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Endogenous androgens, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), are responsible for the normal growth and development of the male sex organs and for maintenance of secondary sex characteristics. These effects include the growth and maturation of prostate, seminal vesicles, penis and scrotum; the development of male hair distribution, such as facial, pubic, chest and axillary hair; laryngeal enlargement, vocal cord thickening, alterations in body musculature and fat distribution.
Male hypogonadism, a clinical syndrome resulting from insufficient secretion of testosterone, has two main etiologies. Primary hypogonadism is caused by defects of the gonads, such as Klinefelter's Syndrome or Leydig cell aplasia, whereas secondary hypogonadism is the failure of the hypothalamus (or pituitary) to produce sufficient gonadotropins (FSH, LH).
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
There is insufficient data to characterize an exposure-response relationship or time course of pharmacodynamic response.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Testosterone undecanoate is a lipophilic molecule that is primarily absorbed into the lymph system after oral administration and then released into the general blood circulation by the thoracic duct, avoiding absorption into the portal vein thereby circumventing first-pass metabolism in the liver. Testosterone undecanoate is converted to testosterone following absorption.
Following administration of 225 mg of TLANDO in ninety-five hypogonadal males, maximum serum testosterone concentrations were observed at a median (Tmax) of about 5 hours. The mean maximum (Cmax) serum testosterone concentrations observed were 979 ng/dL and 989 ng/dL following the morning and evening TLANDO doses, respectively. The average serum testosterone concentrations over 24 hours (Cavg0-24h) observed following TLANDO administration was 476 ng/dL.
Figure 1 shows the mean serum total testosterone concentration-time profile for hypogonadal men (N=90) administered TLANDO.
Figure 1: Mean (±SEM) Serum Total Testosterone Concentrations (ng/dL)
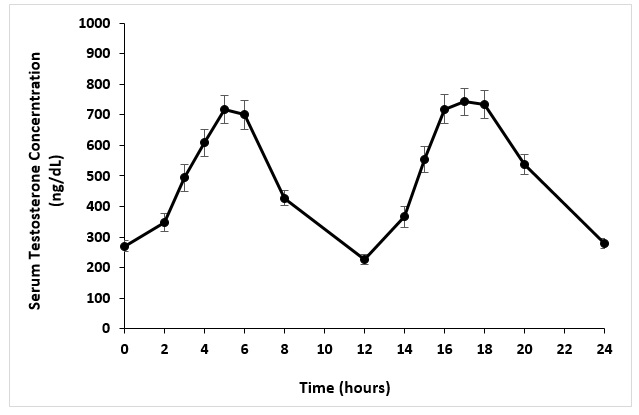
Following TLANDO administration, the mean serum dihydrotestosterone (DHT) Cavg0-24h was 108 ng/dL, the mean serum testosterone undecanoate Cavg0-24h was 11,100 ng/dL and the mean serum dihydrotestosterone undecanoate Cavg0-24h was 4,700 ng/dL.
Effect of Food
Administration of TLANDO with moderate fat containing food did not significantly impact the pharmacokinetic parameters of testosterone compared to high or low fat. However, there is decrease in exposure when administered without food compared to fed conditions.
In studies with 13 to 14 hypogonadal males, mean testosterone Cmax and AUC were comparable when TLANDO was administered with food containing low, moderate or high fat amounts. Administration in fasting conditions resulted in approximately 65 % and 38% lower Cmax and AUC, respectively, compared to administration with food (high fat).
Distribution
Circulating testosterone is primarily bound in serum to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and albumin. Approximately 40% of testosterone in plasma is bound to SHBG, 2% remains unbound (free) and the rest is bound to albumin and other proteins.
Elimination
The elimination half-life of testosterone undecanoate is approximately 2 hours. Once testosterone is formed from testosterone undecanoate, there is considerable variation in the half-life of testosterone as reported in the literature, ranging from 10 to 100 minutes.
Metabolism
Testosterone undecanoate is metabolized to testosterone via ester cleavage of the undecanoate group and reduced to DHTU by 5α-reductase. Testosterone is metabolized to various 17-keto steroids. The major active metabolites of testosterone are DHT and estradiol.
Excretion
About 90% of a dose of testosterone given intramuscularly is excreted in the urine as glucuronic and sulfuric acid conjugates of testosterone and its metabolites. About 6% of a dose is excreted in the feces, mostly in the unconjugated form. Inactivation of testosterone occurs primarily in the liver.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Testosterone has been tested by subcutaneous injection and implantation in mice and rats. In mice, the implant induced cervical-uterine tumors, which metastasized in some cases. There is suggestive evidence that injection of testosterone into some strains of female mice increases their susceptibility to hepatoma. Testosterone is also known to increase the number of tumors and decrease the degree of differentiation of chemically induced carcinomas of the liver in rats.
Mutagenesis
Mutagenic effects of testosterone undecanoate were not detected in a battery of in vitro tests including bacterial mutation assays (Ames test) and chromosomal aberration tests in human lymphocytes. Testosterone undecanoate was also negative in an in vivo bone marrow micronucleus assay in rats. Testosterone was negative in the in vitro Ames and in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assays.
Impairment of Fertility
The administration of exogenous testosterone has been reported to suppress spermatogenesis in the rat, dog and non-human primates, which was reversible on cessation of the treatment.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy and safety of TLANDO was evaluated in Study 16-002 a multicenter, open-label, single-arm study in adult hypogonadal male patients (NCT03242590). Patients received TLANDO 225 mg, orally twice daily with food for approximately 24 days; no titration was performed to adjust the dosage.
A total of 95 hypogonadal men received a dose of TLANDO and were included in the efficacy evaluation. Patients had a median age of 56 years (range 29-74 years), 81% were White, 16% were Black, 2% were mixed race, and 1% were Asian; 26% were Hispanic.
The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients who achieved a 24-hour average serum testosterone concentration (Cavg0-24h) within the normal range of 300-1080 ng/dL on the final visit of the study.
Table 3 shows the proportion of subjects, Study 16-002, with an average serum total testosterone concentration in the normal range (300-1080 ng/dL).
| Parameter | N=95 |
| % subjects with testosterone, Cavg0-24h 300 to 1080 ng/dL | 80% |
| 95 % Confidence Interval | (72%, 88%) |
Secondary endpoints were the percentage of patients with maximum total testosterone concentration (Cmax) meeting three predetermined limits: less than or equal to 1.5 times the upper limit of the normal range (ULN) (1620 ng/dL), between 1.8 and 2.5 times ULN (1944 - 2700 ng/dL), and greater than 2.5 times ULN (2700 ng/dL).
The percentage of patients who received TLANDO and had T Cmax threshold less than or equal to 1620 ng/dL, between 1944 ng/dL and 2700 ng/dL, and greater than 2700 ng/dL at the PK visit were 82%, 5%, and 0%, respectively.
16. How is Tlando supplied
TLANDO capsules for oral administration are available containing 112.5 mg of testosterone undecanoate. The capsules have a white opaque body imprinted with “112” in black ink and a grey opaque cap, banded with a colorless band.
TLANDO capsules are supplied in HDPE bottles with a foil liner and a child resistant cap.
Bottles of 120 capsules: NDC 74676-0112-2.
Store at 20ºC to 25°C (68ºF to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15ºC to 30°C (59ºF to 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispose of unused TLANDO via a take-back option. If a take-back option is unavailable, follow FDA instructions at www.fda.gov/drugdisposal.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patients to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Polycythemia
Advise patients that TLANDO can cause an increase in hematocrit levels that may increase the risk of thromboembolic events. Advise patients about the importance of completing laboratory testing as instructed by their health care provider while on TLANDO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Venous Thromboembolism
Advise patients that TLANDO can cause venous thromboembolism. Advise patients of the signs and symptoms of venous thromboembolism, which may include the following: lower limb pain, edema, or erythema; and dyspnea or chest pain. Advise patients to promptly report the signs and symptoms of venous thromboembolism, discontinue use of TLANDO and seek urgent medical care [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Blood Pressure Increases
Advise patients that TLANDO can increase blood pressure (BP) which can increase cardiovascular risk over time. Advise patients about the importance of monitoring BP periodically while on TLANDO. If BP increases while on TLANDO, antihypertensive medications may need to be started, added, or adjusted to control BP, or TLANDO may need to be discontinued [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Worsening of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) and Potential Risk of Prostate Cancer
Advise patients that TLANDO can cause increased symptoms of BPH and can increase the risk for prostate cancer. Advise patients to contact their health care provider if they have any prostate-related symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Edema
Advise patients with preexisting cardiac, renal, or hepatic disease that TLANDO can cause edema. Advise patients to notify their health care provider if edema develops or worsens [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Sleep Apnea
Advise patients that TLANDO can worsen sleep apnea especially in patients with risk factors such as obesity or chronic lung diseases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
Gynecomastia
Advise patients that TLANDO can cause gynecomastia. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Administration Instructions
- Advise patients to take TLANDO with food [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Verity Pharma Medical Affairs:
1-844-VERITY-1 (1-844-837-4891)
Manufactured for:

Manufactured for Verity Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Ewing, NJ 08628
Manufactured in the United Kingdom
TLANDO® and its design are registered trademarks of Verity Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Verity Pharmaceuticals, Verity Pharma, and their designs are trademarks of Verity Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
© 2024 Verity Pharmaceuticals Inc. All rights reserved.
TLA-001
|
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
Issued: 07/2025 |
|
| MEDICATION GUIDE
TLANDO® (Tee-lan-doh) (testosterone undecanoate) capsules, for oral use CIII |
||
| What is TLANDO?
TLANDO is a prescription medicine that contains testosterone. TLANDO is used to treat adult men who have low or no testosterone due to certain medical conditions. It is not known if TLANDO is safe or effective in children younger than 18 years old. Improper use of TLANDO may affect bone growth in children. TLANDO is a controlled substance (CIII) because it contains testosterone that can be a target for people who abuse prescription medicines. Keep your TLANDO in a safe place to protect it. Never give your TLANDO to anyone else, even if they have the same symptoms you have. Selling or giving away this medicine may harm others and is against the law. TLANDO is not meant for use by women. |
||
Do not take TLANDO if you:
|
||
Before you take TLANDO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
||
| Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Using TLANDO with certain other medicines can affect each other. Especially, tell your healthcare provider if you take:
|
||
|
Know the medicines you take. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of these medicines, if you are not sure. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
||
How should I take TLANDO?
|
||
| What are the possible side effects of TLANDO?
TLANDO may cause serious side effects including:
|
||
| Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the serious side effects listed above.
The most common side effects of TLANDO include: |
||
|
| |
| Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of TLANDO. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||
How should I store TLANDO?
|
||
|
Keep TLANDO and all medicines out of the reach of children. How should I throw away (dispose of) TLANDO?
|
||
| General information about the safe and effective use of TLANDO
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use TLANDO for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give TLANDO to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about TLANDO that is written for health professionals. |
||
| What are the ingredients in TLANDO?
Active ingredient: testosterone undecanoate Inactive ingredients: ascorbyl palmitate, glyceryl monolinoleate, polyethylene glycol 8000, and polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil. Capsule shell: contains black iron oxide, gelatin, and titanium dioxide and imprint ink (ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, propylene glycol, and shellac). Manufactured for: Verity Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Ewing, NJ 08628 Manufactured in the United Kingdom For more information, go to www.TLANDO.com For all medical inquiries contact: Verity Pharma Medical Affairs 1-844-VERITY-1 (1-844-837-4891). |
||
| TLANDO
testosterone undecanoate capsule, liquid filled |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Verity Pharmaceuticals Inc. (117448813) |
Frequently asked questions
- What are the brands of testosterone?
- Is Jatenzo cost covered by insurance?
- Is Xyosted a controlled substance?
More about Tlando (testosterone)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Imprints, shape & color data
- Latest FDA alerts (7)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: androgens and anabolic steroids
- Breastfeeding
- En español
Patient resources
Professional resources
Other brands
AndroGel, Xyosted, Jatenzo, Depo-Testosterone, ... +12 more

