Phentermine and Topiramate: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Dosage form: capsule, extended release
Drug class: Anorexiants
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 8, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Drug Abuse and Dependence
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
- Medication Guide
Highlights of Prescribing Information
PHENTERMINE and TOPIRAMATE extended-release capsules, for oral use, CIV
Initial U.S. Approval: 2012
Indications and Usage for Phentermine and Topiramate
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are a combination of phentermine, a sympathomimetic amine anorectic, and topiramate, indicated in combination with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity to reduce excess body weight and maintain weight reduction long term in:
- Adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with obesity (1)
- Adults with overweight in the presence of at least one weight-related comorbid condition (1)
Limitations of Use:
- The effect of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been established (1).
- The safety and effectiveness of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in combination with other products intended for weight loss, including prescription and over-the-counter drugs, and herbal preparations, have not been established (1).
Phentermine and Topiramate Dosage and Administration
- Take orally once daily in morning. Avoid administration in evening to prevent insomnia (2.2).
- Recommended starting dosage is 3.75 mg/23 mg (phentermine mg/topiramate mg) daily for 14 days; then increase to 7.5 mg/46 mg daily (2.2).
- Escalate dosage based on weight loss in adults or BMI reduction in pediatric patients. See the Full Prescribing Information for details regarding discontinuation or dosage escalation (2.2).
- Gradually discontinue 15 mg/92 mg dosage to prevent possible seizure (2.3).
- Do not exceed 7.5 mg/46 mg dosage for patients with moderate or severe renal impairment or patients with moderate hepatic impairment (2.4, 2.5).
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Contraindications
Warnings and Precautions
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. In patients who can become pregnant, a negative pregnancy test is recommended before initiating phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules and monthly during therapy; advise use of effective contraception. Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are available through a limited program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) (5.1).
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation: Monitor for depression or suicidal thoughts. Discontinue phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules if symptoms develop (5.2).
- Risk of Ophthalmologic Adverse Reactions: Acute myopia and secondary angle closure glaucoma have been reported. Immediately discontinue phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules if symptoms develop. Consider phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules discontinuation if visual field defects occur (5.3).
- Mood and Sleep Disorders: Consider dosage reduction or discontinuation for clinically significant or persistent mood or sleep disorder symptoms (5.4).
- Cognitive Impairment: May cause disturbances in attention or memory, or speech/language problems. Caution patients about operating automobiles or hazardous machinery when starting treatment (5.5).
- Slowing of Linear Growth: Consider dosage reduction or discontinuation if pediatric patients are not growing or gaining height as expected (5.6).
- Metabolic Acidosis: Measure electrolytes before and during treatment. If persistent metabolic acidosis develops, reduce dosage or discontinue phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules (5.7).
- Decrease in Renal Function: Measure creatinine before and during treatment. For persistent creatinine elevations, reduce dosage or discontinue phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules (5.8).
- Serious Skin Reactions: Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules should be discontinued at the first sign of a rash, unless the rash is clearly not drug-related (5.13).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions in:
- Adults (incidence ≥ 5% and at least 1.5 times placebo) are: paraesthesia, dizziness, dysgeusia, insomnia, constipation, and dry mouth (6.1).
- Pediatric patients aged 12 years and older (incidence ≥4% and greater than placebo) are: depression, dizziness, arthralgia, pyrexia, influenza, and ligament sprain (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Teva at 1-888-838-2872 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Oral Contraceptives: Altered exposure of progestin and estrogen may cause irregular bleeding, but not increased risk of pregnancy. Advise patients not to discontinue oral contraceptives if spotting occurs (7).
- CNS Depressants Including Alcohol: May potentiate CNS depressant effects. Avoid excessive use of alcohol (7).
- Non-potassium Sparing Diuretics: May potentiate hypokalemia. Measure potassium before and during treatment (7).
Use In Specific Populations
- Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended (8.2).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 6/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Phentermine and Topiramate
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are indicated in combination with a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity to reduce excess body weight and maintain weight reduction long term in:
- Adults and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with obesity
- Adults with overweight in the presence of at least one weight-related comorbid condition
Limitations of Use
- The effect of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been established.
- The safety and effectiveness of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in combination with other products intended for weight loss, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter drugs, and herbal preparations, have not been established.
2. Phentermine and Topiramate Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Testing Prior to and During Treatment with Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules
Prior to phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule initiation and during treatment with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules, the following is recommended:
- Obtain a negative pregnancy test before initiating phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in patients who can become pregnant and monthly during phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule therapy. Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are contraindicated during pregnancy [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- Obtain a blood chemistry profile that includes bicarbonate, creatinine, and potassium in all patients, and glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on antidiabetic medication prior to initiating phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule treatment and periodically during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.8, 5.12)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Administration
The recommended dosage, titration, and administration of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are as follows:
- Take phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules orally once daily in the morning with or without food. Avoid administration of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in the evening due to the possibility of insomnia.
- The recommended starting dosage of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules is one capsule (containing 3.75 mg of phentermine and 23 mg of topiramate) (3.75 mg/23 mg) taken orally once daily for 14 days; after 14 days increase to the recommended dosage of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg orally once daily.
- After 12 weeks of treatment with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg, evaluate weight loss for adults or BMI reduction for pediatric patients aged 12 years and older. If an adult patient has not lost at least 3% of baseline body weight or a pediatric patient has not experienced a reduction of at least 3% of baseline BMI, increase the dosage to phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 11.25 mg/69 mg orally once daily for 14 days; followed by an increase in the dosage to phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg orally once daily.
- After 12 weeks of treatment with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg, evaluate weight loss for adults or BMI reduction for pediatric patients aged 12 years and older. If an adult patient has not lost at least 5% of baseline body weight or a pediatric patient has not experienced a reduction of at least 5% of baseline BMI, discontinue phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)], as it is unlikely that the patient will achieve and sustain clinically meaningful weight loss with continued treatment.
- Monitor the rate of weight loss in pediatric patients. If weight loss exceeds 2 lbs (0.9 kg)/week, consider dosage reduction.
2.3 Discontinuation of Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules 15 mg/92 mg
Discontinue phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg gradually by taking phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg orally once daily every other day for at least 1 week prior to stopping treatment altogether, due to the possibility of precipitating a seizure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) and Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)].
2.4 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment
- The recommended dosage in patients with mild (CrCl greater or equal to 50 and less than 80 mL/min) renal impairment is the same as the recommended dosage for patients with normal renal function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- In patients with severe [creatinine clearance (CrCl) less than 30 mL/min] or moderate (CrCl greater than or equal to 30 and less than 50 mL/min) renal impairment (CrCl calculated using the Cockcroft-Gault equation with actual body weight), the maximum recommended dosage is phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg once daily.
- Avoid use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in patients with end-stage renal disease on dialysis.
2.5 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
- The recommended dosage of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh 5 to 6) is the same as the recommended dosage in patients with normal hepatic function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 7 to 9), the maximum recommended dosage is phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg orally once daily.
- Avoid use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 10 to 15).
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are available in four strengths (phentermine mg/topiramate mg):
- 3.75 mg/23 mg - White opaque cap printed with WPI, orange opaque body printed with 2196
- 7.5 mg/46 mg - White opaque cap printed with WPI, green opaque body printed with 2195
- 11.25 mg/69 mg - Light yellow opaque cap printed with WPI, white opaque body printed with 2299
- 15 mg/92 mg - White opaque cap printed with WPI, dark scarlet opaque body printed with 2194
4. Contraindications
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are contraindicated in patients:
- Who are pregnant [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]
- With glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- With hyperthyroidism
- Taking or within 14 days of stopping a monoamine oxidase inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7)]
- With known hypersensitivity to phentermine, topiramate or any of the excipients in phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules, or idiosyncrasy to the sympathomimetic amines [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can cause fetal harm. Data from pregnancy registries and epidemiologic studies indicate that a fetus exposed to topiramate in the first trimester of pregnancy has an increased risk of major congenital malformations, including but not limited to cleft lip and/or cleft palate (oral clefts), and of being small for gestational age (SGA). When multiple species of pregnant animals received topiramate at clinically relevant doses, structural malformations, including craniofacial defects, and reduced fetal weights occurred in offspring. A negative pregnancy test is recommended before initiating phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule treatment in patients who can become pregnant and monthly during phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule therapy. Advise patients who can become pregnant of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception during phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS)
Because of the teratogenic risk associated with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule therapy, phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are available through a limited program under the REMS. Under the Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules REMS, only certified pharmacies may distribute phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules. Further information is available at www.PhenTopREMS.com or by telephone at 1-800-269-6816 or by FAX at 1-800-558-6165.
5.2 Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including topiramate, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication. Pooled analyses of 199 placebo-controlled clinical studies (monotherapy and adjunctive therapy, median treatment duration 12 weeks) of 11 different AEDs across several indications showed that patients randomized to one of the AEDs had approximately twice the risk (adjusted Relative Risk 1.8, 95% CI 1.2, 2.7) of suicidal thinking or behavior compared to patients randomized to placebo. The estimated incidence rate of suicidal behavior or ideation among 27,863 AED-treated patients was 0.43%, compared to 0.24% among 16,029 placebo-treated patients, representing an increase of approximately one case of suicidal thinking or behavior for every 530 patients treated. There were four suicides in AED-treated patients in the trials and none in placebo-treated patients, but the number is too small to allow any conclusion about AED effect on suicide. The increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with AEDs was observed as early as 1 week after starting drug treatment with AEDs and persisted for the duration of treatment assessed. Because most trials included in the analysis did not extend beyond 24 weeks, the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior beyond 24 weeks could not be assessed. The risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior was generally consistent among drugs in the data analyzed. The finding of increased risk with AEDs of varying mechanisms of action and across a range of indications suggests that the risk applies to all AEDs used for any indication. The risk did not vary substantially by age in the clinical trials analyzed.
In a phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules clinical trial of pediatric patients aged 12 years and older, 1 (0.6%) of the 167 phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule-treated patients reported suicidal ideation and behavior which required hospitalization. No placebo-treated patients reported suicidal behavior or ideation.
Monitor all patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior. Discontinue phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in patients who experience suicidal thoughts or behaviors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]. Avoid phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in patients with a history of suicidal attempts or active suicidal ideation.
5.3 Risk of Ophthalmologic Adverse Reactions
Acute Myopia and Secondary Angle Closure Glaucoma
A syndrome consisting of acute myopia associated with secondary angle closure glaucoma has been reported in patients treated with topiramate. Symptoms include acute onset of decreased visual acuity and/or ocular pain. Ophthalmologic findings can include myopia, mydriasis, anterior chamber shallowing, ocular hyperemia (redness), choroidal detachments, retinal pigment epithelial detachments, macular striae, and increased intraocular pressure. This syndrome may be associated with supraciliary effusion resulting in anterior displacement of the lens and iris, with secondary angle closure glaucoma. Symptoms typically occur within 1 month of initiating treatment with topiramate but may occur at any time during therapy. In contrast to primary narrow angle glaucoma, which is rare under 40 years of age, secondary angle closure glaucoma associated with topiramate has been reported in pediatric patients as well as adults. The primary treatment to reverse symptoms is discontinuation of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules as rapidly as possible in consultation with the treating physician. Elevated intraocular pressure of any etiology, if left untreated, can lead to serious sequelae including permanent loss of vision.
Visual Field Defects
Visual field defects (independent of elevated intraocular pressure) have been reported in clinical trials and in postmarketing experience in patients receiving topiramate. In clinical trials, most of these events were reversible after topiramate discontinuation. If visual problems occur at any time during treatment, consider discontinuing phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules.
5.4 Mood and Sleep Disorders
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can cause mood disorders, including depression and anxiety, as well as insomnia. Patients with a history of depression may be at increased risk of recurrent depression or other mood disorders while taking phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Consider dosage reduction or discontinuation of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules if clinically significant or persistent symptoms occur. Discontinue phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules if patients have symptoms of suicidal ideation or behavior [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5.5 Cognitive Impairment
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can cause cognitive dysfunction (e.g., impairment of concentration/attention, difficulty with memory, and speech or language problems, particularly word-finding difficulties). Rapid titration or high initial doses of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules may be associated with higher rates of cognitive events such as attention, memory, and language/word-finding difficulties [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The concomitant use of alcohol or central nervous system (CNS) depressant drugs with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules may potentiate CNS depression or other centrally mediated effects of these agents, such as dizziness, cognitive adverse reactions, drowsiness, light-headedness, impaired coordination, and somnolence.
Caution patients about operating hazardous machinery, including automobiles, until they are reasonably certain phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule therapy does not affect them adversely. Caution patients against excessive alcohol intake while receiving phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules.
If cognitive dysfunction persists, consider dosage reduction or discontinuation of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
5.6 Slowing of Linear Growth
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are associated with a reduction in height velocity (centimeters of height gained per year) in obese pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age. In a 56-week study, average height increased from baseline in both phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule- and placebo-treated patients; however, a lower height velocity of -1.3 to -1.4 cm/year was observed in phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule-treated compared to placebo-treated patients. Monitor height velocity in pediatric patients treated with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules. Consider dosage reduction or discontinuation of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules if pediatric patients are not growing or gaining height as expected [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
5.7 Metabolic Acidosis
Hyperchloremic, non-anion gap, metabolic acidosis (decreased serum bicarbonate below the normal reference range in the absence of chronic respiratory alkalosis) has been reported in patients treated with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Manifestations of acute or chronic metabolic acidosis may include hyperventilation, nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue and anorexia, or more severe sequelae including cardiac arrhythmias or stupor. Chronic, untreated metabolic acidosis may increase the risk for nephrolithiasis or nephrocalcinosis and may also result in osteomalacia (referred to as rickets in pediatric patients) and/or osteoporosis with an increased risk for fractures. Chronic metabolic acidosis in pediatric patients may also reduce growth rates, which may decrease the maximal height achieved.
Conditions or therapies that predispose to acidosis (i.e., renal disease, severe respiratory disorders, status epilepticus, diarrhea, surgery, or ketogenic diet) may be additive to the bicarbonate lowering effects of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules. Concomitant use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules and a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor may increase the severity of metabolic acidosis and may also increase the risk of kidney stone formation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]. Avoid use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules with other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. If concomitant use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules with another carbonic anhydrase inhibitor is unavoidable, the patient should be monitored for the appearance or worsening of metabolic acidosis.
Measure electrolytes including serum bicarbonate prior to starting phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules and during phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule treatment. In phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule clinical trials, the peak reduction in serum bicarbonate typically occurred within 4 weeks of titration to the assigned dose, and in most patients, there was a correction of bicarbonate by week 56, without any dosage reduction. However, if persistent metabolic acidosis develops while taking phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules, reduce the dosage or discontinue phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
5.8 Decrease in Renal Function
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can cause an increase in serum creatinine that reflects a decrease in renal function (glomerular filtration rate). In clinical trials, peak increases in serum creatinine were observed after 4 to 8 weeks of treatment. On average, serum creatinine gradually declined but remained elevated over baseline creatinine values. The changes in serum creatinine (and measured GFR) with short-term (4-weeks) phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule treatment appear reversible with treatment discontinuation, but the effect of chronic treatment on renal function is not known.
Measure serum creatinine prior to starting phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules and during phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule treatment. If persistent elevations in creatinine occur, reduce the dosage or discontinue phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9), Adverse Reactions (6.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
5.9 Risk of Seizures with Abrupt Withdrawal of Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules
Abrupt withdrawal of topiramate has been associated with seizures in individuals without a history of seizures or epilepsy. In situations where immediate termination of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules is medically required, appropriate monitoring is recommended. Patients discontinuing phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg should be gradually tapered to reduce the possibility of precipitating a seizure [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)].
5.10 Kidney Stones
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules have been associated with kidney stone formation [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Topiramate inhibits carbonic anhydrase activity and promotes kidney stone formation by reducing urinary citrate excretion and increasing urine pH. Patients on a ketogenic diet may be at increased risk for kidney stone formation. An increase in urinary calcium and a marked decrease in urinary citrate was observed in topiramate-treated pediatric patients in a one-year, active-controlled study. Increased ratio of urinary calcium/citrate increases the risk of kidney stones and/or nephrocalcinosis.
Avoid the use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules with other drugs that inhibit carbonic anhydrase [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Advise patients to increase fluid intake (to increase urinary output), which may decrease the concentration of substances involved in kidney stone formation.
5.11 Oligohidrosis and Hyperthermia
Oligohidrosis (decreased sweating), infrequently resulting in hospitalization, has been reported in association with the use of topiramate. Decreased sweating and an elevation in body temperature above normal characterized these cases. Some of the cases have been reported with topiramate after exposure to elevated environmental temperatures.
The majority of the reports associated with topiramate have been in pediatric patients. Advise all patients and caregivers to monitor for decreased sweating and increased body temperature during physical activity, especially in hot weather. Patients on concomitant medications that predispose them to heat-related disorders may be at increased risk.
5.12 Hypokalemia
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can increase the risk of hypokalemia through its inhibition of carbonic anhydrase activity. In addition, when phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are used in conjunction with non-potassium sparing diuretics this may further potentiate potassium-wasting. Measure potassium before and during treatment with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Drug Interactions (7), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.13 Serious Skin Reactions
Serious skin reactions (Stevens-Johnson Syndrome [SJS] and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis [TEN]) have been reported in patients receiving topiramate. Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules should be discontinued at the first sign of a rash, unless the rash is clearly not drug-related. If signs or symptoms suggest SJS/TEN, use of this drug should not be resumed, and alternative therapy should be considered. Inform patients about the signs of serious skin reactions.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.6)]
- Suicidal Behavior and Ideation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Risk of Ophthalmologic Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Mood and Sleep Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Cognitive Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Slowing of Linear Growth [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Metabolic Acidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Decrease in Renal Function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Risk of Seizures with Abrupt Withdrawal of Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Kidney Stones [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Oligohidrosis and Hyperthermia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Serious Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described herein reflect exposure to phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in two 1-year, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical trials and two supportive trials in 2,318 adult patients with overweight or obesity [936 (40%) patients with hypertension, 309 (13%) patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, 808 (35%) patients with BMI greater than 40 kg/m2] exposed for a mean duration of 298 days. Data in this section also describe adverse reactions from a 1-year, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter clinical trial that evaluated 223 pediatric patients (12 to 17 years old) with obesity [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Adults
Adverse reactions occurring at greater than or equal to 5% and at least 1.5 times placebo in adults include paraesthesia, dizziness, dysgeusia, insomnia, constipation, and dry mouth.
Adverse reactions reported in greater than or equal to 2% of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule-treated adults and more frequently than in the placebo group are shown in Table 1.
|
|
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
|
|
Adverse Reaction |
% |
% |
% |
% |
|
Paraesthesia |
2 |
4 |
14 |
20 |
|
Dry Mouth |
3 |
7 |
14 |
19 |
|
Constipation |
6 |
8 |
15 |
16 |
|
Upper Respiratory Tract Infection |
13 |
16 |
12 |
14 |
|
Headache |
9 |
10 |
7 |
11 |
|
Dysgeusia |
1 |
1 |
7 |
9 |
|
Insomnia |
5 |
5 |
6 |
9 |
|
Nasopharyngitis |
8 |
13 |
11 |
9 |
|
Dizziness |
3 |
3 |
7 |
9 |
|
Sinusitis |
6 |
8 |
7 |
8 |
|
Nausea |
4 |
6 |
4 |
7 |
|
Back Pain |
5 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
|
Fatigue |
4 |
5 |
4 |
6 |
|
Diarrhea |
5 |
5 |
6 |
6 |
|
Vision Blurred |
4 |
6 |
4 |
5 |
|
Bronchitis |
4 |
7 |
4 |
5 |
|
Urinary Tract Infection |
4 |
3 |
5 |
5 |
|
Cough |
4 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
Influenza |
4 |
8 |
5 |
4 |
|
Depression |
2 |
3 |
3 |
4 |
|
Anxiety |
2 |
3 |
2 |
4 |
|
Hypoesthesia |
1 |
1 |
4 |
4 |
|
Irritability |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
Alopecia |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
Disturbance in Attention |
1 |
0 |
2 |
4 |
|
Pain in Extremity |
3 |
2 |
3 |
3 |
|
Muscle Spasms |
2 |
3 |
3 |
3 |
|
Dyspepsia |
2 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
|
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease |
1 |
1 |
3 |
3 |
|
Rash |
2 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
|
Hypokalemia |
0 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
|
Dry Eye |
1 |
1 |
1 |
3 |
|
Gastroenteritis |
2 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Pharyngolaryngeal Pain |
2 |
3 |
1 |
2 |
|
Paraesthesia Oral |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
|
Eye Pain |
1 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
Nasal Congestion |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
|
Thirst |
1 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
Sinus Congestion |
2 |
3 |
3 |
2 |
|
Procedural Pain |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
Palpitations |
1 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
|
Musculoskeletal Pain |
1 |
1 |
3 |
2 |
|
Decreased Appetite |
1 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
Neck Pain |
1 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
|
Dysmenorrhea |
0 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
|
Chest Discomfort |
0 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
Pediatric Patients Aged 12 Years and Older
Adverse reactions occurring in pediatric patients treated with either phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg or phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg at greater than or equal to 4% and higher than placebo include depression, pyrexia, dizziness, arthralgia, influenza, and ligament sprain.
Adverse reactions reported in greater than or equal to 2% of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule-treated pediatric patients and more frequently than in the placebo group from a study in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older are shown in Table 2.
|
Table 2. Adverse Reactions Reported in ≥2% of Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsule-Treated Pediatric Patients Aged 12 to 17 Years and More Frequently than Placebo during 56 Weeks of Treatment |
|||
|
(N = 56) |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg (N = 54) |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules 15 mg/92 mg (N = 113) |
|
|
Adverse Reaction |
% |
% |
% |
|
Depression |
0 |
2 |
4 |
|
Nausea |
4 |
4 |
4 |
|
Pyrexia |
2 |
2 |
4 |
|
Dizziness |
0 |
2 |
4 |
|
Arthralgia |
0 |
2 |
4 |
|
Paraesthesia |
0 |
2 |
3 |
|
Anxiety |
0 |
2 |
3 |
|
Abdominal Pain Upper |
0 |
0 |
3 |
|
Fatigue |
2 |
0 |
3 |
|
Ear Infection |
0 |
2 |
3 |
|
Musculoskeletal Chest Pain |
0 |
0 |
3 |
|
Influenza |
0 |
4 |
2 |
|
Ligament Sprain |
0 |
4 |
2 |
Increase in Heart Rate
In adult and pediatric clinical trials, there was a higher incidence of heart rate elevations observed in phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule-treated compared to placebo-treated patients.
Table 3 and Table 4 provide the numbers and percentages of adult and pediatric patients, respectively, with elevations in heart rate in clinical studies of up to one year.
|
|
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
|
|
Greater than 5 bpm |
1021 (65.4) |
168 (70.0) |
372 (74.7) |
1228 (77.7) |
|
Greater than 10 bpm |
657 (42.1) |
120 (50.0) |
251 (50.4) |
887 (56.1) |
|
Greater than 15 bpm |
410 (26.3) |
79 (32.9) |
165 (33.1) |
590 (37.3) |
|
Greater than 20 bpm |
186 (11.9) |
36 (15.0) |
67 (13.5) |
309 (19.6) |
|
Table 4. Number and Percentage of Pediatric Patients with an Increase in Heart Rate at a Single Time Point from Baseline |
||||
|
N=56 n (%) |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg N=54 n (%) |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules 15 mg/92 mg N=113 n (%) |
||
|
Greater than 5 bpm |
37 (66.1) |
38 (70.4) |
92 (81.4) |
|
|
Greater than 10 bpm |
26 (46.4) |
30 (55.6) |
73 (64.6) |
|
|
Greater than 15 bpm |
17 (30.4) |
18 (33.3) |
48 (42.5) |
|
|
Greater than 20 bpm |
10 (17.9) |
10 (18.5) |
27 (23.9) |
|
Paraesthesia/Dysgeusia
In adult clinical trials, reports of paraesthesia, characterized as tingling in hands, feet, or face, and dysgeusia, characterized as a metallic taste, occurred (see Table 1). Adverse reactions of paraesthesia were also reported in pediatric patients (see Table 2). Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule-treated adult patients discontinued treatment due to these adverse reactions (1% for paraesthesia and 0.6% for dysgeusia); no pediatric patients discontinued treatment due to paraesthesia or dysgeusia.
Mood and Sleep Disorders
The proportion of adult patients in 1-year controlled trials of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules reporting one or more adverse reactions related to mood and sleep disorders was 15% and 21% with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg and 15 mg/92 mg, respectively, compared to 10% with placebo. These events were further categorized into sleep disorders, anxiety, and depression. Reports of sleep disorders were typically characterized as insomnia and occurred in 8.1% and 11% of patients treated with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg and 15 mg/92 mg, respectively, compared to 5.8% of patients treated with placebo. Reports of anxiety occurred in 4.8% and 7.9% of patients treated with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg and 15 mg/92 mg, respectively, compared to 2.6% of patients treated with placebo.
Reports of depression/mood problems occurred in 3.8% and 7.6% of patients treated with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg and 15 mg/92 mg, respectively, compared to 3.4% of patients treated with placebo. Mood and sleep disorder adverse reactions occurred in patients with and without a history of depression.
In a pediatric clinical trial, higher proportions of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule-treated patients reported one or more adverse reactions related to mood (e.g., depression, anxiety) and sleep disorders (e.g., insomnia) compared to placebo-treated patients (see Table 2).
Cognitive Disorders
In the 1-year controlled trials of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in adults, the proportion of patients who experienced one or more cognitive-related adverse reactions was 5.0% for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg and 7.6% for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg, compared to 1.5% for placebo. These adverse reactions were comprised primarily of reports of problems with attention/concentration, memory, and language (word-finding). These events occurred at any time during treatment with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules.
Slowing of Linear Growth
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are associated with a reduction in height velocity (centimeters of height gained per year) in obese pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age. In a 56-week study, average height increased from baseline in both phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule- and placebo-treated patients; however, a lower height velocity of -1.3 to -1.4 cm/year was observed in phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule-treated compared to placebo-treated patients.
Decrease in Bone Mineral Density
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are associated with less bone mineral acquisition in pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age. In a substudy (n=66) evaluating bone mineralization via dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), increases in bone mineral density (BMD) at the lumbar spine and total body less head (TBLH) were smaller in pediatric patients treated with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules compared to those treated with placebo after 1 year of treatment. Declines in BMD Z-scores of -0.5 or greater from baseline for TBLH were observed in 9% of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg-treated patients and 30% of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg-treated patients, compared to 0% of placebo-treated patients. The sample size and study duration were too small to determine if fracture risk is increased. Decreased BMD was not correlated with decreased serum bicarbonate, which commonly occurs with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules treatment, or changes in body weight. No patient had a BMD Z-score that went below -2.0 during the trial. Similar findings were observed in a 1 year, active-controlled trial of topiramate in pediatric patients with another condition.
Nephrolithiasis
In the 1-year controlled trials of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in adults, the incidence of nephrolithiasis was 0.2% for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg and 1.2% for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg, compared to 0.3% for placebo.
Laboratory Abnormalities
Serum Bicarbonate
In the 1-year controlled trials of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in adults, the incidence of persistent decreases in serum bicarbonate below the normal range (levels of less than 21 mEq/L at 2 consecutive visits or at the final visit) was 6.4% for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg and 12.8% for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg, compared to 2.1% for placebo. The incidence of persistent, markedly low serum bicarbonate values (levels of less than 17 mEq/L on 2 consecutive visits or at the final visit) was 0.2% for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg dose and 0.7% for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg dose, compared to 0.1% for placebo.
In a pediatric clinical trial, 60 to 70% phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule-treated patients had a persistent bicarbonate level below the normal range (<21 mEq/L) compared to 43% of placebo-treated patients.
Serum Potassium
In the 1-year controlled trials of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in adults, the incidence of persistent low serum potassium values (less than 3.5 mEq/L at two consecutive visits or at the final visit) during the trial was 3.6% for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg dose and 4.9% for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg, compared to 1.1% for placebo. Of the subjects who experienced persistent low serum potassium, 88% were receiving treatment with a non-potassium sparing diuretic.
The incidence of markedly low serum potassium (less than 3 mEq/L, and a reduction from pre-treatment of greater than 0.5 mEq/L) at any time during the trial was 0.2% for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg dose and 0.7% for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg dose, compared to 0.0% for placebo. Persistent markedly low serum potassium (less than 3 mEq/L, and a reduction from pre-treatment of greater than 0.5 mEq/L at two consecutive visits or at the final visit) occurred in 0.2% receiving phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg dose and 0.1% receiving phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg dose, compared to 0.0% receiving placebo.
Low serum potassium levels (<3.5 mEq/L) were not observed in a 56-week clinical trial of pediatric patients with obesity.
Serum Creatinine
In the 1-year controlled trials of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in adults and pediatric patients, there was an increase in serum creatinine from baseline, peaking between Week 4 to 8 in adults and at Week 16 in pediatric patients. Serum creatinine values declined but remained elevated over baseline over 1 year of treatment. The incidence of increases in serum creatinine of greater than or equal to 0.3 mg/dL at any time during treatment in adults was 7.2% for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg and 8.4% for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg, compared to 2.0% for placebo; 17% of pediatric patients treated with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg or phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg and 0% of patients treated with placebo had a serum creatinine ≥0.3 mg/dL at any time post-randomization. Increases in serum creatinine of greater than or equal to 50% over baseline occurred in 2.0% of adult subjects receiving phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg and 2.8% receiving phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg, compared to 0.6% receiving placebo.
Serum Ammonia
Hyperammonemia with or without encephalopathy has been reported with topiramate. The risk for hyperammonemia with topiramate appears dose related and has been reported more frequently when concomitantly used with valproic acid [see Drug Interactions (7)].
The incidence of hyperammonemia in pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age in clinical trials of another condition was 26% in patients taking topiramate at 100 mg/day (1.1 times the maximum recommended dosage of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules) and 14% in patients taking topiramate at 50 mg/day (0.6 times the maximum recommended dosage of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules), compared to 9% in patients taking placebo. There was also an increased incidence of markedly increased hyperammonemia (defined as 50% above the upper limit of normal reference range) at the 100 mg dose.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during post approval use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules, phentermine, and topiramate. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules
Psychiatric: suicidal ideation, suicidal behavior
Ophthalmic: acute angle closure glaucoma, increased intraocular pressure
Phentermine
Allergic Reactions: urticaria
Cardiovascular: elevation of blood pressure, ischemic events
Central Nervous System: euphoria, psychosis, tremor
Reproductive: changes in libido, impotence
Topiramate
Dermatologic: bullous skin reactions (including erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis), pemphigus
Gastrointestinal: pancreatitis
Hepatic: hepatic failure (including fatalities), hepatitis
Metabolic: hyperammonemia with or without encephalopathy has been reported with concomitant valproic acid [see Drug Interactions (7)], hypothermia
Ophthalmic: maculopathy
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
Table 5 displays clinically significant drug interactions with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules.
|
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors |
|
|
Clinical Impact |
Concomitant use of phentermine with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) increases the risk of hypertensive crisis. |
|
Intervention |
Concomitant use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules is contraindicated during MAOI treatment and within 14 days of stopping an MAOI. |
|
Oral Contraceptives |
|
|
Clinical Impact |
Coadministration of multiple-dose phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg once daily with a single dose of oral contraceptive containing 35 mcg ethinyl estradiol (estrogen component) and 1 mg norethindrone (progestin component), in obese otherwise healthy volunteers, decreased the exposure of ethinyl estradiol by 16% and increased the exposure of norethindrone by 22% [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Although this interaction is not anticipated to increase the risk of pregnancy, irregular bleeding (spotting) may occur more frequently due to both the increased exposure to the progestin and lower exposure to the estrogen, which tends to stabilize the endometrium. |
|
Intervention |
Inform patients not to discontinue their combination oral contraceptive if spotting occurs, but to notify their health care provider if the spotting is troubling to them. |
|
CNS Depressants Including Alcohol |
|
|
Clinical Impact |
The concomitant use of alcohol or CNS depressant drugs (e.g., barbiturates, benzodiazepines, and sleep medications) with phentermine or topiramate may potentiate CNS depression such as dizziness or cognitive adverse reactions, or other centrally mediated effects of these agents. |
|
Intervention |
Advise patients not to drive or operate machinery until they have gained sufficient experience on phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules to gauge whether it adversely affects their mental performance, motor performance, and/or vision. Caution patients against excessive alcohol intake when taking phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules. Consider phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule dosage reduction or discontinuation if cognitive dysfunction persists [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. |
|
Non-Potassium Sparing Diuretics |
|
|
Clinical Impact |
Concurrent use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules with non-potassium sparing diuretics may potentiate the potassium-wasting action of these diuretics. Concomitant administration of hydrochlorothiazide alone with topiramate alone has been shown to increase the Cmax and AUC of topiramate by 27% and 29%, respectively. |
|
Intervention |
When phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are used concomitantly with non-potassium-sparing diuretics, measure potassium before and during phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Antiepileptic Drugs |
|
|
Clinical Impact |
Concomitant administration of phenytoin or carbamazepine with topiramate in patients with epilepsy, decreased plasma concentrations of topiramate by 48% and 40%, respectively, when compared to topiramate given alone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Concomitant administration of valproic acid and topiramate has been associated with hyperammonemia with and without encephalopathy. Concomitant administration of topiramate with valproic acid in patients has also been associated with hypothermia (with and without hyperammonemia). |
|
Intervention |
Consider measuring blood ammonia in patients in whom the onset of hypothermia or encephalopathy has been reported [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors |
|
|
Clinical Impact |
Concomitant use of topiramate with any other carbonic anhydrase inhibitor may increase the severity of metabolic acidosis and may also increase the risk of kidney stone formation. |
|
Intervention |
Avoid the use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules with other drugs that inhibit carbonic anhydrase. If concomitant use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules with another carbonic anhydrase inhibitor is unavoidable, monitor patient for the appearance or worsening of metabolic acidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.10)]. |
|
Pioglitazone | |
|
Clinical Impact |
A decrease in the exposure of pioglitazone and its active metabolites were noted with the concurrent use of pioglitazone and topiramate in a clinical trial. The clinical relevance of these observations is unknown. |
|
Intervention |
Consider increased glycemic monitoring when using pioglitazone and phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules concomitantly [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Amitriptyline |
|
|
Clinical Impact |
Some patients may experience a large increase in amitriptyline concentration in the presence of topiramate. |
|
Intervention |
Any adjustments in amitriptyline dose when used with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules should be made according to the patient's clinical response and not on the basis of amitriptyline levels [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are contraindicated in pregnant patients. The use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can cause fetal harm, and weight loss offers no clear clinical benefit to a pregnant patient (see Clinical Considerations). Available data from pregnancy registries and epidemiologic studies indicate an increased risk of major congenital malformations, including but not limited to cleft lip and/or cleft palate (oral clefts), and of being SGA in infants exposed in utero to topiramate (see Data). When phentermine and topiramate were coadministered to rats at doses of 3.75 and 25 mg/kg, respectively [approximately 2 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) based on area under the curve (AUC)], or at the same dose to rabbits (approximately 0.1 times and 1 time, respectively, the clinical exposures at the MRHD based on AUC), there were no drug-related malformations. However, structural malformations, including craniofacial defects and reduced fetal weights occurred in offspring of multiple species of pregnant animals administered topiramate at clinically relevant doses (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
Clinical Considerations
Disease Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Weight loss during pregnancy may result in fetal harm. Appropriate weight gain based on pre-pregnancy weight is currently recommended for all pregnant patients, including those who are already overweight or obese, due to the obligatory weight gain that occurs in maternal tissues during pregnancy. Maternal obesity increases the risk for congenital malformations, including neural tube defects, cardiac malformations, oral clefts, and limb reduction defects.
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can cause metabolic acidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. The effect of topiramate-induced metabolic acidosis has not been studied in pregnancy; however, metabolic acidosis in pregnancy (due to other causes) can cause decreased fetal growth, decreased fetal oxygenation, and fetal death, and may affect the fetus’ ability to tolerate labor.
Data
Human Data
Data evaluating the risk of major congenital malformations, oral clefts, and being SGA with topiramate exposure during pregnancy is available from the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry and from several larger retrospective epidemiologic studies.
Major Congenital Malformations
The NAAED Pregnancy Registry indicates an increased risk of major congenital malformations, including but not limited to oral clefts in infants exposed to topiramate during the first trimester of pregnancy. Other than oral clefts, no specific pattern of major congenital malformations or grouping of major congenital malformation types were observed. In the NAAED pregnancy registry, when topiramate-exposed infants with only oral clefts were excluded, the prevalence of major congenital malformations (4.1%) was higher than that in infants exposed to a reference antiepileptic drug (AED) (1.8%) or in infants with mothers without epilepsy and without exposure to AEDs (1.1%).
Oral Clefts
In the NAAED Pregnancy Registry, the prevalence of oral clefts among topiramate-exposed infants (1.4%) was higher than the prevalence in infants exposed to a reference AED (0.3%) or the prevalence in infants with mothers without epilepsy and without exposure to AEDs (0.11%). It was also higher than the background prevalence in United States (0.17%) as estimated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The relative risk of oral clefts in topiramate-exposed pregnancies in the NAAED Pregnancy Registry was 12.5 (95% Confidence Interval [CI] 5.9 to 26.37) as compared to the risk in a background population of untreated women. The UK Epilepsy and Pregnancy Register reported a prevalence of oral clefts among infants exposed to topiramate monotherapy (3.2%) that was 16 times higher than the background rate in the UK (0.2%).
Larger retrospective epidemiology studies showed that topiramate monotherapy exposure in pregnancy is associated with an approximately two to five-fold increased risk of oral clefts. The FORTRESS study found an excess risk of 1.5 (95% CI = -1.1 to 4.1) oral cleft cases per 1,000 infants exposed to topiramate during the first trimester.
Small for Gestational Age
Data from the NAAED Pregnancy Registry and population-based birth registry cohort indicate that exposure to topiramate in utero is associated with an increased risk of SGA newborns (birth weight <10th percentile). In the NAAED Pregnancy Registry, 19.7% of topiramate-exposed newborns were SGA compared to 7.9% of newborns exposed to a reference AED and 5.4% of newborns of mothers without epilepsy and without AED exposure. In the medical Birth Registry of Norway, a population-based pregnancy registry, 25% of newborns in the topiramate monotherapy exposure group were SGA compared to 9% in the comparison group unexposed to AEDs. The long-term consequences of the SGA findings are not known.
Animal Data
Phentermine/Topiramate
Embryo-fetal development studies have been conducted in rats and rabbits with combination phentermine and topiramate treatment. Phentermine and topiramate coadministered to rats during the period of organogenesis (gestation day (GD) 6 through 17) caused reduced fetal body weights but did not cause fetal malformations at the maximum dose of 3.75 mg/kg phentermine and 25 mg/kg topiramate [approximately 2 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) based on area under the curve (AUC) estimates for each active ingredient]. In a similar study in rabbits in which the same doses were administered from GD 6 through 18, no effects on embryo-fetal development were observed at approximately 0.1 times (phentermine) and 1 time (topiramate) clinical exposures at the MRHD based on AUC. Significantly lower maternal body weight gain was recorded at these doses in rats and rabbits.
A pre- and post-natal development study was conducted in rats with combination phentermine and topiramate treatment. There were no adverse maternal or offspring effects in rats treated throughout organogenesis and lactation with 1.5 mg/kg/day phentermine and 10 mg/kg/day topiramate (approximately 2- and 3-times clinical exposures at the MRHD, respectively, based on AUC). Treatment with higher doses of 11.25 mg/kg/day phentermine and 75 mg/kg/day topiramate (approximately 5 and 6 times maximum clinical doses based on AUC, respectively) caused reduced maternal body weight gain and offspring toxicity. Offspring effects included lower pup survival after birth, increased limb and tail malformations, reduced pup body weight and delayed growth, development, and sexual maturation without affecting learning, memory, or fertility and reproduction. The limb and tail malformations were consistent with results of animal studies conducted with topiramate alone.
Phentermine
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with phentermine. Limited data from studies conducted with the phentermine/topiramate combination indicate that phentermine alone was not teratogenic but resulted in lower body weight and reduced survival of offspring in rats at 5-fold the MRHD of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules, based on AUC.
Topiramate
Topiramate causes developmental toxicity, including teratogenicity, at clinically relevant doses in multiple animal species.
Developmental toxicity, including teratogenicity, occurred at clinically relevant doses in multiple animal species in which topiramate was administered during the period of organogenesis (GD 6 to 15 in rodents, GD 6 to 18 in rabbits. In these studies, fetal malformations (primarily craniofacial defects such as cleft palate), limb malformations (ectrodactyly, micromelia, and amelia), rib/vertebral column anomalies, and/or reduced fetal weights were observed at dosages ≥ 20 mg/kg in mice (approximately 2 times the MRHD of topiramate in phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg on a mg/m2 basis), 20 mg/kg in rats (2 times the MRHD of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules based on estimated AUC), and 35 mg/kg in rabbits (2 times the MRHD based on estimated AUC). When rats were administered topiramate from GD 15 through lactation day 20, reductions in pre- and/or post-weaning weights occurred at dosages ≥ 2 mg/kg (2 times the MRHD of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules based on estimated AUC).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Topiramate and phentermine are present in human milk. There are no data on the effects of topiramate and phentermine on milk production. Diarrhea and somnolence have been reported in breastfed infants with maternal use of topiramate. There are no data on the effects of phentermine in breastfed infants. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions, including changes in sleep, irritability, hypertension, vomiting, tremor, and weight loss in breastfed infants with maternal use of phentermine, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule therapy.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Pregnancy testing is recommended in patients who can become pregnant before initiating phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules and monthly during phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
Females
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant patient [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Advise patients who can become pregnant to use effective contraception during therapy with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules.
For patients taking combined oral contraceptives (COCs), use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules may cause irregular bleeding [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Advise patients not to discontinue taking their COC and to contact their health care provider.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules as an adjunct to a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity for weight reduction and long-term maintenance of body weight have been established in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with obesity. Use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules for this indication is supported by a 56-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in 223 pediatric patients aged 12 years and above, a pharmacokinetic study in pediatric patients, and studies in adults with obesity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14)].
In a pediatric clinical trial, there was one episode of serious suicidal ideation in a phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule-treated patient requiring hospitalization and pharmacologic treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] more patients treated with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules versus placebo reported adverse reactions related to mood (e.g., depression, anxiety) and sleep disorders (e.g., insomnia) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Increases in bone mineral density and linear growth were attenuated in phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule- versus placebo-treated patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. Serious adverse reactions seen in pediatric patients using topiramate include acute angle glaucoma, oligohidrosis and hyperthermia, metabolic acidosis, cognitive and neuropsychiatric reactions, hyperammonemia and encephalopathy, and kidney stones.
The safety and effectiveness of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in pediatric patients below the age of 12 years have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In the phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules clinical trials, a total of 254 (7%) of the patients were 65 to 69 years of age; no patients 70 years of age or older were enrolled.
Clinical studies of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Compared to healthy volunteers with normal renal function, patients with moderate and severe renal impairment as estimated by the Cockcroft-Gault equation had higher exposures to phentermine and topiramate.
The recommended dosage of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in patients with mild renal impairment (CrCl greater or equal to 50 and less than 80 mL/min) is the same as the recommended dosage for patients with normal renal function.
In patients with moderate (CrCl greater than or equal to 30 to less than 50 mL/min) and severe (CrCl less than 30 mL/min) renal impairment, the maximum recommended dosage is phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg once daily.
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules have not been studied in patients with end-stage renal disease on dialysis. Avoid phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in this patient population [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
In patients with mild (Child-Pugh 5 to 6) and moderate (Child-Pugh 7 to 9) hepatic impairment, exposure to phentermine was higher compared to healthy volunteers with normal hepatic function. Exposure to topiramate was similar among patients with mild and moderate hepatic impairment and healthy volunteers.
The recommended dosage of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh 5 to 6) is the same as the recommended dosage in patients with normal hepatic function.
In patients with moderate hepatic impairment, the maximum recommended dosage is phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg once daily.
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules have not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 10 to 15). Avoid phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in this patient population [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
9.1 Controlled Substance
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules contain phentermine, a Schedule IV controlled substance, and topiramate, which is not a controlled substance.
9.2 Abuse
Phentermine has a known potential for abuse. Abuse is the intentional, non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, for its desirable psychological or physiological effects.
Phentermine is related chemically and pharmacologically to amphetamines. Amphetamines and other stimulant drugs have been extensively abused. Abuse of amphetamines and related drugs (e.g., phentermine) may be associated with impaired control over drug use and severe social dysfunction. There are reports of patients who have increased the dosage of these drugs to many times higher than recommended. Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules as part of a weight reduction and long-term maintenance of body weight program.
9.3 Dependence
Physical dependence may occur in patients treated with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules. Physical dependence is a state that develops as a result of physiological adaptation in response to repeated drug use, manifested by withdrawal signs and symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or a significant dose reduction of a drug.
The following adverse reactions have been associated with the abrupt discontinuation of the individual components of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules:
- For topiramate, abrupt discontinuation has been associated with seizures in patients without a history of seizures or epilepsy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
- For phentermine, abrupt discontinuation following prolonged high dosage administration results in extreme fatigue and mental depression; changes are also noted on a sleep electroencephalogram.
Thus, in situations where rapid withdrawal of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules is required, appropriate medical monitoring is recommended. Patients discontinuing phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg should be gradually tapered to reduce the possibility of precipitating a seizure [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
10. Overdosage
In the event of a significant overdose with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules, if the ingestion is recent, the stomach should be emptied immediately by gastric lavage or by induction of emesis. Appropriate supportive treatment should be provided according to the patient’s clinical signs and symptoms. In the event of an overdose of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules, consider contacting the Poison Help line (1-800-222-1222) or a medical toxicologist for additional overdosage management recommendations.
Acute overdose of phentermine may be associated with restlessness, tremor, hyperreflexia, rapid respiration, confusion, aggressiveness, hallucinations, and panic states. Fatigue and depression usually follow the central stimulation. Cardiovascular effects include arrhythmia, hypertension or hypotension, and circulatory collapse. Gastrointestinal symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. Fatal poisoning usually terminates in convulsions and coma. Manifestations of chronic intoxication with anorectic drugs include severe dermatoses, marked insomnia, irritability, hyperactivity, and personality changes. A severe manifestation of chronic intoxication is psychosis, often clinically indistinguishable from schizophrenia.
Management of acute phentermine intoxication is largely symptomatic and includes lavage and sedation with a barbiturate. Acidification of the urine increases phentermine excretion. Intravenous phentolamine has been suggested for possible acute, severe hypertension, if this complicates phentermine overdosage.
Topiramate overdose has resulted in severe metabolic acidosis. Other signs and symptoms include convulsions, drowsiness, speech disturbance, blurred vision, diplopia, impaired mentation, lethargy, abnormal coordination, stupor, hypotension, abdominal pain, agitation, dizziness, and depression. The clinical consequences were not severe in most cases, but deaths have been reported after overdoses involving topiramate. A patient who ingested a dose between 96 and 110 gm topiramate was admitted to hospital with coma lasting 20 to 24 hours followed by full recovery after 3 to 4 days.
Hemodialysis is an effective means of removing topiramate from the body.
11. Phentermine and Topiramate Description
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are comprised of immediate-release phentermine hydrochloride (expressed as the weight of the free base) and extended-release topiramate. Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules contain phentermine hydrochloride USP, a sympathomimetic amine anorectic, and topiramate USP, a sulfamate-substituted monosaccharide.
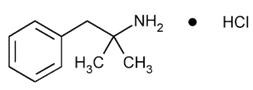
Phentermine Hydrochloride, USP
The chemical name of phentermine hydrochloride, USP is α,α-dimethylphenethylamine hydrochloride. The molecular formula is C10H15N • HCl and its molecular weight is 185.7 (hydrochloride salt) or 149.2 (free base). Phentermine hydrochloride, USP is a white, odorless, hygroscopic, crystalline powder that is soluble in water, methanol, and ethanol. Its structural formula is:
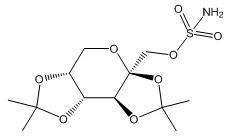
Topiramate, USP
Topiramate, USP is 2,3:4,5-di-O-isopropylidene-β-D-fructopyranose sulfamate. The molecular formula is C12H21NO8S and its molecular weight is 339.4. Topiramate, USP is a white to off-white crystalline powder with a bitter taste. It is freely soluble in methanol and acetone, sparingly soluble in pH 9 to pH 12 aqueous solutions and slightly soluble in pH 1 to pH 8 aqueous solutions. Its structural formula is:
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are for oral administration and available in four dosage strengths:
- 3.75 mg/23 mg (phentermine 3.75 mg and topiramate 23 mg extended-release) (equivalent to 4.67 mg of phentermine hydrochloride, USP).
- 7.5 mg/46 mg (phentermine 7.5 mg and topiramate 46 mg extended-release) (equivalent to 9.33 mg of phentermine hydrochloride, USP).
- 11.25 mg/69 mg (phentermine 11.25 mg and topiramate 69 mg extended-release) (equivalent to 14.0 mg of phentermine hydrochloride, USP).
- 15 mg/92 mg (phentermine 15 mg and topiramate 92 mg extended-release) (equivalent to 18.66 mg of phentermine hydrochloride, USP).
Each capsule contains the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, copovidone, ethylcellulose, gelatin, hypromellose, microcrystalline cellulose, polysorbate 80, povidone K-30, sugar spheres (which contain sucrose and corn starch), talc, and titanium dioxide. The 3.75 mg/23 mg strength also contains iron oxide red and iron oxide yellow. The 7.5 mg/46 mg strength also contains FD&C Blue #2 and iron oxide yellow. The 11.25 mg/69 mg strength also contains iron oxide yellow. The 15 mg/92 mg strength also contains iron oxide red. The imprinting ink contains ammonium hydroxide, iron oxide black, propylene glycol, and shellac glaze.
12. Phentermine and Topiramate - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Phentermine is a sympathomimetic amine with pharmacologic activity similar to the prototype drugs of this class used in obesity, amphetamine (d- and d/l-amphetamine). Drugs of this class used in obesity are commonly known as “anorectics” or “anorexigenics”. The effect of phentermine on weight reduction and long-term maintenance of body weight is likely mediated by release of catecholamines in the hypothalamus, resulting in reduced appetite and decreased food consumption, but other metabolic effects may also be involved. The exact mechanism of action is not known.
The precise mechanism of action of topiramate on weight reduction and long-term maintenance of body weight is not known. Topiramate’s effect on weight reduction and long-term maintenance of body weight may be due to its effects on both appetite suppression and satiety enhancement, induced by a combination of pharmacologic effects including augmenting the activity of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyrate, modulation of voltage-gated ion channels, inhibition of AOBMPA/kainite excitatory glutamate receptors, or inhibition of carbonic anhydrase.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Typical actions of amphetamines include central nervous system stimulation and elevation of blood pressure. Tachyphylaxis and tolerance have been demonstrated with drugs in this class.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules on the QTc interval was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled (400 mg moxifloxacin), and parallel group/crossover thorough QT/QTc study. A total of 54 healthy subjects were administered phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg at steady state and then titrated to phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 22.5 mg/138 mg at steady state. Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 22.5 mg/138 mg [a supra-therapeutic dose resulting in a phentermine and topiramate maximum concentration (Cmax) of 4- and 3-times higher than those at phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg, respectively] did not affect cardiac repolarization as measured by the change from baseline in QTc.
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Healthy obese males and females received phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules daily for 4 weeks (3.75 mg/23 mg on Days 1 to 3, 7.5 mg/46 mg on Days 4 to 6, 11.25 mg/69 mg on Days 7 to 9, and 15 mg/92 mg on Days 10 to 28). The glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of these participants was assessed via iohexol clearance. On average, GFR decreased during phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule-treatment and returned to baseline within 4 weeks after discontinuing phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Phentermine
Upon oral administration of a single phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule 15 mg/92 mg, the resulting mean plasma phentermine maximum concentration (Cmax), time to Cmax (Tmax), area under the concentration curve from time zero to the last time with measurable concentration (AUC0-t), and area under the concentration curve from time zero to infinity (AUC0-∞) are 49.1 ng/mL, 6 hr, 1,990 ng•hr/mL, and 2,000 ng•hr/mL, respectively. A high fat meal does not affect phentermine pharmacokinetics for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg. Phentermine pharmacokinetics are approximately dose-proportional from phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 3.75 mg/23 mg to phentermine 15 mg/topiramate 100 mg. Upon dosing phentermine 15 mg/topiramate 100 mg fixed dose combination capsule to steady state, the mean phentermine accumulation ratios for AUC and Cmax are both approximately 2.5.
Topiramate
Upon oral administration of a single phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule 15 mg/92 mg, the resulting mean plasma topiramate Cmax, Tmax, AUC0-t, and AUC0-∞, are 1,020 ng/mL, 9 hr, 61,600 ng•hr/mL, and 68,000 ng•hr/mL, respectively. A high fat meal does not affect topiramate pharmacokinetics for phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg. Topiramate pharmacokinetics are approximately dose-proportional from phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 3.75 mg/23 mg to phentermine 15 mg/topiramate 100 mg.
Upon dosing phentermine 15 mg/topiramate 100 mg fixed dose combination capsule to steady state, the mean topiramate accumulation ratios for AUC and Cmax are both approximately 4.0.
Distribution
Phentermine
Phentermine is 17.5% plasma protein bound. The estimated phentermine apparent volume of distribution (Vd/F) is 348 L via population pharmacokinetic analysis.
Topiramate
Topiramate is 15 to 41% plasma protein bound over the blood concentration range of 0.5 to 250 mcg/mL. The fraction bound decreased as blood topiramate increased. The estimated topiramate Vc/F (volume of the central compartment), and Vp/F (volume of the peripheral compartment) are 50.8 L, and 13.1 L, respectively, via population pharmacokinetic analysis.
Elimination
Metabolism and Excretion
Phentermine
Phentermine has two metabolic pathways, namely p-hydroxylation on the aromatic ring and N-oxidation on the aliphatic side chain. Cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 primarily metabolizes phentermine but does not show extensive metabolism. Monoamine oxidase (MAO)-A and MAO-B do not metabolize phentermine. Seventy to 80% of a dose exists as unchanged phentermine in urine when administered alone. The mean phentermine terminal half-life is about 20 hours. The estimated phentermine oral clearance (CL/F) is 8.79 L/h via population pharmacokinetic analysis.
Topiramate
Topiramate does not show extensive metabolism. Six topiramate metabolites (via hydroxylation, hydrolysis, and glucuronidation) exist, none of which constitutes more than 5% of an administered dose. About 70% of a dose exists as unchanged topiramate in urine when administered alone. The mean topiramate terminal half-life is about 65 hours. The estimated topiramate CL/F is 1.17 L/h via population pharmacokinetic analysis.
Specific Populations
Patients with Renal Impairment
A single-dose, open-label study was conducted to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg in adult patients with varying degrees of chronic renal impairment compared to healthy volunteers with normal renal function. The study included patients with renal impairment classified on the basis of creatinine clearance as mild (greater or equal to 50 and less than 80 mL/min), moderate (greater than or equal to 30 and less than 50 mL/min), and severe (less than 30 mL/min). Creatinine clearance was estimated from serum creatinine based on the Cockcroft-Gault equation.
Compared to healthy volunteers, phentermine AUC0-inf was 91%, 45%, and 22% higher in patients with severe, moderate, and mild renal impairment, respectively; phentermine Cmax was 2% to 15% higher. Compared to healthy volunteers, topiramate AUC0-inf was 126%, 85%, and 25% higher for patients with severe, moderate, and mild renal impairment, respectively; topiramate Cmax was 6% to 17% higher. An inverse relationship between phentermine or topiramate Cmax or AUC and creatinine clearance was observed.
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules have not been studied in patients with end-stage renal disease on dialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
A single-dose, open-label study was conducted to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg in healthy volunteers with normal hepatic function compared with patients with mild (Child-Pugh score 5 to 6) and moderate (Child-Pugh score 7 to 9) hepatic impairment. In patients with mild and moderate hepatic impairment, phentermine AUC was 37% and 60% higher compared to healthy volunteers. Pharmacokinetics of topiramate was not affected in patients with mild and moderate hepatic impairment when compared with healthy volunteers. Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules have not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 10 to 15) [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 years old
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted to evaluate the population pharmacokinetics of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules using data from 37 pediatric patients (12 to 17 years of age) with obesity. Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule dosages of 3.75 mg/23 mg, 7.5 mg/46 mg, and 15 mg/92 mg were studied. phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules exposure in the pediatric patients appeared comparable to that in adults.
Drug Interaction Studies
In Vitro Assessment of Drug Interactions
Phentermine
Phentermine is not an inhibitor of CYP isozymes CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4, and is not an inhibitor of monoamine oxidases. Phentermine is not an inducer of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, and CYP3A4. Phentermine is not a P-glycoprotein substrate.
Topiramate
Topiramate is not an inhibitor of CYP isozymes CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4/5. However, topiramate is a mild inhibitor of CYP2C19. Topiramate is a mild inducer of CYP3A4. Topiramate is not a P-glycoprotein substrate.
Effects of Phentermine/Topiramate on Other Drugs
Table 7 describes the effect of phentermine/topiramate on the pharmacokinetics of coadministered drugs.
|
Phentermine/Topiramate |
Coadministered Drug and Dosing Regimen |
||
|
Drug and Dose (mg) |
Change in AUC |
Change in |
|
|
*15 mg/92 mg dose QD for 16 days |
Metformin 500 mg BID for 5 days |
↑ 23% |
↑ 16% |
|
*15 mg/92 mg dose QD for 21 days |
Sitagliptin 100 mg QD for 5 days |
↓ 3% |
↓ 9% |
|
**15 mg/92 mg dose QD for 15 days |
Oral contraceptive single dose norethindrone 1 mg ethinyl estradiol 35 mcg |
↑ 16% ↓ 16% |
↑ 22% ↓ 8% |
|
*A single study examined the effect of multiple-dose phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg once daily on the pharmacokinetics of multiple-dose 500 mg metformin twice daily and multiple-dose 100 mg sitagliptin once daily in 10 males and 10 females (mean BMI of 27.1 kg/m2 and range of 22.2 to 32.7 kg/m2). The study participants received metformin, sitagliptin, phentermine/topiramate only, phentermine/topiramate plus probenecid, phentermine/topiramate plus metformin, and phentermine/topiramate plus sitagliptin on Days 1 to 5, 6 to 10, 11 to 28, 29, 30 to 34, and 35 to 39, respectively. The significance of these interactions is unknown. **See Drug Interactions (7) |
|||
Effect of Other Drugs on Phentermine/Topiramate
Table 8 describes the effect of other drugs on the pharmacokinetics of phentermine/topiramate.
|
Coadministered Drug and Dosing Regimen |
Phentermine/Topiramate |
||
|
Dose (mg) |
Change in AUC |
Change in |
|
|
Topiramate 92 mg single dose |
15 mg phentermine single dose |
↑ 42% |
↑ 13% |
|
Phentermine 15 mg single dose |
92 mg topiramate single dose |
↑ 6% |
↑ 2% |
|
*Metformin 500 mg BID for 5 days |
15 mg/92 mg dose QD for 16 days phentermine topiramate |
↑ 5% ↓ 5% |
↑ 7% ↓ 4% |
|
*Sitagliptin 100 mg QD for 5 days |
15 mg/92 mg dose QD for 21 days phentermine topiramate |
↑ 9% ↓ 2% |
↑ 10% ↓ 2% |
|
*Probenecid 2 g QD |
15 mg/92 mg dose QD for 11 days phentermine topiramate |
↓ 0.3% ↑ 0.7% |
↑ 4% ↑ 3% |
|
*The same single study examined the effect of multiple-dose 500 mg metformin twice daily, a single-dose 2 g probenecid, and multiple-dose 100 mg sitagliptin once daily on the pharmacokinetics of multiple-dose phentermine/topiramate 15 mg/92 mg once daily in 10 males and 10 females (mean BMI of 27.1 kg/m2 and range of 22.2 to 32.7 kg/m2). The study participants received metformin, sitagliptin, phentermine/topiramate only, phentermine/topiramate plus probenecid, phentermine/topiramate plus metformin, and phentermine/topiramate plus sitagliptin on Days 1 to 5, 6 to 10, 11 to 28, 29, 30 to 34, and 35 to 39, respectively. |
|||
Effects of Topiramate Alone on Other Drugs and Effects of Other Drugs on Topiramate
Antiepileptic Drugs
Potential interactions between topiramate and standard antiepileptic (AED) drugs were assessed in controlled clinical pharmacokinetic studies in patients with epilepsy. The effects of these interactions on mean plasma AUCs are summarized in Table 9.
In Table 9, the second column (AED concentration) describes what happens to the concentration of the AED listed in the first column when topiramate is added. The third column (topiramate concentration) describes how the coadministration of a drug listed in the first column modifies the concentration of topiramate in experimental settings when topiramate was given alone [see Drug Interactions (7)].
|
AED |
AED |
Topiramate |
|
Phenytoin |
NC or 25% increasea |
48% decrease |
|
Carbamazepine (CBZ) |
NC |
40% decrease |
|
CBZ epoxideb |
NC |
NE |
|
Valproic acid |
11% decrease |
14% decrease |
|
Phenobarbital |
NC |
NE |
|
Primidone |
NC |
NE |
|
Lamotrigine |
NC at TPM doses up to 400 mg/day |
13% decrease |
|
a Plasma concentration increased 25% in some patients, generally those on a twice a day dosing regimen of phenytoin. |
||
Digoxin
In a single-dose study, serum digoxin AUC was decreased by 12% with concomitant topiramate administration. The clinical relevance of this observation has not been established.
Hydrochlorothiazide
A drug-drug interaction study conducted in healthy volunteers evaluated the steady-state pharmacokinetics of hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) (25 mg q24h) and topiramate (96 mg q12h) when administered alone and concomitantly. The results of this study indicate that topiramate Cmax increased by 27% and AUC increased by 29% when HCTZ was added to topiramate. The clinical significance of this change is unknown. The steady-state pharmacokinetics of HCTZ were not significantly influenced by the concomitant administration of topiramate. Clinical laboratory results indicated decreases in serum potassium after topiramate or HCTZ administration, which were greater when HCTZ and topiramate were administered in combination [see Drug Interactions (7) and Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Pioglitazone
A drug-drug interaction study conducted in healthy volunteers evaluated the steady-state pharmacokinetics of topiramate (96 mg twice daily) and pioglitazone (30 mg daily) when administered alone and concomitantly for 7 days. A 15% decrease in the area under the concentration-time curve during a dosage interval at steady state (AUCτ,ss) of pioglitazone with no alteration in maximum steady-state plasma drug concentration during a dosage interval (Cmax,ss) was observed. This finding was not statistically significant. In addition, a 13% and 16% decrease in Cmax,ss and AUCτ,ss respectively, of the active hydroxy-metabolite was noted as well as a 60% decrease in Cmax,ss and AUCτ,ss of the active keto-metabolite [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Glyburide
A drug-drug interaction study conducted in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus evaluated the steady-state pharmacokinetics of glyburide (5 mg/day) alone and concomitantly with topiramate (150 mg/day). There was a 22% decrease in Cmax and a 25% reduction in AUC24 for glyburide during topiramate administration. Systemic exposure (AUC) of the active metabolites, 4-trans-hydroxyglyburide (M1), and 3-cis-hydroxyglyburide (M2), was reduced by 13% and 15%, and Cmax was reduced by 18% and 25%, respectively. The steady-state pharmacokinetics of topiramate were unaffected by concomitant administration of glyburide.
Lithium
In patients, the pharmacokinetics of lithium were unaffected during treatment with topiramate at doses of 200 mg/day; however, there was an observed increase in systemic exposure of lithium (27% for Cmax and 26% for AUC) following topiramate doses up to 600 mg/day.
Haloperidol
The pharmacokinetics of a single dose of haloperidol (5 mg) were not affected following multiple dosing of topiramate (100 mg every 12 hours) in 13 healthy adults (6 males, 7 females).
Amitriptyline
There was a 12% increase in AUC and Cmax for amitriptyline (25 mg per day) in 18 normal subjects (9 males, 9 females) receiving 200 mg/day of topiramate [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Sumatriptan
Multiple dosing of topiramate (100 mg every 12 hrs) in 24 healthy volunteers (14 males, 10 females) did not affect the pharmacokinetics of single-dose sumatriptan either orally (100 mg) or subcutaneously (6 mg).
Risperidone
When administered concomitantly with topiramate at escalating doses of 100, 250, and 400 mg/day, there was a reduction in risperidone systemic exposure (16% and 33% for steady-state AUC at the 250 and 400 mg/day doses of topiramate). No alterations of 9-hydroxyrisperidone levels were observed. Coadministration of topiramate 400 mg/day with risperidone resulted in a 14% increase in Cmax and a 12% increase in AUC12 of topiramate. There were no clinically significant changes in the systemic exposure of risperidone plus 9-hydroxyrisperidone or of topiramate; therefore, this interaction is not likely to be of clinical significance.
Propranolol
Multiple dosing of topiramate (200 mg/day) in 34 healthy volunteers (17 males, 17 females) did not affect the pharmacokinetics of propranolol following daily 160 mg doses. Propranolol doses of 160 mg/day in 39 volunteers (27 males, 12 females) had no effect on the exposure to topiramate, at a dose of 200 mg/day of topiramate.
Dihydroergotamine
Multiple dosing of topiramate (200 mg/day) in 24 healthy volunteers (12 males, 12 females) did not affect the pharmacokinetics of a 1 mg subcutaneous dose of dihydroergotamine. Similarly, a 1 mg subcutaneous dose of dihydroergotamine did not affect the pharmacokinetics of a 200 mg/day dose of topiramate in the same study.
Diltiazem
Coadministration of diltiazem hydrochloride extended-release with topiramate (150 mg/day) resulted in a 10% decrease in Cmax and a 25% decrease in diltiazem AUC, a 27% decrease in Cmax and an 18% decrease in des-acetyl diltiazem AUC, and no effect on N-desmethyl diltiazem. Coadministration of topiramate with diltiazem hydrochloride extended-release resulted in a 16% increase in Cmax and a 19% increase in AUC12 of topiramate.
Venlafaxine
Multiple dosing of topiramate (150 mg/day) in healthy volunteers did not affect the pharmacokinetics of venlafaxine or O-desmethyl venlafaxine. Multiple dosing of venlafaxine (150 mg extended release) did not affect the pharmacokinetics of topiramate.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Phentermine/Topiramate
No animal studies have been conducted with the combination of phentermine/topiramate to evaluate carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, or impairment of fertility. The following data are based on findings in studies performed individually with phentermine or topiramate, phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule’s two active ingredients.
Phentermine
Phentermine was not mutagenic or clastogenic with or without metabolic activation in the Ames bacterial mutagenicity assay, a chromosomal aberration test in Chinese hamster lung (CHL-K1) cells, or an in vivo micronucleus assay.
Rats were administered oral doses of 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg/day phentermine for 2 years. There was no evidence of carcinogenicity at the highest dose of phentermine (30 mg/kg) which is approximately 11 to 15 times the maximum recommended clinical dose of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg based on AUC exposure.
No animal studies have been conducted with phentermine to determine the potential for impairment of fertility.
Topiramate
Topiramate did not demonstrate genotoxic potential when tested in a battery of in vitro and in vivo assays. Topiramate was not mutagenic in the Ames test or the in vitro mouse lymphoma assay; it did not increase unscheduled DNA synthesis in rat hepatocytes in vitro; and it did not increase chromosomal aberrations in human lymphocytes in vitro or in rat bone marrow in vivo.
An increase in urinary bladder tumors was observed in mice given topiramate (20, 75, and 300 mg/kg) in the diet for 21 months. The elevated bladder tumor incidence, which was statistically significant in males and females receiving 300 mg/kg, was primarily due to the increased occurrence of a smooth muscle tumor considered histomorphologically unique to mice. Plasma exposures in mice receiving 300 mg/kg were approximately 2 to 4 times steady-state exposures measured in patients receiving topiramate monotherapy at the MRHD of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg. The relevance of this finding to human carcinogenic risk is uncertain. No evidence of carcinogenicity was seen in rats following oral administration of topiramate for 2 years at doses up to 120 mg/kg (approximately 4 to 10 times the MRHD of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules based on AUC estimates).
No adverse effects on male or female fertility were observed in rats at doses up to 100 mg/kg (approximately 4 to 8 times male and female MRHD exposures of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules based on AUC).
14. Clinical Studies
Clinical Studies in Adults
The effect of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules on weight loss in conjunction with reduced caloric intake and increased physical activity was studied in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies in patients with obesity (Study 1) and patients with obesity or overweight with two or more significant co-morbidities (Study 2). Both studies had a 4-week titration period, followed by 52 weeks of treatment. There were two co-primary efficacy outcomes measured after 1 year of treatment (Week 56): 1) the percent weight loss from baseline; and 2) treatment response defined as achieving at least 5% weight loss from baseline.
In Study 1, patients with obesity (BMI greater than or equal to 35 kg/m2) were randomized to receive 1 year of treatment with placebo (N=514), phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 3.75 mg/23 mg (N=241), or phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg (N=512) in a 2:1:2 ratio. Patients ranged in age from 18-71 years old (mean age 43) and 83% were female. Approximately 80% were White, 18% were Black or African American, and 15% were Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. At the beginning of the study the average weight and BMI of patients was 116 kg and 42 kg/m2, respectively. Patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were excluded from participating in Study 1. During the study, a well-balanced, reduced-calorie diet to result in an approximate 500 kcal/day decrease in caloric intake was recommended to all patients and patients were offered nutritional and lifestyle modification counseling.
In Study 2, patients with overweight or obesity were randomized to receive 1 year of treatment with placebo (N=994), phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg (N=498), or phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg (N=995) in a 2:1:2 ratio. Eligible patients had to have a BMI greater than or equal to 27 kg/m2 and less than or equal to 45 kg/m2 (there was no lower limit on BMI for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus) and two or more of the following obesity-related co-morbid conditions:
- Elevated blood pressure (greater than or equal to 140/90 mmHg, or greater than or equal to 130/85 mmHg for diabetics) or requirement for greater than or equal to 2 antihypertensive medications;
- Triglycerides greater than 200 to 400 mg/dL or were receiving treatment with 2 or more lipid-lowering agents;
- Elevated fasting blood glucose (greater than 100 mg/dL) or diabetes; and/or
- Waist circumference greater than or equal to 102 cm for men or greater than or equal to 88 cm for females.
Patients ranged in age from 19 to 71 years of age (mean age 51) and 70% were female. Approximately 86% were White, 12% were Black or African American, and 13% were Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. The average weight and BMI of patients at the start of the study was 103 kg and 36.6 kg/m2, respectively. Approximately half (53%) of patients had hypertension at the start of the study. There were 388 (16%) patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at the start of the study. During the study, a well-balanced, reduced-calorie diet to result in an approximate 500 kcal/day decrease in caloric intake was recommended to all patients and patients were offered nutritional and lifestyle modification counseling.
The percentage of randomized patients who withdrew from each study prior to week 56 was 40% in Study 1, and 31% in Study 2.
Table 10 provides the results for weight loss at 1 year in Studies 1 and 2. After 1 year of treatment with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules, all dose levels resulted in statistically significant weight loss compared to placebo (see Table 10, Figure 1 and Figure 2). A statistically significant greater proportion of the patients randomized to phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules than placebo achieved 5% and 10% weight loss.
|
Analysis Method |
Study 1 (Obesity) |
Study 2 (Obesity or Overweight with |
||||
|
Placebo |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
Placebo |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules 15 mg/92 mg |
|
|
ITT-LOCF (Primary)* |
n = 498 |
n = 234 |
n = 498 |
n = 979 |
n = 488 |
n = 981 |
|
Weight (kg) | ||||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) |
115.7 (21.4) |
118.6 (21.9) |
115.2 (20.8) |
103.3 (18.1) |
102.8 (18.2) |
103.1 (17.6) |
|
% LS Mean Change from baseline (SE)** |
-1.6 (0.4) |
-5.1 (0.5)† |
-10.9 (0.4)†‡ |
-1.2 (0.3) |
-7.8 (0.4)† |
-9.8 (0.3)†‡ |
|
Difference from placebo |
3.5 |
9.4 |
6.6 |
8.6 |
||
|
Percentage of patients losing greater than or equal to 5% body weight |
17% |
45%† |
67%†‡ |
21% |
62%† |
70%†‡ |
|
Risk Difference vs. placebo (95% CI) |
27.6 |
49.4 |
41.3 |
49.2 |
||
|
Percentage of patients losing greater than or equal to 10% body weight |
7% |
19%† |
47%†‡ |
7% |
37%† |
48%†‡ |
|
Risk Difference vs. placebo (95% CI) |
11.4 |
39.8 |
29.9 |
40.3 |
||
|
SD=standard deviation; LS=least-squares; SE=standard error; CI=confidence interval * Uses all available data from subjects in ITT population, including data collected from subjects who discontinued drug but remained on study. Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF) method used to impute missing data. † p < 0.0001 vs. placebo based on least-squares (LS) mean from an analysis of covariance. ‡ p < 0.01 vs. 3.75 mg/23 mg (Study 1) or 7.5 mg/46 mg (Study 2) dose. Type 1 error was controlled across all pairwise treatment comparisons. ** Adjusted for baseline bodyweight (Study 1) and baseline bodyweight and diabetic status (Study 2). |
||||||
|
Figure 1. Study 1 Percent Weight Change from Baseline to |
Figure 2. Study 2 Percent Weight Change from Baseline to |
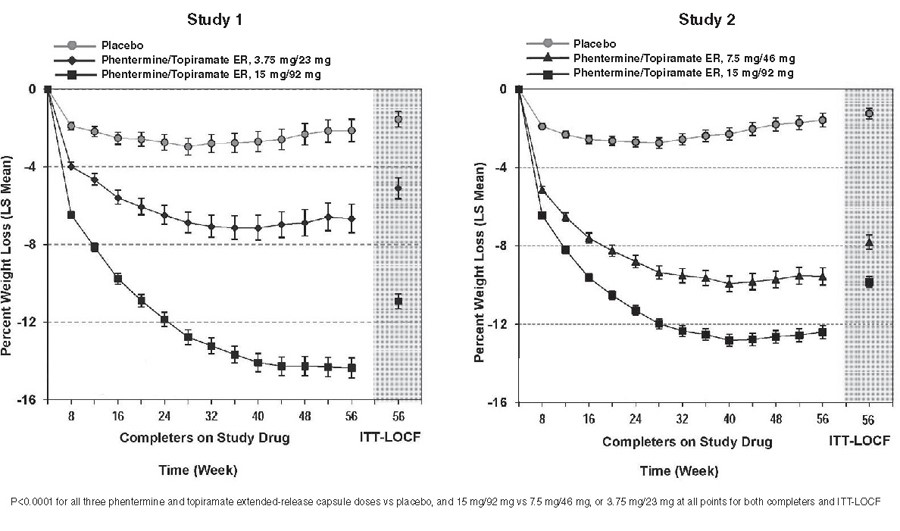
The changes in cardiovascular, metabolic, and anthropometric risk factors associated with obesity from Study 1 and 2 are presented in Table 11 and Table 12.
|
Study 1 (Obesity) |
|
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules – Placebo: LS Mean |
|
|
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
||||
|
Heart Rate, bpm | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) |
73.2 (8.8) |
72.3 (9.2) |
73.1 (9.6) |
+1.1 |
+1.8 |
|
LS Mean Change (SE) |
-0.8 (0.5) |
+0.3 (0.6) |
+1.0 (0.5) | ||
|
Systolic Blood Pressure, mmHg | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) |
121.9 (11.5) |
122.5 (11.1) |
121.9 (11.6) |
-2.8 |
-3.8 |
|
LS Mean Change (SE) |
+0.9 (0.6) |
-1.8 (0.8) |
-2.9 (0.6) | ||
|
Diastolic Blood Pressure, mmHg | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) |
77.2 (7.9) |
77.8 (7.5) |
77.4 (7.7) |
-0.5 |
-1.9 |
|
LS Mean Change (SE) |
+0.4 (0.4) |
-0.1 (0.6) |
-1.5 (0.4) | ||
|
Total Cholesterol, % | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) |
194.3 (36.7) |
196.3 (36.5) |
192.7 (33.8) |
-1.9 |
-2.5 |
|
LS Mean Change (SE) |
-3.5 (0.6) |
-5.4 (0.9) |
-6.0 (0.6) | ||
|
LDL-Cholesterol, % | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) |
120.9 (32.2) |
122.8 (33.4) |
120.0 (30.1) |
-2.2 |
-2.8 |
|
LS Mean Change (SE) |
-5.5 (1.0) |
-7.7 (1.3) |
-8.4 (0.9) | ||
|
HDL-Cholesterol, % | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) |
49.5 (13.3) |
50.0 (11.1) |
49.7 (11.7) |
+0.5 |
+3.5 |
|
LS Mean Change (SE) |
+0.0 (0.8) |
+0.5 (1.1) |
+3.5 (0.8) | ||
|
Triglycerides, % | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) |
119.0 (39.3) |
117.5 (40.3) |
114.6 (37.1) |
-3.9 |
-14.3 |
|
LS Mean Change (SE) |
+9.1 (2.3) |
+5.2 (3.1) |
-5.2 (2.2) | ||
|
Fasting Glucose, mg/dL | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) |
93.1 (8.7) |
93.9 (9.2) |
93.0 (9.5) |
-1.2 |
-2.5 |
|
LS Mean Change (SE) |
+1.9 (0.5) |
+0.8 (0.7) |
-0.6 (0.5) | ||
|
Waist Circumference, cm | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) |
120.5 (14.0) |
121.5 (15.2) |
120.0 (14.7) |
-2.5* |
-7.8* |
|
LS Mean Change (SE) |
-3.1 (0.5) |
-5.6 (0.6) |
-10.9 (0.5) | ||
|
SD=standard deviation; SE=standard error |
|||||
|
* Statistically significant versus placebo based on the pre-specified method for controlling Type I error across multiple doses |
|||||
|
† Study 1 adjusted for baseline bodyweight |
|||||
|
|
|
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules
15 mg/92 mg |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules – Placebo: LS Mean |
|
|
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
||||
|
Heart Rate, bpm | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) LS Mean Change (SE) |
72.1 (9.9) |
72.2 (10.1) |
72.6 (10.1) |
+0.6 |
+1.7 |
|
Systolic Blood Pressure, mmHg | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) LS Mean Change (SE) |
128.9 (13.5) |
128.5 (13.6) |
127.9 (13.4) |
-2.3 |
-3.2 |
|
Diastolic Blood Pressure, mmHg | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) LS Mean Change (SE) |
81.1 (9.2) |
80.6 (8.7) |
80.2 (9.1) |
-0.7 |
-1.1 |
|
Total Cholesterol, % | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) LS Mean Change (SE) |
205.8 (41.7) |
201.0 (37.9) |
205.4 (40.4) |
-1.6 |
-3.0 |
|
LDL-Cholesterol, % | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) LS Mean Change (SE) |
124.2 (36.2) |
120.3 (33.7) |
123.9 (35.6) |
+0.4 |
-2.8 |
|
HDL-Cholesterol, % | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) LS Mean Change (SE) |
48.9 (13.8) |
48.5 (12.8) |
49.1 (13.8) |
+4.0 |
+5.6 |
|
Triglycerides, % | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) LS Mean Change (SE) |
163.5 (76.3) |
161.1 (72.2) |
161.9 (73.4) |
-13.3 |
-15.3 |
|
Fasting Insulin, (µIU/mL) | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) LS Mean Change (SE) |
17.8 (13.2) |
18.0 (12.9) |
18.4 (17.5) |
-4.2 |
-4.7 |
|
Fasting Glucose, mg/dL | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) LS Mean Change (SE) |
106.6 (23.7) |
106.2 (21.0) |
105.7 (21.4) |
-2.4 |
-3.6 |
|
Waist Circumference, cm | |||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) LS Mean Change (SE) |
113.4 (12.2) |
112.7 (12.4) |
113.2 (12.2) |
-5.2*
|
-6.8*
|
|
SD=standard deviation; SE=standard error |
|||||
|
* Statistically significant versus placebo based on the pre-specified method for controlling Type I error across multiple doses |
|||||
|
† Study 2 adjusted for baseline bodyweight and diabetic status |
|||||
Among the 388 subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated in Study 2, reductions in HbA1c from baseline (6.8%) were 0.1% for placebo compared to 0.4% and 0.4% with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg and phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg, respectively.
Clinical Studies in Pediatric Patients Aged 12 Years and Older
The effect of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules on BMI in conjunction with reduced caloric intake and increased physical activity was evaluated in Study 3 (NCT03922945), a 56-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in pediatric patients (12 to 17 years of age) with BMI ≥ 95th percentile standardized by age and sex. Patients were randomized to receive treatment with placebo (N=56), phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg (N=54), or phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules 15 mg/92 mg (N=113) in a 1:1:2 ratio. During the study, a well-balanced, reduced-calorie diet to result in an approximate 500 kcal/day decrease in caloric intake was recommended to all patients and patients were offered a family-based lifestyle modification program for adolescents.
Patients’ mean age was 14 years old, approximately 55% were female, 67% were White, 26% were Black or African American, and 33% were Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. At the beginning of the study, the average weight and BMI of patients was 106 kg and 38 kg/m2, respectively, with approximately 81% considered severely obese (120% of the 95th percentile or greater for BMI standardized by age and sex). Thirty-eight (38%) of randomized patients withdrew from the study prior to week 56.
The primary efficacy parameter was mean percent change in BMI. Table 13 provides results for BMI reduction at Week 56 in Study 3. After 56 weeks of treatment with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules, all dose levels resulted in statistically significant reduction in BMI compared to placebo (see Table 13, Figure 3). A greater proportion of patients randomized to phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules than placebo achieved 5%, 10%, and 15% BMI reduction.
|
Table 13. Change in BMI at Week 56 in Pediatric Patients Aged 12 to 17 Years in Study 3 (Obesity) |
|||
|
Analysis Method |
Placebo |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules 7.5 mg/46 mg |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules 15 mg/92 mg |
|
ITT-Washout (Primary)* |
n = 56 |
n = 54 |
n = 113 |
|
BMI (kg/m2) Primary Efficacy Endpoint |
|||
|
Baseline mean (SD) |
36.4 (6.4) |
36.9 (6.7) |
39.0 (7.4) |
|
% LS Mean Change from baseline (SE) |
+3.3 (1.4) |
-4.8 (1.3) |
-7.1 (1.0) |
|
Difference from placebo (95% CI) |
-8.1 (-11.9, -4.3) |
-10.4 (-13.9, -7.0) |
|
|
Percentage of patients with a reduction of greater than or equal to 5% BMI |
13.6% |
44.0% |
52.2% |
|
Difference vs. placebo (95% CI) |
29.7% (11.2, 48.3) |
38.6% (23.1, 54.1) |
|
|
Percentage of patients with a reduction of greater than or equal to 10% BMI |
4.5% |
33.5% |
44.4% |
|
Difference vs. placebo (95% CI) |
28.8% (13.6, 44.0) |
40.5% (28.4, 52.6) |
|
|
Percentage of patients with a reduction of greater than or equal to 15% BMI |
2.9% |
13.6% |
28.9% |
|
Difference vs. placebo (95% CI) |
11.7% (1.3, 22.2) |
27.4% (17.7, 37.1) |
|
|
SD=standard deviation; LS=least-squares; SE=standard error; CI=confidence interval |
|||
Figure 3. Study 3 Percent BMI Change from Baseline to Week 56 in Pediatric Patients Aged 12 to 17 Years with Obesity
The changes in cardiovascular, metabolic, and anthropometric risk factors associated with obesity from Study 3 are presented in Table 14.
|
Table 14. Change from Baseline and Treatment Difference from Placebo in Cardiometabolic Parameters in Pediatric Patients Aged 12 to 17 Years Following 56 Weeks of Treatment in Study 3 (Obesity) |
||||||
|
ITT Population |
|
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules
15 mg/92 mg |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules – Placebo |
||
|
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules |
|||||
|
Heart Rate, bpm* | ||||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) Mean Change (SD) |
76.8 (9.9) |
78.6 (9.6) |
76.2 (9.6) 5.7 (11.4) |
-5.6 |
3.2 |
|
|
Systolic Blood Pressure, mmHg | ||||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) LS Mean Change (SE) |
117.7 (10.4) |
121.4 (9.2) |
117.4 (10.2) |
-2.8 |
-1.0 |
|
|
Diastolic Blood Pressure, mmHg | ||||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) LS Mean Change (SE) |
71.7 (8.3) +3.4 (1.5) |
75.8 (6.7) +0.2 (1.3) |
72.9 (7.3) +1.2 (1.0) |
-3.2 |
-2.2 |
|
|
Total Cholesterol, mg/dL* | ||||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) Mean % Change (SD) |
164.9 (30.9) -1.8 (10.7) |
160.6 (26.1) -3.2 (13.1) |
159.4 (32.7) -3.0 (14.5) |
-1.4 |
-1.2 |
|
|
LDL-Cholesterol, mg/dL* | ||||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) Mean % Change (SD) |
94.1 (26.8) 0.2 (23.3) |
89.4 (23.7) -3.7 (15.5) |
90.2 (27.3) -2.3 (21.6) |
-3.9 |
-2.5 |
|
|
HDL-Cholesterol, mg/dL | ||||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) LS Mean % Change (SE) |
47.2 (9.7) -4.3 (15.1) |
47.2 (8.9) +2.1 (11.5) |
46.7 (10.1) +0.7 (9.6) |
6.4 |
5.0 |
|
|
Triglycerides, mg/dL | ||||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) LS Mean % Change (SE) |
118.3 (46.1) +5.6 (8.4) |
120.1 (61.6) -6.2 (8.0) |
112.2 (63.2) -5.6 (7.2) |
-11.7 |
-11.2 |
|
|
HbA1c, %* | ||||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) Mean Change (SD) |
5.5 (0.3) -0.2 (0.2) |
5.6 (0.4) -0.4 (0.3) |
5.5 (0.4) -0.2 (0.3) |
-0.2 |
0.0 |
|
|
Waist Circumference, cm | ||||||
|
Baseline mean (SD) LS Mean Change (SE) |
111.1 (14.0) +0.6 (1.4) |
111.9 (15.5) -5.0 (1.4) |
116.5 (16.8) -7.0 (1.1) |
-5.6 |
-7.6 |
|
|
SD=standard deviation; SE=standard error |
||||||
|
* Parameter was not pre-specified for inferential statistics; descriptive summary of change from baseline provided for subjects with non-missing data at baseline and Week 56. |
||||||
16. How is Phentermine and Topiramate supplied
Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are available as follows (see Table 15):
|
Strength |
Description |
How Supplied |
NDC # |
|
3.75 mg/23 mg |
White opaque cap printed with WPI, orange opaque body printed with 2196 |
Unit of Use Bottle (30 capsules) |
0480-3297-56 |
|
7.5 mg/46 mg |
White opaque cap printed with WPI, green opaque body printed with 2195 |
Unit of Use Bottle (30 capsules) |
0480-3296-56 |
|
11.25 mg/69 mg |
Light yellow opaque cap printed with WPI, white opaque body printed with 2299 |
Unit of Use Bottle (30 capsules) |
0480-2299-56 |
|
15 mg/92 mg |
White opaque cap printed with WPI, dark scarlet opaque body printed with 2194 |
Unit of Use Bottle (30 capsules) |
0480-3295-56 |
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep container tightly closed and protect from moisture. Keep out of reach of children.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Inform patients who can become pregnant that phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can cause fetal harm and patients should avoid getting pregnant while taking phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7), and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Advise patients who can become pregnant:
- that pregnancy testing is recommended before initiating phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules and monthly during therapy;
- to use effective contraception during phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule therapy;
- who experience spotting while taking a combined oral contraceptive to notify their health care provider;
- with a known or suspected pregnancy to stop phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules immediately and notify their health care provider.
Access to Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules
Advise patients that phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules is only available through certified pharmacies that are enrolled in the phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules certified pharmacy network. Advise patients on how to access phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules through certified pharmacies. Additional information may be obtained via the website www.PhenTopREMS.com or by telephone at 1-800-269-6816 or by FAX at 1-800-558-6165.
Suicidal Behavior and Ideation and Mood and Sleep Disorders
Inform patients that phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can increase the risk of mood changes, sleep disorders, depression, and suicidal ideation. Advise patients to tell their health care provider(s) immediately if mood changes, depression, or suicidal ideation occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4)].
Ophthalmologic Adverse Reactions
Inform patients that phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can increase the risk of acute myopia, secondary angle closure glaucoma, and visual field defects. Advise patients to immediately report symptoms of severe and persistent eye pain or significant changes in their vision to their health care provider(s) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Cognitive Impairment
Inform patients that phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can cause confusion, concentration, and word-finding difficulties. Inform patients that the concomitant use of alcohol or central nervous system (CNS) depressant drugs with phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules, may increase the risk of dizziness, cognitive adverse reactions, drowsiness, light-headedness, impaired coordination and somnolence.
Advise patients to tell their health care provider(s) about any changes in attention, concentration, memory, difficulty finding words, or other cognitive functions.
Advise patients not to drive or operate machinery until they have gained sufficient experience on phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules to gauge whether it adversely affects their mental performance, motor performance, and/or vision. Advise patients to avoid excessive alcohol intake while taking phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Slowing of Linear Growth
Discuss with the patient and caregiver that long-term phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules treatment may attenuate growth as reflected by slower height increase in pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6).
Metabolic Acidosis
Inform patients that phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can increase the risk of metabolic acidosis. Advise patients to tell their health care provider(s) about any factors that can increase the risk of acidosis (e.g. prolonged diarrhea, surgery, and high protein/low carbohydrate diet, and/or concomitant medications such as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Risk of Seizures with Abrupt Withdrawal of Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules
Inform patients that abrupt withdrawal of topiramate has been associated with seizures in individuals without a history of seizures or epilepsy. Advise patients not to abruptly stop phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules without first talking to their health care provider(s) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Kidney Stones
Inform patients that use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules has been associated with kidney stone formation. Advise patients to increase fluid intake to increase urinary output which can decrease the concentration of substances involved in kidney stone formation. Advise patients to report symptoms of severe side or back pain, and/or blood in their urine to their health care provider(s) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Oligohidrosis and Hyperthermia
Inform patients that oligohidrosis (decreased sweating) has been reported in association with the use of topiramate, particularly in pediatric patients. Advise patients to monitor for decreased sweating and increased body temperature during physical activity, especially in hot weather [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
Serious Skin Reactions
Inform patients that serious skin reactions have been reported with use of topiramate. Inform patients of the signs of serious skin reactions and advise patients to report signs of a skin reaction to their health care provider(s) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
Lactation
Advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsule treatment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
How to Take Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules
Instruct patients on the dosage titration schedule of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules. Advise patients to take phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in the morning with or without food [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Brands listed are the trademarks of their respective owners.
Dispense with Medication Guide available at: www.tevausa.com/medguides
Manufactured In Bulgaria By:
Balkanpharma Dupnitsa AD
Dupnitsa 2600, Bulgaria
Manufactured For:
Teva Pharmaceuticals
Parsippany, NJ 07054
Rev. C 6/2025
Medication Guide
Dispense with Medication Guide available at: www.tevausa.com/medguides
|
MEDICATION GUIDE |
|||
|
What is the most important information I should know about phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules? Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can cause serious side effects, including:
If you become pregnant while taking phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules, stop taking phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules immediately and tell your health care provider right away. Health care providers and patients who become pregnant should report all cases of pregnancy to:
Because of the risk for birth defects (cleft lip and cleft palate), phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are available through a restricted program called the Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS). Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules are only available through certified pharmacies that participate in the Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-Release Capsules REMS. Your health care provider can give you information about how to find a certified pharmacy. For more information, go to www.PhenTopREMS.com or call 1-800-269-6816.
Call your health care provider right away if you have any of these symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
Do not stop phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules without first talking to a health care provider.
How can I watch for early symptoms of suicidal thoughts and actions?
These problems can lead to permanent vision loss if not treated. Tell your health care provider right away if you have any new eye symptoms. Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can have other serious side effects. See “What are the possible side effects of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules?”. |
|||
|
What are phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules?
|
|||
|
Who should not take phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules? Do not take phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules if you:
|
|||
|
Before taking phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules, tell your health care provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your health care provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules taken with other medicines may affect how each medicine works and may cause side effects. Especially tell your health care provider if you take:
Ask your health care provider or pharmacist for a list of these medicines, if you are not sure. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your health care provider and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine. Do not start a new medicine without talking to your health care provider. |
|||
|
How should I take phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules?
|
|||
 |  | 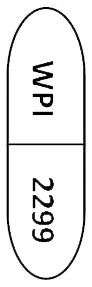 |  |
|
Figure A Phentermine and Topiramate White opaque cap and orange opaque body with black printing |
Figure B Phentermine and Topiramate White opaque cap and green opaque body with black printing |
Figure C Phentermine and Topiramate Light yellow opaque cap and white opaque body with black printing |
Figure D Phentermine and Topiramate White opaque cap and dark scarlet opaque body with black printing |
|
If you take too many phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules, call your health care provider or Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222 or go to the nearest emergency room right away. |
|||
|
What should I avoid while taking phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules?
|
|||
|
What are the possible side effects of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules? Phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules can cause serious side effects, including:
Common side effects of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in adults include:
Common side effects of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules in children 12 years and older include:
Tell your health care provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or does not go away. These are not all of the possible side effects of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules. For more information, ask your health care provider or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. You can also report side effects to Teva at 1-888-838-2872. |
|||
|
How should I store phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules?
Keep phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|||
|
General Information about the safe and effective use of phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or health care provider for information about phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules that is written for health professionals. |
|||
|
What are the ingredients in phentermine and topiramate extended-release capsules? Brands listed are the trademarks of their respective owners. Manufactured In Bulgaria By: Balkanpharma Dupnitsa AD, Dupnitsa 2600, Bulgaria |
|||
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Rev. C 6/2025
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0480-3297-56
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-release Capsules CIV
3.75 mg/23 mg
PHARMACIST: Dispense the accompanying Medication Guide to each patient.
Rx only
30 Capsules

PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0480-3296-56
Phentermine and Topiramate Extended-release Capsules CIV
7.5 mg/46 mg
PHARMACIST: Dispense the accompanying Medication Guide to each patient.
Rx only
30 Capsules
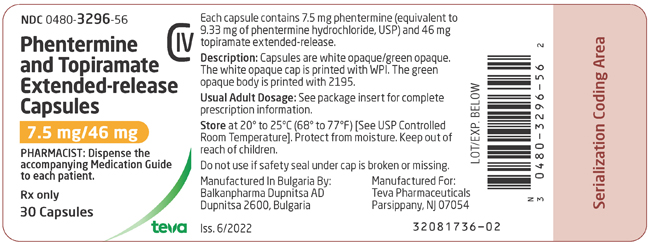
| PHENTERMINE AND TOPIRAMATE
phentermine and topiramate capsule, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHENTERMINE AND TOPIRAMATE
phentermine and topiramate capsule, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHENTERMINE AND TOPIRAMATE
phentermine and topiramate capsule, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHENTERMINE AND TOPIRAMATE
phentermine and topiramate capsule, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Teva Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (022629579) |
More about phentermine / topiramate
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (692)
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: anorexiants
- En español