Hernexeos: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: zongertinib
Dosage form: tablets
Drug class: HER2 inhibitors
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 17, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
HERNEXEOS® (zongertinib tablets), for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2025
Indications and Usage for Hernexeos
HERNEXEOS is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable or metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have HER2 (ERBB2) tyrosine kinase domain activating mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test, and who have received prior systemic therapy. (1)
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on objective response rate and duration of response. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial. (1)
Hernexeos Dosage and Administration
- Select patients for treatment with HERNEXEOS based on the presence of HER2 (ERBB2) tyrosine kinase domain activating mutations. (2.1)
- The recommended dosage of HERNEXEOS is based on body weight: (2.2)
- Take HERNEXEOS orally once daily with or without food until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 60 mg (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hepatotoxicity: Monitor liver function tests including ALT, AST, and total bilirubin at baseline prior to administration, every 2 weeks during the first 12 weeks, and then monthly thereafter as clinically indicated, with more frequent testing in patients who develop transaminase elevations. Interrupt, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue HERNEXEOS based on severity. (5.1)
- Left Ventricular Dysfunction: Before initiating, evaluate LVEF and monitor at regular intervals during treatment and as clinically indicated. Interrupt, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue HERNEXEOS based on severity. (5.2)
- Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis: Monitor for new or worsening symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis (e.g., dyspnea, cough, fever). Interrupt, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue HERNEXEOS based on severity. (5.3)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) are diarrhea, hepatotoxicity, rash, fatigue, and nausea. (6.1)
The most common (≥ 2%) Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were decreased lymphocytes, increased alanine aminotransferase, increased aspartate aminotransferase, decreased potassium, and increased gamma glutamyl transferase. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-542-6257 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Strong CYP3A Inducers: Avoid concomitant use with strong CYP3A inducers. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, increase HERNEXEOS dose. (7.1)
- BCRP Substrates: Avoid concomitant use with certain BCRP substrates where minimal concentration increase may lead to serious adverse reactions and consider alternative therapies. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, monitor patients closely for adverse reactions and follow recommendations provided in the BCRP substrate approved product labeling. For other BCRP substrates, monitor for increased adverse reactions and adjust the dosages of those substrates as clinically appropriate. (7.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 8/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Hernexeos
HERNEXEOS is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable or metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have HER2 (ERBB2) tyrosine kinase domain activating mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test, and who have received prior systemic therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on objective response rate and duration of response [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
2. Hernexeos Dosage and Administration
2.1 Patient Selection
Select patients for treatment of unresectable or metastatic NSCLC based on the presence of HER2 (ERBB2) tyrosine kinase domain activating mutations in tumor specimens [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Information on FDA-approved tests for HER2 (ERBB2) tyrosine kinase domain activating mutations is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Administration
The recommended dosage of HERNEXEOS is based on body weight:
- < 90 kg: 120 mg
- ≥ 90 kg: 180 mg
Take HERNEXEOS orally once daily with or without food until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Swallow HERNEXEOS tablets whole with water. Do not split, crush, or chew tablets.
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dose reductions for adverse reactions are presented in Table 1.
| Current HERNEXEOS Dose | First Reduction | Second Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| 180 mg | 120 mg | 60 mg |
| 120 mg | 60 mg | Permanently discontinue |
| Permanently discontinue HERNEXEOS in patients who are unable to tolerate 60 mg once daily. | ||
The recommended dosage modifications for adverse reactions are presented in Table 2.
| Adverse Reaction | Severity | Dosage Modification |
|---|---|---|
| ALT = alanine aminotransferase; AST = aspartate aminotransferase; CTCAE = Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events; ULN = upper limit of normal | ||
| Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | Grade 3 or 4 ALT and/or AST without increased total bilirubin |
|
| Grade 3 total bilirubin |
|
|
| Grade 4 total bilirubin |
|
|
| ALT or AST ≥ 3× ULN with total bilirubin ≥ 2× ULN |
|
|
| Left Ventricular Dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | LVEF 40 to 50% and decrease from baseline of 10 to 19% |
|
| LVEF 20 to 39% or ≥ 20% decrease from baseline |
|
|
| Symptomatic Congestive Heart Failure |
|
|
| Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | Grade 2 |
|
| Grade 3 or Grade 4 |
|
|
| Diarrhea [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] | Grade 2 |
|
| Grade 2 lasting ≥ 2 days despite anti-diarrheal treatment |
|
|
| Grade 3 or Grade 4 |
|
|
| Other Adverse Reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] | Grade 3 |
|
| Grade 4 |
|
|
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions
Strong CYP3A Inducers
Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers with HERNEXEOS.
If concomitant use cannot be avoided, increase the HERNEXEOS dose based on body weight [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]:
- < 90 kg: from 120 mg to 240 mg
- ≥ 90 kg: from 180 mg to 360 mg
After discontinuing a CYP3A inducer, resume the HERNEXEOS dose (7 to 14 days after discontinuing the CYP3A inducer) that was taken prior to initiating the CYP3A inducer.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
60 mg tablets: yellow, oval, biconvex, film-coated tablets, debossed with "L6" on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol on the other side. Each tablet contains 60 mg of zongertinib.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hepatotoxicity
HERNEXEOS can cause severe and life-threatening hepatotoxicity, including drug induced liver injury. In a pooled safety population [see Adverse Reaction (6.1)], based on adverse reaction data, hepatotoxicity occurred in 27% of patients treated with HERNEXEOS. Grade 3 drug induced liver injury occurred in 1.5% and Grade 4 in 0.4% of patients treated with HERNEXEOS. Grade 3 hepatic failure occurred in 0.4% of patients treated with HERNEXEOS.
Based on laboratory data, 35% of patients treated with HERNEXEOS experienced increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT), including 4.3% Grade 3 and 1.2% Grade 4. Increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST) occurred in 31% of patients treated with HERNEXEOS, including 3.5% Grade 3 and 0.8% Grade 4. Increased bilirubin occurred in 20% of patients treated with HERNEXEOS, including 0.8% Grade 3 and 0.4% Grade 4.
HERNEXEOS was interrupted for an adverse reaction of hepatotoxicity in 8% of patients, the dose was reduced in 3.5% and permanently discontinued in 1.5%.
Monitor liver function tests including ALT, AST, and total bilirubin at baseline prior to administration of HERNEXEOS, every 2 weeks during the first 12 weeks, and then monthly thereafter as clinically indicated, with more frequent testing in patients who develop transaminase elevations. Interrupt, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue HERNEXEOS based on the severity of the adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.2 Left Ventricular Dysfunction
HERNEXEOS can cause severe left ventricular dysfunction. Left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEF) decrease occurred with anti-HER2 therapies, including HERNEXEOS. Treatment with HERNEXEOS has not been studied in patients with a history of clinically significant cardiac disease or LVEF less than 50% prior to initiation of treatment.
In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], LVEF decrease occurred in 6% of patients treated with HERNEXEOS, including 1.9% Grade 3. Two patients with Grade 3 LVEF decrease required permanent discontinuation. The median time to onset of decreased LVEF was 9 weeks (range: 2.9 to 63 weeks).
Before initiating HERNEXEOS, evaluate LVEF and monitor at regular intervals during treatment and as clinically indicated. Interrupt, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue HERNEXEOS based on the severity of the adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis
HERNEXEOS can cause severe and life-threatening interstitial lung disease (ILD)/pneumonitis.
In the pooled safety population [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)], ILD/pneumonitis occurred in 1.2% of patients (N=3) treated with HERNEXEOS. The median time to first onset of ILD/pneumonitis was 19 weeks (range: 6 to 65 weeks). One patient was able to resume therapy after resolution of pneumonitis. One patient required permanent discontinuation and one patient died with unresolved pneumonitis > 30 days after discontinuing HERNEXEOS.
Monitor patients for new or worsening symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis (e.g., dyspnea, cough, fever). Interrupt, reduce the dose or permanently discontinue HERNEXEOS based on severity of confirmed ILD/pneumonitis [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, HERNEXEOS can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In an animal reproduction study, oral administration of zongertinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis caused structural abnormalities and alterations to growth at maternal exposures ≥ 19 times the human exposure based on AUC at the recommended dose.
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with HERNEXEOS and for 2 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Left Ventricular Dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The pooled safety population described in WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflects exposure to HERNEXEOS in 260 patients with unresectable or metastatic non-squamous NSCLC with HER2 (ERBB2) mutations who received HERNEXEOS as a single agent at 120 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity in Beamion LUNG-1 [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Among 260 patients who received HERNEXEOS, 58% of patients were exposed for 6 months or longer and 13% were exposed for greater than one year. In this pooled safety population, the most common (> 20%) adverse reactions were diarrhea (53%), hepatotoxicity (27%), rash (27%), fatigue (22%), and nausea (21%). The most common (≥ 2%) Grade 3 or 4 laboratory abnormalities were decreased lymphocytes (9%), increased alanine aminotransferase (5%), increased aspartate aminotransferase (4.3%), decreased potassium (2.7%), and increased gamma glutamyl transferase (2.7%).
Beamion LUNG-1
The safety of HERNEXEOS was evaluated in Beamion LUNG-1 in 105 patients with previously treated unresectable or metastatic non-squamous NSCLC with HER2 tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) mutations; all patients had received prior platinum-based chemotherapy, and 34 patients had received prior treatment with a HER2-directed antibody drug conjugate (ADC) [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Patients received HERNEXEOS as a single agent at 120 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Among patients who received HERNEXEOS, 72% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 30% were exposed for greater than one year. The median age of patients who received HERNEXEOS was 61 years (range 30 to 85), 69% were female, 40% White, 49% Asian, and 0% Black or African American; 11% had unknown race data; 1.9% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity; and 33% had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance score of 0 and 67% had an ECOG performance score of 1.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 34% of patients receiving HERNEXEOS. Serious adverse reactions in ≥ 2% of patients included dyspnea (4.8%), pulmonary embolism (4.8%), hepatotoxicity (2.9%), and pneumonia (2.9%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1% of patients who received HERNEXEOS, due to pneumonia.
Permanent discontinuation of HERNEXEOS due to an adverse reaction occurred in 2.9% of patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of HERNEXEOS were hepatotoxicity, increased blood alkaline phosphatase, dyspnea, increased gamma-glutamyl transferase, hemoptysis, and pyrexia.
Dosage interruption of HERNEXEOS due to an adverse reaction occurred in 28% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption in ≥ 2% of patients were hepatotoxicity, decreased ejection fraction, and rash.
Dose reductions of HERNEXEOS due to adverse reactions occurred in 7% of patients. Adverse reactions which required dose reductions in ≥ 1% of patients were hepatotoxicity, decreased ejection fraction, increased blood creatinine phosphokinase, increased gamma-glutamyl transferase, and decreased neutrophil count.
Tables 3 and 4 summarize adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities observed in Beamion LUNG-1.
| Adverse Reaction | HERNEXEOS N = 105 |
|
|---|---|---|
| All Grades1
% | Grade 3 or 4 % |
|
| Events were graded using NCI CTCAE version 5.0. | ||
| 1No Grade 4 or Grade 5 adverse reactions occurred. | ||
| *Grouped term. | ||
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Diarrhea* | 52 | 1 |
| Nausea | 24 | 1 |
| Vomiting | 15 | 1.9 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||
| Rash* | 32 | 1 |
| Nail disorders* | 19 | 0 |
| General Disorders | ||
| Fatigue* | 25 | 0 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | ||
| Cough* | 24 | 0 |
| Dyspnea* | 15 | 6 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||
| Musculoskeletal pain* | 24 | 1.9 |
| Infections and Infestations | ||
| Upper respiratory tract infections* | 21 | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 15% of patients who received HERNEXEOS included stomatitis, dry skin, pruritus, and peripheral neuropathy.
| Laboratory Parameter | HERNEXEOS N = 105 |
|
|---|---|---|
| All Grades1
% | Grade 3 or 4 % |
|
| Events were graded using NCI CTCAE version 5.0. | ||
| 1No Grade 5 adverse reactions occurred. | ||
| Hematology | ||
| Lymphocytes decreased | 52 | 15 |
| Leukocytes decreased | 43 | 1 |
| Hemoglobin decreased | 37 | 0 |
| Activated partial thromboplastin time increased | 25 | 0 |
| Platelets decreased | 23 | 1 |
| Chemistry | ||
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 39 | 7 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 33 | 2.9 |
| Lipase increased | 30 | 0 |
| Bilirubin increased | 26 | 1 |
| Triglycerides increased | 26 | 0 |
| Calcium decreased | 25 | 0 |
| Amylase increased | 24 | 0 |
| Sodium decreased | 23 | 0 |
| Creatinine kinase increased | 22 | 0 |
| Albumin decreased | 21 | 0 |
| Cholesterol increased | 20 | 1.4 |
| Alkaline phosphatase increased | 20 | 1 |
| Magnesium decreased | 20 | 1 |
| Potassium decreased | 20 | 0 |
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on HERNEXEOS
Avoid concomitant use of HERNEXEOS with strong CYP3A inducers. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, increase HERNEXEOS dose as recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Zongertinib is a CYP3A substrate. Strong CYP3A4 inducers decrease zongertinib exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may reduce effectiveness of HERNEXEOS.
7.2 Effects of HERNEXEOS on Other Drugs
BCRP Substrates
Avoid concomitant use of HERNEXEOS with certain BCRP substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions. If coadministration cannot be avoided, monitor for increased adverse reactions and follow recommendations provided in the approved product labeling for the BCRP substrate. For other BCRP substrates, monitor for increased adverse reactions and adjust the dosages of those substrates as clinically appropriate.
Zongertinib is a BCRP inhibitor. HERNEXEOS increases exposure of BCRP substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], HERNEXEOS can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on the use of HERNEXEOS in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. Oral administration of zongertinib to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis caused structural abnormalities and alterations to growth at maternal exposures ≥ 19 times the human exposure based on AUC at the recommended dose [see Data]. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study, pregnant rats received oral doses of 10, 30, or 60 mg/kg/day of zongertinib during the period of organogenesis (gestation day 7 to 18). Zongertinib caused decreased fetal weights, delayed development of the urinary system, and kidney hydronephrosis at 60 mg/kg/day (approximately 19 times the human exposure based on AUC at the recommended dose). In an embryo-fetal development study in rabbits, there were no adverse embryo-fetal findings in pregnant animals administered oral doses of zongertinib up to 120 mg/kg/day (2.4 times the human exposure based on AUC at the recommended dose) during the period of organogenesis (gestation day 6 to 19).
A literature-based assessment of the effects on reproduction demonstrated that mice expressing catalytically inactive HER2 die at mid-gestation due to cardiac dysfunction.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of zongertinib or its metabolites in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with HERNEXEOS and for 2 weeks after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, HERNEXEOS can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating HERNEXEOS.
Infertility
Females
Based on findings from animal studies, HERNEXEOS may impair fertility in females. The effects in female animals were reversible [see Nonclinical Toxicology 13.1].
Males
Based on findings from animal studies, HERNEXEOS may impair fertility in males of reproductive potential. The effect on testes in animals was not reversible within a 4-week recovery period [see Nonclinical Toxicology 13.1].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of HERNEXEOS have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 260 patients with non-squamous NSCLC with HER2 (ERBB2) mutations who received HERNEXEOS in clinical studies, 46% were 65 years of age and older and 12% were 75 years and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of HERNEXEOS were observed between older and younger adult patients.
10. Overdosage
Overdose in one patient who ingested 600 mg of HERNEXEOS resulting in nausea and vomiting.
11. Hernexeos Description
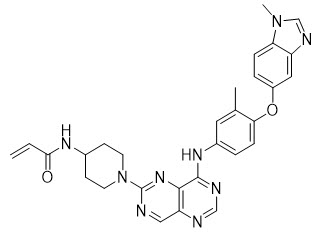
HERNEXEOS tablets for oral administration contain zongertinib, a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name of zongertinib is 2-Propenamide, N-[1-[8-[[3-methyl-4-[(1-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl)oxy]phenyl] amino]pyrimido[5,4-d]pyrimidin-2-yl]-4-piperidinyl]-. Its molecular formula is C29H29N9O2 and the molecular weight is 535.6. The structural formula is:
Zongertinib is a yellow to dark yellow or orange solid. Zongertinib is slightly soluble at pH 1.2, and practically insoluble at pHs 3.6, 4.5, 5.4 and 6.8.
Each film-coated tablet of HERNEXEOS contains 60 mg of zongertinib and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose acetate succinate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium stearyl fumarate. In addition, the film-coating contains the following inactive ingredients: ferric oxide (yellow), glycerol mono and dicaprylocaprate, polyvinyl alcohol, sodium lauryl sulfate, talc, and titanium dioxide.
12. Hernexeos - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Zongertinib is a kinase inhibitor of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). In vitro, zongertinib inhibited phosphorylation of HER2, downstream signaling of HER2 (phosphorylation of ERK), and proliferation of lung cancer cells harboring HER2 tyrosine kinase domain activating mutations. In vivo, zongertinib demonstrated anti-tumor activity in mouse xenograft models of NSCLC harboring HER2 tyrosine kinase domain activating mutations.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The exposure-response relationship and time-course of pharmacodynamic response of zongertinib have not been fully characterized.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Zongertinib pharmacokinetics were observed at steady state in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors with HER2 aberrations at the approved recommended dosage and are presented as geometric mean (CV%), unless otherwise specified.
Zongertinib maximum concentration (Cmax,ss) is 3.0 (37%) µmol/L and the total systemic exposure (AUC) is 34 (34%) µmol*h/L following HERNEXEOS 120 mg orally daily. Zongertinib Cmax and AUC increase in an approximately dose proportional manner across the dose range of 60 mg (0.5 times the approved recommended dosage) to 360 mg (3 times the approved recommended dosage). Zongertinib accumulation is approximately 1.5-fold for AUC and 1.3-fold for Cmax at the approved recommended dosage. Steady state is achieved within 2.5 days.
Absorption
Zongertinib median (min, max) time to maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) is approximately 2 hours (min, max: 2, 6 hours). Zongertinib absolute oral bioavailability is 76%.
Distribution
Zongertinib plasma protein binding is > 99%. The apparent (oral) volume of distribution is 118 L (29%).
Elimination
Zongertinib effective half-life is 12 hours (21%) with an apparent (oral) clearance of 115 mL/min (31%).
Metabolism
Based on in vitro metabolite profiling, CYP-mediated oxidation pathways represent 48% to 62% (mainly CYP3A4 and CYP3A5), glucuronidation 13% to 25% (mainly UGT1A4), and glutathione conjugation 13% to 26% of total hepatic metabolism. Unchanged zongertinib represented the majority (75%) of total radioactivity in plasma.
Specific Populations
The apparent volume of distribution and clearance of zongertinib increase with increasing body weight (34 to 122 kg).
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of zongertinib were observed based on age (30 to 88 years), sex, race (36% White, 49% Asian, 1.3% Black/African American), mild renal impairment (eGFR 60 to < 90 mL/min) or mild hepatic impairment (AST > ULN and total bilirubin ≤ ULN; or total bilirubin >1 to 1.5× ULN and any AST). The effect of moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30 to < 60 mL/min), severe renal impairment (eGFR 15 to < 30 mL/min), end-stage renal disease (eGFR < 15 mL/min), moderate hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 1.5 to 3× ULN and any AST) or severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 3× ULN and any AST) on the pharmacokinetics of zongertinib have not been studied.
Drug Interaction Studies
CYP3A Inducers: Zongertinib AUC decreased by 63% and Cmax decreased by 43% following concomitant use of carbamazepine (strong CYP3A inducer) 600 mg once daily for 7 days. The effect of concomitant use of moderate CYP3A inducers on zongertinib Cmax and AUC are unknown.
BCRP Substrates: Rosuvastatin (BCRP substrate) Cmax increased by 3-fold and AUC by 2.3-fold following concomitant use of a single dose of HERNEXEOS 120 mg daily for 12 days.
Other Drugs: No clinically significant differences in zongertinib pharmacokinetics were observed when used concomitantly with strong CYP3A, P-gp, BCRP inhibitors and rabeprazole (proton pump inhibitor). No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of the following were observed when used concomitantly with HERNEXEOS: midazolam (a CYP3A substrate), dabigatran (a P-gp substrate), metformin (a OCT2 and MATE1/2-K substrate), or repaglinide (a sensitive CYP2C8 substrate).
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Mutagenesis
Zongertinib was not mutagenic in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay. Zongertinib was not genotoxic in an in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus test and did not induce DNA breaks in a comet assay in liver or duodenum.
Impairment of Fertility
Dedicated animal fertility studies have not been conducted with zongertinib. In a 13-week repeat-dose toxicity study in rats, oral administration of zongertinib induced dose-dependent vacuolation in the testis at doses ≥ 10 mg/kg/day (≥ 5.7 times the human exposure based on AUC at the recommended dose), atrophy in the prostate gland at doses ≥ 30 mg/kg/day (≥ 8.4 times the human exposure based on AUC at the recommended dose), and atrophy in the uterus and hyperplasia/hyperkeratosis of the cervix and vagina at a dose of 90 mg/kg/day (approximately 17 times the human exposure based on AUC at the recommended dose). Findings in reproductive organs in female rats and prostate gland atrophy in male rats were reversible following a 4-week recovery period. Vacuolation in the testis of male rats was not reversible within a 4-week recovery period.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In a 4-week repeat-dose toxicology study in dogs, oral administration of zongertinib induced lesions of the oral mucosa (hard palate, buccal mucosa, tongue, lips) at doses ≥ 10 mg/kg/day (≥ 0.3 times the human exposure based on AUC at the recommended dose), which correlated with histologic erosion/ulcer and impaired food consumption. These findings were not present following a 4-week recovery period.
14. Clinical Studies
HERNEXEOS was evaluated in Beamion LUNG-1 (NCT04886804), a single arm, open-label, multi-center, multi-cohort trial. Eligible patients were required to have unresectable or metastatic NSCLC with HER2 (ERBB2) mutations. Patients with stable brain metastases were eligible to enroll. The study excluded patients who had a history of non-infectious interstitial lung disease/pneumonitis.
Patients received HERNEXEOS 120 mg orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. The major efficacy outcome measures were objective response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR) by Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.1 as assessed by blinded independent central review (BICR).
The efficacy population included 71 patients with unresectable or metastatic, non-squamous NSCLC with HER2 (ERBB2) tyrosine kinase domain (TKD) mutations based on prospective local testing. Of those, tumor tissue samples from 52% (37/71) of patients were retrospectively tested using Oncomine™ Dx Target Test (Life Technologies Corporation, Tissue-test). While 84% (31/37) of samples were positive for HER2 (ERBB2) TKD mutations, 2.7% (1/37) did not have HER2 (ERBB2) TKD mutations identified, and 13.5% (5/37) were unevaluable.
The baseline demographic and disease characteristics of the efficacy population were: 62 years (range: 30 to 80); 70% female, 55% Asian, 35% White, 0% Black or African American; 10% had unknown race data; 1.4% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity; 39% Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS) 0 and 61% ECOG PS 1; 65% never smoked; 100% metastatic disease; and 37% with brain metastases. The median number of prior therapies was 1 (range: 1 to 10); 100% of patients had prior platinum therapy and 78% had prior treatment with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibody. No patient had received previous treatment with a HER2-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) or HER2-targeted antibody-drug conjugate (ADC).
Efficacy results are summarized in Table 5.
| Efficacy Parameter | HERNEXEOS N = 71 |
|---|---|
| Abbreviation: CI = Confidence Interval, +: Ongoing response. | |
| 1Based on Wilson confidence interval. | |
| 2Based on observed duration of response. | |
| Objective Response Rate (ORR), % (95% CI)1 | 75 (63, 83) |
| Complete response, % | 6 |
| Partial response, % | 69 |
| Duration of Response (DOR) | N = 53 |
| Range, months | 1.3+, 15+ |
| DOR ≥ 6 months,2 % | 58 |
Among the 71 patients, 5 patients had measurable CNS metastases at baseline as assessed by BICR and had not received radiation therapy to the brain within 2 months prior to treatment with HERNEXEOS. Based on Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology Brain Metastases (RANO-BM) criteria per BICR, responses were observed in 3 patients.
HERNEXEOS was also evaluated in 34 patients with unresectable or metastatic HER2 (ERBB2) TKD mutation-positive non-squamous NSCLC who had received previous treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy and a HER2-targeted ADC. Eligibility criteria were otherwise similar to the efficacy population described above. The median age was 58 years (range: 31 to 85); 65% female, 35% Asian, 50% White, 0% Black or African American; 15% had unknown race data; and 2.9% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity. Baseline ECOG performance status was 0 (21%) or 1 (79%); 65% never smoked. 100% patients had metastatic disease and 74% had brain metastases. The median number of prior therapies was 3 (range: 1 to 8); 100% of patients had prior platinum therapy and 77% had prior treatment with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibody; 2.9% of patients had received previous treatment with a HER2-targeted TKI. Confirmed ORR by RECIST v1.1 based on BICR was 44% (95% CI 29, 61), with 2.9% of patients having a complete response. Median DOR was 5.4 months (95% CI 2.8, not estimable), and 27% of responders had an observed DOR ≥ 6 months.
16. How is Hernexeos supplied
60 mg tablets: yellow, oval, biconvex, film-coated, debossed with "L6" on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol on the other side. They are packaged in a bottle containing two silica gel desiccants and with a child-resistant closure, available as follows:
| Cartons containing one bottle of 60 tablets each | NDC: 0597-9257-86 |
Storage and Handling
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Store in the original container to protect from moisture. Keep the bottle tightly closed. Do not remove the desiccants. Once opened, use within 3 months. Discard any unused tablets 3 months after opening the bottle.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients that HERNEXEOS can cause severe and life-threatening hepatotoxicity and that they will need to undergo lab tests to monitor liver enzymes during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity.
Left Ventricular Dysfunction
Inform patients that HERNEXEOS can cause severe left ventricular dysfunction. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for new or worsening cardiovascular symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis
Inform patients that HERNEXEOS can cause severe or life-threatening ILD/pneumonitis. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for new or worsening respiratory symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Diarrhea
Inform patients that HERNEXEOS can cause diarrhea. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for signs and symptoms of diarrhea [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with HERNEXEOS and for 2 weeks after the last dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with HERNEXEOS and for 2 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Advise females and males of reproductive potential that HERNEXEOS may impair fertility [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Administration Instructions
Instruct patients weighing < 90 kg to take two 60 mg tablets once daily to achieve a complete 120 mg dose and instruct patients weighing ≥ 90 kg to take three 60 mg tablets once daily to achieve a complete 180 mg dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. HERNEXEOS film-coated tablets can be taken with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Instruct patients to swallow HERNEXEOS tablets whole with water. Do not split, crush, or chew tablets.
Inform patients that if they miss a dose of HERNEXEOS within 12 hours, they should take it as soon as they remember. If the next dose is missed by more than 12 hours, the patient should skip the missed dose and wait until the next scheduled dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
If a dose is vomited, do not take an additional dose. Take the next dose at the regularly scheduled time.
Distributed by:
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Ridgefield, CT 06877 USA
Licensed from:
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, Ingelheim, Germany
HERNEXEOS is a registered trademark of and used under license from Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH.
The other brands listed are trademarks of their owners and are not trademarks of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
COL13134AH062025
SPL13174A
| Patient Information HERNEXEOS® (her-nex-ee-ose) (zongertinib tablets) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Issued: Aug 2025 | ||
| What is HERNEXEOS?
HERNEXEOS is a prescription medicine used to treat adults with a type of lung cancer called non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that:
It is not known if HERNEXEOS is safe and effective in children. |
|||
Before taking HERNEXEOS, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider or pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
|||
How should I take HERNEXEOS?
|
|||
| What are the possible side effects of HERNEXEOS? HERNEXEOS may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|||
The most common side effects of HERNEXEOS include:
HERNEXEOS may cause fertility problems in females and males, which may affect your ability to have children. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you. These are not all of the possible side effects of HERNEXEOS. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|||
How should I store HERNEXEOS?
|
|||
| General information about the safe and effective use of HERNEXEOS.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use HERNEXEOS for any condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give HERNEXEOS to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about HERNEXEOS that is written for health professionals. |
|||
| What are the ingredients in HERNEXEOS?
Active ingredient: zongertinib Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose acetate succinate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium stearyl fumarate. The film-coating contains ferric oxide (yellow), glycerol mono and dicaprylocaprate, polyvinyl alcohol, sodium lauryl sulfate, talc, and titanium dioxide. |
|||
| Distributed by: Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Ridgefield, CT 06877 USA Licensed from: Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, Ingelheim, Germany HERNEXEOS is a registered trademark of and used under license from Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. Copyright © 2025 Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH ALL RIGHTS RESERVED COL13134AH062025 For more information about HERNEXEOS, including the current prescribing information and Patient Information, go to www.hernexeos.com, scan the code, or call Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-542-6257.  |
|||
| HERNEXEOS
zongertinib tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (603175944) |
| Registrant - Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (603175944) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sixarp, LLC - Praxis Packaging Solutions | 016329513 | PACK(0597-9257) , LABEL(0597-9257) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH and Co. KG | 551147440 | PACK(0597-9257) , LABEL(0597-9257) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eurofins CDMO Alphora Inc. | 243895310 | API MANUFACTURE(0597-9257) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| HOVIONE FARMACIENCIA, S.A. | 449818434 | MANUFACTURE(0597-9257) | |
More about Hernexeos (zongertinib)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Drug images
- Dosage information
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: HER2 inhibitors
Patient resources
Professional resources
Related treatment guides
Copyright 2025 Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED