Edaravone: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Dosage form: injection, solution
Drug class: Miscellaneous central nervous system agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 29, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Use In Specific Populations
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
EDARAVONE injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2017
Indications and Usage for Edaravone
- Edaravone injection is indicated for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). ( 1)
Edaravone Dosage and Administration
- Edaravone injection: The recommended dosage is 60 mg administered as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes ( 2.1)
- Initial treatment cycle: daily dosing for 14 days followed by a 14- day drug-free period ( 2.1)
- Subsequent treatment cycles: daily dosing for 10 days out of 14- day periods, followed by 14-day drug-free periods ( 2.1)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Contraindications
Patients with a history of hypersensitivity to edaravone or any of the inactive ingredients in edaravone injection ( 4)
Warnings and Precautions
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (at least 10% of patients treated with edaravone injection and greater than placebo) are contusion, gait disturbance, and headache ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact XGen Pharmaceuticals DJB, Inc. at 1-866-390-4411 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 3/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Edaravone
Edaravone injection is indicated for the treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
2. Edaravone Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosage Information
The recommended dosage of edaravone injection is as follows:
- an intravenous infusion of 60 mg administered over a 60-minute period.
Administer edaravone injection according to the following schedule:
- An initial treatment cycle with daily dosing for 14 days, followed by a 14-day drug-free period
- Subsequent treatment cycles with daily dosing for 10 days out of 14-day periods, followed by 14-day drug-free periods
2.2 Preparation and Administration Information for Edaravone Injection
Edaravone injection is for intravenous infusion only.
Preparation
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Vial may be inverted for use with a medical infusion set. Prepare the dose for administration by inserting a vented intravenous set through the septum of the 100 mL vial. Examine the container contents before dose preparation or administering. DO NOT USE if particulate matter or discoloration is observed, or if the flip off seal is not intact.
Administration
30 mg/100 mL single-dose vials:Administer each 60 mg dose of edaravone injection as two consecutive 30 mg intravenous infusion single-dose vials over a total of 60 minutes (infusion rate approximately 1 mg per minute [3.33 mL per minute]).
60 mg/100 mL single-dose vials:Administer a 60 mg dose of edaravone injection as an intravenous infusion single-dose vial over a total of 60 minutes (infusion rate approximately 1 mg per minute [1.67 mL per minute]).
Promptly discontinue the infusion upon the first observation of any signs or symptoms consistent with a hypersensitivity reaction [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ( 5.1, 5.2)] .
Other medications should not be injected into the single-dose vial or mixed with edaravone injection.
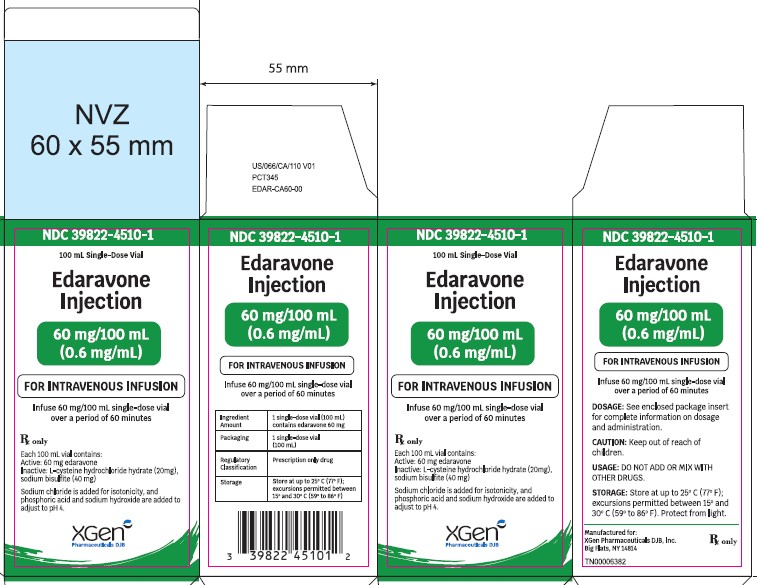
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Edaravone injection is supplied for intravenous infusion in a single-dose USP Type 1 Glass Vial containing 30 mg or 60 mgof edaravone in 100 mL of clear, colorless aqueous solution.
4. Contraindications
Edaravone injection is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to edaravone or any of the inactive ingredients in this product. Hypersensitivity reactions and anaphylactic reactions have occurred [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ( 5.1, 5.2)] .
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions (redness, wheals, and erythema multiforme) and cases of anaphylaxis (urticaria, decreased blood pressure, and dyspnea) have been reported in spontaneous postmarketing reports with edaravone injection.
Patients should be monitored carefully for hypersensitivity reactions. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue edaravone injection, treat per standard of care, and monitor until the condition resolves [see CONTRAINDICATIONS (4)] .
5.2 Sulfite Allergic Reactions
Edaravone injection contains sodium bisulfite, a sulfite that may cause allergic type reactions, including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in susceptible people. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown. Sulfite sensitivity occurs more frequently in asthmatic than non-asthmatic people.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)]
- Sulfite Allergic Reactions [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In randomized, placebo-controlled trials, 184 patients with ALS were administered edaravone injection 60 mg in treatment cycles for 6 months. The population consisted of Japanese patients who had a median age of 60 years (range 29-75) and were 59% male. Most (93%) of these patients were living independently at the time of screening.
Most Common Adverse Reactions Observed During Clinical Studies
Table 2 lists the adverse reactions that occurred in ≥2% of patients in the edaravone injection-treated group and that occurred at least 2% more frequently than in the placebo-treated group in randomized placebo-controlled ALS trials. The most common adverse reactions that occurred in ≥10% of edaravone injection-treated patients were contusion, gait disturbance, and headache.
| Adverse Reaction |
Edaravone Injection (N=184) % |
Placebo (N=184) % |
| Contusion | 15 | 9 |
| Gait disturbance | 13 | 9 |
| Headache | 10 | 6 |
| Dermatitis | 8 | 5 |
| Eczema | 7 | 4 |
| Respiratory failure, respiratory disorder, hypoxia | 6 | 4 |
| Glycosuria | 4 | 2 |
| Tinea infection | 4 | 2 |
aPooled placebo-controlled studies include two additional studies with 231 additional patients, all using the same treatment regimen [see CLINICAL STUDIES (14)] .
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of edaravone injection. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions and anaphylaxis [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ( 5.1, 5.2)].
Related/similar drugs
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with the use of edaravone injection in pregnant women. In animal studies, administration of edaravone to pregnant rats and rabbits resulted in adverse developmental effects (increased mortality, decreased growth, delayed sexual development, and altered behavior) at clinically relevant doses. Most of these effects occurred at doses that were also associated with maternal toxicity ( see ANIMAL DATA).
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively. The background risk for major birth defects and miscarriage in patients with ALS is unknown.
Data
Animal Data
In rats, intravenous administration of edaravone (0, 3, 30, or 300 mg/kg/day) throughout the period of organogenesis resulted in reduced fetal weight at all doses. In dams allowed to deliver naturally, offspring weight was reduced at the highest dose tested. Maternal toxicity was also observed at the highest dose tested. There were no adverse effects on reproductive function in the offspring. A no-effect dose for embryofetal developmental toxicity was not identified; the low dose is less than the recommended human dose of 60 mg for edaravone injection on a body surface area (mg/m 2) basis.
In rabbits, intravenous administration of edaravone (0, 3, 20, or 100 mg/kg/day) throughout the period of organogenesis resulted in embryofetal death at the highest dose tested, which was associated with maternal toxicity. The higher no-effect dose for embryofetal developmental toxicity is approximately 6 times the recommended human dose (RHD) for edaravone injection on a body surface area (mg/m 2) basis.
The effects on offspring of edaravone (0, 3, 20, or 200 mg/kg/day), administered by intravenous injection to rats from GD 17 throughout lactation, were assessed in two studies. In the first study, offspring mortality was observed at the high dose and increased activity was observed at the mid and high doses. In the second study, there was an increase in stillbirths, offspring mortality, and delayed physical development (vaginal opening) at the highest dose tested. Reproduction function in offspring was not affected in either study. Maternal toxicity was evident in both studies at all but the lowest dose tested. The no-effect dose for developmental toxicity (3 mg/kg/day) is less than the RHD on a mg/m 2 basis.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of edaravone in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production. Edaravone and its metabolites are excreted in the milk of lactating rats. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for edaravone injection and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from edaravone injection or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of edaravone injection in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 184 patients with ALS who received edaravone injection in 3 placebo-controlled clinical trials, a total of 53 patients were 65 years of age and older, including 2 patients 75 years of age and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
11. Edaravone Description
The active ingredient in edaravone injection is edaravone, which is a member of the substituted 2-pyrazolin-5-one class. The chemical name of edaravone is [3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one]. The molecular formula is C 10H 10N 2O and the molecular weight is 174.20.
The chemical structure is:
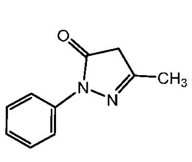
Edaravone is a white crystalline powder with a melting point of 129.7°C. It is freely soluble in acetic acid, methanol, or ethanol and slightly soluble in water or diethyl ether.
Edaravone injection is a clear, colorless liquid provided as a sterile solution.
30 mg/100 mL single-dose vials:Edaravone injection is supplied for intravenous infusion in a USP Type 1 Glass Vial containing 30 mg edaravone in 100 mL isotonic, sterile, aqueous solution. Individual vial will be placed in a carton (secondary packaging). Each single-dose vial contains the following inactive ingredients: L-cysteine hydrochloride hydrate (10 mg), sodium bisulfite (20 mg). Sodium chloride is added for isotonicity and phosphoric acid and sodium hydroxide are added to adjust to pH 4.
60 mg/100 mL single-dose vials:Edaravone injection is supplied for intravenous infusion in a USP Type 1 Glass Vial containing 60 mg edaravone in 100 mL isotonic, sterile, aqueous solution. Individual vial will be placed in a carton (secondary packaging). Each single-dose vial contains the following inactive ingredients: L-cysteine hydrochloride hydrate (20 mg), sodium bisulfite (40 mg). Sodium chloride is added for isotonicity and phosphoric acid and sodium hydroxide are added to adjust to pH 4.
12. Edaravone - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism by which edaravone injection exerts its therapeutic effect in patients with ALS is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At exposures at least 5 times higher than that of the recommended doses of edaravone injection, edaravone does not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Edaravone injection is administered by IV infusion. The maximum plasma concentration (C max) of edaravone was reached by the end of infusion. There was a trend of more than dose-proportional increase in area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) and C max of edaravone. With multiple-dose administration, edaravone does not accumulate in plasma.
Distribution
Edaravone is bound to human serum proteins (92%), mainly to albumin, with no concentration dependence in the range of 0.1 to 50 micromol/L. Edaravone has a mean volume of distribution after intravenous administration of 63.1 L.
Elimination
The mean terminal elimination half-life of edaravone is approximately 4.5 to 9 hours. The half-lives of its metabolites are 3 to 6 hours. Following intravenous administration, the total clearance of edaravone is estimated to be 35.9 L/h.
Metabolism
Edaravone is metabolized to a sulfate conjugate and a glucuronide conjugate, which are not pharmacologically active. The glucuronide conjugation of edaravone involves multiple uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) isoforms (UGT1A1, UGT1A6, UGT1A7, UGT1A8, UGT1A9, UGT1A10, UGT2B7, and UGT2B17). In human plasma, edaravone is mainly detected as the sulfate conjugate, which is presumed to be formed by sulfotransferases.
Excretion
In Japanese and Caucasian healthy volunteer studies, edaravone was excreted mainly in the urine as its glucuronide conjugate (60-80% of the dose up to 48 hours). Approximately 6-8% of the dose was recovered in the urine as the sulfate conjugate, and < 1% of the dose was recovered in the urine as the unchanged drug. In vitro studies suggest that the sulfate conjugate of edaravone is hydrolyzed back to edaravone, which is then converted to the glucuronide conjugate in the kidney before excretion into the urine.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
No age effect on edaravone pharmacokinetics has been found [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.5)].
Patients with Renal Impairment
Following single IV infusion of 30 mg edaravone (half the recommended dosage of edaravone injection) over 60 minutes, mean C max and AUC 0-∞ of unchanged edaravone were 1.15- and 1.20-fold greater in the subjects with mild renal impairment (eGFR 60-89 mL/min/1.73m 2), and were 1.25- and 1.29-fold greater in the subjects with moderate renal impairment (eGFR 30-59 mL/min/1.73m 2) when compared to subjects with normal renal function, respectively. These changes in exposures are not considered to be clinically significant and therefore no dosage adjustments are necessary in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment. The effects of severe renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of edaravone have not been studied.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Following single IV infusion of 30 mg edaravone (half of the recommended dose of edaravone injection) over 60 minutes, mean C max and AUC 0-∞ of unchanged edaravone were 1.20- and 1.07-fold greater in the subjects with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 5 or 6), were 1.24- and 1.14-fold greater in the subjects with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 7 to 9), and were 1.20- and 1.19-fold greater in the subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 10 to 14) when compared to subjects with normal hepatic function, respectively. These changes in exposures are not considered to be clinically significant and therefore no dosage adjustments are necessary in patients with hepatic impairment.
Male and Female Patients
No gender effect on edaravone pharmacokinetics has been found.
Racial or Ethnic Groups
There were no significant racial differences in C max and AUC of edaravone between Japanese and Caucasian subjects.
Drug Interaction Studies
The pharmacokinetics of edaravone is not expected to be significantly affected by inhibitors of cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, UGTs or major transporters.
In vitro studies demonstrated that, at the recommended dosage, edaravone and its metabolites are not expected to significantly inhibit CYP enzymes (CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A), conjugating enzymes UGT1A1 and UGT2B7, or other transporters (P-gp, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, OCT2, MATE1, and MATE2-K) in humans. Edaravone and its metabolites are not expected to induce CYP1A2, or CYP2B6, at the recommended dosage of edaravone.
In vitro data indicated that edaravone was not a substrate of OATP1B1 or OATP1B3.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies of edaravone using the intravenous route have not been conducted.
Mutagenesis
Edaravone was negative in in vitro (bacterial reverse mutation and Chinese hamster lung chromosomal aberration) and in vivo (mouse micronucleus) assays.
Impairment of Fertility
Intravenous administration of edaravone (0, 3, 20, or 200 mg/kg) prior to and throughout mating in male and female rats and continuing in females to gestation day 7 had no effect on fertility; however, disruption of the estrus cycle and mating behavior was observed at the highest dose tested. No effects on reproductive function were observed at the lower doses, which are up to approximately 3 times the RHD for edaravone injection (60 mg) on a body surface area (mg/m 2) basis.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of edaravone injection for the treatment of ALS was established in a 6-month, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study conducted in Japanese patients with ALS who were living independently and met the following criteria at screening:
- Functionality retained most activities of daily living (defined as scores of 2 points or better on each individual item of the ALS Functional Rating Scale - Revised [ALSFRS-R; described below])
- Normal respiratory function (defined as percent-predicted forced vital capacity values of [%FVC] ≥80%)
- Definite or Probable ALS based on El Escorial revised criteria
- Disease duration of 2 years or less
The study enrolled 69 patients in the edaravone injection arm and 68 in the placebo arm. Baseline characteristics were similar between these groups, with over 90% of patients in each group being treated with riluzole.
Edaravone injection was administered as an intravenous infusion of 60 mg given over a 60-minute period according to the following schedule:
- An initial treatment cycle with daily dosing for 14 days, followed by a 14-day drug-free period (Cycle 1)
- Subsequent treatment cycles with daily dosing for 10 days out of 14-day periods, followed by 14-day drug-free periods (Cycles 2-6).
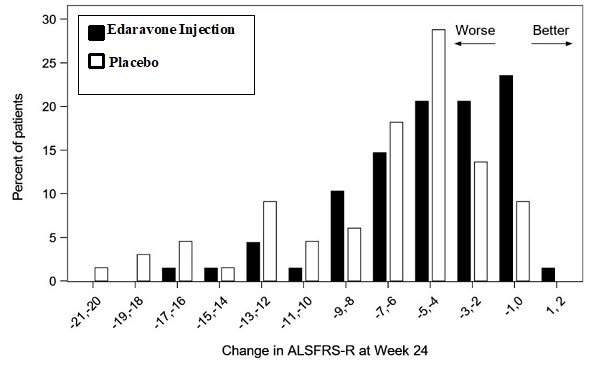
The primary efficacy endpoint was a comparison of the change between treatment arms in the ALSFRS-R total scores from baseline to Week 24. The ALSFRS-R scale consists of 12 questions that evaluate the fine motor, gross motor, bulbar, and respiratory function of patients with ALS (speech, salivation, swallowing, handwriting, cutting food, dressing/hygiene, turning in bed, walking, climbing stairs, dyspnea, orthopnea, and respiratory insufficiency). Each item is scored from 0-4, with higher scores representing greater functional ability. The decline in ALSFRS-R scores from baseline was significantly less in the edaravone injection-treated patients as compared to placebo (see Table 3). The distribution of change in ALSFRS-R scores from baseline to Week 24 by percent of patients is shown in Figure 1.
| Treatment |
Change from Baseline LS Mean ± SE(95% CI) |
Treatment Difference
| p-value |
| Edaravone Injection | −5.01±0.64 | 2.49 (0.99, 3.98) | 0.0013 |
| Placebo | −7.50±0.66 |
Figure 1 Distribution of Change from Baseline to Week 24 in ALSFRS-R Scores
16. How is Edaravone supplied
16.1 How Supplied
Edaravone injection is supplied as a 30 mg/100 mL (0.3 mg/mL) clear, colorless, sterile solution for intravenous infusion in single-dose USP Type 1 Glass Vial [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.2)and HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING (16.2)] . These are supplied in cartons as listed below.
- 30 mg/100 mL: NDC 39822-4500-1 single-dose glass vial, 2 vial per carton NDC 39822-4500-2
- 60 mg/100 mL: NDC 39822-4510-1 single-dose glass vial, 1 vial per carton NDC 39822-4510-1
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patients to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients to seek immediate medical care if they experience signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)] .
Sulfite Allergic Reactions
Advise patients about potential for sulfite sensitivity. Inform patients that edaravone injection contains sodium bisulfite, which may cause allergic type reactions including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes, and to seek immediate medical care if they experience these signs or symptoms [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.2)] .
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during edaravone injection therapy [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.1)] .
Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they intend to breastfeed or are breastfeeding an infant [see USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS (8.2)] .
Manufactured in India
Rx only
Manufactured for:
XGen Pharmaceuticals DJB, Inc.
Big Flats, NY 14814
Revised: 09/2024
EDAR-PI-01
RADICAVA ORS® is a registered trademark of Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation.
TN00006382
Patient Counseling Information
EDARAVONE INJECTION
(e-dar-a-vone)
For Intravenous Infusion
What is edaravone injection?
Edaravone injection is a prescription medicine used to treat people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
It is not known if edaravone injection is safe and effective in children.
Do not receive edaravone injection if you are allergic to edaravone or any of the ingredients in edaravone injection. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in edaravone injection.
Before you receive edaravone injection, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have asthma.
- are allergic to other medicines.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if edaravone injection will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if edaravone passes into your breastmilk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will receive edaravone injection or breastfeed.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
How will I receive edaravone injection?
- You will be prescribed edaravone injection by a healthcare provider and told how often you will receive edaravone injection.
- Edaravone injection will be given by intravenous (IV) infusion into your vein.
- It takes about 1 hour to receive the full dose of edaravone injection.
- Your healthcare provider will monitor you closely during your treatment with edaravone injection.
What are the possible side effects of edaravone injection?
Edaravone injection may cause serious side effects including:
- Hypersensitivity (allergic) reactions. Hypersensitivity reactions have happened in people receiving edaravone injection and can happen after your medicine has been given. Tell your healthcare provider right away or go to the nearest emergency room if you have any of the following symptoms:
- hives
- swelling of the lips, tongue, face
- breathing problems
- dizziness
- itching
- wheezing
- fainting
- Sulfite allergic reactions. Edaravone injection contains sodium bisulfite, a sulfite that may cause a type of allergic reaction that can be serious and life-threatening. Sodium bisulfite can also cause less severe allergic reactions, for example, asthma episodes, in certain people. Sulfite sensitivity can happen more often in people who have asthma than in people who do not have asthma. Tell your healthcare provider right away or go to the nearest emergency room if you have any of the following symptoms:
- hives
- swelling of the lips, tongue, face
- trouble breathing or swallowing
- dizziness
- itching
- asthma attack (in people with asthma)
- wheezing
- fainting
Your healthcare provider will monitor you during treatment to watch for signs and symptoms of all serious side effects and allergic reactions.
The most common side effects of edaravone injection include bruising (contusion), problems walking (gait disturbance), and headache.
These are not all the possible side effects of edaravone injection. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. You may also report side effects to www.fda.gov/medwatch or XGen Pharmaceuticals DJB, Inc. at 1-866-390-4411.
What are the ingredients in edaravone injection?
Active ingredient: edaravone
Inactive ingredients: L-cysteine hydrochloride hydrate, sodium bisulfite, sodium chloride (tonicity agent), phosphoric acid (pH adjuster), and sodium hydroxide (pH adjuster).
Manufactured in India for:
XGen Pharmaceuticals DJB, Inc., Big Flats, NY 14814
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Issued: 09/2024
EDAR-PIL-01
| EDARAVONE
edaravone injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| EDARAVONE
edaravone injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - XGen Pharmaceuticals DJB, Inc. (117380305) |
| Registrant - XGen Pharmaceuticals DJB, Inc. (117380305) |
More about edaravone
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: miscellaneous central nervous system agents
- En español