Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
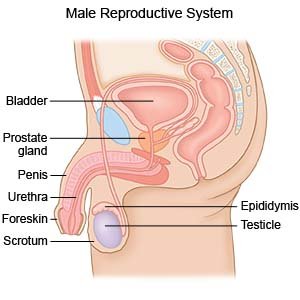
An enlarged prostate (BPH) is a common condition in older adults. BPH develops because the number of prostate cells increases (hyperplasia) or the cells get bigger (hypertrophy). The prostate wraps around the urethra. An enlarged prostate can press on the urethra. This may cause problems with storing urine or emptying your bladder completely.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your doctor or urologist if:
- You see blood in your urine.
- You are not able to urinate.
- Your bladder feels very full and painful.
- You have new or worsening symptoms.
- You have a fever.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Medicines:
- Medicines may be used to relax the muscles in your prostate and bladder. This may help you urinate more easily. You may also need medicine that helps shrink, or slow the growth of your prostate.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
What you can do to manage your symptoms:
- Urinate on a regular schedule. This will train your bladder to hold urine longer. A larger amount of urine may make it easier to urinate.
- Drink less liquid during the day. Do not have liquid for several hours before you go to bed at night. Do not drink large amounts of any liquid at one time.
- Limit alcohol and caffeine. These can irritate your bladder and make your symptoms worse.
- Eat less salt. Salt can cause fluid buildup and make it harder to urinate. Examples of salty foods are chips, cured meats, and canned soups. Do not use table salt.
- Elevate your legs if you have swelling. Elevate (raise) your legs above the level of your heart. This can relieve swelling caused by fluid buildup. You may not have to get up in the night to urinate.

- Exercise regularly. Exercise can help improve your symptoms. Ask your healthcare provider what a healthy weight for you is. Aim to get at least 30 minutes of exercise on most days of the week.

Follow up with your doctor or urologist as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Enlarged Prostate
- Anticholinergic Drugs to Avoid in the Elderly
- Enlarged Prostate (BPH) Medications and Alcohol Interactions
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
