Diabetic Retinopathy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
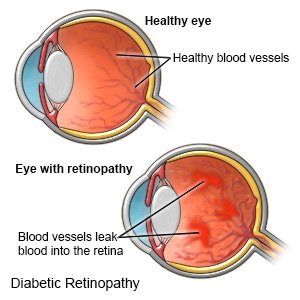
Diabetic retinopathy (DR)
is eye damage caused by long-term high blood sugar levels. DR can develop in anyone who has type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Over time, too much sugar in your blood damages the blood vessels in the back of the eye (retina). New, weak blood vessels grow, and leak blood into your eye. This can lead to blindness.
 |
Common symptoms include the following:
- Blurred vision
- Seeing red or black wavy lines that look like a curtain or spider web
- Seeing light flashes or red, black, or grey floating spots (floaters)
- Vision loss
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) or have someone call if:
- You suddenly cannot see.
Call your doctor or eye specialist if:
- Your blurred vision gets worse, or you start to see double.
- You see more floating spots.
- You see dark spots.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Related medications
Screening for DR
means you are checked for DR before you have signs or symptoms. You will be checked within 5 years of a type 1 diabetes diagnosis, because DR can take 5 years to develop. Your provider will tell you when to get checked. You will need to be checked immediately after a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. You may need screening every 1 to 2 years if you do not have DR on 1 or more yearly exams. Your provider will tell you how often to get screening in the future.
Treatment
may not be needed if you have mild DR. Healthcare providers will check your eyes regularly to monitor the damage to your retinas. Treatment may include any of the following:
- Laser treatment may slow DR and prevent blindness. This treatment shrinks the new blood vessels and seals the areas that have leaks.
- Anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) treatment helps slow or reverse DR, reduces swelling, and improves vision. During this treatment, medicine is injected into the vitreous of the eye. The vitreous is the gel-like material that fills the inside of the eye.
- Corticosteroids may be injected into the vitreous of the eye. These injections may help reduce swelling and inflammation in the eye.
- Vitrectomy is surgery for severe DR. A vitrectomy may be needed if there is bleeding in the vitreous that does not clear.
- Medicines may be used to control your blood pressure and prevent kidney disease. Medicines may also help lower your cholesterol or triglyceride (fatty acid) levels.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Prevent or control DR:
Regular eye exams and control of your blood sugar are the best ways to lower your risk. The following are tools that can help:
- Control your blood sugar. Keep your blood sugar levels as close to your goal as possible. You may need to check your blood sugar levels 3 times each day. Your provider may want to check your A1c level. This test shows your average blood sugar level over the past 2 to 3 months.
- Get your eyes checked at least 1 time each year. You will need yearly eye exams if you have DR. You may need eye exams more often if your DR symptoms worsen.
- Check your blood pressure as directed. High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in your eyes. A healthy blood pressure is 119/79 or lower. Talk to your healthcare provider about your blood pressure goals. Together you can create a plan to lower your blood pressure, if needed, and keep it in a healthy range. The plan may include lifestyle changes or medicines to lower your blood pressure.

- Talk to your healthcare provider about your cholesterol level. Lab tests are used to measure the amount of cholesterol in your blood. Your provider can help you create a plan to lower your cholesterol level if needed. You may need to make lifestyle changes or take medicines to control your cholesterol level.
- Plan for pregnancy if you are female. Pregnancy increases the risk for DR. Pregnancy can worsen existing DR and lead to serious vision problems. You may need an eye exam before pregnancy and during each trimester. Your eye doctor may want to monitor your eyes monthly if your DR is severe.
- Get regular physical activity. Physical activity can help you get to your target blood sugar level goal and manage your weight. Ask your healthcare provider or eye specialist about the best exercise plan for you. If you have proliferative or severe DR, you may not be able to exercise hard or do resistance training. These activities increase the risk for retinal detachment (pulling away) or other vision problems.

- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can damage blood vessels in your eyes. These also make it more difficult to manage your diabetes. Do not use e-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco in place of cigarettes or to help you quit. They still contain nicotine. Ask your provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit.
Follow up with your diabetes care specialist or eye specialist as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Diabetic Retinopathy
- Diabetes Medications and Alcohol Interactions
- OneTouch Blood Glucose Meters
- Top 10 Diabetes Treatments You May Have Missed
Treatment options
- Medications for Diabetes, Type 1
- Medications for Diabetic Macular Edema
- Medications for Diabetic Retinopathy
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
