Bynfezia: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: octreotide acetate
Dosage form: subcutaneous injection
Drug class: Somatostatin and somatostatin analogs
J Code (medical billing code): J2353 (1 mg, injection)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Feb 26, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
BYNFEZIA PEN® (octreotide acetate) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1988
Indications and Usage for Bynfezia
BYNFEZIA PEN is a s o matostatin analogue indicated: (1)
- Acromegaly: To reduce blood levels of growth hormone (GH) and insulin growth factor 1 (IGF-1; somatomedin C) in acromegaly patients who have had inadequate response to or cannot be treated with surgical resection, pituitary irradiation, and bromocriptine mesylate at maximally tolerated doses. (1 .1)
- Carcinoid Tumors: For the symptomatic treatment of patients with m eta static c a rcinoid t u mo rs where it suppresses or inhibits the severe diarrhea and flushing episodes associated with the disease. (1 .2)
- Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide Tumors (VIPomas): For the treatment of profuse watery diarrhea associated with VIP-secreting tumors . (1 .3)
Limitations of Use (1)
Improvement in clinical signs and symptoms, or reduction in tumor size or rate of growth, were not shown in clinical trials performed with octreotide injection; these trials were not optimally designed to detect such effects. (1.4) (1)
Bynfezia Dosage and Administration
• BYNFEZIA PEN is administered subcutaneously; alternate injection site periodically (2.1)
• Acromegaly: Recommended initial BYNFEZIA dosage is 50 mcg three times daily during the initial 2 weeks of therapy. Maintenance dose 100 mcg to 500 mcg three times daily. (2.2)
• Carcinoid Tumors: Recommended dosage range of 100 mcg to 600 mcg daily in two to four divided doses during the initial 2 weeks of therapy. (2.3)
• VIPomas: Recommended dosage range of 200 mcg to 300 mcg daily in two to four divided doses during the initial 2 weeks of therapy. (2.4) (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
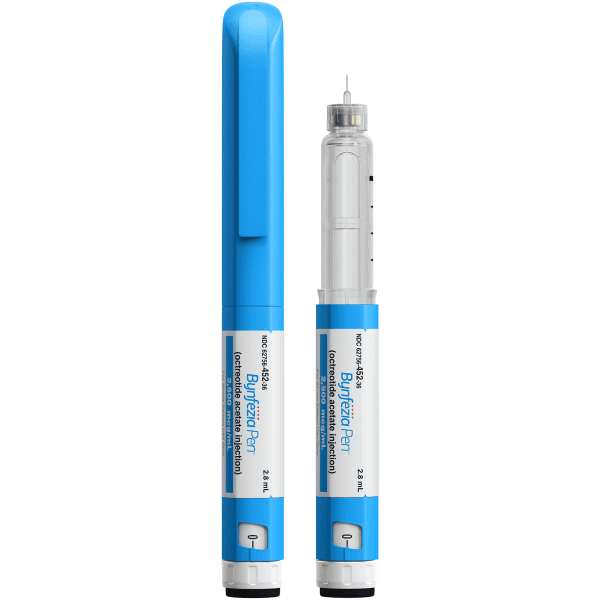
Injection: 7,000 mcg/2.8 mL (2,500 mcg/mL) octreotide (as acetate) in a 2.8 mL single-patient-use prefilled pen (3) (3)
Contraindications
- Sensitivity to this drug or any of the components (4)
Warnings and Precautions
• Cardiac Conduction Abnormalities: Bradycardia, arrhythmias, or conduction abnormalities may occur. Use with caution in at-risk patients. Dosage adjustment of cardiac medications may be necessary. (5.1)
• Cholelithiasis and Complications of Cholelithiasis: Monitor periodically. Discontinue if complications of cholelithiasis are suspected. (5.2)
• Glucose Metabolism: Hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia may occur. Glucose monitoring is recommended and anti-diabetic treatment may need adjustment. (5.3)
• Thyroid Function: Hypothyroidism may occur. Monitor thyroid levels periodically. (5.4)
• Steatorrhea and Malabsorption of Dietary Fats: New onset steatorrhea, stool discoloration, loose stools, abdominal bloating, and weight loss may occur. If new occurrence or worsening of these symptoms are reported, evaluate for potential pancreatic exocrine insufficiency. (5.5) (5)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (> 10%): (6.1) (6)
- Acromegaly: Gallbladder abnormalities, sinus bradycardia, diarrhea, loose stools nausea, abdominal discomfort, hyperglycemia, and hypothyroidism.
- Carcinoid Tumors and VIPomas: Gallbladder abnormalities.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc. at 1-800-818-4555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch (6)
Drug Interactions
- The following drugs require monitoring and possible dose adjustment when used with BYNFEZIA PEN : cyclosporine, insulin, oral hypoglycemic agents, beta-blockers, and bromocriptine. (7)
- Lutetium Lu 177 Dotatate Injection : Discontinue BYNFEZIA PEN at least 24 hours prior to each lutetium Lu 177 dotatate dose. (7.6)
Use In Specific Populations
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Advise premenopausal females of the potential for an unintended pregnancy. (8.3) (8)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 2/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Bynfezia
1.1 Acromegaly
BYNFEZIA PEN is indicated to reduce blood levels of growth hormone (GH) and insulin gro wth factor-1 (I GF-1; somatomedin C) in acromegaly patients who have had inadequate response to or cannot be treated with surgical resection, pituitary irradiation, and bromocriptine mesylate at maximally tolerated doses.
1.2 Carcinoid Tumors
BYNFEZIA PEN is indicated for treat ment of severe diarrhea and flushing episodes associated with metastatic carcinoid tumors.
2. Bynfezia Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosage and Administration Overview
- Inspect visually for particulate matter and discoloration. Only use BYNFEZIA PEN if the solution appears colorless with no visible particles.
- BYNFEZIA PEN should be at room temperature before injecting to reduce potential injection site reactions.
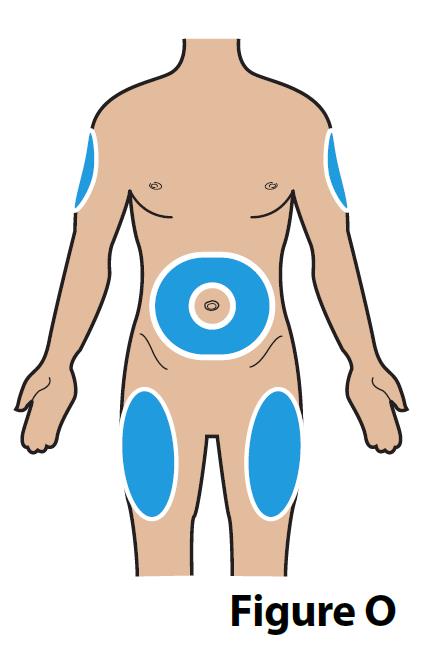
- Administer BYNFEZIA PEN by subcutaneous injection into the abdomen, the front of the middle thighs, or the back/outer area of the upper arms.
- Rotate injection sites so that the same site is not used repeatedly. Injection sites should be at least 2 inches away from your last injection site.
- Provide proper training to patients and/or caregivers on the administration of BYNFEZIA PEN prior to use according to the “Instructions for Use”.
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Monitoring for Acromegaly
The recommended initial dosage of BYNFEZIA PEN is 50 mcg three times daily to be administered subcutaneously. Increase BYNFEZIA dose based upon GH or IGF-1 levels. The goal is to achieve GH levels less than 5 ng/mL or IGF-I levels within normal range. Monitor GH or IGF-1 every two weeks after initiating BYNFEZIA PEN therapy or with dosage change, and to guide titration.
The most common dosage is 100 mcg three times daily, but some patients require up to 500 mcg three times daily for maximum effectiveness. Doses greater than 300 mcg/day seldom result in additional biochemical benefit, and if an increase in dose fails to provide additional benefit, the dose should be reduced.
BYNFEZIA PEN should be withdrawn yearly for approximately 4 weeks from patients who have received irradiation to assess disease activity. If GH or IGF-I levels increase and signs and symptoms recur, BYNFEZIA PEN therapy may be resumed.
2.3 Recommended Dosage and Monitoring for Carcinoid Tumors
The recommended daily dosage of BYNFEZIA PEN during the first 2 weeks of therapy ranges from 100 to 600 mcg/day in two to four divided doses given subcutaneously (mean daily dosage is 300 mcg). In the clinical studies, the median daily maintenance dosage was approximately 450 mcg, but clinical and biochemical benefits were obtained in some patients with as little as 50 mcg, while others required doses up to 1,500 mcg/day. However, experience with doses above 750 mcg/day is limited. Measurement of urinary 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid, plasma serotonin, plasma Substance P may be useful in monitoring the progress of therapy.
2.4 Recommended Dosage and Monitoring for Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide Tumors
Daily dosage of 200 mcg to 300 mcg in two to four divided doses given subcutaneously are recommended during the initial 2 weeks of therapy (range, 150 mcg to 750 mcg) to control symptoms of the disease. On an individual basis, dosage may be adjusted to achieve a therapeutic response; but usually doses above 450 mcg/day are not required. Measurement of Plas ma vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) may be useful in monitoring the progress of therapy.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
BYNFEZIA PEN is available as:
- Injection: 7,000 mcg/2.8 mL (2,500 mcg/mL) octreotide (as acetate) as a clear, colorless solution in a single-patient-use prefilled pen.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Cardiac Conduction Abnormalities
Cardiac conduction abnormalities have occurred during treatment with octreotide. In acromegalic patients, bradycardia (< 50 bpm) developed in 25%; conduction abnormalities occurred in 10% and arrhythmias occurred in 9% of patients during octreotide therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Other electrocardiogram (ECG) changes observed included QT prolongation, axis shifts, early repolarization, low voltage, R/S transition, and early R-wave progression. These ECG changes are not uncommon in acromegalic patients. Dose adjustments in drugs such as beta-blockers that have bradycardia effects may be necessary. In one acromegalic patient with severe congestive heart failure (CHF), initiation of octreotide therapy resulted in worsening of CHF with improvement when drug was discontinued. Confirmation of a drug effect was obtained with a positive rechallenge.
5.2 Cholelithiasis and Complications of Cholelithiasis
BYNFEZIA PEN may inhibit gallbladder contractility and decrease bile secretion, which may lead to gallbladder abnormalities or sludge. Acute cholecystitis, ascending cholangitis, biliary obstruction, cholestatic hepatitis, or pancreatitis have been reported with octreotide therapy. In clinical trials (primarily patients with acromegaly or psoriasis), the incidence of biliary tract abnormalities was 63% (27% gallstones, 24% sludge without stones, 12% biliary duct dilatation). The incidence of stones or sludge in patients who received octreotide for 12 months or longer was 52%. Less than 2% of patients treated with octreotide for 1 month or less developed gallstones. One patient developed ascending cholangitis during octreotide therapy and died. If complications of cholelithiasis are suspected, discontinue BYNFEZIA PEN and treat appropriately.
5.3 Hyperglycemia and Hypoglycemia
BYNFEZIA PEN alters the balance between the counter-regulatory hormones, insulin, glucagon and GH, which may result in hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. The hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia which occurs during octreotide therapy is usually mild but may result in overt diabetes mellitus or necessitate dose changes in insulin or other anti-diabetic agents. Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia occurred on octreotide in 3% and 16% of acromegalic patients, respectively [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Severe hyperglycemia, subsequent pneumonia, and death following initiation of octreotide therapy was reported in one patient with no history of hyperglycemia.
Monitor glucose levels during BYNFEZIA PEN therapy. Adjust dosing of insulin or other anti-diabetic therapy accordingly.
5.4 Thyroid Function Abnormalities
Octreotide suppresses secretion of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), which may result in hypothyroidism. Baseline and periodic assessment of thyroid function (TSH, total, and/or free T4) is recommended during chronic therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5.5 Steatorrhea and Malabsorption of Dietary Fats
New onset steatorrhea, stool discoloration and loose stools have been reported in patients receiving somatostatin analogs, including octreotide. Somatostatin analogs reversibly inhibit secretion of pancreatic enzymes and bile acids, which may result in malabsorption of dietary fats and subsequent symptoms of steatorrhea, loose stools, abdominal bloating, and weight loss. If new occurrence or worsening of these symptoms are reported in patients receiving octreotide, evaluate patients for potential pancreatic exocrine insufficiency and manage accordingly.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Cardiac Conduction Abnormalities [Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Cholelithiasis and Complications of Cholelithiasis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hyperglycemia and Hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Thyroid Function Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Steatorrhea and Malabsorption of Dietary Fats [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Changes in Vitamin B12 Levels [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of BYNFEZIA PEN has been established based on clinical studies of octreotide acetate injection. Below is a description of the adverse reactions from the clinical studies.
Gallbladder Abnormalities
Gallbladder abnormalities, especially stones and/or biliary sludge, frequently develop in patients on chronic octreotide therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. In clinical trials (primarily patients with acromegaly or psoriasis) (BYNFEZIA PEN is not indicated for the treatment of psoriasis)], the incidence of biliary tract abnormalities was 63% (27% gallstones, 24% sludge without stones, 12% biliary duct dilatation). The incidence of stones or sludge in patients who received octreotide for 12 months or longer was 52%. Less than 2% of patients treated with octreotide for 1 month or less developed gallstones.
Cardiac
In acromegalics, sinus bradycardia (<50 bpm) developed in 25%; conduction abnormalities occurred in 10% and arrhythmias developed in 9% of patients during octreotide therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Gastrointestinal
Diarrhea, loose stools, nausea, and abdominal discomfort were each seen in 34% to 61% of acromegalic patients in U.S. studies. 2.6% of the patients discontinued therapy due to these symptoms. These symptoms were seen in 5% to 10% of patients with carcinoid tumors and VIPomas.
The frequency of these symptoms was not dose related, but diarrhea and abdominal discomfort generally resolved more quickly in patients treated with 300 mcg/day than in those treated with 750 mcg/day. Vomiting, flatulence, abnormal stools, abdominal distention, and constipation were each seen in less than 10% of patients.
In rare instances, gastrointestinal side effects may resemble acute intestinal obstruction, with progressive abdominal distension, severe epigastric pain, abdominal tenderness, and guarding.
Hypo/Hyperglycemia
Hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia occurred in 3% and 16% of acromegalic patients, respectively, but only in about 1.5% of other patients. Symptoms of hypoglycemia were noted in approximately 2% of patients.
Hypothyroidism
In acromegalics, biochemical hypothyroidism alone occurred in 12% while goiter occurred in 8% and 4% required initiation of thyroid replacement therapy during octreotide therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. In patients without acromegaly, hypothyroidism has only been reported in several isolated patients and goiter has not been reported.
Other Adverse Events
Pain on injection was reported in 7.7%, headache in 6%, and dizziness in 5%. Pancreatitis was also observed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Other Adverse Events 1% to 4%
Other events, each observed in 1% to 4% of patients, included fatigue, weakness, pruritus, joint pain, backache, urinary tract infection, cold symptoms, flu symptoms, injection site hematoma, bruise, edema, flushing, blurred vision, pollakiuria, fat malabsorption, hair loss, visual disturbance, and depression.
Anaphylactoid reactions, including anaphylactic shock, have been reported in several patients receiving octreotide.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of octreotide acetate injection. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hepatobiliary: cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, cholangitis and pancreatitis, which have sometimes required cholecystectomy
Gastrointestinal: intestinal obstruction, pancreatic exocrine insufficiency
Hematologic: thrombocytopenia
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Cyclosporine
Octreotide has been associated with alterations in nutrient absorption, so it may have an effect on absorption of orally administered drugs. Concomitant administration of BYNFEZIA PEN with cyclosporine may decrease blood levels of cyclosporine and result in transplant rejection.
7.2 Insulin and Oral Hypoglycemic Drugs
Octreotide inhibits the secretion of insulin and glucagon. Therefore, blood glucose levels should be monitored when BYNFEZIA PEN treatment is initiated or when the dose is altered and anti-diabetic treatment should be adjusted accordingly.
7.3 Bromocriptine
Concomitant administration of octreotide and bromocriptine increases the availability of bromocriptine.
7.4 Other Concomitant Drug Therapy
Concomitant administration of bradycardia-inducing drugs (e.g., beta-blockers) may have an additive effect on the reduction of heart rate associated with octreotide. Dose adjustments of concomitant medication may be necessary.
Octreotide has been associated with alterations in nutrient absorption, so it may have an effect on absorption of orally administered drugs.
7.5 Drug Metabolism Interactions
Li mited published data indicate that so matostatin analogs might decrease the metabolic clearance of co mpounds known to be metabolized by cytochro me P450 enzy mes, which may be due to the suppression of GH. Since it cannot be excluded that octreotide may have this effect, other drugs mainly metabolized by CYP3A4 and which have a low therapeutic index (e.g., quinidine, terfenadine) should therefore be used with caution.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The limited data with octreotide acetate in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk for major birth defects and miscarriage. In animal reproduction studies, no adverse developmental-effects were observed with IV administration of octreotide to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis at doses 7 and 13 times, respectively the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 1.5 mg/day based on body surface area (BSA). Transient growth retardation, with no impact on postnatal development, was observed in rat offspring from a pre- and post-natal study of octreotide at IV doses below the MRHD based on BSA (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
In postmarketing data, a limited number of exposed pregnancies have been reported in patients with acromegaly. Most women were exposed to octreotide during the first trimester of pregnancy at doses ranging from 100 to 300 mcg/day of octreotide or 20 mg to 30 mg once a month of octreotide acetate for injectable suspension, however some women elected to continue octreotide therapy throughout pregnancy. In cases with a known outcome, no congenital malformations were reported.
Animal Data
In embryo-fetal development studies in rats and rabbits, pregnant animals received IV doses of octreotide up to 1 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. A slight reduction in body weight gain was noted in pregnant rats at 0.1 and 1 mg/kg/day. There were no maternal effects in rabbits or embryo-fetal effects in either species up to the maximum dose tested. At 1 mg/kg/day in rats and rabbits, the dose multiple was approximately 7 and 13 times, respectively, at the highest recommended human dose of 1.5 mg/day based on BSA.
In a pre- and post-natal development rat study at IV doses of 0.02–1 mg/kg/day, a transient growth retardation of the offspring was observed at all doses which was possibly a consequence of GH inhibition by octreotide. The doses attributed to the delayed growth are below the human dose of 1.5 mg/day, based on BSA.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information available on the presence of octreotide in human milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production. Studies show that octreotide administered subcutaneously passes into the milk of lactating rats; however, due to species-specific differences in lactation physiology, animal data may not reliably predict drug levels in human milk (see Data). The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for BYNFEZIA PEN, and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from BYNFEZIA PEN or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Following a subcutaneous dose (1 mg/kg) of octreotide to lactating rats, transfer of octreotide into milk was observed at a low concentration compared to plasma (milk/plasma ratio of 0.009).
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Discuss the potential for unintended pregnancy with premenopausal women as the therapeutic benefits of a reduction in GH levels and normalization of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) concentration in acromegalic females treated with octreotide may lead to improved fertility.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of octreotide injection in the pediatric population have not been demonstrated.
No formal controlled clinical trials have been performed to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of octreotide injection in pediatric patients under age 6 years. In post-marketing reports, serious adverse events, including hypoxia, necrotizing enterocolitis, and death, have been reported with octreotide injection use in children, most notably in children under 2 years of age. The relationship of these events to octreotide has not been established as the majority of these pediatric patients had serious underlying co-morbid conditions.
The efficacy and safety of octreotide injection using the octreotide acetate for injectable suspension formulation was examined in a single randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 6 month pharmacokinetics study in 60 pediatric patients age 6 to 17 years with hypothalamic obesity resulting from cranial insult. The mean octreotide concentration after 6 doses of 40 mg octreotide acetate for injectable suspension administered by intramuscular (IM) injection every 4 weeks was approximately 3 ng/mL. Steady-state concentrations was achieved after 3 injections of a 40 mg dose. Mean body mass index (BMI) increased 0.1 kg/m2 in octreotide acetate for injectable suspension-treated subjects compared to 0.0 kg/m2 in saline control-treated subjects. Efficacy was not demonstrated. Diarrhea occurred in 11 of 30 (37%) patients treated with octreotide acetate for injectable suspension. No unexpected adverse events were observed. However, with octreotide acetate for injectable suspension at 40 mg once a month, the incidence of new cholelithiasis in this pediatric population (33%) was higher than that seen in other adult indications such as acromegaly (22%) or malignant carcinoid syndrome (24%), where octreotide acetate for injectable suspension was 10 mg to 30 mg once a month.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of octreotide did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
10. Overdosage
A limited number of accidental overdoses of octreotide in adults have been reported. In adults, the doses ranged from 2,400 to 6,000 mcg/day administered by continuous infusion (100 to 250 mcg/hour) or subcutaneously (1,500 mcg 3 times a day). Adverse events in some patients included arrhythmia, hypotension, cardiac arrest, brain hypoxia, pancreatitis, hepatitis steatosis, hepatomegaly, lactic acidosis, flushing, diarrhea, lethargy, weakness, and weight loss.
If overdose occurs, symptomatic management is indicated. Up-to-date information about the treatment of overdose can often be obtained from the National Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222.
11. Bynfezia Description
BYNFEZIA PEN (octreotide acetate) injection contains octreotide as its acetate salt. Octreotide is a somatostatin analogue. Octreotide acetate known chemically as L-Cysteinamide, D-phenylalanyl-L-cysteinyl-L-phenylalanyl-D-tryptophyl-L-lysyl-L-threonyl-N-[2-hydroxy-1-(hydroxymethyl)propyl]-, cyclic (2→7)-disulfide; [R-(R*, R*)] acetate salt.
The molecular formula of octreotide free base is C49H66N10O10S2 and its molecular weight is 1019.3 and its structural formula as acetate salt is:
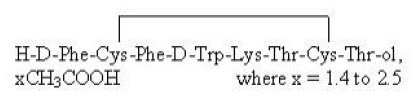
BYNFEZIA PEN (octreotide acetate) injection is available as a disposable single-patient-use prefilled pen containing 7,000 mcg of octreotide (as acetate)/2.8 mL. Each milliliter of octreotide acetate injection contains 2,500 mcg octreotide (present as octreotide acetate, USP), 3.4 mg lactic acid, 22.5 mg mannitol, 5 mg phenol, and Water for Injection (q.s.). The pH of the solution is adjusted to 4.2 ± 0.3 by the addition of aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution.
12. Bynfezia - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
BYNFEZIA PEN (octreotide acetate) exerts pharmacologic actions similar to the natural hormone, somatostatin. It is an even more potent inhibitor of GH, glucagon, and insulin than somatostatin. Like somatostatin, it also suppresses luteinizing hormone (LH) response to gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH), decreases splanchnic blood flow, and inhibits release of serotonin, gastrin, VIP, secretin, motilin, and pancreatic polypeptide.
By virtue of these pharmacological actions, octreotide has been used to treat the symptoms associated with metastatic carcinoid tumors (flushing and diarrhea), and VIP secreting adenomas (watery diarrhea).
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Octreotide substantially reduces GH and/or IGF-I (somatomedin C) levels in patients with acromegaly.
Single doses of octreotide have been shown to inhibit gallbladder contractility and to decrease bile secretion in normal volunteers. In controlled clinical trials, the incidence of gallstone or biliary sludge formation was markedly increased [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Octreotide suppresses secretion of TSH.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After subcutaneous injection, octreotide is absorbed rapidly and co mpletely from the injection site. Peak concentrations of 5.2 ng/ mL (100 mcg dose) were reached 0.4 hours after dosing. Peak concentrations and area under the curve (AUC) values were dose proportional after subcutaneous single doses up to 500 mcg and after subcutaneous multiple doses up to 500 mcg 3 times a day (1,500 mcg/day). In patients with acromegaly, a mean peak concentration of 2.8 ng/mL (100 mcg dose) was reached in 0.7 hours after subcutaneous dosing.
Distribution
In healthy volunteers, the distribution of octreotide from plas ma was rapid (tα1/2 = 0.2 h), the volu me of distribution (Vdss) was esti mated to be 13.6 L, and the total body clearance ranged from 7 L/hr to 10 L/hr. In blood, the distribution into the erythrocytes was found to be negligible and about 65% was bound in the plas ma in a concentration-independent manner. Binding was mainly to lipoprotein and, to a lesser extent, to albu min. In patients with acromegaly, the volume of distribution (Vdss) was estimated to be 21.6 ± 8.5 L, and the total body clearance was increased to 18 L/h. The mean percent of the drug bound was 41.2%.
Elimination
The eli mination of octreotide from plas ma had an apparent half-life of 1.7 to 1.9 hours co m pared with 1 to 3 minutes with the natural hor mone. The duration of action of octreotide injection is variable but extends up to 12 hours depending upon the type of tu mor. About 32% of the dose is excreted unchanged into the urine. In an elderly population, dose adjustments may be necessary due to a significant increase in the half-life (46%) and a significant decrease in the clearance (26%) of the drug.
In patients with acromegaly, the disposition and elimination half-lives were similar to normal subjects.
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment
In patients with mild renal i mpair ment (C LCR 40 to 60 m L/ min), octreotide t1/2 was 2.4 hours and total body clearance was 8.8 L/hr, in moderate i mpair ment (CLCR 10 to 39 m L/ min) t1/2 was 3.0 hours and total body clearance 7.3 L/hr. In patients with severe renal i mpairment not requiring dialysis (CLCR <10 m L/ min), octreotide t1/2 was 3.1 hours and total body clearance was 7.6 L/hr. In patients with severe renal failure requiring dialysis, total body clearance was reduced to about half that found in healthy subjects (from approximately 10 L/hr to 4.5 L/hr).
Hepatic Impairment
Patients with liver cirrhosis showed prolonged elimination of drug, with octreotide t1/2 increasing to 3.7 hr and total body clearance decreasing to 5.9 L/hr, whereas patients with fatty liver disease showed t1/2 increased to 3.4 hr and total body clearance of 8.2 L/hr.
12.6 Immunogenicity
Evaluation of 20 patients treated for at least 6 months has failed to demonstrate titers of antibodies exceeding background levels. However, antibody titers to octreotide injection were subsequently reported in 3 patients and resulted in prolonged duration of drug action in 2 patients.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies in laboratory animals have demonstrated no mutagenic potential of octreotide injection.
No carcinogenic potential was demonstrated in mice treated subcutaneously for 85 to 99 weeks at doses up to 2,000 mcg/kg/day (8 x the human exposure based on BSA). In a 116-week subcutaneous study in rats, a 27% and 12% incidence of injection-site sarcomas or squamous cell carcinomas was observed in males and females, respectively, at the highest dose level of 1,250 mcg/kg/day (10 x the human exposure based on BSA) compared to an incidence of 8% to 10% in the vehicle-control groups. The increased incidence of injection site tumors was most probably caused by irritation and the high sensitivity of the rat to repeated subcutaneous injections at the same site. Rotating injection sites would prevent chronic irritation in humans. There have been no reports of injection-site tumors in patients treated with octreotide for up to 5 years. There was also a 15% incidence of uterine adenocarcinomas in the 1,250 mcg/kg/day females compared to 7% in the saline-control females and 0% in the vehicle-control females. The presence of endometritis coupled with the absence of corpora lutea, the reduction in mammary fibroadenomas, and the presence of uterine dilatation suggest that the uterine tumors were associated with estrogen dominance in the aged female rats which does not occur in humans.
Octreotide did not impair fertility in rats at doses up to 1,000 mcg/kg/day, which represents 7 times the human exposure based on BSA.
16. How is Bynfezia supplied
How Supplied
BYNFEZIA PEN ( octreotide acetate) injection, 7,000 mcg/2.8 mL (2,500 mcg /mL) octreotide is a clear colorless solution and it is available as:
|
Dosage Unit |
Package Size | NDC # |
| 2.8 mL single -patient-use prefilled pen | Carton of 1 | NDC 62756-452-36 |
| 2.8 mL single -patient-use prefilled pen | Carton of 2 | NDC 62756-452-37 |
Dispense in the original sealed carton with the enclosed Instructions for Use.
Storage and Handling
Before first use, store BYNFEZIA PEN in the refrigerator between 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and store in outer carton in order to protect from light. After first use, store pens at controlled room temperature between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Excursions between 15°C (59°F) and 30°C (86°F) are allowed for up to 28 days. Discard the pen 28 days after first use. Do not freeze.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise patient and/or caregivers to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Instructions for Use).
Sterile Subcutaneous Injection Technique
Careful instruction in sterile subcutaneous injection technique should be given to the patients and to other persons who may administer BYNFEZIA PEN.
Cholelithiasis and Complications of Cholelithiasis
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they experience signs or symptoms of gallstones (cholelithiasis) or complications of cholelithiasis (e.g., cholecystitis, cholangitis, and pancreatitis) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Steatorrhea and Malabsorption of Dietary Fats
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they experience new or worsening of steatorrhea, stool
discoloration, loose stools, abdominal bloating, and weight loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Pregnancy
Inform female patients that treatment with BYNFEZIA PEN may result in unintended pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Distributed by:
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc.
Cranbury, NJ 08512
Manufactured by:
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., India
At M/s. OneSource Specialty Pharma Limited
Plot No. 2-D1, Obadenahalli,
Doddaballapura, 3rd Phase,
Industrial Area, Doddaballapura Taluk,
Bengaluru Rural, 561203, Karnataka INDIA
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
BYNFEZIA PEN® (ben-FEZ-ee-uh PEN)
(octreotide acetate) Prefilled Pen
Read these instructions before you start using the BYNFEZIA PEN. It is important that you understand and follow these instructions to use the pen correctly. BYNFEZIA PEN is a prefilled pen that you or your caregiver can use to give more than 1 dose of medicine.
Ask your healthcare provider about your dose of BYNFEZIA PEN and how to inject BYNFEZIA PEN the right way before you inject it for the first time. If your healthcare provider decides that you or your caregiver can give your BYNFEZIA PEN at home, you or your caregiver should receive training on how to use the pen.
Contact your healthcare provider if you or your caregiver have any questions.
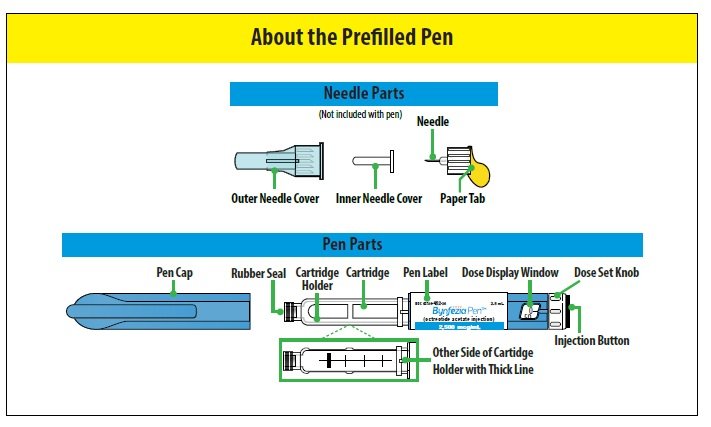
| Important | ||
|
• Do not use a pen for more than 28 days after first use. After 28 days throw away (dispose of) the pen, even if the pen still has medicine in it. • Do not place the pen in water or any other liquid. • Keep your pen and needles out of the reach of children. • Do not use if any part of your pen appears broken or damaged. • If you drop your pen, prime it before you use it again to make sure the pen still works correctly (see step 3. Prime Your Pen). • Do not take BYNFEZIA PEN solution out of the pen and put it into a syringe. • Do not share your pen or needles with another person. You may give an infection to them or get an infection from them. • Do not remove the outer needle cover or inner needle cover until you are ready to inject. • Do not press the injection button unless a needle is attached to the pen. |
||
| How should I store my BYNFEZIA PEN? | ||
|
Before First Use: • Store new unused pens in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) and store in the outer carton in order to protect from light. • Do not freeze. Throw away (dispose of) the pen if it has been frozen. • Do not store the pen in direct sunlight. After First Use or During Use: • Store the pen at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C) for up to 28 days. • Store the pen with the pen cap on. • Throw away (dispose of) the pen 28 days after first use in a sharps container, even if the pen still has medicine in it (see step 6. Additional Disposal Information). • Do not store a pen with a needle attached. |
||
| How do I give a dose larger than 200 mcg (more than 1 injection)? | ||
|
1. Turn the dose set knob to 200 mcg (highest dose setting) and give the first injection. Choose a different injection site for each injection at least 2 inches from the area you used for your last injection. 2. Calculate the remaining dose by subtracting 200 mcg from the prescribed dose. 3. Turn the dose set knob to the line for your remaining dose up to the highest dose setting of 200 mcg. Give the second injection at least 2 inches away from the first injection. 4. You may need more injections to give your total prescribed dose (see examples below). See the following examples to give a total dose larger than 200 mcg: |
||
| Example Dose | Steps to give a total dose larger than 200 mcg | Number of injections needed to give the total dose |
| For example, if your total dose is 300 mcg |
|
2 |
| For example, if your total dose is 450 mcg |
|
3 |
| 1. Check the Pen
|
||
| A. Wash your hands with soap and water (Figure A). |  |
|
|
B. Check the expiration (EXP) date (Figure B).
Do not use if the expiration date has passed. |  |
|
| C. Pull the pen cap straight off the pen (Figure C). | 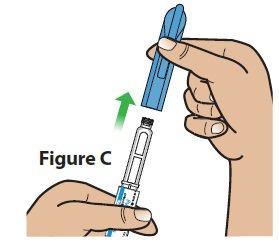 |
|
|
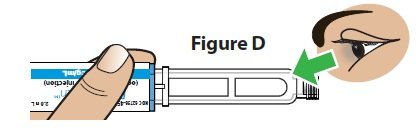
D. Check the medicine (Figure D).
Do not use if the medicine looks cloudy, colored, or has lumps or particles in it. The pen cartridge may look empty because the medicine is clear and colorless.
|   |
|
E. Allow the pen to reach room temperature.
| ||
| 2. Attach a Needle
|
||
A. Gather the following additional supplies (Figure F):
|  |
|
| B. Wipe the rubber seal on the pen with an alcohol swab (Figure G). | 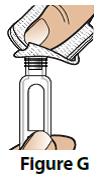 |
|
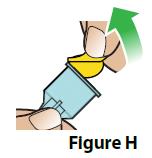
C. Attach a new needle.
|   |
|
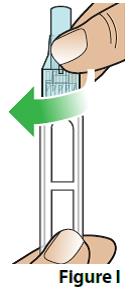
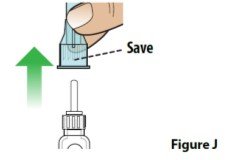
D. Remove the outer needle cover and set it aside (Figure J).
|  |
|
| E. Remove the inner needle cover and throw it away (Figure K). | 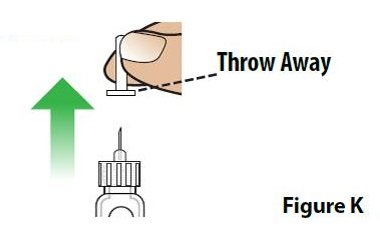 |
|
|
Are you using a new pen?
|
||
| 3. Prime Your Pen
|
||
| Note: The following steps are only needed if you are using a new pen for the first time or if you drop the pen. To prime the pen, follow the steps below to dial the pen to 100 mcg and press the injection button until a stream of medicine comes from the needle tip.
| ||
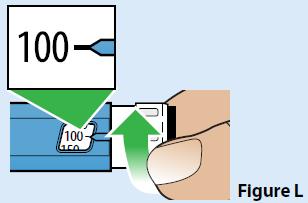
| A. Turn the dose set knob to dial the pen to 100 mcg (Figure L).
|  |
|
| B. Hold the pen with the needle pointing up.
| ||
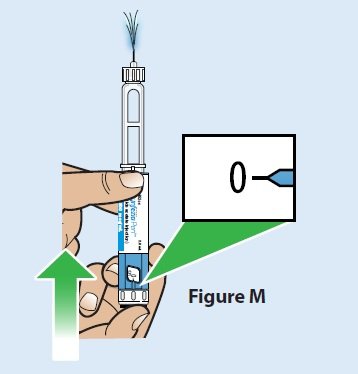
| C. Press the injection button all the way in until it stops and the dose display window returns to “0” (Figure M).
|  |
|
| D. A stream of medicine should be seen coming from the needle tip (Figure N). If you do not see a stream of medicine coming from the needle tip, repeat the priming steps. If you still do not see a stream of medicine coming from the needle tip after you repeat the priming steps 3 times, the pen may be damaged. Throw away (dispose of) the pen and use a new pen. Call Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc. at 1-800-818-4555or your healthcare provider for help or to get a new pen. | 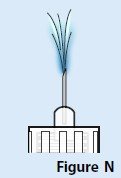 |
|
| 4. Prepare the Injection
|
||
A. Choose an injection site (see Figure O) for injection under the skin (subcutaneous).
|  |
|
|
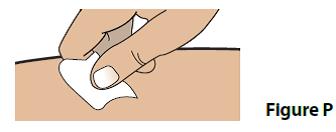
B. Clean your injection site with an alcohol swab (Figure P).
|  |
|
|
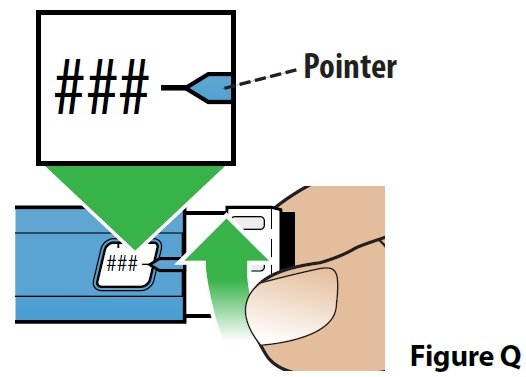
C. Dial your dose (Figure Q).
If your prescribed dose is more than 200 mcg, see the section “How should I give a dose larger than 200 mcg (more than 1 injection)?” in these instructions.
|  |
|
| Note: The pen cannot be dialed past the number of micrograms (mcgs) of medicine left in the pen. If the pen does not have enough medicine to give the full dose, throw away (dispose of) the pen and use a new one. | ||
| 5. Give the Injection | ||
| A. Insert the needle straight into the injection site (Figure R). | 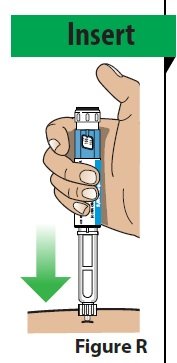 |
|
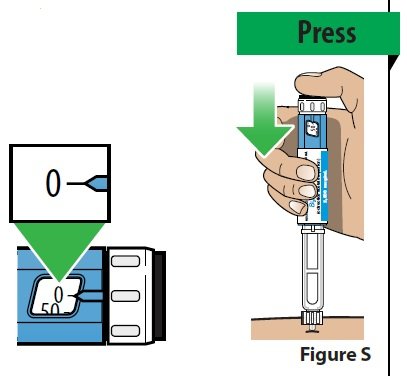
B. Deliver your dose.
|  |
|
| C. Continue to hold the injection button down and slowly count to 10 to make sure the full dose of medicine is given (Figure T). |  |
|
D. Remove the pen from the injection site.
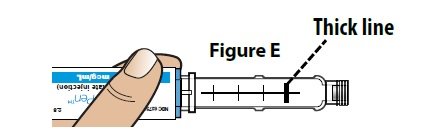
Note: As the pen is used, a plunger will appear in the cartridge and move towards the thick line. | 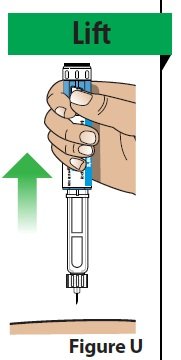 |
|
| 6. After the Injection
|
||
A. Carefully place the outer needle cover back onto the needle.
|  |
|
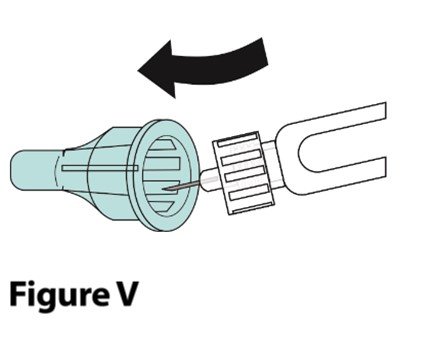
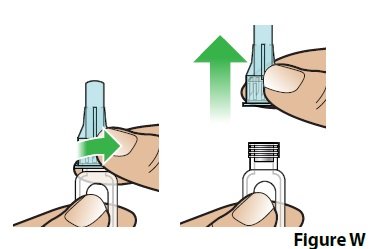
B. Unscrew and remove the covered needle (Figure W).
|  |
|
| C. Throw away (dispose of) the covered needle in a FDA-cleared sharps container (Figure X). | 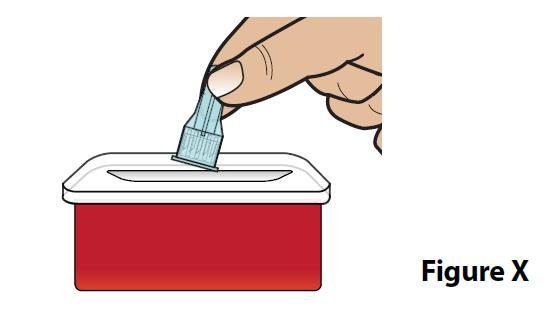 |
|
|
D. Put the pen cap back on the pen (Figure Y) and store the pen.
|  |
|
E. Treat the injection site.
| ||
| Cleaning the Pen
|
||
| ||
| Additional Disposal Information
|
||
|
Put used pens and needles in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) pens and needles in the household trash. If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal
| ||
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Distributed by:
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc.
Cranbury, NJ 08512
Manufactured by:
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., India
At M/s. OneSource Specialty Pharma Limited
Plot No. 2-D1, Obadenahalli,
Doddaballapura, 3rd Phase,
Industrial Area, Doddaballapura Taluk,
Bengaluru Rural, 561203, Karnataka INDIA
For more information, call 1-800-818-4555.
Issued: 10/2024
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Rx only
NDC 62756-452-37
Bynfezia Pen® (octreotide acetate Injection)
7,000 mcg/2.8mL (2,500 mcg/mL)
Two 2.8 mL disposable single-patient-use prefilled pens
Subcutaneous use only
For doses of 50 mcg, 100 mcg, 150 mcg, and 200 mcg of octreotide per injection.
For Single Patient Use Only
Dispense in this sealed carton
SUN PHARMA

| BYNFEZIA PEN
octreotide acetate injection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc. (146974886) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| OneSource Specialty Pharma Limited | 867530307 | ANALYSIS(62756-452) , MANUFACTURE(62756-452) , PACK(62756-452) | |
More about Bynfezia Pen (octreotide)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Drug images
- Latest FDA alerts (1)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: somatostatin and somatostatin analogs
- Breastfeeding
- En español

