Pulmonary Contusion
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is a pulmonary contusion?
A pulmonary contusion is bruising or bleeding of your lung tissue that may cause pain and trouble breathing.
 |
What are the signs and symptoms of a pulmonary contusion?
You may have more than one of the following:
- Chest pain
- Trouble breathing
- Coughing up blood or large amounts of watery sputum (spit)
- Fast and shallow breathing
- High-pitched wheezing when you breathe out
Related medications
How is a pulmonary contusion treated?
Your treatment will depend on how severe your injury is. Healthcare providers will use different treatments to help you breathe easier and get enough oxygen into your body. You may need more than one of the following:
- Pain medicines help decrease your pain and make it easier for you to breathe. You may be given pain medicine as a shot, in your IV, or through an epidural (a small tube inserted into your back).
- Breathe deeply and cough to open the air passages and bring up sputum from your lungs. You can breathe deeply and cough on your own, or with the help of an incentive spirometer. An incentive spirometer is a device that can help you take deeper breaths.
- Extra oxygen may help if you have trouble breathing. You breathe the oxygen through a face mask or a nasal cannula. A nasal cannula is a pair of short, thin tubes that rest just inside your nose.
- Suctioning helps remove any blood or mucus that is blocking your air passages. Healthcare providers may insert a tube connected to a suction machine into your mouth, nasal passages, or ET tube.
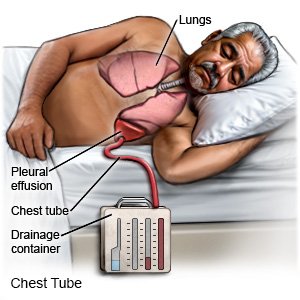
- A chest tube is used to remove air, blood, or fluid from around your lungs or heart. This lets your lungs fill with air when you breathe, and helps your heart beat normally. A tube may be inserted through an incision in your chest to drain the air or fluid. The chest tube is attached to a container to collect the blood or fluid.
- A ventilator may help you breathe. The machine gives you air through a mask or mouthpiece. If a mask is used, it may go over your nose and mouth, or just your nose.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You cough up blood.
- You feel dizzy, lightheaded, or faint.
- You have trouble breathing.
- You have chest pain or a heavy feeling in your chest that lasts more than a few minutes.
- You have pain that starts in your chest then spreads to your shoulders, neck, or arms.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
