Hyperparathyroidism
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
Hyperparathyroidism
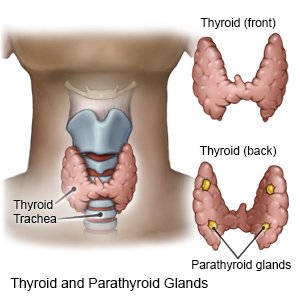
is a condition that causes your parathyroid glands to make too much parathyroid hormone (PTH). The parathyroid glands are 4 small glands located near the thyroid gland in your neck. PTH keeps the level of calcium balanced in your blood. High levels of PTH causes too much calcium to build up in your blood. High calcium levels can cause health problems such as osteoporosis (weak, brittle bones), high blood pressure, and kidney stones.
 |
Common signs and symptoms of hyperparathyroidism include the following:
You may have no signs or symptoms or you may have any of the following:
- Muscle weakness
- Fatigue
- Depression or anxiety
- General body aches and pains
- Bone and joint pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain
- Constipation
- Confusion or forgetfulness
- Increased thirst and urination
Seek care immediately if:
- You heart beats faster or slower than normal, or it feels like fluttering in your chest.
- You have nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- You cannot think clearly.
Related medications
Contact your healthcare provider if:
- You have bone and joint pain.
- You have increased thirst or you are urinating more often than usual.
- You have a loss of appetite.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Treatment:
You may not need any treatment if you do not have symptoms. Your healthcare provider may monitor your condition through regular visits and blood tests. You may need medicines to control the amount of PTH your parathyroid glands make. You may also need medicine to keep your bones strong. Surgery may be done to remove an adenoma or your parathyroid glands.
Manage hyperparathyroidism:
You may need to do the following if you will not have surgery to treat your hyperparathyroidism.
- Limit your calcium intake. Your healthcare provider may tell you to limit your intake to less than 1200 mg each day. You may also need to limit vitamin D to less than 600 IU each day.
- Drink liquids as directed. Liquids can help prevent kidney stones. Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
- Exercise regularly. Ask your healthcare provider about the best exercise plan for you. Exercise can help build and strengthen your bones.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Hyperparathyroidism
Treatment options
- Medications for Hyperparathyroidism
- Medications for Hyperparathyroidism Secondary to Renal Impairment
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
