Duodenitis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 23, 2025.
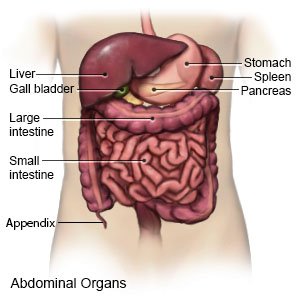
Duodenitis is inflammation or irritation of the duodenum. The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine, just below your stomach.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Return to the emergency department if:
- You have severe abdominal pain.
- You have bloody or black, tarry bowel movements or vomit.
Call your doctor if:
- You have new or worsening symptoms, even after treatment.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
- Medicines may be given to treat an infection or to control stomach acid.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Related medications
Follow up with your healthcare provider as directed:
You may need ongoing tests or treatment. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
Do not smoke:
Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause blood vessel and lung damage. Ask your provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your provider before you use these products.
Limit or do not drink alcohol:
Alcohol can make your duodenitis worse. Talk to your provider if you need help to stop drinking.
Keep batteries and similar objects out of the reach of children:
Babies often put items in their mouths to explore them. Button batteries are easy to swallow and can cause serious damage. Keep the battery covers of electronic devices such as remote controls taped closed. Store all batteries and toxic materials where children cannot get to them. Use childproof locks to keep children away from dangerous materials.
Manage or prevent duodenitis:
- Do not take NSAIDs or aspirin unless directed. These and similar medicines can cause irritation. It may help to take NSAIDs with food, but you may not be able to take them at all.
- Do not eat foods that cause irritation. Foods such as oranges and salsa can cause burning or pain. Eat a variety of healthy foods. Examples include fruits (not citrus), vegetables, low-fat dairy products, beans, whole-grain breads, and lean meats and fish. Try to eat small meals, and drink water with your meals. Do not eat for at least 3 hours before you go to bed.

© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Duodenitis
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
