Brain Tumors
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
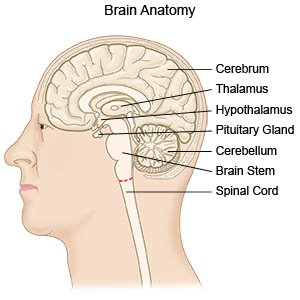
A brain tumor is a mass that grows in your brain, or in an area near the brain. Examples include nerves in your skull, pituitary gland, or the membranes that cover your brain. The tumor may start in your brain or travel to your brain from another part of your body. There are many kinds of brain tumors. Each kind is named for where it begins and what it does in the brain. A tumor may be malignant (cancer), or benign (not cancer). It may grow quickly or slowly.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have a seizure.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your arm or leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
- You have new problems walking or moving one side of your body.
- You have new or worsening headaches or body swelling.
Call your doctor or oncologist if:
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Anticonvulsants may be given to prevent or control seizures.
- Steroids may be given to reduce swelling.
- Blood thinners help prevent blood clots. Clots can cause strokes, heart attacks, and death. Many types of blood thinners are available. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions for the type you are given. The following are general safety guidelines to follow while you are taking a blood thinner:
- Watch for bleeding and bruising. Watch for bleeding from your gums or nose. Watch for blood in your urine and bowel movements. Use a soft washcloth on your skin, and a soft toothbrush to brush your teeth. This can keep your skin and gums from bleeding. If you shave, use an electric shaver. Do not play contact sports.
- Tell your dentist and other healthcare providers that you take a blood thinner. Wear a bracelet or necklace that says you take this medicine.
- Do not start or stop any other medicines or supplements unless your healthcare provider tells you to. Many medicines and supplements cannot be used with blood thinners.
- Take your blood thinner exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not skip a dose or take less than prescribed. Tell your provider right away if you forget to take your blood thinner, or if you take too much.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Manage your symptoms:
- Ask for support. A brain tumor can change the way you act, think, and feel. Your memory, concentration, and ability to learn may decline. You may act without thinking or become more emotional. Talk with family and friends about these changes and about continuing care, treatments, and home services. Go to all follow-up appointments.
- Rest as needed. You may need more rest than usual, especially after cancer treatment.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can cause brain and lung damage. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your healthcare provider before you use these products.
- Eat a variety of healthy foods. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, lean meats, fish, nuts, and cooked beans. Try to eat small meals if you have any nausea. Ask if you need to be on a special diet.

- Be physically active, as directed. Physical activity, such as exercise, can increase your energy and help keep your immune system strong. Your healthcare provider can help you create a physical activity plan.

- Go to physical, occupational, or speech therapy as directed. A physical therapist can help you build muscle strength and coordination. An occupational therapist can help you find ways to do your daily activities more easily. A speech therapist can help you if your tumor caused problems with speaking.
Follow up with your doctor or oncologist as directed:
You may need tests such as an MRI or PET scan every 3 months. These tests help check for new or returning tumors. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
For support and more information:
- American Brain Tumor Association
8550 West Bryn Mawr Avenue, Suite 550
Chicago , IL 60631
Phone: 1- 800 - 886-2282
Web Address: http://www.abta.org
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Brain Tumors
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
