Bone Marrow and Stem Cell Transplant
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
AMBULATORY CARE:
What you need to know about bone marrow and stem cell transplant:
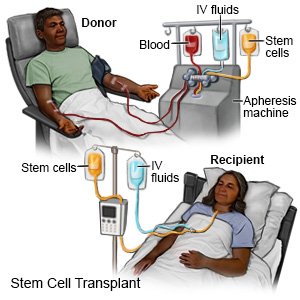
A bone marrow and stem cell transplant is a procedure to remove stem cells from blood or bone marrow. The stem cells are put into your body to treat disease. Stem cells are able to become other cells, such as red blood cells. Stem cells can also travel to your bone marrow and can become new bone marrow cells.
How to prepare for stem cell transplant:
- You may need several days of tests to make sure your body is ready for stem cell transplant. You may need blood tests to check for viruses such as hepatitis B, or get information about your overall health. Your healthcare provider will insert a long IV through a large vein in your chest or neck and into your heart. This IV is called a central line, and may stay in place for your entire treatment.
- If you have an autologous stem cell transplant, you will have your own blood or bone marrow removed from your body about 2 weeks before your transplant. Before stem cells are removed, you will receive medicine to increase the amount of stem cells in your body. Stem cells may be taken from your bone marrow or from a vein. Before a stem cell transplant, you may receive cancer treatment, such as chemo or radiation. These treatments help kill cancer and other damaged cells. They may also help stop your immune system from attacking the transplanted cells.
What will happen during stem cell transplant:
You may be given medicine to decrease side effects from the preservative that contains the stem cells. You may also be given IV fluids. Stem cells will be transplanted into your body through your central line. The procedure may take several hours. You will be on a heart monitor and your vital signs will be closely monitored to follow your heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. A heart monitor is an EKG that stays on continuously to record your heart's electrical activity.
 |
What to expect after stem cell transplant:
- You will be monitored very closely after stem cell transplant. You may spend days to weeks in the hospital to monitor for, or treat, complications or infection. Your body may feel very weak and you may get tired very easily. You may need blood transfusions until your bone marrow is able to produce blood cells on its own.
- Your appetite may be poor and you may need nutritional support. You may also need medicines to treat side effects from the stem cell transplant. Your healthcare providers and visitors may wear special gowns or masks to prevent you from getting an infection. You may need to wear a mask when leaving your hospital room. Tell your family and friends not to visit you if they are sick.
Risks of stem cell transplant:
- Your body may reject the new stem cells. You may have stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. You may also have weight gain, a fever, or a rash. You may get sores inside your mouth. You may be unable get pregnant. You may need blood transfusions until your bone marrow is able to make blood cells. Your immune system may not work as well as before the transplant, and you may get a serious infection.
- If you get an autologous stem cell transplant, it may contain cancer cells, and the cancer may spread to other parts of your body. One or more of your organs may become damaged. You may get a blood clot in an arm or leg. The blood clot can break loose and travel to your lungs. A blood clot in your lungs can cause chest pain and trouble breathing. This problem can be life-threatening.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) for any of the following:
- You have a seizure.
- You feel lightheaded, short of breath, and have chest pain.
- You cough up blood.
- You have any of the following signs of a stroke:
- Numbness or drooping on one side of your face
- Weakness in an arm or leg
- Confusion or difficulty speaking
- Dizziness, a severe headache, or vision loss
Seek care immediately if:
- Your arm or leg feels warm, tender, and painful. It may look swollen and red.
- Your skin or the whites of your eyes turn yellow.
- Your heart rate is faster than normal.
- You have stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
- You have a rash or sores on your skin.
- You have a fever.
Call your doctor if:
- Your pain is not controlled.
- You gain weight.
- You have sores, swelling, or redness in your mouth.
- You have a cough that does not go away.
- You have blood in your bowel movement or urine.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Self-care:
- Clean your teeth and mouth as directed. Good oral hygiene may decrease mouth discomfort caused by side effects of medicine. Use a soft brush. Brush your teeth and gums 2 to 3 times a day. Floss gently. Ask your healthcare provider about oral rinses that may decrease pain.
- Drink liquids as directed. Medicines given before or after stem cell transplant may cause damage to the kidneys or bladder. Liquids help flush the medicines out of your body and prevent complications.
- Follow your prescribed meal plan. You may have side effects such as nausea and vomiting after stem cell transplant. Talk to your healthcare provider about planning meals and choosing foods that will give you enough nutrition.
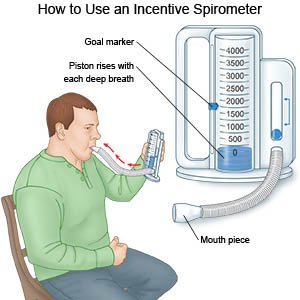
- Deep breathe and cough. Take deep breaths and cough 10 times each hour. This will decrease your risk for a lung infection. Take a deep breath and hold it for as long as you can. Let the air out and then cough strongly. Deep breaths help open your airway. You may be given an incentive spirometer to help you take deep breaths. Put the plastic piece in your mouth and take a slow, deep breath, then let the air out and cough. Repeat these steps 10 times every hour.
- Slowly increase your activity. Ask your healthcare provider when you can return to normal activities, and when you can drive. Start slowly with activities such as short walks. Rest when you need to. Do more as you feel better and have more energy.
- Know the signs of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Ask your healthcare provider for more information on the signs of GVHD.
Prevent an infection:
- Wash your hands often. Use soap and water. Use germ-killing gel if soap and water are not available. Wash your hands after you use the bathroom, change a diaper, and sneeze. Wash your hands before you touch your face, and prepare or eat food.

- Keep your home clean. Wipe down bathroom and kitchen surfaces with cleaners that contain bleach. Clean floors and carpets regularly.
- Use safe food practices. Do not eat fresh fruits or vegetables until your healthcare provider says it is okay. Cook meat thoroughly. Store extra food and leftovers in the refrigerator within 2 hours after preparation.
- Practice good hygiene. Bathe every day. Tell your healthcare provider if you notice sores on your skin. If you are female, always wipe from front to back after going to the bathroom. Do not use tampons. Tampons may increase your risk of an infection.
- Do not spend time with people who are sick. This includes people who have a cold, flu, infection, or rash. You should stay out of crowded places, such as malls and elevators.
- Be careful with pets and animals. Do not change your cat's litter box. Play gently with cats. Scratches from cats or other animals can get infected. Stay away from puppies, kittens, and young animals. They can spread disease and cause you to get an infection.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
You may need to return for more blood and urine tests. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Bone Marrow and Stem Cell Transplant
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
