Appendicitis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is appendicitis?
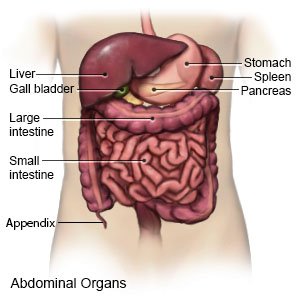
Appendicitis is inflammation of your appendix. The appendix is a small pouch in the lower right side of your abdomen. It is attached to the first part of the large intestine. A blockage or infection can cause your appendix to become inflamed. Inflammation may cause your appendix to swell, fill with pus, and rupture. You will need immediate care to prevent a ruptured appendix. A ruptured appendix can cause bacteria to leak into the abdomen. This can lead to a serious infection called peritonitis.
 |
What are the signs and symptoms of appendicitis?
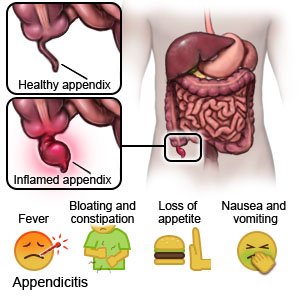
Symptoms may start suddenly. The most common symptom is pain that starts at the belly button and moves to the lower right side of your abdomen. The pain worsens when you touch your abdomen, move, sneeze, cough, or take a deep breath. You may also have any of the following:
- Abdomen that feels hard
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fever
 |
How is appendicitis diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine you and check for pain or tenderness in your abdomen. You may also need any of the following:
- Blood tests may show if you have an infection.
- CT, ultrasound, or MRI pictures of your abdomen may be used to check your appendix. You may be given contrast liquid to help your appendix show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- A fluid culture test may be used if your appendix bursts. Your provider may take a fluid sample from your abdomen during a drainage procedure or appendectomy. This test will show which bacteria is causing the infection.
Related medications
How is appendicitis treated?
- Antibiotics may be given to prevent or treat an infection.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Drainage may be needed if you develop an abscess after a burst appendix. To drain the abscess, your healthcare provider guides a tube through your skin and into the abscess. Infected fluid drains through the tube.
- An appendectomy is surgery to remove your appendix. Your appendix may be removed through small incisions in your abdomen. If your appendix has burst, you may need an open appendectomy. A single, larger incision is made to remove the appendix and clean out the abdomen.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have abdominal pain that gets worse or does not go away, even after you take medicine.
- You have a fast heartbeat or feel weak or faint.
- You have trouble thinking clearly.
- You are vomiting and cannot keep food down.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever or shaking chills.
- You have trouble having a bowel movement, or you have diarrhea.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Appendicitis
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
