Acute Graft versus Host Disease
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
GVHD can happen after you have a bone marrow or stem cell transplant. In GVHD, cells transplanted from the donor (the graft) attack your body (the host). This most commonly causes damage to your skin, liver, or digestive system. Acute GVHD happens in the first 100 days after your transplant.
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have trouble breathing.
Seek care immediately if:
- Your heart is beating faster than usual.
- You feel weak, dizzy, or faint.
- Your abdominal pain suddenly gets worse.
- You urinate very little or stop urinating.
- Your skin begins to peel or fall off.
- You have blood in your urine or bowel movements.
- You vomit blood.
Call your doctor if:
- You have a fever greater than 100.4°F or chills.
- Your symptoms do not get better with treatment.
- Your skin is red, swollen, or draining pus.
- You have open areas on your skin.
- You cannot stop vomiting.
- You cannot take your medicine.
- You have eye pain or changes in your vision.
- You have sores, bumps, or a rash on your genitals.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
- Medicines may be given to stop donor cells from attacking your body. Medicines may also be given to manage diarrhea, nausea, and skin problems. Antibiotics may be given to prevent a bacterial infection.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Related medications
Care for your skin:
- Apply cream or lotion as directed. Use a moisturizing lotion without a scent or apply prescription cream as directed.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing. This will help prevent rubbing against your skin.
- Do not scratch your skin. This can increase your risk for infection.
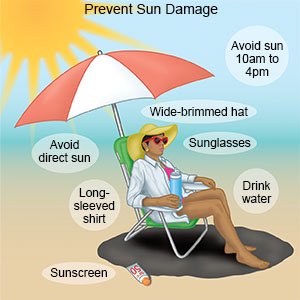
- Protect your skin from sunlight. Sunlight can make symptoms of GVHD worse. Wear sunscreen that is at least SPF 30. Reapply sunscreen every 1 to 2 hours while you are outside. Also wear a hat, a long-sleeved shirt, and pants when you are in the sun. Try to stay in the shade as much as possible.
Manage your diarrhea:
- Drink plenty of liquids. Liquids will help replace body fluids lost through diarrhea. You may also need to drink an oral rehydration solution (ORS). An ORS has the right amounts of sugar, salt, and minerals in water to replace body fluids. ORS can be found at most grocery stores or pharmacies. Ask how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
- Do not drink or eat foods that may make your symptoms worse. These include milk and dairy products, greasy and fatty foods, spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol. Keep a food diary to see if your symptoms are caused by certain foods. Bring this to your follow-up visits.
- Eat foods that may help your symptoms. These include bananas, boiled potatoes, cooked carrots, cooked chicken, plain rice, and toast.
- Care for your rectal area. Clean this area with warm water and soap after you have a bowel movement. You can also use soft cleansing wipes. Ask your healthcare provider about medicated wipes that may decrease discomfort.
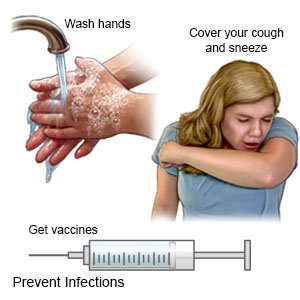
Prevent infection:
- Wash your hands often. Use soap and water or a germ-killing gel. Wash your hands after you use the bathroom, change a diaper, and sneeze. Wash your hands before you touch your face, and prepare or eat food.

- Keep your home clean. Wipe down bathroom and kitchen surfaces with cleaners that contain bleach. Clean floors and carpets regularly.
- Use safe food practices. Cook meat and vegetables thoroughly. Store extra food and leftovers in the refrigerator within 2 hours after preparation.
- Do not spend time with people who are sick. This includes people who have a cold, flu, infection, or rash. You should stay out of crowded places, such as malls and elevators.
- Be careful with pets and animals. Do not change your cat's litter box. Play gently with cats. Scratches from cats or other animals can get infected. Stay away from puppies, kittens, and young animals. They can spread disease and cause you to get an infection.
- Wear a mask as directed. You may need to wear a mask when you leave your house or when people visit.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about vaccines. Your provider can tell you if you should also get vaccines not listed below:
- Get an influenza (flu) vaccine as directed. The flu vaccine is recommended for everyone 6 months or older. Get the vaccine as soon as recommended each year, usually in September or October.
- Get a COVID-19 vaccine as directed. At least 1 dose of an updated vaccine is recommended for everyone 6 months or older. COVID-19 vaccines are given as a shot in 1 to 3 doses, depending on the age of the person who receives it. COVID-19 vaccines are updated throughout the year. Your healthcare provider can help you schedule all needed doses as updated vaccines become available.
- Get a pneumonia vaccine as directed. The vaccine is recommended for all adults aged 50 or older. Adults aged 19 to 49 years who are at high risk for pneumonia should also receive the vaccine. You may need 1 dose or 2. The number depends on the vaccine used and your risk factors. Children routinely receive 4 doses of the pneumonia vaccine, starting at 2 months.
 |
Get enough nutrition:
A registered dietitian can help you find an eating plan that is right for you. You may need a special diet.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
