Selenious Acid Injection: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Dosage form: injection, solution
Drug class: Minerals and electrolytes
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 14, 2025.
On This Page
Highlights of Prescribing Information
Indications and Usage for Selenious Acid Injection
Selenious Acid Injection is a trace element indicated in adult and pediatric patients as a source of selenium for parenteral nutrition when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated. (1)
Selenious Acid Injection Dosage and Administration
• Pharmacy Bulk Package: Not for direct intravenous infusion. (2.1)
• See full prescribing information for information on preparation, administration, and general dosing considerations. (2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5)
Recommended Dosage (2.5)
• Selenious Acid Injection provides 60 mcg/mL of selenium.
• Individualize the dosage based upon the patient’s clinical condition, nutritional requirements, and the contribution of oral or enteral selenium intake. The following dosages are general recommendations intended for most patients. However, based upon clinical requirements, some patients may require a higher dosage:
o Adults: 60 mcg/day
Pediatric Patients 7 kg and above: 2 mcg/kg/day (up to 60 mcg/day)
o Pediatric Patients less than 7 kg: 2 to 4 mcg/kg/day
• Monitor selenium concentrations during treatment.
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Selenious Acid Injection, USP: (3)
• Pharmacy Bulk Package: 600 mcg/10 mL (60 mcg/mL) of selenium
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
• Pulmonary Embolism due to Pulmonary Vascular Precipitates: If signs of pulmonary distress occur, stop the infusion and initiate a medical evaluation. (5.1)
• Vein Damage and Thrombosis: Solutions with osmolarity of 900 mOsmol/L or more must be infused through a central venous catheter. (2.1, 5.2)
• Aluminum Toxicity: Increased risk in patients with renal impairment, including preterm infants. (5.3, 5.4)
• Monitoring and Laboratory Tests: Monitor selenium concentrations, fluid and electrolyte status, serum osmolarity, blood glucose, liver and kidney function, blood count and coagulation parameters throughout treatment. (5.4, 2.5)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
No selenium-related adverse reactions in patients receiving intravenously administered parenteral nutrition solutions containing selenious acid within the recommended dosage range. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Gland Pharma Limited at 609-250-7990 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch (6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 8/2024
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Selenious Acid Injection
Selenious Acid Injection is indicated in adult and pediatric patients as a source of selenium for parenteral nutrition when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated.
2. Selenious Acid Injection Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Administration Information
Selenious Acid Injection is supplied as a pharmacy bulk package for admixing use only. It is not for direct intravenous infusion. Prior to administration, Selenious Acid Injection must be transferred to a separate parenteral nutrition container, prepared and used as an admixture in parenteral nutrition solutions.
The Pharmacy Bulk Package vial of Selenious Acid Injection is intended for dispensing of single doses to multiple patients in a pharmacy admixture program.
The final parenteral nutrition solution is for intravenous infusion into a central or peripheral vein. The choice of a central or peripheral venous route should depend on the osmolarity of the final infusate. Solutions with osmolarity of 900 mOsmol/L or greater must be infused through a central venous catheter [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2.2 Preparation and Administration Instructions
• Selenious Acid Injection is not for direct intravenous infusion. Prior to administration, Selenious Acid Injection must be prepared and used as an admixture in parenteral nutrition solutions.
• Selenious Acid Injection is to be prepared only in a suitable work area such as a laminar flow hood (or an equivalent clean air compounding area). The key factor in the preparation is careful aseptic technique to avoid inadvertent touch contamination during mixing of solutions and addition of other nutrients.
• Visually inspect the prepared parenteral nutrition solution containing Selenious Acid Injection for particulate matter before admixing, after admixing, and prior to administration.
2.3 Preparation Instructions for Admixing Using a Parenteral Nutrition Container
• Inspect Selenious Acid Injection vials for particulate matter.
• Transfer Selenious Acid Injection to the parenteral nutrition solution following the admixture of amino acids, dextrose, lipid (if added), and electrolytes solutions.
• Because additives may be incompatible, evaluate all additions to the parenteral nutrition container for compatibility and stability of the resulting preparation. Consult with pharmacist, if available. Questions about compatibility may be directed to Gland Pharma. If it is deemed advisable to introduce additives to the parenteral nutrition container, use aseptic technique.
• Inspect the final parenteral nutrition solution containing Selenious Acid Injection to ensure that:
o Precipitates have not formed during mixing or addition of additives.
o The admixed emulsion has not separated, if a lipid emulsion has been added. Separation of the admixed emulsion can be visibly identified by a yellowish streaking or the accumulation of yellowish droplets.
• Discard if any precipitates are observed.
Stability and Storage
• Pharmacy Bulk Package vial (10 mL): Penetrate vial closure only one time with a suitable sterile transfer device or dispensing set that allows measured dispensing of the contents.Use Selenious Acid Injection for admixing promptly once the sterile transfer set has been inserted into the Pharmacy Bulk Package container or not more than 4 hours at room temperature (25ºC/77ºF) after the container closure has been penetrated. Discard any remaining drug.
• Use parenteral nutrition solutions containing Selenious Acid Injection promptly after mixing. Any storage of the admixture should be under refrigeration from 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and limited to a period of time no longer than 9 days. After removal from refrigeration, use promptly and complete the infusion within 24 hours. Discard any remaining admixture.
• Protect the admixed parenteral nutrition solution from light.
2.4 Dosing Considerations
• The dosage of the final parenteral nutrition solution containing Selenious Acid Injection must be based on the concentrations of all components in the solution and the recommended daily nutritional requirements [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Consult the prescribing information of all added components to determine the recommended nutritional requirements for dextrose, amino acids and lipid emulsion, as applicable.
• Prior to administration of parenteral nutrition solution containing Selenious Acid Injection, correct severe fluid, electrolyte and acid-base disorders.
2.5 Recommended Dosage and Monitoring in Adults and Pediatric Patients
• The dosage strength for Selenious Acid Injection: 60 mcg/mL of selenium.
• The dosage of Selenious Acid Injection should be individualized based on the patient’s clinical condition, nutritional requirements, and the contribution of oral or enteral selenium intake.
• The dosages in Table 1 are general recommendations intended for most patients. However, based on clinical requirements, some patients may require a higher dosage.
Table 1: Recommended Dosage of Selenious Acid Injection for Adults and Pediatric Patients by Estimated Weight
| Population
| Recommended Dosage
|
| Adults | 60 mcg/day |
| Pediatric Patients 7 kg and above | 2 mcg/kg/day (up to 60 mcg/day) |
| Pediatric Patients less than 7 kg | 2 to 4 mcg/kg/day |
• Monitor selenium concentrations during treatment. Selenium concentrations may vary depending on the assay used and the laboratory reference range.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Selenious Acid Injection, USP is a clear colorless solution available in the following:
• Pharmacy Bulk Package: 600 mcg/10 mL (60 mcg/mL) of selenium
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Pulmonary Embolism due to Pulmonary Vascular Precipitates
Pulmonary vascular precipitates causing pulmonary vascular emboli and pulmonary distress have been reported in patients receiving parenteral nutrition. The cause of precipitate formation has not been determined in all cases; however, in some fatal cases, pulmonary emboli occurred as a result of calcium phosphate precipitates. Precipitation has occurred following passage through an in-line filter; in vivo precipitate formation may also have occurred. If signs of pulmonary distress occur, stop the parenteral nutrition infusion and initiate a medical evaluation. In addition to inspection of the solution [see Dosage and Administration (2.2,2.3)], the infusion set and catheter should also periodically be checked for precipitates.
5.2 Vein Damage and Thrombosis
Selenious Acid Injection has a low pH and must be prepared and used as an admixture in parenteral nutrition solutions. It is not for direct intravenous infusion.
In addition, consider the osmolarity of the final parenteral nutrition solution in determining peripheral versus central administration. Solutions with an osmolarity of 900 mOsmol/L or greater must be infused through a central catheter [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. The infusion of hypertonic nutrient injections into a peripheral vein may result in vein irritation, vein damage, and/or thrombosis. The primary complication of peripheral access is venous thrombophlebitis, which manifests as pain, erythema, tenderness or a palpable cord. Remove the catheter as soon as possible, if thrombophlebitis develops.
5.3 Aluminum Toxicity
Selenious Acid Injection contains aluminum that may be toxic.
Aluminum may reach toxic levels with prolonged parenteral administration if kidney function is impaired. Preterm infants are particularly at risk for aluminum toxicity because their kidneys are immature, and they require large amounts of calcium and phosphate solutions, which also contain aluminum.
Patients with impaired kidney function, including preterm neonates, who receive greater than 4 to 5 mcg/kg/day of parenteral aluminum can accumulate aluminum to levels associated with central nervous system and bone toxicity. Tissue loading may occur at even lower rates of administration.
Exposure to aluminum from Selenious Acid Injection is not more than 0.6 mcg/kg/day. When prescribing Selenious Acid Injection for use in parenteral nutrition containing other small volume parenteral products, the total daily patient exposure to aluminum from the admixture should be considered and maintained at no more than 5 mcg/kg/day [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.4 Monitoring and Laboratory Tests
Monitor selenium concentrations, fluid and electrolyte status, serum osmolarity, blood glucose, liver and kidney function, blood count and coagulation parameters during treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
No selenium-related adverse reactions have been reported in clinical studies or postmarketing reports in patients receiving intravenously administered parenteral nutrition solutions containing selenious acid within the recommended dosage range.
The following adverse reactions associated with use of other components of parenteral nutrition solutions were identified in clinical studies or postmarketing reports. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure:
• Pulmonary embolism due to pulmonary vascular precipitates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
• Vein damage and thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
• Aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Related/similar drugs
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Administration of the recommended dose of Selenious Acid Injection in parenteral nutrition is not expected to cause major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with intravenous selenious acid.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations are unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated Maternal and/or Embryo-Fetal Risk
Deficiency of trace elements, including selenium, is associated with adverse pregnancy and fetal outcomes. Pregnant women have an increased metabolic demand for trace elements, including selenium. Parenteral nutrition with selenium should be considered if a pregnant woman’s nutritional requirements cannot be fulfilled by oral or enteral intake.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Selenium is present in human milk. Administration of the approved recommended dose of Selenious Acid Injection in parenteral nutrition is not expected to cause harm to a breastfed infant. There is no information on the effects of selenious acid on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Selenious Acid Injection and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Selenious Acid Injection or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Selenious Acid Injection is approved for use in the pediatric population, including neonates, as a source of selenium for parenteral nutrition when oral or enteral nutrition is not possible, insufficient, or contraindicated. Safety and dosing recommendations in pediatric patients are based on clinical experience [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Because of immature renal function, preterm infants receiving prolonged parenteral nutrition treatment with Selenious Acid Injection may be at higher risk of aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Reported clinical experience with intravenous selenious acid has not identified a difference in selenium requirements between elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection should be individualized based on the patient’s clinical condition, nutritional requirements, and additional nutritional intake provided orally or enterally to the patient.
10. Overdosage
There are no known cases of overdosage with intravenous selenious acid in parenteral nutrition.
Overdosage has been reported with oral selenium. Available selenium concentrations in these subjects have been reported using various assays and laboratory-based reference ranges over a period of time. Interpret results in the context of current reported ranges.
For oral selenium, the Tolerable Upper Limit (UL) is 400 mcg/day and the No Observed Adverse Effect Level (NOAEL) is 800 mcg/day. The estimated oral bioavailability of selenium is approximately 70%.
Acute Oral Toxicity Effects
Serious adverse events and deaths have been reported with acute oral toxicity, however, there is no clear correlation between the amount ingested, signs and symptoms of toxicity, or selenium blood concentrations.
With severe toxicity, the most common presenting symptoms within a few hours post-ingestion of oral doses greater than 1 gram/day of selenium are gastrointestinal (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain), altered mental status, and “garlic” breath odor.
Death from circulatory collapse has been reported after oral ingestion of 5 to 10 grams of selenium. Selenium serum or blood concentrations in fatal cases have been reported in the range of 190 mcg/dL to 3,800 mcg/dL.
Mild to moderate intoxication (myalgia, muscle spasms, and irritability) has been reported in patients with selenium serum or blood concentrations in the range of 41 to 750 mcg/dL.
Chronic Selenosis
Chronic daily exposure to selenium from dietary sources (0.003 to 0.007 grams/day) or oral supplements (0.0016 to 0.25 grams/day) may result in alopecia and nail brittleness. Other signs include gastrointestinal disturbances, skin rash, garlic breath, fatigue, irritability, and nervous system abnormalities including paresthesia and ataxia.
Selenium serum or blood concentrations in patients in China exposed through oral (non-dietary) supplementation were in the range of 32 to 150 mcg/dL.
Management
There is no known antidote for acute selenium toxicity. Management of selenium overdosage is supportive care based on presenting signs and symptoms.
11. Selenious Acid Injection Description
Selenious Acid Injection, USP is a sterile, non-pyrogenic, clear, colorless solution intended for use as a trace element and additive to intravenous solutions for parenteral nutrition.
Each 600 mcg/10 mL Pharmacy Bulk Package vial contains 10 mL of selenious acid solution.
None of the presentations contain preservatives.
Each mL of the 60 mcg/mL strength contains 60 mcg of selenium present as 98 mcg of selenious acid, nitric acid for pH adjustment (1.8 to 2.4), and water for injection q.s.
Selenious Acid Injection 60 mcg/mL contains no more than 2,500 mcg/L of aluminum and has a calculated osmolarity of 16 mOsmol/L.
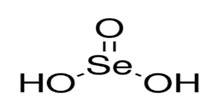
Selenious acid has a molecular weight of 128.97 g/mol and a formula of H2SeO3. The structural formula is:
12. Selenious Acid Injection - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Selenious acid is converted in vivo to hydrogen selenide via glutathione-involved electron reductions. Hydrogen selenide acts as a selenium pool to form selenoproteins which include, but are not limited to, glutathione peroxidase, iodothyronine deiodinase, peroxidase and thioredoxins.
16. How is Selenious Acid Injection supplied
Selenious Acid Injection, USP is a clear, colorless solution available as:
• 600 mcg/10 mL (60 mcg/mL) of selenium in a 10 mL pharmacy bulk package. Carton of 5 vials (NDC 68083-660-05).
The vial closure for each presentation is not made with natural rubber latex.
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]
For storage of admixed solution, see Dosage and Administration (2.3).
17. Patient Counseling Information
Inform patients, caregivers or home healthcare providers of the following risks of Selenious Acid Injection:
• Pulmonary embolism due to pulmonary vascular precipitates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
• Vein damage and thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
• Aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Manufactured by: Gland Pharma Limited
Hyderabad-502 307, India
ML No: 2/MD/TS/2015/F/G
Revised Date: August 2024
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Container Label
NDC 68083-660-01 Rx Only
Selenious Acid
Injection, USP
600 mcg*/10 mL
(60 mcg*/mL) of Selenium
Pharmacy Bulk Package -
Not for Direct Infusion
For intravenous use
after dilution and admixing
PRESERVATIVE FREE 10 mL

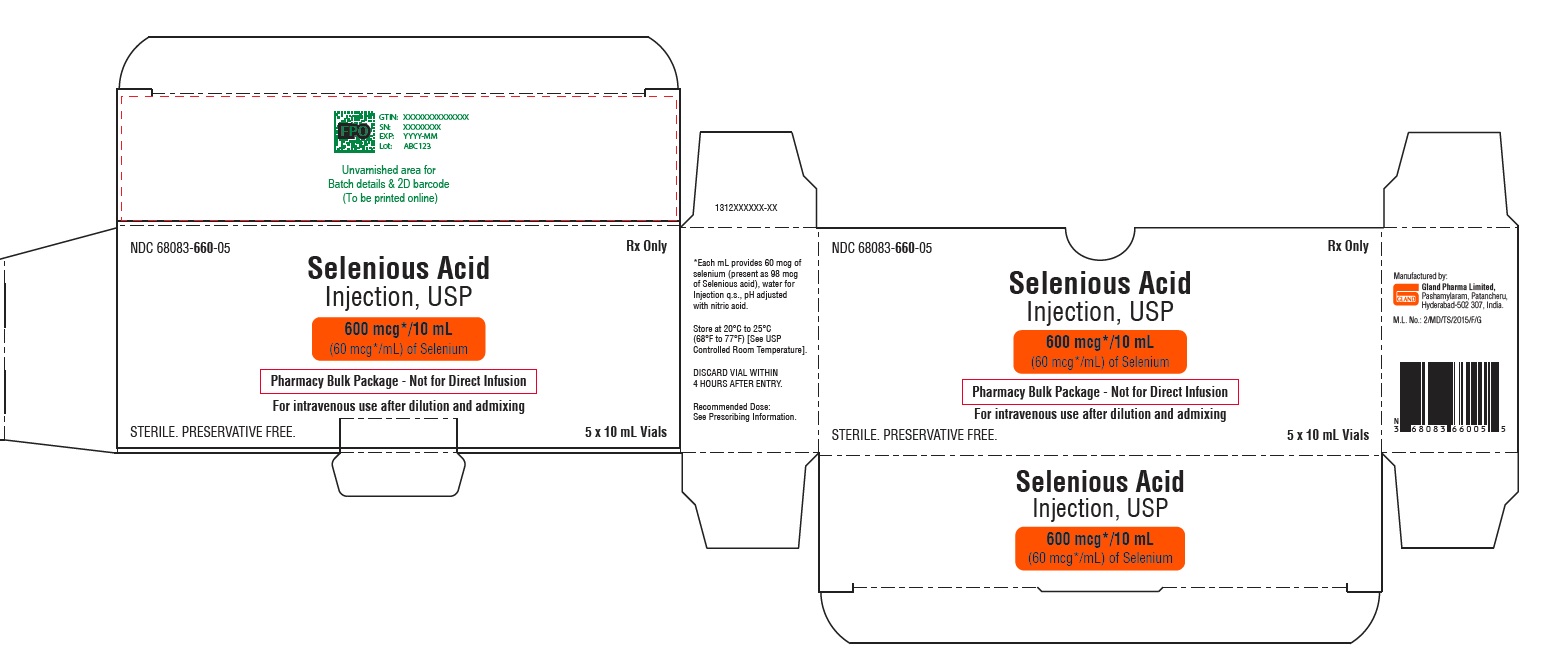
Carton Label
NDC 68083-660-05 Rx Only
Selenious Acid
Injection, USP
600 mcg*/10 mL
(60 mcg*/mL) of Selenium
Pharmacy Bulk Package -
Not for Direct Infusion
For intravenous use
after dilution and admixing
STERILE. PRESERVATIVE FREE 5 x 10 mL Vials
| SELENIOUS ACID
selenious acid injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Gland Pharma Limited (918601238) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLAND PHARMA LIMITED | 858971074 | ANALYSIS(68083-660) , LABEL(68083-660) , MANUFACTURE(68083-660) , PACK(68083-660) | |
Frequently asked questions
- What foods are high in selenium and what are the health benefits?
- What are antioxidants and should you take supplements?
More about selenium
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (6)
- Side effects
- Drug class: minerals and electrolytes
- En español
