Onapgo: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: apomorphine hydrochloride
Dosage form: injection, solution
Drug class: Dopaminergic antiparkinsonism agents
J Code (medical billing code): J0364 (1 mg, injection)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 31, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Drug Abuse and Dependence
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ONAPGO (apomorphine hydrochloride) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2004
Indications and Usage for Onapgo
ONAPGO is a dopaminergic agonist indicated for the treatment of motor fluctuations in adults with advanced Parkinson's disease. ( 1)
Onapgo Dosage and Administration
- For subcutaneous use by infusion only. ( 2.1)
- Maximum recommended total daily dosage of ONAPGO, including the continuous dosage and any extra dose(s), is 98 mg generally administered over the waking day (e.g., 16 hours). ( 2.3)
- The recommended initial continuous dosage is 1 mg/hr with a maximum of 6 mg/hr for up to 16 hours per day. ( 2.3)
- The extra dose may be titrated in increments of 0.5 mg or 1 mg based on clinical response and tolerability. Subsequent extra doses are between 0.5 mg and 2 mg, with at least 3 hours between extra doses and a maximum of 3 extra doses per day. ( 2.3)
- Treatment with trimethobenzamide is recommended, starting 3 days prior to the first dose of ONAPGO, and should only be continued as long as necessary to control nausea and vomiting, and generally no longer than two months. ( 2.2, 5.2, 6.1, 17)
- ONAPGO is not substitutable for apomorphine products intended for intermittent use. ( 2.3)
- For patients with mild or moderate renal impairment, the recommended initial extra dose is 0.5 mg to 1 mg and should not exceed 1 mg. ( 2.5)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 98 mg/20 mL (4.9 mg/mL) of apomorphine hydrochloride in single-dose cartridges. ( 3)
Contraindications
Warnings and Precautions
- Subcutaneous use only; thrombus formation and pulmonary embolism have followed intravenous administration of ONAPGO. ( 5.1)
- May cause nausea and vomiting. ( 2.2, 5.2)
- Falling asleep during activities of daily living and daytime somnolence may occur. ( 5.3)
- May cause hypotension/orthostatic hypotension and syncope may occur. ( 5.4)
- May cause or increase the risk of falls. ( 5.5)
- May cause infusion site reactions and infections. Monitor and change infusion site every day. ( 2.4, 5.6)
- May cause hallucinations and psychotic-like behavior. ( 5.7)
- May cause dyskinesia or exacerbate pre-existing dyskinesia. ( 5.8)
- May cause hemolytic anemia. ( 5.9)
- May cause impulse control/ compulsive and impulsive behaviors. Consider dose reductions or stopping ONAPGO. ( 5.10)
- May cause cardiac events. ( 5.11)
- May prolong QTc and cause torsades de pointes or sudden death. ( 5.12)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥10% on ONAPGO and at least twice the rate of placebo) were infusion site nodule, nausea, somnolence, infusion site erythema, dyskinesia, headache, and insomnia. ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact MDD US Operations, LLC, a subsidiary of Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at toll-free number 1-833-366-2746 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 2/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Onapgo
ONAPGO is indicated for the treatment of motor fluctuations in adults with advanced Parkinson's disease.
2. Onapgo Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Information
- ONAPGO is indicated for subcutaneous use by infusion only [see Warnings & Precautions (5.1)] .
- Patients selected for treatment with ONAPGO should be capable of understanding and trained on using the delivery system, either themselves or with the assistance of a caregiver [see Healthcare Provider Instructions for Use and Patient Instructions for Use].
- ONAPGO initiation and dose titrations should be done under medical supervision.
- The prescribed dose of ONAPGO should be expressed in "mg/hr" for the continuous dosage and "mg" for an extra dose.
2.2 Premedication and Concomitant Medication
Because of the incidence of nausea and vomiting with ONAPGO, it is recommended that treatment with trimethobenzamide 300 mg three times a day start 3 days prior to the initial dose of ONAPGO [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] . Alternatively, consider starting ONAPGO therapy, without antiemetics, at 1 mg/hour and titrate based upon effectiveness and tolerance.
If trimethobenzamide is used, it should be continued only as long as necessary to control nausea and vomiting, and generally no longer than two months after initiation of treatment with ONAPGO, as trimethobenzamide increases the incidence of somnolence, dizziness, and falls in patients treated with ONAPGO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
Based on reports of profound hypotension and loss of consciousness when apomorphine was administered with ondansetron, the concomitant use of apomorphine with drugs of the 5HT 3antagonist class including antiemetics (e.g., ondansetron, granisetron, dolasetron, palonosetron) and alosetron are contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)] .
After starting ONAPGO, adjustment of concomitant anti-Parkinson's disease medications may be necessary.
2.3 Recommended Dosage
ONAPGO (apomorphine hydrochloride) is administered as a subcutaneous infusion with the ONAPGO pump [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Healthcare Provider Instructions for Use, and Patient Instructions for Use].
The daily dosage is determined by individualized patient titration and is composed of a continuous dosage and as needed extra dose(s).
The maximum recommended total daily dosage of ONAPGO, including the continuous dosage and any extra dose(s), is 98 mg per day, generally administered over the waking day (e.g., 16 hours).
Continuous Dosage
The recommended initial continuous dosage (continuous infusion) of ONAPGO is 1 mg/hr. Titrate the continuous dosage, as needed, in 0.5 mg/hr to 1 mg/hr increments. Dose adjustments may be made daily, or at longer intervals, through the titration process. Patients in clinical studies used a mean of 4 mg/hr of ONAPGO. The maximum continuous dosage is 6 mg/hour administered over the waking day (e.g., 16 hours).
Extra Dose
Extra doses of ONAPGO may be used:
- upon starting in the morning; or
- when restarting the continuous dosage after a 1-hour or longer break in use (i.e., as a loading dose); or
- as a supplement to the continuous dosage to manage acute OFF symptoms that are not controlled
The extra dose may be titrated to clinical response and tolerability with adjustments in increments of 0.5 mg or 1 mg. Subsequent extra doses may be between 0.5 mg and 2 mg.
Administer no more than 3 extra doses per day over 16 hours with at least 3 hours between extra doses.
If 3 extra doses are routinely required during daily infusion, consider further adjustment of the continuous dosage.
The maximum recommended total daily dosage, including extra doses, is 98 mg during the waking day (e.g., 16 hours).
2.4 Preparation and Administration Instructions
Patients and caregivers should receive education and be trained on the proper use of ONAPGO and the device delivery system prior to first use [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)and Patient Instructions for Use].
- Visually inspect solution for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Solution should be clear, almost colorless. Do not use if solution is discolored or contains particles.
- Keep the infusion site clean and use aseptic technique.
- Administer ONAPGO subcutaneously in one of the following areas:
- Abdomen at least 2 inches away from the navel
- Top of thigh
- Lower back
- Upper back, only when the infusion site is being prepared by a caregiver or healthcare provider
- Change the infusion site every day
- Do notselect an infusion site that is bruised, has bumps or nodules, or is irritated.
- A new single-dose cartridge and cartridge holder should be used each day. Discard unused portion.
2.5 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment
For patients with mild or moderate renal impairment, the recommended initial extra dose is 0.5 mg to 1 mg and should not exceed 1 mg [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]. No adjustment is needed for the continuous dose, maximum recommended daily dose, or subsequent extra doses after the initial extra dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Patients with severe renal impairment have not been studied.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 98 mg/20 mL (4.9 mg/mL) apomorphine hydrochloride is a clear, almost colorless solution available in a single-dose prefilled cartridge.
4. Contraindications
ONAPGO is contraindicated in patients:
- Using concomitant 5HT 3antagonists, including antiemetics (e.g., ondansetron, granisetron, dolasetron, palonosetron) and alosetron [see Drug Interactions (7.1)] . There have been reports of profound hypotension and loss of consciousness when apomorphine was administered with ondansetron.
- With hypersensitivity/allergic reaction to apomorphine or any of the excipients of ONAPGO, including sulfite (i.e., sodium metabisulfite). Angioedema or anaphylaxis may occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Serious Adverse Reactions After Intravenous Administration
Following intravenous administration of apomorphine, serious adverse reactions including thrombus formation and pulmonary embolism caused by intravenous crystallization of apomorphine have occurred. Do not administer ONAPGO intravenously.
5.2 Nausea and Vomiting
ONAPGO is known to cause nausea and vomiting, which may be severe. In Study 1 [see Clinical Studies (14)] 87% of patients were pretreated with an antiemetic. Twenty-two percent of patients treated with ONAPGO reported nausea and 7% reported vomiting, compared to 9% and 4%, respectively, of patients who received placebo. The ability of concomitantly administered antiemetic drugs (other than trimethobenzamide) to reduce apomorphine-associated nausea/vomiting has not been studied. Antiemetics with anti-dopaminergic actions (e.g., haloperidol, chlorpromazine, promethazine, prochlorperazine, metoclopramide) have the potential to worsen the symptoms in patients with PD and therefore the benefits and risks of treatment with these antiemetics should be carefully considered. The use of ONAPGO with 5HT 3antiemetics is contraindicated.
5.3 Falling Asleep During Activities of Daily Living and Somnolence
Somnolence is commonly associated with ONAPGO .Patients treated with dopaminergic medications, including apomorphine, have also reported falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living, including the operation of motor vehicles, which sometimes resulted in accidents. Patients may not perceive warning signs, such as excessive drowsiness, or they may report feeling alert immediately prior to the event. In the double-blind placebo-controlled trial (Study 1), somnolence was reported in 22% of patients treated with ONAPGO and 4% of patients in the placebo group.
Falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living usually occurs in patients experiencing preexisting somnolence, although patients may not give such a history. Therefore, prescribers should reassess patients for drowsiness or sleepiness while using ONAPGO, especially because some of the events occur well after the start of treatment. Prescribers should also be aware that patients may not acknowledge drowsiness or sleepiness until directly questioned about drowsiness or sleepiness during specific activities.
Before initiating treatment with ONAPGO, advise patients of the risk of drowsiness and ask them about factors that could increase the risk with ONAPGO, such as concomitant sedating medications and the presence of sleep disorders. If a patient develops significant daytime sleepiness or falls asleep during activities that require active participation (e.g., conversations, eating, etc.), ONAPGO should ordinarily be discontinued. If a decision is made to continue ONAPGO, patients should be advised not to drive and to avoid other potentially dangerous activities. There is insufficient information to determine whether dose reduction will eliminate episodes of falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living.
5.4 Syncope/Hypotension/Orthostatic Hypotension
Dopamine agonists, including ONAPGO, may cause orthostatic hypotension at any time, but especially during dose escalation. Patients with PD may also have an impaired capacity to respond to an orthostatic challenge. For these reasons, PD patients being treated with dopaminergic agonists should be monitored for signs and symptoms of orthostatic hypotension, especially during dose escalation, and should be informed of this risk.
When evaluated at various times after dosing in Study 1, patients undergoing titration of ONAPGO showed an increased incidence (from 4.5% pre-dose to 44.4% post-dose) of systolic orthostatic hypotension (≥ 20 mm Hg decrease upon standing) compared to placebo (7.1% pre-dose to 16.3% post-dose). Similarly, increased incidences of diastolic orthostatic hypotension (≥ 10 mm Hg decrease upon standing) were noted in patients titrated with ONAPGO (4.5% pre-dose to 44.4% post-dose) compared to placebo (11.9% pre-dose to 30.2% post-dose). Through the 12-week treatment period, these differences in incidence rates for systolic and diastolic orthostatic hypotension remained similar between ONAPGO and placebo patients. Patients in both ONAPGO and placebo groups developed severe systolic orthostatic hypotension (≥ 40 mm Hg decrease) and/or diastolic orthostatic hypotension (≥ 20 mm Hg decrease).
In Study 1, 13% of patients treated with ONAPGO reported hypotension or orthostatic hypotension compared to 2% of patients who received placebo [hypotension (7% vs 0%), orthostatic hypotension (4% vs 2%), and orthostatic intolerance (2% vs 0%)]. In the double-blind period of Study 1, one patient (2%) experienced a serious adverse event of hypotension and withdrew from the study compared to none in placebo.
Syncope has been reported in patients who have received subcutaneous apomorphine.
Patients with PD may also have an impaired capacity to respond to an orthostatic challenge. For these reasons, PD patients being treated with dopaminergic agonists ordinarily require careful monitoring for signs and symptoms of orthostatic hypotension, especially during dose escalation, and should be informed of this risk. Patients should avoid alcohol when using ONAPGO [see Drug Interactions (7.3)] . Patients taking ONAPGO should lie down before and after taking sublingual nitroglycerin. Other vasodilators and antihypertensives may also increase the hypotensive effects of ONAPGO. Monitor blood pressure for hypotension and orthostatic hypotension in patients taking ONAPGO with concomitant antihypertensive medications or vasodilators [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
5.5 Falls
Patients with Parkinson's disease are at risk of falling due to underlying postural instability, possible autonomic instability, and syncope caused by the blood pressure lowering effects of the drugs used to treat Parkinson's disease. ONAPGO might increase the risk of falling by simultaneously lowering blood pressure and altering mobility [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Falls, including serious falls, have been reported in patients treated with apomorphine.
5.6 Infusion Site Reactions and Infections
ONAPGO can cause infusion site reactions and infections.
In Study 1, one or more infusion site reactions were reported in 63% of patients treated with ONAPGO and 15% in patients who received placebo. Various types of reactions at the infusion site have been reported including nodules, erythema, hematomas, inflammation, pruritus, swelling, discoloration, hemorrhage, hypersensitivity, induration, edema, pain, rash, or bruising [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . In Study 1, 2% of patients treated with ONAPGO and no patient who received placebo discontinued treatment because of an infusion site reaction.
Infusion site infections occurred in 4% of patients treated with ONAPGO compared to no patients who received placebo. The most frequent infusion site infection reported was cellulitis. If an infection is suspected at the infusion site, the cannula should be removed from the infusion site. If the cannula is removed for an infection, a new cannula should be placed at a new infusion site. In the event of a prolonged interruption of treatment with ONAPGO, the patient should be prescribed oral medications to treat their Parkinson's disease [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.7 Hallucinations/Psychotic-Like Behavior
In Study 1, 4% of patients treated with ONAPGO reported hallucinations compared to 4% of patients who received placebo. Psychotic disorder was reported in 2% of patients treated with ONAPGO compared to none who received placebo.
Postmarketing reports with intermittent subcutaneous apomorphine indicate that patients may experience new or worsening mental status and behavioral changes, which may be severe, including psychotic-like behavior after starting or increasing the dose of apomorphine. Other drugs prescribed to improve the symptoms of PD can have similar effects on thinking and behavior. This abnormal thinking and behavior can consist of one or more of a variety of manifestations, including paranoid ideation, delusions, hallucinations, confusion, disorientation, aggressive behavior, agitation, and delirium. Consider the risks and benefits prior to initiating treatment with ONAPGO in patients with a major psychotic disorder because of the risk of exacerbating psychosis. In addition, certain medications used to treat psychosis may exacerbate the symptoms of PD and may decrease the effectiveness of ONAPGO [see Drug Interactions (7.3)] .
5.8 Dyskinesia
ONAPGO may cause dyskinesia or exacerbate pre-existing dyskinesia. In Study 1, dyskinesia or worsening of dyskinesia was reported in approximately 15% of patients treated with ONAPGO compared to no patients who received placebo.
5.9 Hemolytic Anemia
Hemolytic anemia requiring hospitalization has been reported with apomorphine treatment in a postmarketing setting. Many of the reported cases included positive direct antiglobulin test (Coombs test), suggesting a potential immune-mediated hemolysis. Severe anemia, angina, and dyspnea have occurred with hemolytic anemia. Some patients were treated with high dose glucocorticoids or blood transfusions. Hemolytic anemia can occur at any time after apomorphine treatment. If a patient develops anemia while taking ONAPGO, consider a workup for hemolytic anemia. If hemolytic anemia occurs, consider discontinuing treatment with ONAPGO. In Study 1, hemolytic anemia was reported in 2% of patients treated with ONAPGO compared to no patient who received placebo.
5.10 Impulse Control/Compulsive Behaviors
Patients may experience intense urges to gamble, increased sexual urges, intense urges to spend money uncontrollably, and other intense urges and the inability to control these urges while taking one or more of the medications, including ONAPGO, that increase central dopaminergic tone and that are generally used for the treatment of PD. In some cases, although not all, these urges were reported to have stopped when the dose was reduced, or the medication was discontinued. Because patients may not recognize these behaviors as abnormal, it is important for prescribers to specifically ask patients or their caregivers about the development of new or increased gambling urges, sexual urges, uncontrolled spending, or other urges while being treated with ONAPGO. Physicians should consider dose reduction or stopping the medication if a patient develops such urges while taking ONAPGO
5.11 Cardiac Events
In Study 1, 4 patients treated with ONAPGO experienced cardiac disorders, including left bundle branch block (2%), myocardial infarction (2%), palpitations (2%), or tachycardia (2%), compared to no patients who received placebo. In patients treated with apomorphine subcutaneous injection, cardiac arrest and/or sudden death has occurred; some cases of angina and myocardial infarction occurred in close proximity to apomorphine dosing (within 2 hours), while other cases of cardiac arrest and sudden death were observed at times unrelated to dosing.
ONAPGO has been shown to reduce resting systolic and diastolic blood pressure and may have the potential to exacerbate cardiac (and cerebral) ischemia in patients with known cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease. If patients develop signs and symptoms of cardiac or cerebral ischemia, prescribers should re-evaluate the continued use of ONAPGO.
5.12 QTc Prolongation and Potential for Proarrhythmic Effects
There is a dose-related prolongation of QTc interval after apomorphine exposure similar to that achieved with therapeutic doses of ONAPGO [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)] . In Study 1, 4% of patients treated with ONAPGO experienced prolonged QTc interval compared to none who received placebo.
Drugs that prolong the QTc interval have been associated with torsades de pointes and sudden death. The relationship of QTc prolongation to torsades de pointes is clearest for larger increases (20 msec and greater), but it is possible that smaller QTc prolongations may also increase risk, or increase it in susceptible individuals, such as those with hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, bradycardia, concomitant use of other drugs that prolong the QTc interval, or genetic predisposition (e.g., congenital prolongation of the QT interval). Although torsades de pointes has not been observed in association with the use of ONAPGO at recommended doses in clinical studies, experience is too limited to rule out an increased risk. Palpitations and syncope may signal the occurrence of an episode of torsades de pointes.
The risks and benefits of ONAPGO treatment should be considered prior to initiating treatment with ONAPGO in patients with risk factors for prolonged QTc.
5.13 Hypersensitivity
In Study 1, 11% of patients treated with ONAPGO reported rash (4%), infusion site pruritus (4%), infusion site rash (2%), hypersensitivity (2%), or infusion site hypersensitivity (2%) compared to no patient who received placebo. Hypersensitivity/allergic reactions characterized by urticaria, rash, pruritus, and/or various manifestations of angioedema may occur because of ONAPGO or because of its sulfite excipient. ONAPGO contains sodium metabisulfite, a sulfite that may cause allergic-type reactions, including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in certain susceptible people. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown and probably low. Sulfite sensitivity is seen more frequently in asthmatic than in nonasthmatic people.
5.14 Fibrotic Complications
Cases of retroperitoneal fibrosis, pulmonary infiltrates, pleural effusion, pleural thickening, and cardiac valvulopathy have been reported in some patients treated with ergot-derived dopaminergic agents. While these complications may resolve when the drug is discontinued, complete resolution does not always occur. Although these adverse reactions are believed to be related to the ergoline structure of these dopamine agonists, whether other, non-ergot-derived dopamine agonists, such as ONAPGO, can cause these reactions is unknown.
5.15 Priapism
In clinical studies of intermittent apomorphine injection, painful erections were reported in 3 of 361 men treated with subcutaneous injection, and one patient withdrew from therapy because of priapism. Although no patients in the clinical studies required surgical intervention, severe priapism may require surgical intervention.
5.16 Retinal Pathology in Albino Rats
In a two-year carcinogenicity study of apomorphine in albino rat, retinal atrophy was detected at all subcutaneous doses tested (up to 0.8 mg/kg/day or 2 mg/kg/day in males or females, respectively; less than the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 98 mg/day on a body surface area [mg/m 2] basis). Retinal atrophy/degeneration has been observed in albino rats treated with other dopamine agonists for prolonged periods (generally during two-year carcinogenicity studies). Retinal findings were not observed in a 39-week subcutaneous toxicity study of apomorphine in monkey at doses up to 1.5 mg/kg/day, a dose similar to the MRHD on a mg/m 2basis. The clinical significance of the finding in rat has not been established but cannot be disregarded because disruption of a mechanism that is universally present in vertebrates (e.g., disk shedding) may be involved.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious Adverse Reactions After Intravenous Administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Nausea and Vomiting [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Falling Asleep During Activities of Daily Living and Somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Syncope/Hypotension/Orthostatic Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Falls [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Infusion Site Reactions and Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hallucinations/Psychotic-Like Behavior [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Dyskinesia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Hemolytic Anemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Impulse Control/Compulsive Behaviors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Cardiac Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- QTc Prolongation and Potential for Proarrhythmic Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Fibrotic Complications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
- Priapism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice. A total of 197 Parkinson's disease patients were exposed to ONAPGO in Study 1 and subsequent open-label studies.
In Study 1 [see Clinical Studies (14)], the most common adverse reactions (incidence 10% or greater in patients treated with ONAPGO and at a rate at least twice the placebo rate) were infusion site nodule, nausea, somnolence, infusion site erythema, dyskinesia, headache, and insomnia.
Table 1 presents adverse reactions that occurred in ≥5% of patients treated with ONAPGO and that occurred more frequently than placebo in patients who were enrolled in Study 1.
| ONAPGO
*
N=54 % | Placebo
N=53 % |
|
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Infusion site nodule | 44 | 0 |
| Nausea | 22 | 9 |
| Somnolence | 22 | 4 |
| Infusion site erythema | 17 | 4 |
| Dyskinesia | 15 | 0 |
| Headache | 13 | 4 |
| Insomnia | 11 | 2 |
| Dizziness | 9 | 4 |
| Hypotension | 7 | 0 |
| Asthenia | 7 | 0 |
| Fatigue | 7 | 2 |
| Constipation | 7 | 6 |
| Vomiting | 7 | 4 |
Infusion Site Reactions
In Study 1, infusion site reactions were most commonly reported as nodule formation (44% of patients treated with ONAPGO compared to no patients who received placebo) or erythema (17% of patients treated with ONAPGO compared to 4% of patients who received placebo).
Less Common Adverse Reactions
Other adverse reactions, including hallucinations, psychotic disorder, impulse control disorder, prolonged QT interval, and infusion site infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)] , have been reported in patients treated with ONAPGO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.10. 5.12)].
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation of ONAPGO Treatment
Six (11%) of patients treated with ONAPGO reported one of the following adverse reactions as the reason for discontinuing from Study 1: nausea, orthostatic intolerance, visual hallucination, gait disturbance, infusion site nodule, and hypotension. None of the patients who received placebo discontinued from Study 1 because of an adverse reaction.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of apomorphine. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hematologic and Lymphatic Systems: hemolytic anemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 5HT 3Antagonists
Based on reports of profound hypotension and loss of consciousness when apomorphine was administered with ondansetron, the concomitant use of ONAPGO with 5HT 3antagonists, including antiemetics (e.g., ondansetron, granisetron, palonosetron) and alosetron, is contraindicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
7.2 Antihypertensive Medications and Vasodilators
In clinical studies with intermittent subcutaneous administration of apomorphine, the following adverse reactions were experienced more commonly in patients receiving concomitant antihypertensive medications or vasodilators (n=94) than in patients not receiving these medications (n=456): hypotension (10% vs 4%) myocardial infarction (3% vs 1%), [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.11)].
In a study of healthy subjects, concomitant administration of 0.4 mg sublingual nitroglycerin with subcutaneous apomorphine caused greater decreases in blood pressure than with subcutaneous apomorphine alone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Patients treated with ONAPGO should lie down before and after taking sublingual nitroglycerin to decrease the potential risks associated with hypotension .
7.3 Alcohol
In a study of healthy subjects, concomitant administration of high dose (0.6 g/kg) or low dose (0.3 g/kg) ethanol with apomorphine caused greater decreases in blood pressure than with apomorphine alone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . Patients should be advised not to consume alcohol while treated with ONAPGO because it may cause greater decreases in blood pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] .
7.4 Dopamine Antagonists
Because ONAPGO is a dopamine agonist, it is possible that concomitant use of dopamine antagonists, such as the neuroleptics (phenothiazines, butyrophenones, thioxanthenes) or metoclopramide, may diminish the effectiveness of ONAPGO. Antiemetics with anti-dopaminergic actions should be avoided [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Patients with major psychotic disorders, treated with neuroleptics, should be treated with dopamine agonists only if the potential benefits outweigh the risks [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
7.5 Drugs Prolonging the QT/QTc Interval
Caution should be exercised when prescribing ONAPGO concomitantly with drugs that prolong the QT/QTc interval [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)] .
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with use of ONAPGO in pregnant women. In animal reproduction studies, apomorphine had adverse developmental effects in rats (increased neonatal deaths) and rabbits (increased incidence of malformation) when administered during pregnancy at clinically relevant doses. These doses were also associated with maternal toxicity. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown.
Data
Animal Data
No adverse developmental effects were observed when apomorphine (0.3, 1, or 3 mg/kg/day) was administered by subcutaneous injection to pregnant rats throughout organogenesis; the highest dose tested is less than the maximum recommended human dose (MRRD) of 98 mg on a mg/m 2basis. Administration of apomorphine (0.3, 1, or 3 mg/kg/day) by subcutaneous injection to pregnant rabbits throughout organogenesis resulted in an increased incidence of malformations of the heart and/or great vessels at the mid and high doses; maternal toxicity was observed at the highest dose tested. The no-effect dose (0.3mg/kg/day) for adverse effects is less than the MRHD on a mg/m 2basis.
Apomorphine (0.3, 1, or 3 mg/kg/day), administered by subcutaneous injection to female rats throughout gestation and lactation, resulted in increased offspring mortality at the highest dose tested, which was associated with maternal toxicity. There were no effects on developmental parameters or reproductive performance in surviving offspring. The no-effect dose (1 mg/kg/day) for developmental toxicity is less than the MRHD on a mg/m 2basis.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of apomorphine in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for ONAPGO and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from ONAPGO or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of comorbid disease or other drug therapy.
Clinical studies of ONAPGO did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Clinical experience with intermittent subcutaneous use of apomorphine has shown that the following adverse reactions were reported more frequently in patients 65 years of age or older (n=311) compared to patients less than 65 years of age (n=239): confusion; hallucinations; serious adverse reactions (life-threatening events or events resulting in hospitalization and/or increased disability); falls (experiencing bone and joint injuries); cardiovascular events; respiratory disorders; gastrointestinal events; and discontinuation of treatment as a result of one or more adverse reactions.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The initial extra dose of ONAPGO should not exceed 1 mg in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment because of increased apomorphine concentration and exposure (C maxand AUC) in these patients. Studies in patients with severe renal impairment have not been conducted [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Exercise caution and closely monitor if ONAPGO is administered to patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment because of increased apomorphine concentration and exposure (C maxand AUC) in these patients. Studies in patients with severe hepatic impairment have not been conducted [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
9.2 Abuse
In premarketing clinical experience, apomorphine did not reveal any tendency for a withdrawal syndrome or any drug-seeking behavior. However, there are rare postmarketing reports of abuse of medications containing apomorphine. In general, these reports consist of patients taking increasing doses of medication in order to achieve a euphoric state. Abuse is the intentional, non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, for its desirable psychological or physiological effects.
11. Onapgo Description
ONAPGO (apomorphine hydrochloride) contains apomorphine hydrochloride hemihydrate, a non-ergoline dopamine agonist. It is chemically designated as 6aβ-aporphine-10,11-diol hydrochloride hemihydrate with a molecular formula of C 17H 17NO 2∙HCl∙½H 2O. Its structural formula and molecular weight are:
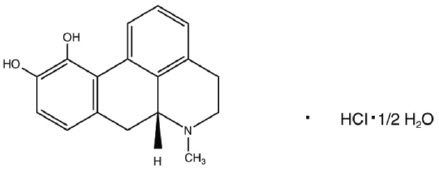
Apomorphine hydrochloride hemihydrate appears as minute, white or grayish-white glistening crystals or as white powder that is soluble in water at 80°C. ONAPGO injection is a clear, almost colorless, sterile solution for subcutaneous infusion and is available in 98 mg/20 mL (4.9 mg/mL) single-dose prefilled cartridges. The solution has a pH of 3.0 -4.0. Each mL contains 4.9 mg of apomorphine hydrochloride (equivalent to 4.27 mg apomorphine) and 0.5 mg of sodium metabisulfite in water for injection. In addition, each mL may contain hydrochloric acid used to adjust the pH.
12. Onapgo - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
ONAPGO is a non-ergoline dopamine agonist with high in vitro binding affinity for the dopamine D4 receptor, and moderate affinity for the dopamine D2, D3, and D5, and adrenergic α1D, α2B, α2C receptors. The precise mechanism of action of ONAPGO as a treatment for Parkinson's disease is unknown, although it is believed to be due to stimulation of post-synaptic dopamine D2-type receptors within the caudate-putamen in the brain.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Prolongation of the QTc Interval and Cardiac Electrophysiology
In a thorough QT study, the mean increase in QTcF was 12.5 ms (90% two-sided upper confidence interval = 18.0 ms) after administration of a continuous dose of ONAPGO 6 mg/hr (maximum recommended infusion rate) in healthy subjects. A mean increase in QTcF of 14.6 ms (90% two-sided confidence interval = 20.1 ms) was observed at a dose and exposure similar to that expected with the maximum recommended total daily dosage of 98 mg. The maximum placebo-corrected increase in heart rate was 14.1 bpm (90% two-sided upper confidence interval = 17.4 bpm) at the dose and exposure similar to that expected with the maximum recommended total daily dose of 98 mg.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After subcutaneous administration, apomorphine appears to have bioavailability equal to that of intravenous administration. Steady-state concentrations are reached in approximately two hours after initiation of a continuous dose. If an extra dose is administered at the initiation of the continuous dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] , time to reach half (50%) of infusion steady-state concentrations can be shortened by 50-75%. If an extra dose is administered two hours or later following initiation of a continuous dose, the supplemental exposure from the extra dose reaches peak concentration in 20-40 minutes.
Distribution and Binding
The plasma-to-whole blood apomorphine concentration ratio is equal to one. Mean (range) apparent volume of distribution was 218 L (123 to 404 L). Protein binding in humans is 89% and concentration independent.
Elimination
The mean apparent clearance of apomorphine from plasma is 261 to 280 L/hr for ONAPGO with infusion rates ranging from 2 to 6 mg/hr. After administration of an extra dose, the mean elimination half-life is approximately 40 minutes.
Metabolism
Apomorphine metabolism is primarily via conjugation. Within 0.5 hours of administering a subcutaneous dose of 14C-apomorphine, only 8.3% of plasma radioactivity was apomorphine, while 83% was associated with the apomorphine sulfate, 3.5% with apomorphine glucuronide, and 1% with nor-apomorphine glucuronide.
Excretion
Eighty-six percent of the subcutaneously administered dose of 14C-apomorphine was recovered in the urine within 48 hours as apomorphine sulfate, apomorphine glucuronide and nor-apomorphine glucuronide. Another 4.6% of the administered dose was recovered in the feces over 144 hours as apomorphine sulfate, apomorphine glucuronide, and apomorphine.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of apomorphine were observed based on age, gender, weight, duration of Parkinson's disease, levodopa dose, or duration of therapy.
Renal Impairment
In a study comparing patients with renal impairment (moderately impaired as determined by estimated creatinine clearance) to healthy matched volunteers, the AUC 0-infand C maxwere increased by approximately 16% and 50%, respectively, following a single subcutaneous administration of apomorphine into the abdominal wall. The mean time to peak concentrations and the mean terminal half-life of apomorphine were unaffected by the renal status of the individual. Studies in patients with severe renal impairment have not been conducted [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)] .
Hepatic Impairment
In a study comparing patients with hepatic impairment (moderately impaired as determined by the Child-Pugh classification method) to healthy matched volunteers, the AUC 0-infand C maxvalues were increased by approximately 10% and 25%, respectively, following a single subcutaneous administration of apomorphine into the abdominal wall. Studies in patients with severe hepatic impairment have not been conducted [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)] .
Drug Interaction Studies
Carbidopa/levodopa
Pharmacokinetics of levodopa were unchanged when subcutaneous apomorphine and levodopa were co-administered in patients. However, motor response differences were significant.
Ethanol and Nitroglycerin
Co-administration of low dose ethanol (0.3 g/kg), or nitroglycerin (0.4 mg) with an apomorphine injection dose of 6 mg in healthy individuals did not have a significant impact on the pharmacokinetics of apomorphine, but high dose ethanol (0.6 g/kg), equivalent to approximately 3 standardized alcohol-containing beverages, increased the C maxof apomorphine by about 63%. The hypotensive effect of apomorphine was increased by the concomitant use of alcohol or of sublingual nitroglycerin. When high-dose ethanol (0.6 g/kg) and subcutaneous apomorphine were concomitantly administered to healthy subjects, the mean largest decrease (the mean of each subject's largest drop in blood pressure measured within the 6-hour period following administration of subcutaneous apomorphine) for supine systolic and diastolic blood pressure was 9.1 mm Hg and 10.5 mm Hg, respectively. The mean largest standing systolic and diastolic blood pressure decrease was 11.3 mm Hg and 12.6 mm Hg, respectively. In some individuals, the decrease was as high as 61 mm Hg and 51 mm Hg, respectively, for standing systolic and diastolic blood pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Drug Interactions (7.2, 7.3)].
Other Drugs Eliminated Via Hepatic Metabolism
Based upon an in vitrostudy, cytochrome P450 enzymes play a minor role in the metabolism of apomorphine. In vitrostudies have also demonstrated that drug interactions are unlikely due to apomorphine acting as a substrate, an inhibitor, or an inducer of cytochrome P450 enzymes.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Lifetime carcinogenicity studies of apomorphine were conducted in male (0.1, 0.3, or 0.8 mg/kg/day) and female (0.3, 0.8, or 2 mg/kg/day) rats. Apomorphine was administered by subcutaneous injection for 22 months or 23 months, respectively. In males, there was an increase in Leydig cell tumors at the highest dose tested. This finding is of questionable significance because the endocrine mechanisms believed to be involved in the production of Leydig cell tumors in rats are not relevant to humans. No drug-related tumors were observed in females. The highest doses tested in males and females are less than the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) on a mg/m 2basis.
In a 26-week carcinogenicity study in p53-knockout transgenic mice, there was no evidence of carcinogenic potential when apomorphine was administered by subcutaneous injection at doses up to 20 mg/kg/day in males or 40 mg/kg/day in females.
Mutagenesis
Apomorphine was mutagenic in the in vitrobacterial reverse mutation (Ames) and the in vitromouse lymphoma tkassays. Apomorphine was clastogenic in the in vitrochromosomal aberration assay in human lymphocytes and in the in vitromouse lymphoma tkassay. Apomorphine was negative in the in vivomicronucleus assay in mice.
Impairment of Fertility
Apomorphine was administered subcutaneously at doses up to 3 mg/kg/day to male and female rats prior to and throughout the mating period and continuing in females through gestation day 6. There was no evidence of adverse effects on fertility or on early fetal viability. The highest dose tested is less than the MRHD on a mg/m 2basis. A significant decrease in testis weight was observed in a 39-week study in cynomolgus monkey at all subcutaneous doses tested (0.3, 1, or 1.5 mg/kg/day); the lowest dose tested is less than the MRHD on a mg/m 2basis.
In a published fertility study, apomorphine was administered to male rats at subcutaneous doses of 0.2, 0.8, or 2 mg/kg prior to and throughout the mating period. Fertility was reduced at the highest dose tested.
14. Clinical Studies
Study 1 (NCT02006121) was a multicenter, parallel-group, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of ONAPGO subcutaneous infusion in patients with Parkinson's disease who had motor fluctuations while receiving carbidopa/levodopa and other concomitant medications to treat PD. The study design included a double-blind, 12-week treatment period, inclusive of 1-4 weeks of dose titration and then continued treatment with study medication at an individualized, stable dosage. Patients then had the option to receive ONAPGO in a 52-week, open-label treatment period.
The modified intent-to-treat (mITT) population included 53 patients treated with ONAPGO and 51 patients who received placebo. At baseline, patients experienced OFF episodes averaging ≥3 hours per day. In the mITT population, the mean age was 63.4 years, 62% were male, and 100% were White. At baseline, all patients were taking at least one concomitant medication to treat PD (e.g., dopamine agonist 87%, COMT-inhibitor 58%, MAO-B inhibitor 40%, amantadine 27%) in addition to oral immediate or extended-release levodopa plus a dopa decarboxylase inhibitor. The mean duration of PD was 11.9 years in the ONAPGO-treated group and 10.8 years in the placebo-treated group.
During titration, adjustments in concomitant medications to treat PD were made when clinically indicated. All patients treated with ONAPGO in the double-blind study were maintained on levodopa.
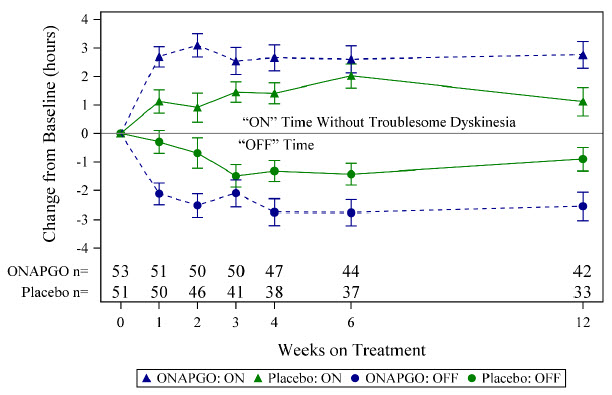
The primary efficacy endpoint for Study 1 was the change in total daily OFF time assessed from baseline to the end of the 12-week treatment period based on patient diaries. A key secondary endpoint was the change in daily ON time without troublesome dyskinesia from baseline to the end of the 12-week treatment period. There was a statistically significant reduction in the amount of daily OFF time in patients treated with ONAPGO compared to placebo (p=0.0114; see Table 2). There was also a statistically significant increase in daily ON time without troublesome dyskinesia in patients treated with ONAPGO compared to placebo (p=0.0188; see Table 3).
| N | Baseline (hours)
(mean ± SD) | LS Mean Change from Baseline at Week 12
(hours) (mean ± SE) | LSD
*vs Placebo
(95% CI) † p-value |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo | 51 | 6.72 ± 2.547 | -0.90 ± 0.416 | -- |
| ONAPGO | 53 | 6.69 ± 2.224 | -2.55 ± 0.487 | -1.65
(-2.91, -0.38) p=0.0114 |
| N | Baseline (hours)
(mean ± SD) | LS Mean Change from Baseline at Week 12
(hours) (mean ± SE) | LSD
*vs Placebo
(95% CI) † p-value |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo | 51 | 8.64 ± 2.496 | 1.12 ± 0.500 | -- |
| ONAPGO | 53 | 8.56 ± 2.329 | 2.76 ± 0.471 | 1.64
(0.28, 3.00) p=0.0188 |
In addition, the time course showed numerically greater improvement in daily OFF time and daily ON time without troublesome dyskinesia in patients treated with ONAPGO compared to placebo, at all post-baseline timepoints (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Mean Change from Baseline in Daily OFF Time and ON Time Without Troublesome Dyskinesia
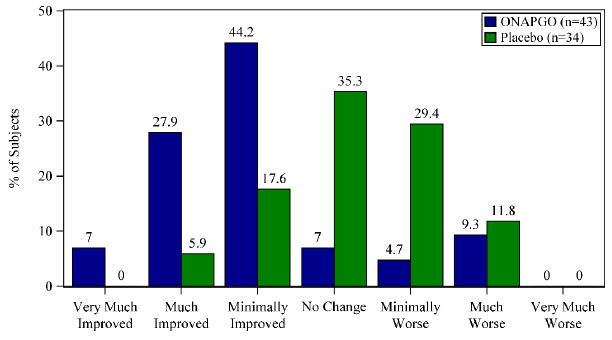
A patient reported outcome, the Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) was also assessed. The PGIC evaluates the change in Parkinson's disease symptoms as perceived by the patient in a seven-point single-item scale ranging from 'very much worse' to 'very much improved' (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Week 12 Patient Global Impression of Change
16. How is Onapgo supplied
16.1 How Supplied
ONAPGO injection is supplied as one carton (NDC 27505-006-05) that contains five single-dose prefilled glass cartridges, each containing 98 mg/20 mL (4.9 mg/mL) apomorphine hydrochloride as a clear, almost colorless solution.
The ONAPGO Pump Kit, ONAPGO Cartridge Holders, and appropriate infusion sets are supplied separately.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Administration Information
Refer patients to the Instructions for Use for complete administration instructions. Inform patients of aseptic technique and of subcutaneous administration site selection and rotation [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Advise patients that a new single-dose cartridge and cartridge holder and a new infusion line should be used each day.
Advise patients that ONAPGO is intended only for subcutaneous use and must not be given intravenously because of the risk of serious complications, such as thrombus formation and pulmonary embolism due to crystallization [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
Hypersensitivity/Allergic Reactions
Advise patients that hypersensitivity/allergic reactions characterized by urticaria, rash, pruritus, and/or various manifestations of angioedema may occur because of ONAPGO or any of its excipients, including a sulfite (i.e., sodium metabisulfite). Inform patients with a sulfite sensitivity that they may experience various allergic-type reactions, including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening asthmatic attacks [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)] . Advise patients who experience any hypersensitivity/allergic reaction to ONAPGO that they should not take ONAPGO again [see Contraindications (4)].
Nausea and Vomiting
Advise patients that they may experience nausea and vomiting, which may be severe. Advise patients that their ONAPGO dosage may be adjusted to start at 1mg/hr, and titration can be based upon effectiveness and tolerability. Treatment with an antiemetic that is a non-5HT3 antagonist may be used if needed. Oral trimethobenzamide 300 mg 3 times per day for 3 days prior to starting ONAPGO infusion has been used in clinical studies to help lessen these symptoms. Advise patients that ONAPGO taken with trimethobenzamide may increase the risk for somnolence, dizziness, and falls, and to consult their healthcare provider before discontinuing trimethobenzamide [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Falling Asleep Suddenly and Sedation/Sleepiness
Alert patients to the potential sedating effects of ONAPGO, including somnolence and falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living. Instruct patients not to drive a car or engage in other potentially dangerous activities until they have gained sufficient experience with ONAPGO to gauge whether or not it affects their mental and/or motor performance adversely. Advise patients that if increased somnolence or episodes of falling asleep during activities of daily living (e.g., watching television, passenger in a car, etc.) occur, they should not drive or participate in potentially dangerous activities until they have contacted their physician [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hypotension/Orthostatic Hypotension
Advise patients that they may develop postural (orthostatic) hypotension with or without symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, syncope, and sometimes sweating. Hypotension and/or orthostatic symptoms may occur more frequently during initial therapy or with an increase in dose at any time (cases have been seen after months of treatment). Instruct patients to rise slowly after sitting or lying down while using ONAPGO. Inform patients that alcohol and nitroglycerin (and possibly other vasodilators and antihypertensive medications) may worsen the potential effects of hypotension caused by ONAPGO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Instruct patients ideally to lie down before taking sublingual nitroglycerin and to remain supine and avoid standing for at least 45 minutes after nitroglycerin. Instruct patients to avoid alcohol while using ONAPGO.
Falls
Alert patients that they may have increased risk for falling when using ONAPGO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Infusion Site Reactions and Infections
Inform patients that infusion of ONAPGO may result in infusion site reactions, including, but not limited to nodules, erythema, bruising, and infection. Infusion site infections were reported in <5% of patients on ONAPGO in clinical trials [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)and Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . Instruct patients to change the infusion site every day and to observe proper aseptic technique [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)and Instructions for Use] .
Hallucinations and/or Psychotic-Like Behavior
Inform patients that ONAPGO may cause hallucinations or other manifestations of psychotic-like behavior. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider if they have a major psychotic disorder or are taking any treatments for psychosis. Patients with a major psychotic disorder should also be aware that many treatments for psychosis may decrease the effectiveness of ONAPGO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] .
Dyskinesia
Inform patients that ONAPGO may cause and/or exacerbate pre-existing dyskinesia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Hemolytic Anemia
Inform patients and caregivers that hemolytic anemia may occur and to contact their healthcare provider if they develop any signs or symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)] .
Impulse Control / Compulsive Behaviors
Patients and their caregivers should be alerted to the possibility that they may experience intense urges to spend money uncontrollably, intense urges to gamble, increased sexual urges, binge eating and/or other intense urges and the inability to control these urges while using ONAPGO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Cardiac Events
Inform patients that ONAPGO may cause cardiac (and cerebral) ischemia, and these outcomes could possibly be related to significant hypotension/orthostatic hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
QTc Prolongation and Potential for Proarrhythmic Effects
Alert patients that ONAPGO may cause QTc prolongation and might produce proarrhythmic effects that could cause torsades de pointes and sudden death. Palpitations and syncope may signal the occurrence of an episode of torsades de pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Priapism
Advise patients that ONAPGO may cause prolonged painful erections and that if this occurs, they should seek medical attention immediately [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
ONAPGO Manufactured for: MDD US Operations, LLC, 9715 Key West Ave., Rockville, MD 20850.
MDD US Operations, LLC is a subsidiary of Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
ONAPGO is a trademark of BRITUSWIP LTD.
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
© 2025 MDD US Operations, LLC, a subsidiary of Supernus Pharmaceuticals Inc.
RA-ONG-V1
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Issued: 2/2025 | |||
| PATIENT INFORMATION
ONAPGO™ (on-AP-goh) (apomorphine hydrochloride) injection, for subcutaneous use |
||||
| What is ONAPGO? | ||||
| ONAPGO is a prescription medicine used to treat motor fluctuations (OFF episodes) in adults with advanced Parkinson's disease. | ||||
| It is not known if ONAPGOis safe and effective in children. | ||||
| Who should not use ONAPGO? | ||||
| Do not use ONAPGO if you are: | ||||
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
| What should I tell my healthcare provider before using ONAPGO? | ||||
| Before you start using ONAPGO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: | ||||
|
||||
| Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription (over-the-counter) medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. | ||||
| ONAPGO and certain other medicines may affect each other and how they work. Using ONAPGO with other medicines can cause serious side effects. | ||||
|
||||
| Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider or pharmacist when you get a new medicine. | ||||
| How should I use ONAPGO? | ||||
|
||||
| What should I avoid while using ONAPGO? | ||||
|
||||
| What are the possible side effects of ONAPGO? | ||||
| ONAPGO may cause serious side effects, including: | ||||
|
||||
| Other common side effects of ONAPGO include: | ||||
|
||||
| Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. | ||||
| These are not all the possible side effects of ONAPGO. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. | ||||
| Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | ||||
| How should I store ONAPGO? | ||||
|
||||
| Keep ONAPGO and all medicines out of the reach of children. | ||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of ONAPGO. | ||||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use ONAPGO for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ONAPGO to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. | ||||
| You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about ONAPGO that is written for health professionals. | ||||
| What are the ingredients in ONAPGO? | ||||
| Active ingredient:apomorphine hydrochloride | ||||
| Inactive ingredients:hydrochloric acid, sodium metabisulfite in water for injection. | ||||
| Manufactured for: MDD US Operations, LLC, 9715 Key West Ave., Rockville, MD 20850. | ||||
| MDD US Operations, LLC is a subsidiary of Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | ||||
| MDD US Operations, LLC is the exclusive licensee and distributor of ONAPGO in the United States and Its territories. | ||||
| ONAPGO is a trademark of BRITUSWIP LTD. | ||||
| ©2025 MDD US Operations, LLC, a subsidiary of Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | ||||
| For more information, go to ONAPGO.comor call 1-833-366-2746 | ||||
RA-ONG-PPI-V1
Patient INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE ONAPGO™ (on-AP-goh)

This Instructions for Use contains information on how to use the ONAPGO Infusion System.
Please see the Important Safety Information, Full Prescribing Information, and Patient Information for ONAPGO.
MDD US Operations, LLC
| Table of Contents | 3 |
| ONAPGO Infusion System | 5 |
| Indication for Use | 5 |
| Introduction to the Infusion System | 5 |
| Important Information | 6 |
| Pump Warnings and Precautions | 6 |
| Pump Kit | 9 |
| Pump Diagram | 9 |
| Pump Screen Icons | 11 |
| Other Supplies Provided Separately | 12 |
| Storage | 13 |
| Glass Drug Cartridge Storage | 13 |
| Pump Storage | 13 |
| Important Information You Need to Know Before Infusing ONAPGO | 13 |
| Important Safety Information | 13 |
| Check Pump Settings | 14 |
| Step 1: Check Pump Settings | 14 |
| Setup | |
| Set Up the Pump | 23 |
| Step 2: Wash Your Hands and Gather Supplies | 23 |
| Step 3: Assemble Plastic Cartridge Holder | 25 |
| Step 4: Prime the Infusion Line | 33 |
| Prepare the Infusion Site | 38 |
| Step 5: Select and Clean the Infusion Site | 38 |
| Step 6: Connect the Cannula to the Body | 39 |
| Connect the Infusion Line to Body | 40 |
| Step 7: Connect the Infusion Line to the Cannula | 40 |
| Start the Infusion | 41 |
| Step 8: Start the Infusion | 41 |
| Wear the Pump | 43 |
| Step 9: Wear the Pump | 43 |
| Reading the Pump Screen | 45 |
| ON (Infusing Screen) | 45 |
| Paused | 46 |
| Primed | 46 |
| Off | 46 |
| Extra Dose / Pause / End | |
| Give a + Dose (Extra Dose) | 51 |
| Step 10: Give an Extra Dose | 51 |
| Another Way of Giving an Extra Dose | 53 |
| Understanding the Extra Dose Features | 54 |
| Pause and Resume the Infusion | 55 |
| Step 11: Pausing the Infusion | 55 |
| Step 12: Resuming the Infusion | 57 |
| Ending the Infusion | 59 |
| Step 13: Ending the Infusion Early | 59 |
| Step 14: Ending the Infusion Regularly | 64 |
| Disconnecting in an Emergency | 68 |
| Step 15: Disconnecting in an Emergency | 68 |
| Pump Care | |
| Disposal | 73 |
| Glass Drug Cartridge, Plastic Cartridge Holder, and Infusion Line Disposal | 73 |
| Pump Disposal | 73 |
| Cleaning and Disinfecting the Pump | 74 |
| Step 16: Clean and Disinfect the Pump | 75 |
| Maintenance and Repair | 75 |
| Replacing the Battery | 81 |
| Step 17: Replacing the Battery | 81 |
| Alarms & Errors | |
| Alarms and Troubleshooting | 91 |
| Error Codes | 91 |
| Troubleshooting: If Your Infusion Line Did Not Prime | 98 |
| Symbols Used on the ONAPGO Pump | 99 |
| Technical characteristics of the Pump | 100 |
| Electromagnetic Compatibility | 102 |
| Tests of Accuracy | 104 |
| Limited Warranty | 105 |
| Contact & Support | 105 |
ONAPGO Infusion System
| Indication for Use |
The ONAPGO Infusion Pump is for the subcutaneous infusion of ONAPGO (apomorphine hydrochloride). ONAPGO is a prescription medicine used to treat motor fluctuations in adults with advanced Parkinson's disease (PD).
Only use the ONAPGO Infusion Pump if you have received instruction and training on how to correctly and safely use it. If you cannot use ONAPGO by yourself, contact your healthcare provider.
Only the accessories supplied by CANÈ S.p.A. (plastic cartridge holder and supplies provided in the infusion pump kit) may be used in conjunction with this pump. The pump must be set (programmed) by a trained healthcare provider or a trained nurse provided by the company (nurse navigator).
| Introduction to the Infusion System |
Below are common terms used throughout this Instructions for Use.
- Pump:controls the rate and amount of ONAPGO delivered to the body. It is programmed by a healthcare provider based on the patient's prescription. The pump displays the status of medicine delivery.
- Priming:refers to the task of removing all air from the infusion line (fluid pathway) before the infusion line is connected to the body.
- Flow Rate:the constant flow of ONAPGO given to the body over an extended period of time. The flow rate is expressed as milligrams per hour (mg/hr).
- Infusion Time:the total time that ONAPGO is infused per day.
-
Extra Dose (+ Dose):a boost of ONAPGO (bolus dose) given over a short period of time in addition to the prescribed flow rate. Your healthcare provider will decide the number of extra doses that you could have each day. Your healthcare provider might prescribe an extra dose to be used as follows:
- when you start the infusion each day, which can help the medicine work faster.
- When you restart your medicine after not having it for 1 hour or more.
- if you have an OFF episode during an infusion.
- Extra Dose (+ Dose) Lock:the amount of time before another extra dose can be given.
- Pump Settings:the patient's prescribed Flow Rate, Maximum Infusing Time Per Day, + Dose Quantity, + Dose Volume, and + Dose Lock. These settings can only be changed by a healthcare provider or clinical nurse navigator.
| Important Information |
- Read this entire Instructions for Use before using the infusion system.
If any of the information is not clear, or if you have any questions, please contact Customer Support at 1-833-3ONAPGO (1-833-366-2746) - Understanding how to use the pump and the potential alarms will help you avoid harm.
- You may hear motor noise when the pump is On and delivering ONAPGO. This noise is normal and means the pump is working correctly.
-
The pump screen falls asleep (goes dark) after 30 seconds of inactivity. Press the UP ARROW button (
 ) to wake up the screen.
) to wake up the screen.
| Pump Warnings and Precautions |
Failure to follow the warnings and precautions below could cause return of your symptoms, damage to the pump, serious injury, or may lead to death in rare cases.
 WARNINGS:
WARNINGS:
- Always check that the pump settings match the prescription before starting an infusion.
See the Check Pump Settingssection on pages 14 to 18 for how to check the pump settings to make sure they are correct. If any of these settings do not match the prescription, contact your healthcare provider and/or clinical nurse navigator. - The patient should receive no more than 98 mg of ONAPGO every 24 hours. This corresponds to one complete cartridge per day. Only use the pump with ONAPGO (apomorphine hydrochloride). ONAPGO comes in a glass cartridge that contains 98 mg/20 mL (4.9 mg/mL) of medicine. Only use the pump system within the temperatures on page 13 and other conditions for use in this Instructions for Use. Using the medicine and pump outside of these conditions may result in a system alarm.
- Only use the pump with the supplied plastic cartridge holder. Any other cartridge holder could damage the Pump and cause harm. Any non- approved cartridge holder voids warranty. MMD US Operations, LLC or its manufacturer is not responsible for any damages or injuries that happen if a different cartridge holder is used.
- Use the infusion set that is provided by your specialty pharmacy. The use of an inappropriate infusion set can cause loss or leakage of drug. Use a new infusion set at the beginning of every infusion. Ask your healthcare provider and/or clinical nurse navigator for more information.
- Do notprime the infusion line when it is connected to the body.
- Do notinsert the cannula into a blood vessel.
- If the medicine is cloudy, green, or contains particles, throw the glass drug Cartridge in a sharps container. (See the Disposalsection on page 73 for information on how to safely throw away ONAPGO). Get a new cartridge for your infusion.
- Clean the top of the glass drug cartridge with a new alcohol wipe before attaching the plastic cartridge holder.
- Always clean the selected infusion site with a new alcohol wipe. Make sure the site is dry before going on to the next step.
- Before starting your infusion, check for any leaks. Do notuse the pump if there are leaks. Contact Customer Support at 1-833-3ONAPGO (1-833-366-2746).
- Be careful when handling the Infusion Set to prevent needle sticks.
- Supplies included with your pump could pose a choking hazard for small children. Make sure that the pump and all supplies are kept away from small children.
- Supplies included with your pump (such as the infusion line) could pose a strangulation hazard. Arrange the infusion line to minimize the risk of strangulation. Make sure that these parts are stored in a secure place when not in use.
- Throw away (discard) the battery if it becomes damaged. Use a new, unopened battery.
See Replacing the Batterysection on pages 81 to 85 (Steps 17.1 through 17.9) for instructions on how to replace the battery. - The pump can detect a blockage in the line. If a partial blockage occurs, the pump will work the way it should until the line has a full blockage. An alarm will sound if the line has a full blockage.
- Be sure to disconnect the infusion line from the body before clearing a blockage alarm. If a blockage alarm is cleared while the infusion line is still attached, you may receive a small amount of additional medicine. See the Alarms and Troubleshootingsection on page 91.
- Confirm that the plastic cartridge holder and infusion line packaging are sealed and have not been damaged. If the packaging looks damaged, throw it away in a sharps container, and do not use it for your infusion. See the Disposalsection on page 73 for information on how to safely throw away ONAPGO. Use a new, undamaged product.
- If the battery becomes hot, do not continue with your infusion and call Customer Support at 1-833-3ONAPGO (1-833-366-2746).
- If your glass drug cartridge breaks while assembled in the plastic cartridge holder, do not separate it from the plastic cartridge holder. Disconnect the assembled cartridge from the pump and throw both away in a sharps container. See the Disposalsection on page 73 for information on how to safely throw away ONAPGO.
- Do notsnag or kink the infusion line while wearing the pump. Snagging or kinking the infusion line can cause a blockage (occlusion) or an interruption to the infusion.
- Always check the expiration date on the infusion set, plastic cartridge holder and glass drug cartridge prior to use. Do notuse expired materials.
- Do notuse expired or rechargeable batteries with the pump.
- If the glass drug cartridge is dropped, it should not be used and should be thrown away in a sharps container.
- If the pump gets wet, pause the infusion, disconnect the infusion line from the body, and store the pump in a dry place. This includes when swimming, showering, or excessively sweating.
- If your ONAPGO pump has expired, do not use it. Call your healthcare provider and/or clinical nurse navigator for a replacement of your ONAPGO pump.
 PRECAUTIONS:
PRECAUTIONS:
- Do notuse sharp objects to press the pump buttons. Only use your fingertips to press the pump buttons.
- Do notuse a damaged pump. If you have any concern about the correct functioning of the pump, or how to respond to an error, contact Customer Support at 1-833-3ONAPGO (1-833-366-2746).
- Read the infusion set Instructions for Use before using the infusion line.
- All pump settings, including sounds, are locked for your safety.
- Do notattempt to change the pump's prescribed settings. These can only be changed by a healthcare provider and/or clinical nurse navigator.
- Do notdisconnect the infusion line from the plastic cartridge holder while the pump is infusing.
- Only clean the infusion site with an alcohol wipe. Do not clean the infusion site with or apply disinfectants, perfumes, deodorants, or lotions to it.
- Free-flow is if gravity causes the drug to come out of the cartridge. The pump's pusher is made to have a secure connection with the rubber plunger in the cartridge to prevent free flow of the drug.
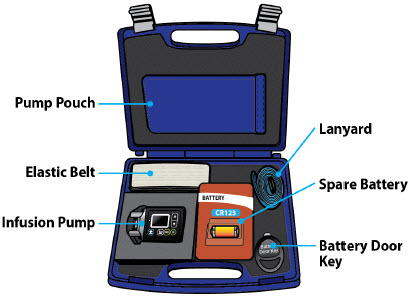
| Pump Kit (Figure A) |
| Pump Diagram (Figures B, C, and D) |
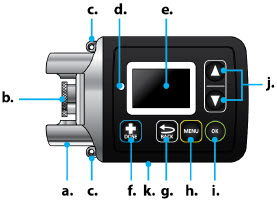 Figure B Figure B |  Figure D | |
 Figure C Figure C |
All buttons will respond with a single press. If the screen is dark, press the UP ARROW button (
 ) to wake up the screen.
) to wake up the screen.
| Item | Pump Feature | Description |
|---|---|---|
| a | Cartridge Connection | Area where assembled glass drug cartridge and plastic cartridge holder is attached to the pump. |
| b | Pump Pusher | Pushes ONAPGO from the glass drug cartridge into the infusion line. |
| c | Neck Lanyard Clips | Slots to clip on the lanyard. |
| d | LED | Lights up when an error cannot be displayed on the screen. |
| e | Screen | Where messages and menus appear. |
| f |
| +DOSE button gives an extra dose (+ dose) (if prescribed). |
| g |
| BACK button allows you to return to a previous screen, menu, or cancel an action. |
| h |
| MENU button allows you to access the menus. |
| i |
| OK button allows you to confirm menu selections or go on to the next value. |
| j |
| UP and DOWN ARROW buttons allow you to scroll through menus. |
| k | Battery Door | Door to access the battery. |
| Pump Screen Icons |
The following table shows Icons that appear on the pump screen.
| Icon | Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Back Arrow | The back arrow is shown when checking the pump settings. This icon is used to show that pressing the BACK button will return to a previous screen (Item 'g' in Figure B). | |
 | Caution | Caution is shown when an error or alarm is occurring. | |
 | Check Mark | A check mark is shown when the pump successfully completes a task. | |
 | Droplet | A blinking droplet is shown on the Infusing Screen when an infusion is on. | |
 | Dead Battery | The dead battery is shown when the pump battery is dead and must be replaced. | |
 | Low Battery | The Low Battery is shown when the pump battery is low and should be replaced before the next infusion. | |
 | OK Arrow | The OK Arrow is shown when checking the pump settings. This icon is used to show that pressing the OK button will confirm a selection or go on to the next value (Item 'i' in Figure B). | |
 | Padlock | Padlock is shown when the +Dose (extra dose) is not available. |  |
 | Pause | Pause is shown when the infusion is paused. | |
 | +Dose (Extra Dose) | A +refers to the +Dose (extra dose) function. | |
| Other Supplies Provided Separately |
Additional supplies not in the pump kit include (Figure E):
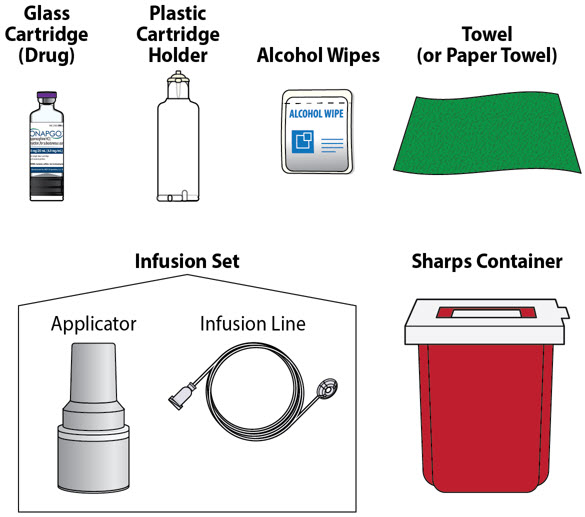 |
| Note:The plastic cartridge holder, glass drug cartridge and infusion set parts are sterile. |
| Figure E |
Storage
| Glass Drug Cartridge Storage |
Store the glass drug cartridges at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C). Store in original container.
| Pump Storage |
If the pump will not be used for 1 month or more, remove the battery. See Replacing the Batterysection on pages 81 to 85 (Steps 17.1 through 17.9) for instructions on how to remove the battery.
Store the pump in a dry place between -13°F to 158°F (-25°C to +70°C).
Keep the pump away from:
- Children and pets.
- Sources of heat or cold such as radiators, burners, stoves, freezer, or other heat or cold sources. Ask your healthcare provider or clinical nurse navigator if you are not sure.
- Direct sunlight.
- Strong electromagnetic fields such as magnets, speakers, mobile devices.
- Ionizing radiation, a type of device for radiotherapy or diagnostic radiology.
- Ultrasound devices.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) devices. The pump should not be used with an MRI.
If you are not sure about what to keep your pump away from, please contact your Customer Support at 1-833-3ONAPGO (1-833-366-2746).
Important Information You Need to Know Before Infusing ONAPGO
| Important Safety Information |
This Instructions for Use is for patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers or clinical nurse navigators and describes how to use the infusion system.
- The Instructions for Use are important for the safe and correct use of this infusion system.
- Read the entire Instructions for Use before using the infusion system.
Check Pump Settings
| Step 1: Check Pump Settings |
Confirm your pump settings match your prescription by doing the following steps.
|
| Do notstart an infusion if any of the pump settings do not match your prescription. If this happens, contact your healthcare provider or clinical nurse navigator. |
| Step 1.1
Look at the pump. If the pump screen is dark, press the Up Arrow button (
|  Figure F Figure F
|
| You will then see the Infusion Off screen (Figure G). |
|
| Step 1.2
Press the MENU button (
|
|
| Step 1.3
Highlight Settings on the screen using the DOWN ARROW button (
|  Figure I Figure I
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure J Figure J
|
| Step 1.4
Make sure the flow rate (mg/hr) matches your prescription (Figure K). | 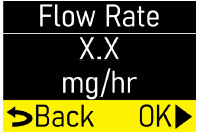 Figure K Figure K
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure L Figure L
|
| Step 1.5
Make sure the infusion time (hr) matches your prescription (Figure M). | 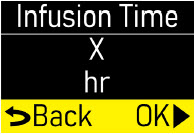 Figure M Figure M
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure N Figure N
|
| Step 1.6
Make sure the number of +Doses/ Day (extra doses/day) matches your prescription (Figure O). | 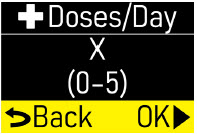 Figure O Figure O
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure P Figure P
|
| Step 1.7
Make sure the +Dose (extra dose) amount (mg) matches your prescription (Figure Q). |  Figure Q Figure Q
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure R Figure R
|
| Step 1.8
Make sure +Dose Lock (extra dose lock) time (hr, min) matches your prescription (Figure S). | 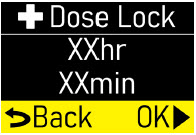 Figure S Figure S
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure T Figure T
|
| Step 1.9
You will see the software version (Figure U). |  Figure U Figure U
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure V Figure V
|
| Step 1.10
Exitwill be highlighted on the Menu screen (Figure W). |  Figure W Figure W
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure X Figure X
|
| You will then see the Infusion Off screen (Figure Y). Set the pump aside on a clean surface and continue to the Set up the Pump section. |  Figure Y Figure Y
|
| Setup | |
| Within this section you will find: | |
| Set up the Pump | 23 |
| Prepare the Infusion Site | 38 |
| Connect the Infusion Line to Body | 40 |
| Start the Infusion | 41 |
| Wear the Pump | 43 |
| Reading the Pump Screen | 45 |
Set Up the Pump
| Step 2: Wash Your Hands and Gather Supplies |
| Step 2.1
Go to a sink and wash your hands with soap and water, then dry your hands (Figure Z). | 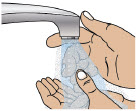 Figure Z Figure Z
|
| Step 2.2
Prepare a clean, flat surface such as a table to work on (Figure AA). |  Figure AA Figure AA |
Step 2.3
Take the blue case and open it (Figure AB). Gather the additional supplies not included in the case (Figure AC).
Infusion System Kit Supplies Included in the Case (Figure AB):
- Pump Pouch
- Elastic Belt
- Pump
- Lanyard
- Spare Battery
- Battery Door Key
Additional Supplies not Included in the Case (Figure AC):
- Glass drug Cartridge (Sterile)
- Plastic Cartridge Holder (Sterile)
- Infusion Set parts (Sterile)
- Alcohol Wipes
- Towel (or Paper Towels)
- Sharps Container. See the DisposalSection on page 73 for information on how to safely throw away ONAPGO.
 | Do notuse other drug cartridges with the pump. The pump must only be used with an ONAPGO glass drug cartridge containing apomorphine hydrochloride 98 mg/20 mL (4.9mg/mL). |
 | Do notuse other cartridge holders with the pump. The Pump must only be used with the plastic cartridge holder that is provided. |
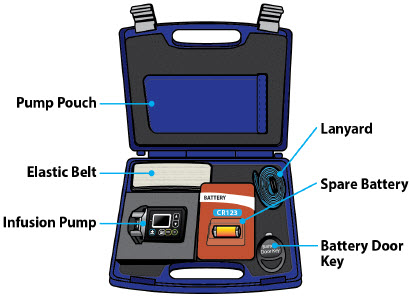
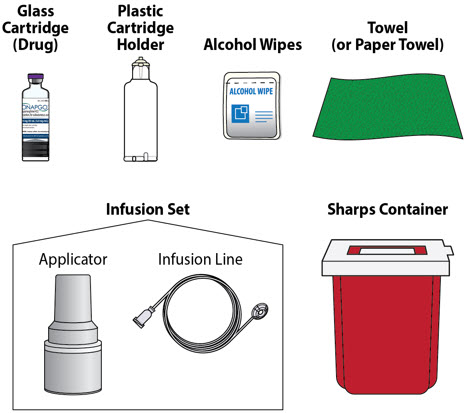
| Step 3: Assemble Plastic Cartridge Holder |
| Step 3.1 Prepare Plastic Cartridge Holder
Look at the plastic cartridge holder package. Make sure the expiration date (EXP) has not passed (Figures AD and AE). |  Figure AD Figure AD
|
| If the expiration date has passed:
Throw the plastic cartridge holder away in a sharps container and get a new plastic cartridge holder. See the Disposalsection on page 73 for information on how to safely throw away ONAPGO. | 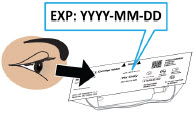 Figure AE Figure AE
|
| Remove the plastic cartridge holder from its package (Figure AF). | 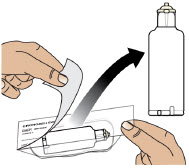 Figure AF Figure AF
|
| Step 3.2 Prepare Infusion Line
Look at the infusion line package. Make sure the expiration date has not passed (Figure AG). If the expiration date has passed: Throw the infusion line away in a sharps container and get a new infusion line. See the Disposalsection on page 73 for information on how to safely throw away ONAPGO. | 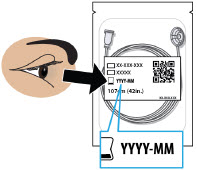 Figure AG Figure AG
|
| Remove the infusion line from its package and tear off the paper tab.
Unravel the infusion line so it is straight (Figure AH). | 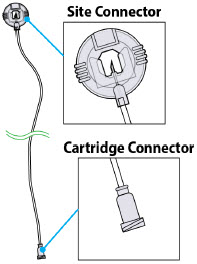 Figure AH Figure AH
|
| Step 3.3 Connect Infusion Line and Plastic Cartridge Holder
Find the cartridge connector end of the infusion line (Figure AI). | 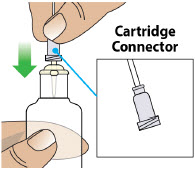 Figure AI Figure AI
|
| Place the cartridge connector end of the infusion line over the tip of the plastic cartridge holder and turn the cartridge connector until it is snug (Figures AJ and AK).
Note:It only takes a small movement to secure the parts together. Do not connect the infusion line to the body at this time.You must prime the infusion line before connecting it to your body. | 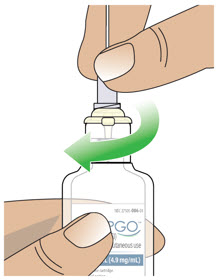 Figure AJ Figure AJ
|
 Figure AK Figure AK
|
|
| Step 3.4 Prepare Glass Drug Cartridge
Remove the glass drug cartridge from its carton and look at the label. Make sure the expiration date has not passed on the glass drug cartridge (Figures AL and AM). | 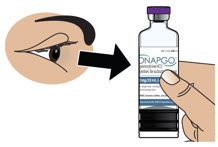 Figure AL Figure AL
|
| If the expiration date has passed:
Throw the glass drug cartridge away in a sharps container and get a new glass drug cartridge. See the Disposalsection on page 73 for information on how to safely throw away ONAPGO. |  Figure AM Figure AM
|
| Step 3.5 Check Medicine
Look at the glass drug cartridge. Make sure the liquid medicine inside the glass drug cartridge is clear, almost colorless, and free from particles (Figure AN). | 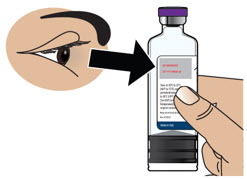 Figure AN Figure AN
|
Important Information
 | If the medicine is cloudy, discolored, or contains particles,throw away the glass drug cartridge in a sharps container and get a new one. See the Disposalsection on page 73 for information on how to safely throw away ONAPGO. |
| Step 3.6 Remove Flip Cap from Glass Drug Cartridge
Hold the glass drug cartridge and remove the flip cap (Figure AO). You may need to push hard to remove the flip cap. You can throw the flip cap away in your household trash. | 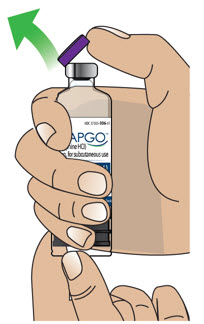 Figure AO Figure AO
|
| Step 3.7 Clean Glass Drug Cartridge
Clean the top of the glass drug cartridge with a new alcohol wipe (Figure AP). | 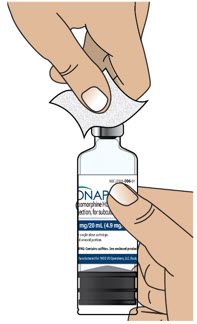 Figure AP Figure AP
|
| Step 3.8 Place Glass Drug Cartridge
Place the glass drug cartridge on a flat surface on top of a towel or paper towel (Figure AQ). |  Figure AQ Figure AQ
|
| Step 3.9 Attach Plastic Cartridge Holder to Glass Drug Cartridge
Take the plastic cartridge holder. Place the plastic cartridge holder, with the infusion line attached, over the glass drug cartridge and push all the way down (Figures AR and AS). | 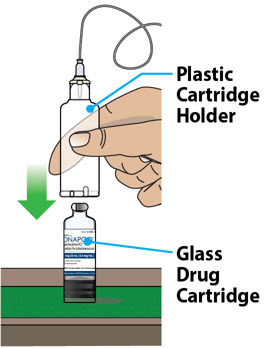 Figure AR Figure AR
|
| Note:After letting go, the plastic cartridge holder may come up a bit so that it is not even with the bottom of the glass drug cartridge. This is normal.
A small amount of liquid medicine might come out of the glass drug cartridge. This is normal. You have now created an "assembled cartridge" (Figure AT). Note:Change the cartridge, cartridge holder, and administration set daily or between uses. Note:If the infusion line is dropped or dirty, throw away (discard) the infusion line. Warning:Do not puncture the cartridge with anything but the specified plastic cartridge holder. | 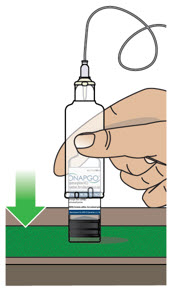 Figure AS Figure AS
|
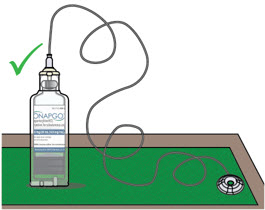 Figure AT Figure AT
|
|
| Step 3.10 Place Assembled Cartridge on Pump
Hold the pump upright as shown (Figure AU). Note:There are ridges at the bottom of the plastic cartridge Holder. You will use these ridges in the next step to align the assembled cartridge with the pump. | 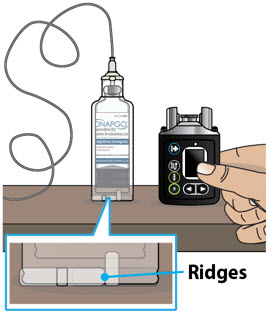 Figure AU Figure AU
|
| Take the assembled cartridge. Position the assembled cartridge above the pump with the ridges facing you (Figure AV). | 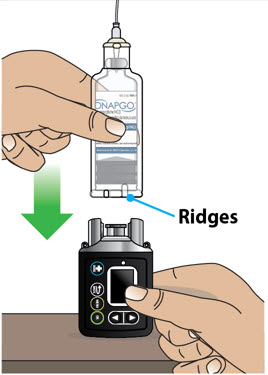 Figure AV Figure AV
|
| Place the assembled cartridge onto the pump, as shown, with the ridges showing in the pump opening (Figure AW). The assembled cartridge should sit flush against the pump with no gap. | 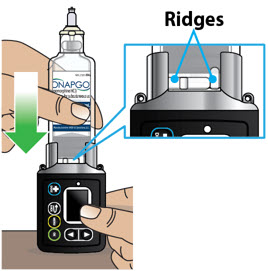 Figure AW Figure AW
|
| Step 3.11 Attach Assembled Cartridge to Pump
Push downthe assembled cartridge firmly and twistuntil you feel it lock into place and the ridges are no longer showing (Figure AX). | 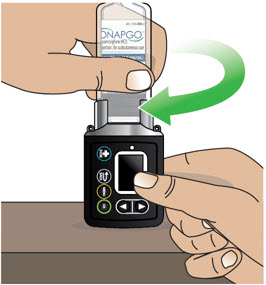 Figure AX Figure AX
|
Look at the Pump opening.
|  Figure AY Figure AY
 Figure AZ Figure AZ |
| Step 4: Prime the Infusion Line |
Priming the infusion line (Figure BA) pushes liquid through the system to remove all air from the glass drug cartridge and infusion line. All air must be removed from the system before the infusion line is connected to the infusion site on the body.

 | Read the Instructions for Use for the infusion set before using the infusion line. |
 | Do notprime the infusion line when it is connected to the infusion site on the body. |
| Step 4.1
Take the site connector end of the infusion line and place it on a towel (Figure BB). |  Figure BB Figure BB
|
|
Step 4.2
|  Figure BC Figure BC
|
| You will then see the Infusion Off screen (Figure BD). |  Figure BD Figure BD |
|
Step 4.3
| 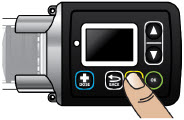 Figure BE Figure BE
|
| Step 4.4
The Primeoption will be highlighted on the Menu screen (Figure BF). |  Figure BF Figure BF
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure BG Figure BG
|
|
Step 4.5
| 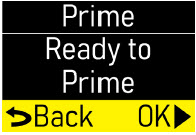 Figure BH Figure BH
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure BI Figure BI
|
| You will then see the Priming screen flashing (Figure BJ). This means that the pump is priming. |  Figure BJ Figure BJ
|
| During Priming…
Check the connector end of the infusion line for drops of liquid medicine (Figure BK). | 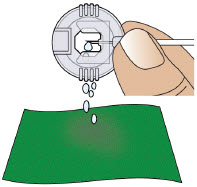 Figure BK Figure BK |
Important Information
 | Do notallow the medicine to come into contact with your clothing, carpeting, or furniture, as it can stain. |
| Step 4.6
When priming is done you will see this screen (Figure BL). |  Figure BL Figure BL
|
| After priming…
Check that all air gaps or large air bubbles are removed from the line (Figure BM). | 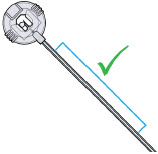 Figure BM Figure BM
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure BN Figure BN
|
| Step 4.7
Did you see drops and confirm no large air bubbles or gaps in the line?
|  Figure BO Figure BO
 Figure BP Figure BP
|
| Step 4.8
You will see a screen that says Wait! Connect Line to Body (Figure BQ). |  Figure BQ Figure BQ
|
| Put down the pump(Figure BR) and follow the next sections to "Prepare the Infusion Site" and "Connect the Infusion Line to Body". | 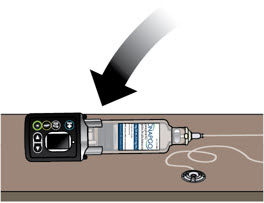 Figure BR Figure BR |
Prepare the Infusion Site
You will insert the cannula (a small tube that allows the medicine to be delivered) into the selected infusion site.
| Step 5: Select and Clean the Infusion Site | |
| Step 5.1
Select one of the following infusion sites (see blue shaded areas in Figure BS):
| 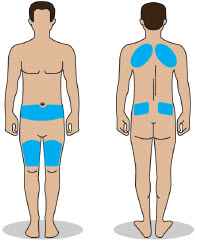 Figure BS Figure BS |
Important Information
 | Change the infusion site every day (rotate sites) to avoid skin-related problems, such as bumps or nodules. |
 | Do notselect an infusion site that is bruised, has bumps or nodules, or is irritated. |
 | Do notselect an infusion site other than those listed and shown in Figure BS. |
| Step 5.2
Get an alcohol wipe. Clean the selected infusion site with a new alcohol wipe (Figure BT). Make sure the area is dry before moving on to Step 6. | 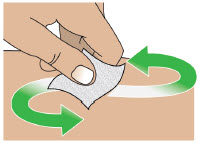 Figure BT Figure BT |
Note:If the infusion line is dropped or dirty, throw away (discard) the infusion line.
| Step 6: Connect the Cannula to the Body | |
| Step 6.1
Following the infusion set Instructions for Use, insert the cannula into the cleaned infusion site (Figure BU). | 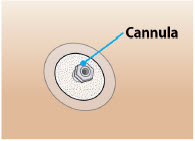 Figure BU Figure BU |
 | Read the Instructions for Use for the infusion set before using the infusion line. |
 | Do notinsert the cannula into a blood vessel. |
 | Do notinsert the cannula into a bump or nodule, as it can result in a blockage (occlusion). |
Connect the Infusion Line to Body
| Step 7: Connect the Infusion Line to the Cannula | |
| Step 7.1
Take the site connector end of the infusion line. Pinch the sides of it and pull on the end of the site connector to open it (Figure BV). | 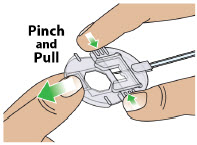 Figure BV Figure BV
|
| Step 7.2
Connect the primed infusion line to the cannula on the body by placing the site connector over the cannula and then closing it (Figures BW and BX). For more information, follow the Instructions for Use provided with the infusion set. | 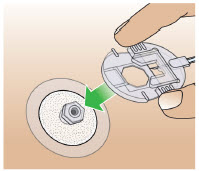 Figure BW Figure BW
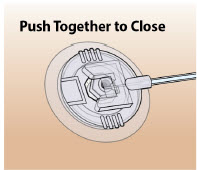 Figure BX Figure BX |
Start the Infusion
| Step 8: Start the Infusion |
| Step 8.1
Pick up the pump. Press the UP ARROW button (
|  Figure BY Figure BY
|
| You will see a screen that says Connect Line to Body (Figure BZ). |  Figure BZ Figure BZ
|
|
Now that you have connected the line to your body, press the OK button (
|  Figure CA Figure CA
|
| You will see a screen that says Confirm Line Connected (Figure CB). | 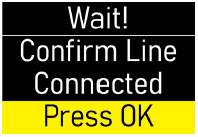 Figure CB Figure CB
|
|
Make sure that the site connector is attached to the body.
|  Figure CC Figure CC
|
| Step 8.2
You will see a screen that says Start Infusion (Figure CD). |  Figure CD Figure CD
|
|
When ready, press the OK button (
|  Figure CE Figure CE
|
| You will then see the Infusion Started screen. The checkmark at the bottom of the screen means that the infusion has successfully started (Figure CF). |  Figure CF Figure CF
|
| After the infusion has started, you will see the Infusing Screen. The flashing droplet means that the pump is now infusing (Figure CG). Next to the droplet, you will also see the amount of time before the infusion ends. |  Figure CG Figure CG |
Wear the Pump
| Step 9: Wear the Pump | |
| You must place the pump inside the pump pouch and then attach it to either the elastic belt or the lanyard, whichever you prefer.
Using the Elastic Belt |
|
| Take the elastic belt and pump pouch. Insert the elastic belt into the loop on the back of the pump pouch (Figure CH). |  Figure CH Figure CH
|
| Take the pump. Place the pump inside of the pump pouch (Figure CI). | 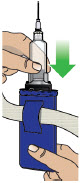 Figure CI Figure CI
|
| Secure the elastic belt around the waist (Figure CJ). | 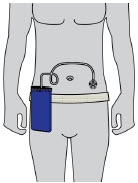 Figure CJ Figure CJ |
 | Do notsnag or kink the infusion line while wearing the pump. Snagging or kinking the infusion line can cause a blockage (occlusion) or an interruption to the infusion. |
Using the Neck Lanyard
| Take the neck lanyard and pump. Hook the lanyard to the neck lanyard Clips (Figure CK) located on the pump. | 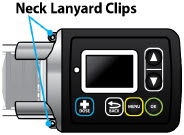 Figure CK Figure CK
|
| Take the pump pouch. Place the pump inside of the pump pouch (Figure CL). |  Figure CL Figure CL
|
| Place the lanyard around patient's neck (Figure CM). | 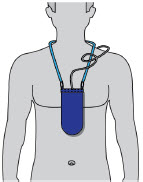 Figure CM Figure CM |
 | Do notsnag or kink the infusion line while wearing the Pump. Snagging or kinking the infusion line can cause a blockage (occlusion) or an interruption to the infusion. |
Reading the Pump Screen
There are 4 main modes for the pump: On (Infusing Screen), Paused, Primed, and Infusion Off. Each mode is described below.
| ON (Infusing Screen) |
| When the pump is On, and the infusion is running, the following icons and information will be seen (Figure CN): |
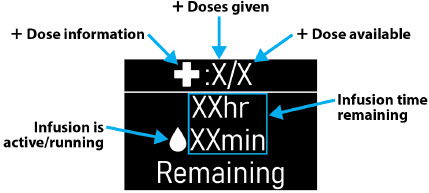 Figure CN Figure CN |
| When the pump is On and you attempt to give an extra dose ( +Dose), the following icon will be seen when the extra dose ( +Dose) is locked out (Figure CO): |
 Figure CO Figure CO |
| Paused |
| When the infusion is paused, the following screen will be seen (Figure CP): |
 Figure CP Figure CP |
| To pause the infusion, see the Pausing the Infusioninstructions on page 55. |
| Primed |
| When the pump is primed, but the infusion has not started, the following screen will be seen (Figure CQ): |
 Figure CQ Figure CQ |
| OFF |
| When the pump is not infusing, the following screen will be seen (Figure CR): |
 Figure CR Figure CR |
| + Dose / Pause / End | |
| Within this section you will find: | |
| Give a +Dose | 51 |
| Pause and Resume the Infusion | 55 |
| Ending the Infusion | 59 |
| Disconnecting in an Emergency | 68 |
Give a +Dose (Extra Dose)
| Step 10: Give an Extra Dose (+ Dose) |
An extra dose ( +Dose) is only available if it has been prescribed by the healthcare provider. If an extra dose ( +Dose) has NOT been prescribed, skip this section.
Note:An extra dose ( +Dose) can only be given after the pump has been primed and while the pump is infusing.
|
Step 10.1
|  Figure CS Figure CS
|
|
Step 10.2
|  Figure CT Figure CT
|
|
You will then see the
+Dose screen. Press the DOWN ARROW button (
|  Figure CU Figure CU
|
|
Step 10.3
|  Figure CV Figure CV
|
| The pump will now give the extra dose ( +Dose ) (Figure CW). |  Figure CW Figure CW
|
| When the extra dose is delivered, you will then see the +Dose Delivered screen with a check mark on the bottom (Figure CX). |  Figure CX Figure CX
|
| The pump will then automatically go back to the Infusing screen (Figure CY).
Note:Administer extra doses ( +Doses) at least 3 hours apart. Administer no more than 3 extra doses a day. |  Figure CY Figure CY |
| Another Way of Giving an Extra Dose (+ Dose) |
 |
Do notrepeat the steps below if you have already given an extra dose using the
+Dose button (
|
|
Take the pump.
|  Figure CZ Figure CZ
|
|
Use the DOWN ARROW button (
|  Figure DA Figure DA
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure DB Figure DB
|
|
You will then see the
+Dose screen.
| 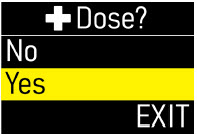 Figure DC Figure DC
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure DD Figure DD |
| Understanding the Extra Dose (+ Dose) Features |
| If you see the
+Dose Locked icon (Figure DE) on the home screen, it means that an extra dose is not allowed.
This is because the minimum amount of time has not passed since the last extra dose ( +Dose) was given. The time between allowable extra doses ( +Doses) is prescribed by the healthcare provider. |  Figure DE Figure DE
|
|
When the
+Dose is locked, you can see the amount of time remaining before another extra dose (
+Dose) can be given, by pressing the
+Dose button (
|  Figure DF Figure DF
|
| If you see the +Dose None Remaining message (Figure DG), it means the maximum number of extra doses has been reached and none remain for that infusion. |  Figure DG Figure DG |
Pause and Resume the Infusion
If the pump is at risk for getting wet, pause the infusion, disconnect the infusion line from the body, and store the pump in a dry place. This includes swimming, showering, or excessive sweating.
| Step 11: Pausing the Infusion | |
|
Step 11.1
|  Figure DH Figure DH
|
|
Step 11.2
|  Figure DI Figure DI
|
| Step 11.3
Pause option will be highlighted on the Menu screen (Figure DJ). | 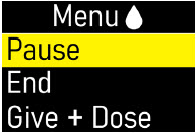 Figure DJ Figure DJ
|
|
Step 11.4
|  Figure DK Figure DK
|
| You will then see the Paused screen (Figure DL). |  Figure DL Figure DL
|
| Step 11.5 (If Needed)
If needed, remove the infusion line from your body (Figure DM) while leaving cannula on your skin. There is no need to cover the site connector once removed, as it is self-sealing. | 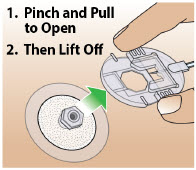 Figure DM Figure DM |
| Step 12: Resuming the Infusion | |
| Step 12.1 (If Needed)
Take the site connector end of the infusion line. Reattach the infusion line to the infusion site (Figure DN). |  Figure DN Figure DN
|
|
Step 12.2
|  Figure DO Figure DO
|
|
Step 12.3
|  Figure DP Figure DP
|
| Step 12.4
Resume option will be highlighted on the Menu screen (Figure DQ). |  Figure DQ Figure DQ
|
|
Step 12.5
|  Figure DR Figure DR
|
| You will then see the Infusion Resumed screen with a check mark on the bottom (Figure DS). |  Figure DS
Figure DS |
| The pump will automatically return to the Infusing Screen (Figure DT). |  Figure DT Figure DT |
Ending the Infusion
The infusion will run for the programmed amount of time, or it can be ended early.
| Step 13: Ending the Infusion Early | |
|
Step 13.1
|  Figure DU Figure DU
|
|
Step 13.2
|  Figure DV Figure DV
|
|
Step 13.3
| 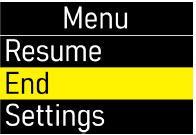 Figure DW Figure DW
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure DX Figure DX
|
|
Step 13.4
|  Figure DY Figure DY
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure DZ Figure DZ
|
| You will then see the Stop! Remove Line From Body screen (Figure EA).
Do notpress the OK button at this time. |  Figure EA Figure EA
|
| Step 13.5
Remove the infusion line from the body (Figure EB). |  Figure EB Figure EB
|
|
Step 13.6
|  Figure EC
Figure EC |
| You will then see the Ending Infusion screen, indicating the ending of the infusion (Figure ED). It may take several minutes to retract the pusher and end the infusion. |  Figure ED Figure ED
|
| When the pump has ended the infusion, you will see the Infusion Off screen (Figure EE). |  Figure EE Figure EE |
|
Note:If you press the back (
|
|
| Step 13.7
Remove the cannula from the body (Figure EF). | 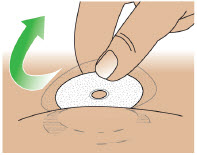 Figure EF Figure EF
|
| Step 13.8
Take a new alcohol wipe. Clean the infusion site with a new alcohol wipe (Figure EG). | 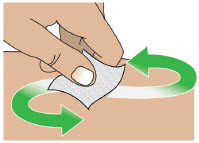 Figure EG Figure EG
|
| Step 13.9
Gently massage the area of the infusion site to break up any excess fluid buildup. This will help prevent skin nodules or bumps and irritations (Figure EH). | 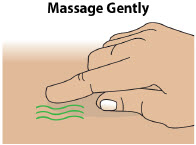 Figure EH Figure EH
|
| Step 13.10
Take the pump. Twist the assembled cartridge to the left (counterclockwise) and lift it straight up to remove the plastic cartridge holder, glass drug cartridge, and infusion line altogether (Figure EI). | 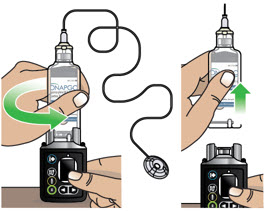 Figure EI Figure EI |
 | Do notseparate the infusion line or the glass drug cartridge from the plastic cartridge holder. |
Note:If the plastic cartridge holder detaches from the glass drug cartridge when removing, continue to remove the plastic cartridge holder. Set aside the plastic cartridge holder and remove the glass drug cartridge by pulling it up and off the pump. Continue to Step 13.11.
| Step 13.11
Throw away the used Infusion line, glass drug cartridge, plastic cartridge holder, and cannula into a sharps container right away after use (Figure EJ). Do notthrow away (dispose of) the infusion line, glass drug cartridge, or plastic cartridge holder in your household trash. See the Disposalsection on page 73 for information on how to safely throw away ONAPGO. | 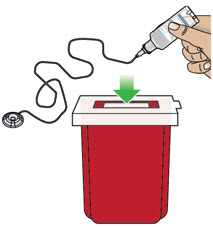 Figure EJ Figure EJ |
| Visually Check the Pump
Right after you use the pump, look it over (visually check) to see if you notice any soiling on the pump. Wipe off any soiling that you see with isopropyl alcohol. (See the Clean and Disinfect the Pumpsection on page 74.) |
| Step 14: Ending the Infusion Regularly | |
| Step 14.1
At 1 hour, 10 minutes, and 5 minutes remaining in the infusion, the pump will give a reminder on the screen and you will hear occasional beeping (Figure EK). |  Figure EK Figure EK
|
|
You must press the OK button (
|  Figure EL Figure EL
|
| Step 14.2
When the infusion ends, the Ended screen will appear with 0 minutes remaining (Figure EM) and you will hear a beep. |  Figure EM Figure EM
|
|
Press the OK button (
|  Figure EN Figure EN
|
| Step 14.3
You will then see the Stop! Remove Line From Body screen (Figure EO). Do notpress the OK button at this time. |  Figure EO Figure EO
|
| Step 14.4
Remove infusion line from the body (Figure EP). |  Figure EP Figure EP |
 | The infusion line must be removed from the infusion site before pressing the OK button. |
|
Step 14.5
|  Figure EQ Figure EQ
|
|
The pump will begin to reset, and you will see the Ending Infusion screen (Figure ER). It may take several minutes to retract the pusher and end the infusion. |  Figure ER Figure ER
|
| Next, you will see the Infusion Off screen (Figure ES). |  Figure ES Figure ES
|
|
Note:If you press the back (
|
|
| Step 14.6
Remove the cannula from the body (Figure ET). |  Figure ET Figure ET
|
| Step 14.7
Take a new alcohol wipe. Clean the infusion site with a new alcohol wipe (Figure EU). |  Figure EU Figure EU
|
| Step 14.8
Gently massage the area of the infusion site to break up any excess fluid buildup. This will help prevent skin bumps or nodules and irritations (Figure EV). |  Figure EV Figure EV
|
| Step 14.9
Take the pump. Twist the plastic cartridge holder to the left (counterclockwise) and lift it straight up to remove the plastic cartridge holder, glass drug cartridge, and infusion line (Figure EW). |  Figure EW Figure EW |
 | Do notseparate the infusion line or the glass drug cartridge from the plastic cartridge holder. |
| Note:If the plastic cartridge holder detaches from the glass drug cartridge when removing, continue to remove the plastic cartridge holder. Set aside the plastic cartridge holder and remove the glass drug cartridge by pulling it up and off the pump. Continue to Step 14.10. | |
| Step 14.10
Put the used infusion line, glass drug cartridge, plastic cartridge holder, and cannula into a sharps container right away after use (Figure EX). Do notthrow away (dispose of) the infusion line, glass drug cartridge, or plastic cartridge holder in your household trash. See the Disposalsection on page 73 for information on how to safely throw away ONAPGO. |  Figure EX Figure EX |
| Visually Check the Pump
Right after you use the pump, look it over (visually check) to see if you notice any soiling. Wipe off any soiling that you see with isopropyl alcohol. (See the Clean and Disinfect the pumpsection on page 74.) |
Disconnecting in an Emergency
If you are having a medical emergency, follow the steps below to disconnect from the pump.
| Step 15: Disconnecting in an Emergency | |
| Step 15.1
In the United States, dial 9-1-1 from any telephone for immediate medical assistance (Figure EY). |  Figure EY Figure EY
|
| Step 15.2
Remove the infusion line from your body (Figure EZ). |  Figure EZ Figure EZ |
| Step 15.3
Follow the Ending the Infusion Earlyinstructions on pages 59 to 63. |
|
| Pump Care | |
| Within this section you will find: | |
| Disposal | 73 |
| Cleaning and Disinfecting the Pump | 74 |
| Replacing the Battery | 81 |
Disposal
| Glass Drug Cartridge, Plastic Cartridge Holder, and Infusion Line Disposal | |
|  Figure FA Figure FA |
| Pump Disposal |
At the end of the expected life of the pump, contact Customer Support at 1-833-3ONAPGO (1-833-366-2746) for information and instructions about safe pump disposal.
Cleaning and Disinfecting the Pump
The Pump is a reusable device and should be cleaned and disinfected whenever you see any traces of dirt.
Follow the instructions below and on the following pages for cleaning and disinfecting the pump.
 | Do notclean and disinfect the pump if it is missing any parts (e.g., battery compartment door) or if you see damage to the front label. |
 | The pump is not waterproof. Do notimmerse the pump in liquid. |
 | Do notplace the pump under running water. |
 | Do notget any liquid inside of the pump. If the pump becomes wet, dry it right away. |
 | When cleaning the pump, dry your hands oftento avoid the build-up of liquid on the pump surface. |
 | Do notclean the pump with bleach or harsh (abrasive) detergents. |
 | Do notsterilize the pump. |
 | Do notclean the pump in a dishwasher. |
 | Do notdry the pump in a microwave. |
| Always carefully follow the steps below when cleaning and disinfecting the pump. | |
| Step 16.1 Preparing to Clean the Pump | |
| Wash and Dry Your Hands
Wash your hands with soap and water, then dry your hands (Figure FB). |  Figure FB Figure FB
|
| Set up a Clean Work Area
Set up a clean work area on a clean flat surface (Figure FC). |  Figure FC Figure FC
|
| Gather Supplies
Gather the following supplies (available at most supermarkets or pharmacies) (Figure FD):
|  Figure FD Figure FD |
 | Do notreuse the disposable gauze when cleaning the Pump. Throw away each piece of gauze after use.
Make sure to follow the instructions provided by the manufacturers of the detergent and the isopropyl alcohol. |
| Step 16.2 Thoroughly Clean the Pump with the Toothbrush | |
 | Always clean and disinfect the toothbrush each time you clean the pump, or use a new toothbrush each time you clean the pump. Replace the toothbrush if the bristles get worn or dirty. |
| Wet the Toothbrush
Use the purified or distilled water to slightly moisten the bristles of the toothbrush. | |
| Add a Drop of Detergent
Add a drop of detergent to the toothbrush. Brush Gently Until Clean Use the toothbrush head to gently brush any areas of the pump that are dirty (Figure FE) until you see the pump is clean. | 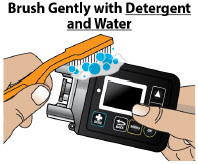 Figure FE Figure FE |
 | Do notvigorously scrub the pump with the toothbrush. |
| Step 16.3 Dry the Pump | |
| Wipe Dry with Gauze
Wipe all areas of the pump with a new dry gauze, to remove excess detergent residue or moisture (Figure FF), then throw away the gauze. Visually Check the Pump Visually check that all dirt and residue has been removed. | 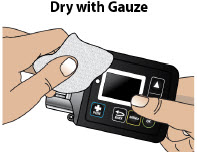 Figure FF Figure FF
|
| Step 16.4 Thoroughly Clean the Pump with Gauze | |
| Dampen a Gauze with Detergent
andWater
Dampen a new gauze with detergent and purified or distilled water. Wipe the Pump with Gauze Wipe the outer surfaces of the pump using the dampened gauze (Figure FG), then throw away the gauze. |  Figure FG Figure FG
|
| 16.5 Dampen a New Gauze with Water
Dampen a new gauze with purified or distilled water. 16.6 Wipe the Pump with Gauze Wipe the outer surfaces of the pump with the dampened gauze to remove any detergent residue (Figure FH), then throw away the gauze. |  Figure FH Figure FH |
| Step 16.7 Dry the Pump | |
| Wipe Dry with Gauze
Dry all areas of the pump with a new dry gauze (Figure FI), then throw away the gauze. | 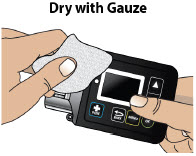 Figure FI Figure FI
|
| Visually Check the Pump
Visually check the pump for any soiling. Repeat the cleaning process if you see any traces of soiling. |
|
| Step 16.8 Disinfect the Pump with 70% Isopropyl Alcohol | |
| Soak a Gauze with Alcohol
Soak a new gauze with 70% isopropyl alcohol. Wipe Pump with Gauze for at least 1 Minute Wipe the outer surfaces of the pump using the soaked gauze for at least one minute(Figure FJ), then throw away the gauze. |  Figure FJ Figure FJ |
 | Do notimmerse the pump in isopropyl alcohol. |
| Step 16.9 Let Pump Air Dry | |
| Let Pump Air Dry for at least 5 Minutes
Set the pump aside on a clean dry surface and let the pump air dry for at least 5 minutes(Figure FK). |  Figure FK Figure FK |
 | The isopropyl alcohol must be in contact with the device surfaces for at least 5 minutesto disinfect the pump. |
| Step 16.10 Disinfect the Pump with 70% Isopropyl Alcohol | |
| Soak a Gauze with Alcohol
Soak a new gauze with 70% isopropyl alcohol. Wipe Pump with Gauze again for at least 1 Minute Wipe the outer surfaces of the pump using the soaked gauze for at least one minute(Figure FL), then throw away the gauze. | 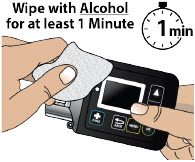 Figure FL Figure FL |
 | Do notimmerse the pump in isopropyl alcohol. |
| Step 16.11 Let Pump Air Dry | |
| Let Pump Air Dry for at least 5 Minutes
Set the pump aside on a clean dry surface and let the pump air dry for at least 5 minutes(Figure FM). |  Figure FM Figure FM |
| Make sure Pump is Dry
Make sure the pump is completely dry, and all the isopropyl alcohol has evaporated. |
|
 | The isopropyl alcohol must be in contact with the device surfaces for at least 5 minutesto disinfect the pump. |
| Step 16.12 Use Water to Remove Alcohol Residue | |
| Dampen Gauze with Water
Dampen a new gauze with purified or distilled water. |  Figure FN Figure FN |
| Wipe the Pump with Gauze
Wipe the outer surfaces of the pump with the dampened gauze to remove any disinfectant residue (Figure FN), then throw away the gauze. |
|
| Step 16.13 Dry the Pump | |
| Wipe Dry with Gauze
Dry all areas of the pump with a new dry gauze (Figure FO), then throw away the gauze. Visually Check the Pump Visually inspect the pump to make sure it is clean. | 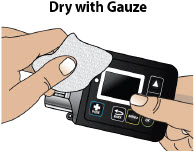 Figure FO Figure FO |
 | If you see any traces of dirt,repeat the entire cleaning and disinfecting procedure. |
 | If the pump has not been cleaned for a long period of time, some stains caused by the liquid medicine may not come off during the cleaning and disinfecting process. |
| Maintenance and Repair | |
| If the pump is used correctly as outlined in this Instructions for Use, the pump does not need programmed service maintenance from the manufacturer (CANÈ S.p.A. Medical Technology Company). |
 | If the pump stops working, is damaged, or shows a numbered error code, contact your Specialty Pharmacyor Customer Support at 1-833-3ONAPGO (1-833-366-2746). |
Replacing the Battery
Always have a replacement lithium CR 123A battery available for use.
 | Do notreplace the battery while the Infusion Line is connected to your body or during an active infusion as this could cause harm. |
 | Do notuse a battery other than lithium CR 123A. |
 | Do notuse expired or rechargeable batteries with the Pump. |
| Step 17: Replacing the Battery |
To replace the battery, follow these steps:
| Step 17.1
You should see the Infusion Off screen (Figure FP). |  Figure FP Figure FP
|
| Step 17.2
Take a new 3 volt lithium battery (model CR 123A) (Figure FQ) and the battery door key (Figure FR). |  Figure FQ Figure FQ
 Figure FR Figure FR
|
| Step 17.3
Take the battery door key and pump. Insert the battery door key into the battery door keyhole on the bottom of the pump (Figure FS). | 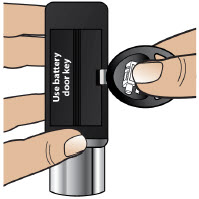 Figure FS Figure FS
|
| Push the battery door key away from the pump (Figure FT) to open the battery door. | 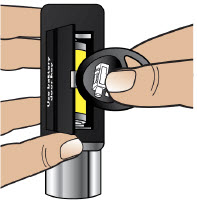 Figure FT Figure FT
|
| Step 17.4
Pull the battery door up and all the way out so that the ribbon attached to the battery door pops out the battery (Figure FU). | 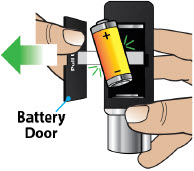 Figure FU Figure FU |
 | Do notuse any other object to remove the battery. |
| If the battery does not pop out: | |
| Hold the pump and the battery door firmly in one hand (Figure FV) and | 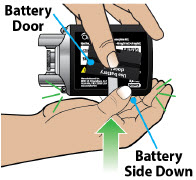 Figure FV Figure FV
|
| Strike the palm of your other hand with the pump, to jolt the battery from the compartment (Figure FW). | 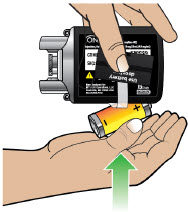 Figure FW Figure FW
|
| Step 17.5
Throw away the expired battery per local guidelines (Figure FX). |  Figure FX Figure FX
|
| Step 17.6
Wait 10 seconds before inserting a new battery (Figure FY). This allows the pump to reset. |  Figure FY Figure FY
|
| Step 17.7
Take your new, unopened 3 volt lithium battery, model CR 123A (Figure FZ). Open the package. |  Figure FZ Figure FZ
|
| Step 17.8
Take the pump. Insert the new battery by placing it on top of the ribbon with the negative end ( -) of the battery towards the silver side of the pump where the plastic cartridge holder is attached, and the positive end ( +) towards the flat end of the pump (Figure GA). Note:The battery should be placed on top of the ribbon to help with future removal and replacement. | 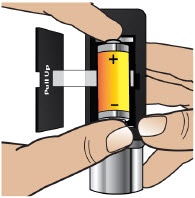 Figure GA Figure GA
|
| Step 17.9 | |
| Close the battery door by pushing it back into place (Figure GB). |  Figure GB Figure GB
|
| You will hear a series of beeps when the new battery is fully inserted (Figure GC). |  Figure GC Figure GC
|
| The pump screen will wake up and show the logo screen followed by the Infusion Off screen (Figure GD). |  Figure GD Figure GD |
| Alarms & Errors | |
| Within this section you will find: | |
| Error Codes | 91 |
| Troubleshooting | 98 |
Alarms and Troubleshooting
| Error Codes |
An error code will display on the screen if there is something wrong with the pump. You will hear a beep when there is an error code, and the LED next to the screen may light up. The table below gives an overview of the possible error codes that may happen, what they mean, and what to do to fix them.
If the corrective actions provided below do not fix the issue, contact Customer Support at 1-833-3ONAPGO (1-833-366-2746).
 | Do nottry to start or continue with your infusion when the screen displays an error. This will help avoid overdose or underdose. |
| Blank Screen Error | ||
| If a Blank Screen Error occurs, follow the steps below. | ||
 Figure GE Figure GE | What is happening? | You will hear intermittent beeps. The screen is blank and the LED lights up (Figure GE). |
| What does it mean? | The pump has detected an error that needs to be addressed. | |
| What to do? | Contact Customer Support at 1-833-3ONAPGO (1-833-366-2746). | |
| Error 2 | ||
| If Error 2 occurs, follow the steps below. | ||
 Figure GF Figure GF
 Figure GG Figure GG | What is happening? | You will hear a continuous tone and the screen will stay on and show a notification (Figure GF) until the error is addressed. |
| What does it mean? | The pump has detected an error that needs to be addressed. | |
| What to do? |
|
|
| Error 3, Error 5, Error 7 | ||
| If Error 3, Error 5, or Error 7 occurs, follow the steps below. | ||
 Figure GH Figure GH
 Figure GI Figure GI | What is happening? | You will hear intermittent beeps. The screen will show a notification (Figure GH) and the LED may light up. |
| What does it mean? | The pump has detected an error that needs to be addressed. | |
| What to do? |
|
|
| Error 4 | ||
| If Error 4 occurs, follow the steps below. | ||
 Figure GJ Figure GJ | What is happening? | You will hear intermittent beeps and the screen will stay on and show a notification (Figure GJ) until the error is addressed. |
| What does it mean? | The pump has detected an error that needs to be addressed. | |
| What to do? | Contact Customer Support at 1-833-3ONAPGO (1-833-366-2746) (Figure GJ). | |
| Error 6, Error 8, Error 9, Error 11 | ||
| If Error 6, Error 8, Error 9, or Error 11 occurs, follow the steps below. | ||
*Note: Images below show Error 6 as an example. Figure GK Figure GK
 Figure GL Figure GL | What is happening? | You will hear intermittent beeps and the screen will stay on and show a notification (Figure GK) until the error is addressed. |
| What does it mean? | The pump has detected an error that needs to be addressed. | |
| What to do? |
|
|
| Blockage | ||
| If the Blockage Error occurs, follow the steps below. | ||
 Figure GM Figure GM
 Figure GN Figure GN
 Figure GO Figure GO
 Figure GP Figure GP | What is happening? | You will hear intermittent beeps and the screen will stay on and show a notification (Figure GM) until the error is addressed. |
| What does it mean? | Too much pressure has been detected in the Infusion Line. Something may be blocking the infusion flow. | |
| What to do? |
|
|
| Warning:If something is blocking the infusion of ONAPGO, such as a kink, be sure to disconnect the infusion line before clearing the blockage alarm. If the infusion line is attached to the body when the error is cleared, you may receive a small additional amount of medicine. | ||
| Low Battery | ||
| If the Low Battery Alert occurs, follow the steps below. | ||
 Figure GQ Figure GQ
 Figure GR Figure GR | What is happening? | You will hear a beep and see a notification (Figure GQ or Figure GR) on the screen. |
| What does it mean? | The battery is getting low. | |
| What to do? | During an Infusion (Figure GQ):
Not during an Infusion (Figure GR):
|
|
| Replace Now (Battery Dead) | ||
| If the Replace Now Alarm occurs, the battery is dead. Follow the steps below. | ||
 Figure GS Figure GS | What is happening? | You will see a notification (Figure GS) on screen. |
| What does it mean? | The battery is dead and must be replaced right away.
Note:The pump will not work if the battery is dead. |
|
| What to do? | The screen will show a notification (Figure GS):
|
|
| Note:The alarms have no intentional delays and are raised as soon as the safety system detects the issue. | ||
| Note:The pump's firmware keeps the safety system under constant control, and an Error 2 alarm is raised if any issue is detected. | ||
| Note:The LED is used only when it is not possible to show the error on the display. The fact that the LED is not used in other alarms does not necessarily mean that they are of a lower priority. | ||
| Troubleshooting: If Your Infusion Line Did Not Prime | |
| Follow the steps below if your infusion line did not prime correctly: | |
| Wake up the pump (if needed) and then repeat the priming procedure. To do this, go to the menu and select Repeat Prime (Figure GT). When priming is complete, continue the procedure by skipping to Step 4.8. |  Figure GT Figure GT |
 | If no liquid drops came out of the site connector end after priming two times, select
Endon the Menu screen and throw away the infusion line in a sharps container. Then connect a new Infusion Line and start the priming process again beginning with Step 4.1 on page 33.
See the Disposalsection on page 73 for information on how to safely throw away ONAPGO. |
Symbols Used on the ONAPGO Pump
 | Caution:Consult accompanying documents for important safety-related information. |
 | CF Applied Part, refer to Technical Manual for more information. |
 | Caution:Consult Instructions for Use. |
 | Do not use in or next to a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) medical device. |
 | Ingress Protection (IP) rating.
Keep pump dry. If wet, wipe off with a dry cloth. The pump must not be immersed in water and must not be used while showering, swimming, or in a sauna. |
 | Prescription device. |
 | Only use the pump with a CR123A battery. |
Technical characteristics of the Pump
| Dimensions and weight | |
| Dimensions | 81 × 49 × 31 mm |
| Dimensions with holder attached | 149 × 49 × 31 mm |
| Weight | 127g |
| Technical data | |
| Power Supply | CR 123A 3V lithium battery |
| Battery life | Approximately 90 infusions |
| Display | Color OLED 96×64 pixels |
| Ingress protection | IP 42 |
| Buzzer sound pressure level | 53 dBA +/- 5 dBA |
| Data retention | The value settings and counters are retained even without the battery. |
| Maximum service life | Two years from date of purchase. |
| Infusion Data
Note: The information below describes what the pump can do, but it may not be the same as your prescription. |
|
| Administrable volume | Max. 20 ml |
| Infusion flow rate range | 1.0 – 8.0 mg/h (drug concentration is 98 mg/20 mL (4.9 mg/ml)) |
| Flow rate programming increment | 0.1 mg/h |
| Shot volume | 20 μl |
| Extra dose (bolus dose) amount | 0.5 - 4.0 mg. May also be set to 0 mg |
| Bolus dose amount programming increment | 0.1 mg |
| Maximum number of extra dose (bolus doses) per day | 0-5 |
| Bolus doses per infusion programming increment | 1 |
| Infusion Time Setting | 1 - 24 h |
| Maximum infusion time programming increment | 1h |
| Minimum interval between extra doses (bolus doses) | 3 h |
| Bolus dose interval programming increment | 30 minutes |
| Bolus dose flow rate | Max. 163 mL/hr |
| Bolus dose accuracy | Low dose 0.5 to 1.0 mg +/- 25%
High dose 1.5 to 4.0 mg +/- 15% |
| Flow rate accuracy | Low flow rate 1.0 to 3.5 mg/hr: +/- 15%
High flow rate 4.0 to 8.0 mg/hr: +/- 10% |
| Maximum difference in height between pump and infusion site | 50 cm |
| Priming volume | Fixed 1 ml (first delivery), 0.6 ml (second delivery) |
| Flow rate during priming | 163 ml/h |
| Occlusion pressure levels | 2.5 +/- 1.5 bar (36 +/- 22 psi) |
| Maximum occlusion detection time (hh:mm) | at a flow rate of 1mg/h: 4h 50m
at a flow rate of 8mg/h: 32m |
| Post-occlusion bolus (ml) | 0.85ml |
| Factory Settings | |
| Infusion flow rate | 1.0 mg/h |
| Maximum infusion time | 1 h |
| Bolus dose amount | 0.0 mg |
| Minimum interval between bolus doses | 3 h |
| Maximum number of bolus doses per infusion | 0 |
| Environmental Conditions for Use | |
| Temperature | +5 – +40 °C (+41 – +104°F) |
| Relative humidity | 15 – 68% |
| Pressure | 0.7 – 1.06 bar (10 – 15 psi) |
| Environmental Conditions for Storage | |
| Temperature | -25 – +70 °C (-13 – +158°F) |
| Relative humidity | Max 68% |
| Pressure | 0.5 – 1.06 bar (7 – 15 psi) |
Electromagnetic Compatibility
This section prescribes the correct environments for use in accordance with the declared regulations on electromagnetic compatibility.
Reference standards
The electromagnetic compatibility tests were carried out in accordance with the following standards:
- IEC 60601-2-24:2012 (medical electrical equipment)
- IEC 60601-1-2:2014 (medical electrical equipment)
Electromagnetic emissions
The manufacturer's declarations and requirements are set out below:
| Emission test | Conformity | Indications regarding electromagnetic environment |
|---|---|---|
| RF emissions CISPR 11 | Group 1 | The pump uses radio frequency only for its internal operation. As a consequence, its RF emissions are very low and would thus not be expected to cause any interference to electronic devices in the vicinity. |
| RF emissions CISPR 11 | Class B | The pump can be used in all environments, including domestic environments that are directly connected to a low-voltage public mains power network. |
Electromagnetic Immunity
The manufacturer's declarations and requirements are set out below:
| Immunity test | Test level | Conformity level | Indications regarding electromagnetic environment. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrostatic discharge (ESD) IEC 61000-4-2 | 15 kV air 8 kV contact | 15 kV air 8 kV contact | The pump must be used in an environment with wood, concrete or ceramic flooring. Where floors are covered with synthetic material, the relative humidity should be at least 30%. |
| Magnetic fields | 30 A/m 50 and 60 Hz | 30 A/m 50 and 60 Hz | |
| Radiated immunity | 80-2700 MHz AM 80% 1 KHz | 10 V/m |
The pump may be subject to interference in the vicinity of devices marked with the following symbol: 
|
|
IEC 61000-4-3 | 380-390 MHz 18Hz PM 50% | 27 V/m | |
| 430-470 MHz 18Hz PM 50% | 28 V/m | ||
| 704-787 MHz 217Hz PM 50% | 9 V/m | ||
| 800-960 MHz 18Hz PM 50% | 28 V/m | ||
| 1700-1990 MHz 217Hz PM 50% | 28 V/m | ||
| 2400-2570 MHz 217Hz PM 50% | 28 V/m | ||
| 5100-5800 MHz 217Hz PM 50% | 9 V/m |
Recommended separation distances from radio frequency devices
Portable radio frequency communication devices (including external antennas and their cables) may interfere with the pump if they are too close to it. These include mobile and cordless phones, LAN routers and intercom systems for children.
To avoid electromagnetic interference, use the pump at a distance at least 30 cm from such devices.
Tests of Accuracy
The accuracy of pump delivery has been evaluated based on tests carried out during an infusion in accordance with the following standards:
- IEC 60601-2-24:2012 (medical electrical equipment)
Note:Pump and drug cartridge have only been tested with Cleo90 infusion set which is recommended for use. Alternative accessories and extensions may cause inaccuracies in flow rate.
The total administrable volume of the drug is a maximum of 20 mL, and the drug concentration is 98 mg/20 mL (4.9 mg/mL). The flow rate programming increment is 0.5 mg per hr. The maximum infusion programming time is in increment of one hour. The accuracy of the pump was tested for a flow rate between 1.0 mg and 8.0 mg per hour. (See the Prescribing Information for recommended dosage). The flow rate stabilizes within minutes from initiation of the infusion, remains stable and delivers accurately for the duration of infusion as described in the technical specifications provided.
Limited Warranty
The pump is covered by a manufacturer's warranty for two (2) years. After this period, the manufacturer shall not be responsible for any repairs.
The manufacturer shall not be liable for damage to persons or property after a pump lifetime of two (2) years.
Contact & Support
For help and additional information on the pump or system, contact Customer Support at 1-833-3ONAPGO (1-833-366-2746).
Manufactured for:
MDD US Operations, LLC, a
subsidiary of Supernus
Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Rockville, MD 20850
MDD US Operations, LLC is the exclusive licensee and distributor of ONAPGO in the United States and Its territories.
©2025. ONAPGO is a registered trademark of BRITUSWIP LTD.
Version 14
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 06/2025
Healthcare Provider INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE ONAPGO™ (on-AP-goh)

This Instructions for Use contains information for healthcare providers on how to program the infusion pump to administer ONAPGO (apomorphine hydrochloride).
Please see the Important Safety Information, full Prescribing Information, and Patient Informationfor ONAPGO.
MDD US Operations, LLC
| Table of Contents | |
| Table of Contents | 2 |
| ONAPGO Infusion System | 3 |
| Indication for Use | 3 |
| Introduction to the Infusion System | 3 |
| Pump Warnings and Precautions | 4 |
| Pump Kit | 5 |
| Pump Diagram | 5 |
| Pump Screen Icons | 7 |
| Programming the ONAPGO Pump | 8 |
| Settings Overview | 8 |
| Step 1: Access Pump Settings | 9 |
| Step 2: Enter Password | 10 |
| Step 3: Program Pump Settings | 11 |
| Symbols Used on the ONAPGO Pump | 20 |
| Limited Warranty | 21 |
| Contact & Support | 21 |
ONAPGO Infusion System
| Indication for Use |
The ONAPGO Infusion Pump is for the subcutaneous infusion of ONAPGO (apomorphine hydrochloride). ONAPGO is indicated for the treatment of motor fluctuations in adults with advanced Parkinson's disease (PD).
It must be used only by individuals who have received instruction and training on its operations and on the correct, safe procedures. If patients are unable to give treatment independently, they must be given assistance and supervision.
Only the accessories supplied by CANÈ S.p.A. (plastic cartridge holder and supplies provided in the infusion pump kit) may be used in conjunction with this pump. The pump must be programmed by an adequately trained healthcare provider and/or a Supernus Pharmaceuticals/MDD US Operations Clinical Nurse Navigator (clinical nurse navigator).
| Introduction to the Infusion System |
Below are the common terms used throughout this Instructions for Use.
- Pump:controls the rate and amount of ONAPGO delivered to the body. It is programmed with the patient's prescription and displays the status of medicine delivery.
- Priming:refers to the task of removing all air from the Infusion Line (fluid pathway) before the infusion line is connected to the body.
- Flow Rate:the constant flow of ONAPGO given to the body over an extended period of time. The flow rate is expressed as milligrams per hour (mg/hr).
- Infusion Time:the total time that ONAPGO is infused per day.
- Extra Dose (+ Dose):a boost of ONAPGO (bolus dose) given over a short period of time in addition to the prescribed flow rate.
- Extra Dose (+ Dose) Lock:the amount of time before another extra dose can be given.
- Pump Settings:the patient's prescribed Flow Rate, Maximum Infusing Time Per Day, +Dose Quantity, +Dose Volume, and +Dose Lock. These settings can only be changed by a Healthcare Provider and/or Supernus Clinical Nurse Navigator.
| Pump Warnings and Precautions |
 WARNINGS:
WARNINGS:
- Do notgive a patient a pump without checking the prescription. Always check that the pump Settings match the patient's prescription before giving the pump to a patient.
- Do notstart an infusion without confirming the patient's prescription. If the pump settings do not match the prescription, do not allow the patient to use the pump. Reprogram the pump to match the prescription.
- Do notgive a patient more than 98 mg of ONAPGO over a 24-hour period.
- Do notdisclose the pump's security codes or other information to the patient. It would allow them access to the programming functions.
- Use ONAPGO drug cartridges with the ONAPGO pump only.
 PRECAUTIONS:
PRECAUTIONS:
- Do notuse sharp objects to press the pump buttons. Only use your fingertips.
- Do notuse a damaged pump. If you have any concerns about the correct functioning of the pump, and/or how to respond to an error contact your customer support representative.
| Pump Kit (Figure A) |
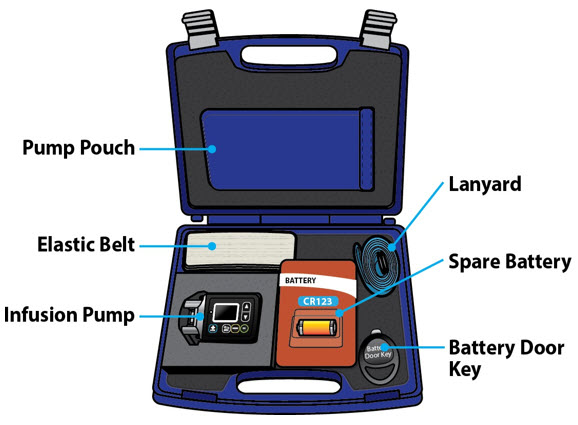
| Pump Diagram (Figures B, C, and D) |
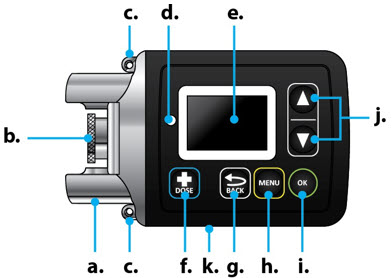 Figure B Figure B |  Figure D | |
 Figure C Figure C |
All buttons will respond with a single press. If the screen is dark, press the UP ARROW (
 ) to wake up the screen.
) to wake up the screen.
| Item | Pump Feature | Description |
|---|---|---|
| a | Cartridge Connection | Area where assembled glass drug cartridge and plastic cartridge holder is attached to the pump. |
| b | Pump Pusher | Pushes ONAPGO from the glass drug cartridge into the Infusion Line. |
| c | Neck Lanyard Clips | Slots to clip on the lanyard. |
| d | LED | Lights up when an error cannot be displayed on the screen. |
| e | Screen | Where messages and menus appear. |
| f |
| +DOSE button gives an extra dose (if prescribed). |
| g |
| BACK button allows you to return to a previous screen, menu, or cancel an action. |
| h |
| MENU button allows you to access the menus. |
| i |
| OK button allows you to confirm menu selections or go on to the next value. |
| j |
| UP and DOWN ARROW buttons allow you to scroll through menus. |
| k | Battery Door | Door to access the battery. |
| Pump Screen Icons |
The following table shows Icons that appear on the Pump screen.
| Icon | Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Back Arrow | The back arrow is shown when checking the pump settings. This icon is used to show that pressing the BACK button will return to a previous screen (Item 'g' in Figure B). | |
 | Caution | Caution is shown when an error or alarm is occurring. | |
 | Check Mark | A check mark is shown when the Pump successfully completes a task. | |
 | Droplet | A blinking droplet is shown on the Infusing Screen when an infusion is on. | |
 | Dead Battery | The dead battery is shown when the Pump battery is dead and must be replaced. | |
 | Low Battery | The low battery is shown when the pump battery is low and should be replaced before the next infusion. | |
 | OK Arrow | The OK arow is shown when checking the pump settings. This icon is used to show that pressing the OK button will confirm a selection or go on to the next value (Item 'i' in Figure B). | |
 | Padlock | Padlock is shown when the +Dose (extra dose) is not available. |  |
 | Pause | Pause is shown when the infusion is paused. | |
 | +Dose
(Extra Dose) | A +symbol refers to the extra dose ( +Dose) function. | |
Programming the ONAPGO Pump
The pump cannot be programmed while infusing.
The pump settings should be programmed according to the patient's prescription before they receive the pump.
| Settings Overview |
When programming the pump, a flashing value is one that you may edit. The table below describes the default pump settings and range of values to which the pump can be programmed. See the Prescribing Information for the recommended dosage regimen, including the recommended flow rate (i.e., 1 mg/hr to 6 mg/hr), infusion time (i.e., generally over 16 waking hours), and extra doses (i.e., no more than 3 per day).
| Icon | Default Pump Setting | Range of Values | Increments | Refer To |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Factory setting | 12:00 AM - 11:59 PM | N/A | Step 3.1
(page 11) |
| Date | Factory setting | mm/dd/yy | N/A | Step 3.2
(page 12) |
| Flow Rate | 1 mg/hr | 1 - 8 mg/hr | 0.5 mg/hr | Step 3.3
(page 13) |
| Infusion Time | 1 hr | 1 - 24 hr | 1 hr | Step 3.4
(page 14) |
| +Doses/Day
(Extra Doses/Day) | 0
(No Bolus) | 0 - 5 | 1 | Step 3.5
(page 15) |
| +Dose | 0 mg | 0.5 - 4 mg | 0.5 mg | Step 3.6
(page 16) |
| +Dose Lock | 3 hr | 0 - 24 hr | 30 min | Step 3.7
(page 17) |
| Step 1: Access Pump Settings |
|
Step 1.1
|  Figure E Figure E
|
| When the pump wakes up, the screen will say Infusion Off (Figure F). |
|
|
Step 1.2
|
|
| Keep holding both buttons until the password screen appears.
You will then see the password screen (Figure H). |  Figure H Figure H |
| Step 2: Enter Password |
Important Information:
 Do notdisclose the pump's security codes or other information to the patient. It would allow them access to the programming functions.
Do notdisclose the pump's security codes or other information to the patient. It would allow them access to the programming functions.
| Step 2.1
Locate the 4-digit password on the back of the pump (Figure I). The password is the 4 numbers following 'AJ'. In the example provided (Figure I), the 4-digit password would be 0001. |
|
|
Step 2.2
|  Figure J Figure J
|
|
When the correct password has been entered, press the OK button (
| 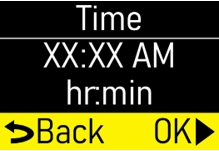 Figure K Figure K |
| Step 3: Program Pump Settings |
If this is the first time the pump will be programmed, the existing values will reflect the default factory settings (Page 8).
For any subsequent programming, the values will reflect the previously programmed patient prescription.
The settings will need to be changed to match the time, date, and patient's prescription.
|
Step 3.1
| 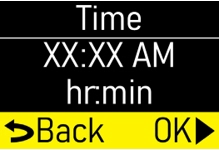 Figure L Figure L
|
|
When the Time is correct, press the OK button (
|  Figure M Figure M
|
|
Step 3.2
|  Figure N Figure N
|
|
When the date is correct, press the OK button (
| 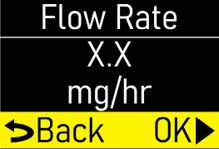 Figure O Figure O
|
|
Step 3.3
| 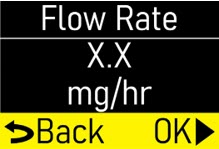 Figure P Figure P
|
|
When the flow rate is correct, press the OK button (
| 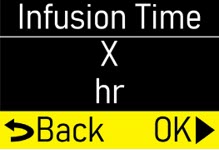 Figure Q Figure Q
|
|
Note:If you are prescribing above the recommended flow rate, a Verify screen will appear (Figure R).
|  Figure R Figure R
|
|
Step 3.4
| 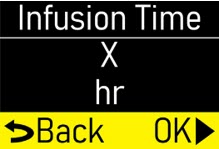 Figure S Figure S
|
|
When the infusion time is correct, press the OK button (
| 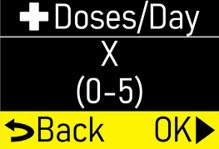 Figure T Figure T
|
|
Note:If you are prescribing above the recommended infusion time, a Verify screen will appear (Figure U).
|  Figure U Figure U
|
|
Step 3.5
| 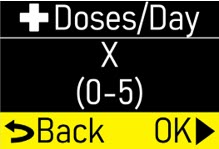 Figure V Figure V
|
|
When the
+Doses/Day (extra doses/ day) number is correct, press the OK button (
| 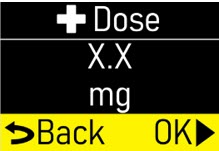 Figure W Figure W
|
|
Note:If you are prescribing above the recommended
+Doses/Day, a Verify screen will appear (Figure X).
|  Figure X Figure X
|
|
Step 3.6
| 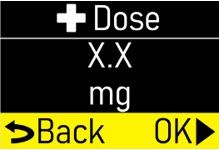 Figure Y Figure Y
|
|
When the
+Dose (extra dose) value is correct, press the OK button (
| 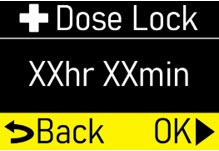 Figure Z Figure Z
|
|
Note:If you are prescribing above the recommended extra doses, a Verify screen will appear (Figure AA). Press the OK button (
|  Figure AA Figure AA
|
|
Step 3.7
| 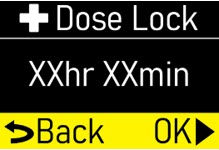 Figure AB Figure AB
|
|
When the + Dose (extra dose) lock time is correct, press the OK button (
|  Figure AC Figure AC
|
|
Step 3.8
|  Figure AD Figure AD
|
|
Continue pressing the DOWN ARROW (
|  Figure AE Figure AE
|
|
Step 3.9
|  Figure AF |
|
When the pump is done saving, the Infusion Off screen will appear (Figure AG).
|  Figure AG Figure AG |
Symbols Used on the ONAPGO Pump
 | Caution:Consult accompanying documents for important safety-related information. |
 | CF Applied Part, refer to Technical Manual for more information. |
 | Caution:Consult Instructions for Use. |
 | Do not use in or next to a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) medical device. |
 | Ingress Protection (IP) rating.
Keep pump dry. If wet, wipe off with a dry cloth. The pump must not be immersed in water and must not be used while showering, swimming, or in a sauna. |
 | Prescription device. |
 | The pump is to only be used with a CR123A battery. |
Note:The symbols displayed on the product label are reduced and simplified compared to the specifications in the reference standard CENELEC EN50419.
Limited Warranty
The pump is covered by a manufacturer's warranty for two (2) years. After this period, the manufacturer shall not be responsible for any repairs.
The manufacturer shall not be liable for damage to persons or property after a pump lifetime of two (2) years.
Contact & Support
For help and additional information on the pump or system, contact Customer Support at 1-833-3ONAPGO (1-833-366-2746).
Manufactured for:
MDD US Operations, LLC, a
subsidiary of Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Rockville, MD 20850
MDD US Operations, LLC is the exclusive licensee and distributor of ONAPGO in the United States and Its territories.
©2025. ONAPGO is a registered trademark of BRITUSWIP LTD.
Version 8
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 06/2025
| ONAPGO
apomorphine hydrochloride injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - MDD US Operations, LLC, a subsidiary of Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc (087875626) |
More about Onapgo (apomorphine)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- FDA approval history
- Drug class: dopaminergic antiparkinsonism agents
- Breastfeeding







 ) to wake up the screen (Figure F).
) to wake up the screen (Figure F).

 ) to find the pump settings (Figure H).
) to find the pump settings (Figure H).
 ) (Figure I).
) (Figure I).
 ) to begin reviewing the pump settings (Figure J).
) to begin reviewing the pump settings (Figure J).
 ) to move to the next screen (Figure L).
) to move to the next screen (Figure L).
 ) to move to the next screen (Figure N).
) to move to the next screen (Figure N).
 ) to move to the next screen (Figure P).
) to move to the next screen (Figure P).
 ) to move to next screen (Figure R).
) to move to next screen (Figure R).
 ) to move to next screen (Figure T).
) to move to next screen (Figure T).
 ) to move to the next screen (Figure V).
) to move to the next screen (Figure V).
 ) to exit the menu (Figure X).
) to exit the menu (Figure X).
 ) to wake up the screen (Figure BC).
) to wake up the screen (Figure BC).
 ) to enter the pump menu (Figure BE).
) to enter the pump menu (Figure BE).
 ) to continue (Figure BG).
) to continue (Figure BG).
 ) to prime the infusion line (Figure BI).
) to prime the infusion line (Figure BI).
 ) for menu options (Figure BN).
) for menu options (Figure BN).
 ) to Continue (Figures BO and BP).
) to Continue (Figures BO and BP).
 ).
).
 ) to prime again.
) to prime again.
 ) to wake up the screen (Figure BY).
) to wake up the screen (Figure BY).
 ) (Figure CA).
) (Figure CA).
 ) (Figure CC).
) (Figure CC).
 ) to start the infusion (Figure CE).
) to start the infusion (Figure CE).
 ) to wake up the screen (Figure CS).
) to wake up the screen (Figure CS).
 ) (Figure CT).
) (Figure CT).
 ) to highlight
) to highlight
 ) to continue (Figure CV).
) to continue (Figure CV).
 ).
).
 ) (Figure CZ).
) (Figure CZ).
 ) to highlight Give
) to highlight Give
 ) to continue (Figure DB).
) to continue (Figure DB).
 ) to highlight Yes (Figure DC)
) to highlight Yes (Figure DC)
 ) to deliver the extra dose (
) to deliver the extra dose (
 ) (Figure DF).
) (Figure DF).
 ) to wake up the screen (Figure DH).
) to wake up the screen (Figure DH).
 ) to enter the pump menu (Figure DI).
) to enter the pump menu (Figure DI).
 ) to pause the infusion (Figure DK).
) to pause the infusion (Figure DK).
 ) to wake up the screen (Figure DO).
) to wake up the screen (Figure DO).
 ) to enter the pump menu (Figure DP).
) to enter the pump menu (Figure DP).
 ) to resume the infusion (Figure DR).
) to resume the infusion (Figure DR).
 ) to wake up the screen (Figure DU).
) to wake up the screen (Figure DU).
 ) to enter the pump menu (Figure DV).
) to enter the pump menu (Figure DV).
 ) to highlight
) to highlight
 ) to end the infusion (Figure DX).
) to end the infusion (Figure DX).
 ) to highlight
) to highlight
 ) to select
) to select
 ) to confirm that the infusion line has been removed from the body (Figure EC).
) to confirm that the infusion line has been removed from the body (Figure EC).
 ) button as the infusion is ending, the pusher reset will pause. Press the OK button (
) button as the infusion is ending, the pusher reset will pause. Press the OK button (
 ) to resume ending the infusion and resetting the pusher.
) to resume ending the infusion and resetting the pusher.
 ) to dismiss the message (Figure EL).
) to dismiss the message (Figure EL).
 ) to select
) to select
 ) to confirm that the infusion line has been removed from the body (Figure EQ).
) to confirm that the infusion line has been removed from the body (Figure EQ).
 ) button as the infusion is ending, the pusher reset will pause. Press the OK button (
) button as the infusion is ending, the pusher reset will pause. Press the OK button (
 ) to resume ending the infusion and resetting the pusher.
) to resume ending the infusion and resetting the pusher.
 ) to clear the error (Figure GF). The pump will try to fix itself.
) to clear the error (Figure GF). The pump will try to fix itself.
 ) to clear the error (Figure GH). The pump will try to fix itself.
) to clear the error (Figure GH). The pump will try to fix itself.
 If attached to the body, remove the infusion line.
If attached to the body, remove the infusion line.
 ) to clear the error (Figure GK). The pump will try to fix itself.
) to clear the error (Figure GK). The pump will try to fix itself.
 If attached to the body, remove the infusion line site connector from your body while leaving the cannula connected to your skin (Figure GM). Press the OK button (
If attached to the body, remove the infusion line site connector from your body while leaving the cannula connected to your skin (Figure GM). Press the OK button (
 ).
).
 ) to clear the error (Figure GN). The pump will try to fix itself.
) to clear the error (Figure GN). The pump will try to fix itself.
 ) (Figure GO).
) (Figure GO).
 ) to clear alert (Figure GQ).
) to clear alert (Figure GQ).
 WARNING! Underdose or overdose due to abnormal pump operation. If the pump is used in the vicinity of other devices, it should be kept under observation in order to verify that no alarms are shown and that the infusion proceeds normally, delivering the drug in the expected time. If in doubt, do not use the device.
WARNING! Underdose or overdose due to abnormal pump operation. If the pump is used in the vicinity of other devices, it should be kept under observation in order to verify that no alarms are shown and that the infusion proceeds normally, delivering the drug in the expected time. If in doubt, do not use the device.





 ) to wake it up (Figure E).
) to wake it up (Figure E).

 ). While continuing to hold, press and hold the UP ARROW at the same time (Figure G), until a password input screen appears (Figure H).
). While continuing to hold, press and hold the UP ARROW at the same time (Figure G), until a password input screen appears (Figure H).
 ) and OK button (
) and OK button (
 ).
).
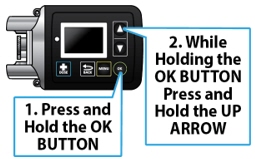

 ) to change the values on the Password screen (Figure J). Flashing values indicate that they are currently being edited. When the selected number matches the pump password, press the OK button (
) to change the values on the Password screen (Figure J). Flashing values indicate that they are currently being edited. When the selected number matches the pump password, press the OK button (
 ) to proceed to the next number. Repeat this process for all 4 numbers.
) to proceed to the next number. Repeat this process for all 4 numbers.
 ) to proceed to the Time screen (Figure K).
) to proceed to the Time screen (Figure K).
 ) to change the hour. As the hour is adjusted, the AM and PM will also change. When the hour and AM/PM are correct, press the OK button (
) to change the hour. As the hour is adjusted, the AM and PM will also change. When the hour and AM/PM are correct, press the OK button (
 ) to change the minutes (Figure L). Use the UP and DOWN ARROWS (
) to change the minutes (Figure L). Use the UP and DOWN ARROWS (
 ) to change the minutes.
) to change the minutes.
 ) to proceed to the Date screen (Figure M) Step 3.2.
) to proceed to the Date screen (Figure M) Step 3.2.
 ) to change the month and press the OK button (
) to change the month and press the OK button (
 ) to continue to change the day and year (Figure N).
) to continue to change the day and year (Figure N).
 ) to proceed to the Flow Rate screen (Figure O) Step 3.3.
) to proceed to the Flow Rate screen (Figure O) Step 3.3.
 ) to change the flow rate (Figure P).
) to change the flow rate (Figure P).
 ) to proceed to the Infusion Time screen (Figure Q) Step 3.4.
) to proceed to the Infusion Time screen (Figure Q) Step 3.4.
 ) to proceed or press the BACK button (
) to proceed or press the BACK button (
 ) to edit the flow rate.
) to edit the flow rate.
 ) to change the Infusion Time (length of time that infusion will run) (Figure S).
) to change the Infusion Time (length of time that infusion will run) (Figure S).
 ) to proceed to the + Doses/Day (extra doses/day) screen (Figure T) Step 3.5.
) to proceed to the + Doses/Day (extra doses/day) screen (Figure T) Step 3.5.
 ) to proceed or press the BACK button (
) to proceed or press the BACK button (
 ) to edit the infusion time.
) to edit the infusion time.
 ) to change the number of allowable
) to change the number of allowable
 ) to proceed to the
) to proceed to the
 ) to proceed to the
) to proceed to the
 ) to proceed or press the BACK button (
) to proceed or press the BACK button (
 ) to edit the
) to edit the
 ) to change the
) to change the
 ) to proceed to the
) to proceed to the
 ) to proceed to the
) to proceed to the
 ) to proceed or press the BACK button (
) to proceed or press the BACK button (
 ) to edit the
) to edit the
 ) to change the + Dose Lock (extra dose lock) time (time patient must wait before another extra dose) (Figure AB).
) to change the + Dose Lock (extra dose lock) time (time patient must wait before another extra dose) (Figure AB).
 ) to proceed to the Verify Rx screen (Figure AC) Step 3.8.
) to proceed to the Verify Rx screen (Figure AC) Step 3.8.
 ) to proceed to the Verify Rx screen (Figure AC) Step 3.8.
) to proceed to the Verify Rx screen (Figure AC) Step 3.8.
 ) to confirm that each pump setting programmed matches the patient's prescription.
) to confirm that each pump setting programmed matches the patient's prescription.
 ) until the Back/OK row is highlighted (Figure AE).
) until the Back/OK row is highlighted (Figure AE).
 ) to save the pump settings (Figure AF).
) to save the pump settings (Figure AF).
 ) to go back to the setting and adjust accordingly.
) to go back to the setting and adjust accordingly.

