Omnipaque Injection: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: iohexol
Dosage form: injection, solution
Drug class: Non-ionic iodinated contrast media
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Mar 26, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
- Storage and Handling
- Patient Counseling Information
Highlights of Prescribing Information
OMNIPAQUE (iohexol) injection, for intrathecal, intra-arterial, intravenous, oral, rectal, intraarticular, or body cavity use
OMNIPAQUE (iohexol) oral solution
Initial U.S. Approval: 1985
WARNING: RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL ADMINISTRATION OF OMNIPAQUE INJECTION 140 and 350 mg IODINE/mL
Use only the iodine concentrations and presentations recommended for intrathecal procedures. Intrathecal administration of a wrong iodine concentration, even if inadvertent, may cause death, convulsions, seizures, cerebral hemorrhage, coma, paralysis, arachnoiditis, acute renal failure, cardiac arrest, rhabdomyolysis, hyperthermia, and brain edema. (2.2, 2.8, 5.1)
Recent Major Changes
Indications and Usage for Omnipaque Injection
OMNIPAQUE is a radiographic contrast agent indicated for intrathecal, intra-arterial, intravenous, oral, rectal, intraarticular, and body cavity imaging procedures in adults and pediatric patients. (1)
Omnipaque Injection Dosage and Administration
- For each imaging procedure, specific dosage forms, concentrations, and presentations are recommended.
- Individualize the concentration and volume according to the specific dosing tables and accounting for factors such as age, body weight, and condition of the patient, and the equipment and imaging technique used. (2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, 2.8, 2.9)
- See full prescribing information for complete dosing and administration information. (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Injection: 140 mg iodine/mL, 180 mg iodine/mL, and 240 mg iodine/mL in single-dose vials/bottles; 300 mg iodine/mL and 350 mg iodine/mL in single-dose vials/bottles and imaging or pharmacy bulk package
- Oral Solution: 9 mg iodine/mL and 12 mg iodine/mL (3)
Contraindications
- Hysterosalpingography during pregnancy (or suspected pregnancy), menstruation (or when menstruation is imminent), within 6 months after termination of pregnancy, within 30 days after conization or curettage, when signs of infection are present in any portion of the genital tract, including the external genitalia, and when reproductive tract neoplasia is known or suspected. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Life-threatening or fatal reactions can occur. Always have emergency equipment and trained personnel available. (5.3)
- Acute Kidney Injury: Acute injury including renal failure can occur. Minimize dose and maintain adequate hydration to minimize risk. (5.4)
- Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions: Hemodynamic disturbances including shock and cardiac arrest may occur during or after administration. (5.5)
- Thyroid Dysfunction in Pediatric Patients 0 to 3 Years of Age: Individualize thyroid function monitoring based on risk factors such as prematurity. (5.9)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 1%) in adult patients
- Intrathecal: Headaches, pain including backache, neckache, stiffness and neuralgia, nausea, vomiting, dizziness
- Intra-arterial or intravenous: Pain, vision abnormalities (including blurred vision and photomas), headache, taste perversion, arrhythmias including premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) and premature atrial contractions (PACs), angina/chest pain, nausea
- Oral: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, flatulence, headache
- Body Cavity: Pain, swelling, heat sensation (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact GE Healthcare at 1-800-654-0118 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
- Lactation: A lactating woman may pump and discard breast milk for 10 hours after OMNIPAQUE administration. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 10/2024
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH INTRATHECAL ADMINISTRATION OF OMNIPAQUE INJECTION 140 mg IODINE/mL and 350 mg IODINE/mL
Use only the OMNIPAQUE iodine concentrations and presentations recommended for intrathecal procedure [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.8)]. Intrathecal administration of OMNIPAQUE of a wrong iodine concentration, even if inadvertent, may cause death, convulsions, seizures, cerebral hemorrhage, coma, paralysis, arachnoiditis, acute renal failure, cardiac arrest, rhabdomyolysis, hyperthermia, and brain edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Omnipaque Injection
1.1 Intrathecal Procedures‡
OMNIPAQUE is indicated for:
- Myelography and computerized tomography (CT) myelography (lumbar, thoracic, cervical, total columnar) in adults and pediatric patients aged 2 weeks and older
- CT cisternography in adults and pediatric patients aged 2 weeks and older
1.2 Intra-arterial Procedures‡
OMNIPAQUE is indicated for:
- Cardiac ventriculography in adults and pediatric patients
- Aortography including studies of aorta and its branches in adults and pediatric patients
- Selective coronary arteriography in adults
- Cerebral arteriography in adults
- Peripheral arteriography in adults
- Intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography (IA-DSA) of the head, neck, abdominal, renal, and peripheral vessels in adults
- Pulmonary angiography in pediatric patients
1.3 Intravenous Procedures‡
OMNIPAQUE is indicated for:
- Excretory urography in adults and pediatric patients
- CT of the head and body in adults and pediatric patients
- Peripheral venography (phlebography) in adults
- Intravenous digital subtraction angiography (IV-DSA) of the head, neck, abdominal, renal, and peripheral vessels in adults
1.4 Oral or Rectal Procedures‡
OMNIPAQUE is indicated for:
- Radiographic examination of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract in adults and pediatric patients
- CT of the abdomen and pelvis in conjunction with intravenous administration of OMNIPAQUE in adults and pediatric patients
1.6 Body Cavity Procedures‡
OMNIPAQUE is indicated for:
- Endoscopic retrograde pancreatography (ERP) and cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) in adults
- Herniography in adults
- Hysterosalpingography in adults
- Voiding cystourethrography (VCU) in pediatric patients
‡ Specific dosage forms, concentrations, and presentations of OMNIPAQUE are recommended for each type of imaging procedure [see Dosage and Administrations (2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, 2.8, 2.9) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
2. Omnipaque Injection Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Instructions
- Specific dosage forms, concentrations, and presentations of OMNIPAQUE are recommended for each type of imaging procedure [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, 2.8, 2.9) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
- Individualize the volume, strength, and rate of administration of OMNIPAQUE injection according to the specific dosing tables [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, 2.8, 2.9)]. Consider factors such as age, body weight, vessel size, blood flow rate within the vessel, anticipated pathology, degree and extent of opacification required, structures or area to be examined, disease processes affecting the patient, and equipment and technique to be employed.
- Hydrate patients before and after administration of OMNIPAQUE injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Use aseptic technique for all handling and administration of OMNIPAQUE injection.
- Administer OMNIPAQUE injection at either body (37°C, 98.6°F) or room temperature (20°C to 25°C, 68°F to 77°F).
- Do not mix OMNIPAQUE injection with, or inject in intravenous lines containing, other drugs or total nutritional admixtures except when OMNIPAQUE injection is administered in an automated contrast injection system or contrast management system suitable for simultaneous injection of OMNIPAQUE injection and 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection [see Dosage and Administration (2.10, 2.11)].
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
- Each container of OMNIPAQUE injection and OMNIPAQUE oral solution in single-dose containers are intended for one procedure only. Discard any unused portion.
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Intrathecal Procedures in Adults
- The recommended doses for intrathecal procedures in adults are shown in Table 1.
- Administer over 1 minute to 2 minutes.
- If sequential or repeat examinations are required, allow at least 48 hours for clearance of the drug from the body before repeat administration; however, whenever possible, 5 days to 7 days is recommended.
- If CT myelography is performed, delay imaging by several hours to reduce the degree of contrast.
| Imaging Procedure | Injection Type | Concentration (mg Iodine/mL) | Volume to Administer |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Lumbar Myelography | Lumbar | 180* | 10 mL to 17 mL |
| 240* | 7 mL to 12.5 mL | ||
| Thoracic Myelography | Lumbar Cervical | 240* | 6 mL to 12.5 mL |
| 300* | 6 mL to 10 mL | ||
| Cervical Myelography | Lumbar | 240* | 6 mL to 12.5 mL |
| 300* | 6 mL to 10 mL | ||
| C1-2 | 180* | 7 mL to 10 mL | |
| 240* | 6 mL to 12.5 mL | ||
| 300* | 4 mL to 10 mL | ||
| Total Columnar Myelography | Lumbar | 240* | 6 mL to 12.5 mL |
| 300* | 6 mL to 10 mL | ||
| CT Cisternography | Lumbar | 180* | 10 mL to 17 mL |
| 240* | 7 mL to 12.5 mL | ||
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Intra-arterial Procedures in Adults
The recommended doses for intra-arterial procedures in adults are shown in Table 2.
| Imaging Procedure | Concentration (mg Iodine/mL) | Volume to Administer per Single Injection for Selective Injection Sites | Maximum Cumulative Total Dose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| Cardiac Ventriculography | 350* | 40 mL (Range of 30 mL to 60 mL) may be combined with selective coronary arteriography | 250 mL | |
| Aortography and Selective Visceral Arteriography | 300* |
| 290 mL | |
| 350* | 250 mL | |||
| Aortic root and arch study when used alone | 350* | 50 mL (Range of 20 mL to 75 mL) | 250 mL | |
| Selective Coronary Arteriography | 350* | 5 mL (Range of 3 mL to 14 mL) | 250 mL | |
| Cerebral Arteriography | 300* |
| 290 mL | |
| Peripheral Arteriography | Aortofemoral Runoffs | 300* | 30 mL to 90 mL | 290 mL |
| 350* | 20 mL to 70 mL | 250 mL | ||
| Selective Arteriogram | 300* | 10 mL to 60 mL | 290 mL | |
| 350* | 10 mL to 30 mL | 250 mL | ||
| IA-DSA (head, neck, abdominal, renal, and peripheral vessels) | 140* |
| 250 mL | |
2.4 Recommended Dosage for Intravenous Procedures in Adults
The recommended doses for intravenous procedures in adults are shown in Table 3.
| Imaging Procedure | Concentration (mg Iodine/mL) | Volume to Administer | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Excretory Urography | 300* | 0.6 mL/kg to 1.2 mL/kg body weight (maximum dose is 102 mL) |
|
| 350* | |||
| CT | Head | 240* | 120 mL to 250 mL by infusion |
| 300† | 70 mL to 150 mL by rapid injection | ||
| 350† | 80 mL by rapid injection | ||
| Body | 300† | 50 mL to 200 mL by rapid injection | |
| 350† | 60 mL to 100 mL by rapid injection | ||
| Peripheral Venography (phlebography) | 240* | 20 mL to 150 mL per leg | |
| 300* | 40 mL to 100 mL per leg | ||
| IV-DSA (head, neck, abdominal, renal, and peripheral vessels) | 350* | 30 mL to 50 mL at 7.5 mL/sec to 30 mL/sec using a pressure injector Frequently three or more doses may be required; the maximum cumulative total dose is 250 mL |
|
2.5 Recommended Dosage for Oral Procedures in Adults
Recommended Dosage for Radiographic Examination of the GI Tract in Adults
The recommended dose for radiographic examination of the GI tract in adults is 50 mL to 100 mL of OMNIPAQUE injection 350 mg iodine/mL administered undiluted orally.
Recommended Dosage for CT of the Abdomen and Pelvis in Conjunction with Intravenous Administration of OMINIPAQUE Injection in Adults
The recommended oral dose using diluted OMNIPAQUE injection or OMNIPAQUE oral solution and concurrent intravenous doses for CT of the abdomen and pelvis in adults are shown in Table 4.
| Concentration (mg Iodine/mL) | Volume to Administer | Administration Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| Oral Dose Using Diluted OMNIPAQUE Injection | ||
| 6 mg Iodine/mL to 12 mg Iodine/mL of Diluted OMNIPAQUE Injection* | 500 mL to 1,000 mL |
|
| Oral Dose Using OMNIPAQUE Oral Solution | ||
| 9 mg Iodine/mL or 12 mg Iodine/mL of OMNIPAQUE Oral Solution | 500 mL to 1,000 mL | Administer the oral dose all at once or over a period of up to 45 minutes if there is difficulty in consuming the required volume. |
| Intravenous Dose of OMNIPAQUE injection in Conjunction with Oral Administration | ||
| 300† | 100 mL to 150 mL | Administer up to 40 minutes AFTER consumption of the oral dose. |
Preparation of Diluted OMNIPAQUE Injection for Oral Administration for CT of the Abdomen and Pelvis in Adults
- Prepare the diluted OMNIPAQUE injection in water, carbonated beverage, milk, infant formula, or juice just prior to administration according to Table 5.
- Discard any unused portion after the procedure.
| Concentration of Diluted OMNIPAQUE injection (mg iodine/mL) | Dilution Method 1 | Dilution Method 2 | Dilution Method 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume of OMNIPAQUE 240 mg Iodine/mL (mL) | Volume of Added Liquid*
(mL) | Volume of OMNIPAQUE 300 mg Iodine/mL (mL) | Volume of Added Liquid*
(mL) | Volume of OMNIPAQUE 350 mg Iodine/mL (mL) | Volume of Added Liquid*
(mL) |
|
|
||||||
| 6 | 25 | 975 | 20 | 980 | 17 | 983 |
| 9 | 38 | 962 | 30 | 970 | 26 | 974 |
| 12 | 50 | 950 | 40 | 960 | 35 | 965 |
| 15 | 63 | 937 | 50 | 950 | 43 | 957 |
| 18 | 75 | 925 | 60 | 940 | 52 | 948 |
| 21 | 88 | 912 | 70 | 930 | 60 | 940 |
2.6 Recommended Dosage for Intraarticular Procedures in Adults
- The recommended doses for intraarticular procedures in adults are shown in Table 6.
- Use passive or active manipulation to disperse the medium throughout the joint space.
| Imaging Procedure | Location | Concentration (mg Iodine/mL) | Volume to Administer | Double Contrast/Single Contrast |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| Arthrography | Knee | 240* | 5 mL to 15 mL | Lower volumes recommended for double-contrast examinations; higher volumes recommended for single-contrast examinations. |
| 300* | 5 mL to 15 mL | |||
| 350* | 5 mL to 10 mL | |||
| Shoulder | 300* | 10 mL | ||
| Temporomandibular | 300* | 0.5 mL to 1 mL | ||
2.7 Recommended Dosage for Body Cavity Procedures in Adults
- The recommended doses for body cavity procedures in adults are shown in Table 7.
- Volume to administer may vary depending on individual anatomy and/or disease state.
| Imaging Procedure | Concentration (mg Iodine/mL) | Volume to Administer | Route of Administration |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Endoscopic retrograde pancreatography (ERP) and cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) | 240* | 10 mL to 50 mL | Intraductal |
| Herniography | 240* | 15 mL to 20 mL | Intraperitoneal |
| 300* | |||
| Hysterosalpingography | 240* | 50 mL | Intrauterine |
2.8 Recommended Dosage for Intrathecal, Intra-arterial, and Intravenous Procedures in Pediatric Patients
Recommended Dosage for Intrathecal Procedures in Pediatric Patients Aged 2 Weeks and Older
- Recommended doses based on age for intrathecal procedures in pediatric patients aged 2 weeks and older are shown in Table 8.
- Administer over 1 minute to 2 minutes.
- If sequential or repeat examinations are required, allow at least 48 hours for clearance of the drug from the body before repeat administration; however, whenever possible, 5 days to 7 days is recommended.
- If CT myelography is performed, delay imaging by several hours to reduce the degree of contrast.
| Imaging Procedure | Injection Type | Age | Concentration (mg Iodine/mL) | Volume to Administer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| Lumbar | 2 weeks up to 3 months | 180* | 2 mL to 4 mL |
| 3 months up to 36 months | 4 mL to 8 mL | |||
| 3 years up to 7 years | 5 mL to 10 mL | |||
| 7 years up to 13 years | 5 mL to 12 mL | |||
| 13 years to 18 years | 6 mL to 15 mL | |||
Recommended Dosage for Intra-arterial Procedures in Pediatric Patients
The recommended doses for intra-arterial procedures in pediatric patients are shown in Table 9.
| Imaging Procedure | Concentration (mg Iodine/mL) | Volume per Body Weight to Administer per Single Injection | Maximum Cumulative Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Cardiac Ventriculography | 300* | 1.75 mL/kg (Range of 1.5 mL/kg to 2 mL/kg) | 6 mL/kg up to a total volume of 290 mL |
| 350* | 1.25 mL/kg (Range of 1 mL/kg to 1.5 mL/kg) | 5 mL/kg up to a total volume of 250 mL | |
| Aortography (aortic root, aortic arch, and descending aorta) | 350* | 1 mL/kg | 5 mL/kg up to a total volume of 250 mL |
| Pulmonary Angiography | 350* | 1 mL/kg | 5 mL/kg up to a total volume of 250 mL |
Recommended Dosage for Intravenous Procedures in Pediatric Patients
The recommended doses for intravenous procedures in pediatric patients are shown in Table 10.
| Imaging Procedure | Concentration (mg Iodine/mL) | Volume per Body Weight to Administer |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Excretory Urography | 300* | 0.5 mL/kg to 3 mL/kg (Maximum single dose: 116 mL) |
| CT of the Head and Body | 240* | 1 mL/kg to 2 mL/kg (with maximum 3 mL/kg) (Maximum single dose: 116 mL) |
| 300† | ||
2.9 Recommended Dosage for Oral or Rectal and Body Cavity Procedures in Pediatric Patients
Recommended Dosage for Radiographic Examination of the GI Tract in Pediatric Patients
- The recommended doses for radiographic examination of the GI tract are shown in Table 11.
- Administer orally or rectally.
| Age | Concentration (mg iodine/mL) | Oral Volume | Rectal Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Less than 3 months | 180* | 5 mL to 30 mL | May be a larger volume than the volume given orally (up to 300 mL) |
| 3 months to 3 years | 180*, 240*, or 300* | Up to 60 mL | |
| 4 years to 10 years | Up to 80 mL | ||
| Greater than 10 years | Up to 100 mL | ||
Recommended Dosage for CT of the Abdomen and Pelvis in Conjunction with Intravenous Administration of OMNIPAQUE in Pediatric Patients
The recommended oral dose using diluted OMNIPAQUE injection or OMNIPAQUE oral solution and concurrent intravenous dose for CT of the abdomen and pelvis in pediatric patients are shown in Table 12.
| Concentration (mg Iodine/mL) | Volume to Administer | Administration Instructions | Maximum Dose by Age or Body Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral Dose Using Diluted OMNIPAQUE Injection | |||
| 9 mg Iodine/mL to 21 mg Iodine/mL of Diluted OMNIPAQUE Injection* | 180 mL to 750 mL |
|
|
| Oral Dose Using OMNIPAQUE Oral Solution | |||
| 6 mg Iodine/mL or 12 mg Iodine/mL of OMNIPAQUE Oral Solution | 180 mL to 750 mL | Administer the oral dose all at once or over a period of up to 45 minutes if there is difficulty in consuming the required volume. |
|
| Intravenous Dose in Conjunction with Oral Administration | |||
| 240† or 300† | 2 mL/kg body weight (with a range of 1 mL/kg to 2 mL/kg) | Administer up to 60 minutes AFTER consumption of the oral dose. | 3 mL/kg (maximum single dose: 116 mL) |
Preparation of Diluted OMNIPAQUE Injection for Oral Administration for CT of the Abdomen and Pelvis in Pediatric Patients
- Prepare the diluted OMNIPAQUE injection in water, carbonated beverage, milk, infant formula, or juice just prior to administration according to Table 13.
- Discard any unused portion after the procedure.
| Concentration of Diluted OMNIPAQUE injection (mg iodine/mL) | Dilution Method 1 | Dilution Method 2 | Dilution Method 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume of OMNIPAQUE 240 mg iodine/mL (mL) | Volume of Added Liquid*
(mL) | Volume of OMNIPAQUE 300 mg Iodine/mL (mL) | Volume of Added Liquid*
(mL) | Volume of OMNIPAQUE 350 mg Iodine/mL (mL) | Volume of Added Liquid*
(mL) |
|
|
||||||
| 6 | 25 | 975 | 20 | 980 | 17 | 983 |
| 9 | 38 | 962 | 30 | 970 | 26 | 974 |
| 12 | 50 | 950 | 40 | 960 | 35 | 965 |
| 15 | 63 | 937 | 50 | 950 | 43 | 957 |
| 18 | 75 | 925 | 60 | 940 | 52 | 948 |
| 21 | 88 | 912 | 70 | 930 | 60 | 940 |
Recommended Dosage for Voiding Cystourethrography in Pediatric Patients
- Voiding cystourethrography (VCU) can be performed in conjunction with excretory urography [see Dosage and Administration (2.8)].
- The concentration of diluted OMNIPAQUE injection may vary depending upon the patient's size and age and with the technique and equipment used.
- Volume ranges of diluted OMNIPAQUE injection 50 mg iodine/mL and 100 mg iodine/mL are shown in Table 14.
- Dilute OMNIPAQUE injection with Sterile Water for Injection according to Table 15, utilizing aseptic technique, just prior to use.
- Discard any unused portion after the procedure.
| Concentration of Diluted OMNIPAQUE Injection*
(mg iodine/mL) | Volume to Administer |
|---|---|
| 50 | 50 mL to 600 mL by intravesical administration |
| 100 | 50 mL to 300 mL by intravesical administration |
| Concentration of Diluted OMNIPAQUE injection (mg iodine/mL) | Dilution Method 1 | Dilution Method 2 | Dilution Method 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volume of OMNIPAQUE 240 mg Iodine/mL (mL) | Volume of Sterile Water for Injection (mL) | Volume of OMNIPAQUE 300 mg Iodine/mL (mL) | Volume of Sterile Water for Injection (mL) | Volume of OMNIPAQUE 350 mg Iodine/mL (mL) | Volume of Sterile Water for Injection (mL) |
|
| 50 | 100 | 380 | 100 | 500 | 100 | 600 |
| 60 | 100 | 300 | 100 | 400 | 100 | 483 |
| 70 | 100 | 243 | 100 | 330 | 100 | 400 |
| 80 | 100 | 200 | 100 | 275 | 100 | 338 |
| 90 | 100 | 167 | 100 | 233 | 100 | 289 |
| 100 | 100 | 140 | 100 | 200 | 100 | 250 |
2.10 Directions for Use of the 500 mL Bottles of OMNIPAQUE Injection 300 mg Iodine/mL and 350 mg Iodine/mL as Imaging Bulk Package
- OMNIPAQUE injection 300 mg iodine/mL and OMNIPAQUE injection 350 mg iodine/mL in 500 mL bottles may be used as an Imaging Bulk Package (IBP) for intravenous use [see Dosage and Administration (2.4, 2.8)].
- When used as an IBP, check the appropriate box on the container label to indicate that the selected container is to be utilized as an Imaging Bulk Package. This container is for use only with an automated contrast injection system, contrast management system, or contrast media transfer set approved or cleared for use with this contrast agent in this IBP. See device labeling for information on devices indicated for use with this IBP and techniques to help assure safe use.
- Use the OMNIPAQUE IBP and 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP in a room designated for radiological procedures that involve administration of a contrast agent.
- Using aseptic technique, penetrate the container closure only one time with a suitable sterile component of the automated contrast injection system, contrast management system, or contrast media transfer set cleared for use with the OMNIPAQUE IBP.
- If 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP is used with the OMNIPAQUE IBP, prepare the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP sterile port in accordance with the dosage and administration section of its approved prescribing information and affix the saline tag provided with the OMNIPAQUE IBP on the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP container.
- Once the OMNIPAQUE IBP and 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection containers are punctured, do not remove them from the work area during the entire period of use. Maintain the OMNIPAQUE IBP in an inverted position such that container contents are in continuous contact with the dispensing set.
- After the container closure is punctured, if the integrity of the OMNIPAQUE IBP, the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, and the delivery system cannot be assured through direct continuous supervision, discard the IBP, 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP, and all associated disposables for the contrast media transfer set.
- A maximum time from initial puncture is 8 hours. Discard any unused portion.
2.11 Directions for Use of the 500 mL Bottles of OMNIPAQUE Injection 300 mg Iodine/mL and 350 mg Iodine/mL as Pharmacy Bulk Package
- OMNIPAQUE injection 300 mg iodine/mL and OMNIPAQUE injection 350 mg iodine/mL in 500 mL bottles contain many single doses and may be used as a Pharmacy Bulk Package (PBP).
- When used as a PBP, check the appropriate box on the container label to indicate that the selected container is to be utilized as a Pharmacy Bulk Package. This container is not for direct infusion; it is for use in pharmacy admixture service to dispense aliquots using a suitable dispensing set under a laminar flow hood or equivalent clean air compounding area using aseptic technique.
- Penetrate the container closure only one time, utilizing a suitable transfer device and aseptic technique.
- The withdrawal of container contents should be accomplished without delay. However, should this not be possible, a maximum time of 8 hours from initial closure entry is permitted to complete fluid transfer operations.
- Do not remove the container from the aseptic area during the entire 8-hour period.
- The temperature of the container should not exceed 37°C (98.6°F), after the closure has been entered.
- Discard any unused portion after 8 hours from the initial closure entry.
2.12 Directions for Use of the 150 mL Bottles of OMNIPAQUE Injection 300 mg Iodine/mL and 350 mg Iodine/mL with an Automated Contrast Injection System or Contrast Management System
- OMNIPAQUE injection 300 mg iodine/mL and OMNIPAQUE injection 350 mg iodine/mL in 150 mL bottles may be used with a contrast media management system cleared for use with OMNIPAQUE injection 300 mg iodine/mL and 350 mg iodine/mL in 150 mL bottles.
- See device labeling for information on device indications, instructions for use, and techniques to help assure safe use.
- Using aseptic technique, penetrate the container closure only one time with a suitable sterile component of the contrast media management system cleared for use with OMNIPAQUE 300 mg iodine/mL and 350 mg iodine/mL in 150 mL bottles.
- Once the container is punctured, do not remove the bottle from the work area during the entire period of use.
- Maximum use time is 4 hours after initial puncture.
- Each bottle is for one procedure only. Discard unused portion.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection and Oral Solution: Colorless to pale yellow solution available in the following presentations:
| Dosage Form | Concentration (mg of iodine/mL) | Package Size | Package Type |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Injection | 140 | 50 mL | Single-Dose Bottle |
| 180 | 10 mL | Single-Dose Vial | |
| 240 | 10 mL and 20 mL | Single-Dose Vial | |
| 50 mL and 100 mL | Sigle-Dose Bottle | ||
| 300 | 10 mL | Single-Dose Vial | |
| 30 mL, 50 mL, 100 mL, 125 mL, and 150 mL | Single-Dose Bottle | ||
| 500 mL* | Imaging or Pharmacy Bulk Package | ||
| 350 | 50 mL, 75 mL, 100 mL, 125 mL, 150 mL, and 200 mL | Single-Dose Bottle | |
| 500 mL* | Imaging or Pharmacy Bulk Package | ||
| Oral Solution | 9 | 500 mL | Single-Dose Bottle |
| 12 | 500 mL | Single-Dose Bottle | |
4. Contraindications
OMNIPAQUE for hysterosalpingography is contraindicated during pregnancy or suspected pregnancy, menstruation or when menstruation is imminent, within 6 months after termination of pregnancy, within 30 days after conization or curettage, when signs of infection are present in any portion of the genital tract including the external genitalia, and when reproductive tract neoplasia is known or suspected because of the risk of peritoneal spread of neoplasm.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Risks Associated with Intrathecal Administration of OMNIPAQUE Injection 140 mg Iodine/mL and 350 mg Iodine/mL
Use only the iodine concentrations and presentations recommended for intrathecal procedures [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.8)]. Intrathecal administration of OMNIPAQUE of a wrong iodine concentration, even if inadvertent, can cause death, convulsions, seizures, cerebral hemorrhage, coma, paralysis, arachnoiditis, acute renal failure, cardiac arrest, rhabdomyolysis, hyperthermia, and brain edema.
5.2 Risks Associated with Parenteral Administration of OMNIPAQUE Oral Solution
Adverse reactions such as hemolysis may occur if OMNIPAQUE oral solution is administered intravenously or intraarterially due to low osmolality [see Description (11)]. OMNIPAQUE oral solution is for oral use only.
5.3 Hypersensitivity Reactions
OMNIPAQUE can cause life-threatening or fatal hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis. Manifestations include respiratory arrest, laryngospasm, bronchospasm, angioedema, and shock. Most severe reactions develop shortly after the start of the injection (within 1 to 3 minutes), but delayed reactions can also occur. There is an increased risk in patients with a history of a previous reaction to contrast agent and known allergic disorders (i.e., bronchial asthma, drug, or food allergies) or other hypersensitivities. Premedication with antihistamines or corticosteroids does not prevent serious life-threatening reactions but may reduce both their incidence and severity.
Obtain a history of allergy, hypersensitivity, or hypersensitivity reactions to iodinated contrast agents and always have emergency resuscitation equipment and trained personnel available prior to OMNIPAQUE administration. Monitor all patients for hypersensitivity reactions.
5.4 Acute Kidney Injury
Acute kidney injury, including renal failure, may occur after parenteral administration of OMNIPAQUE. Risk factors include: pre-existing renal impairment, dehydration, diabetes mellitus, congestive heart failure, advanced vascular disease, elderly age, concomitant use of nephrotoxic or diuretic medications, multiple myeloma/paraproteinaceous diseases, repetitive and/or large doses of an iodinated contrast agent.
Use the lowest necessary dose of OMNIPAQUE in patients with renal impairment. Adequately hydrate patients prior to and following parenteral administration of OMNIPAQUE. Do not use laxatives, diuretics, or preparatory dehydration prior to OMNIPAQUE administration.
5.5 Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions
Life-threatening or fatal cardiovascular reactions including hypotension, shock, cardiac arrest have occurred with the parenteral administration of OMNIPAQUE. Most deaths occur during injection or five to ten minutes later, with cardiovascular disease as the main aggravating factor. Cardiac decompensation, serious arrhythmias, and myocardial ischemia or infarction can occur during coronary arteriography and ventriculography.
Based on clinical literature, reported deaths from the administration of iodinated contrast agents range from 6.6 per million (0.00066%) to 1 in 10,000 (0.01%). Use the lowest necessary dose of OMNIPAQUE in patients with congestive heart failure and always have emergency resuscitation equipment and trained personnel available. Monitor all patients for severe cardiovascular reactions.
5.6 Thromboembolic Events
Serious, rarely fatal, thromboembolic events causing myocardial infarction and stroke can occur during angiocardiography procedures with iodinated contrast agents including OMNIPAQUE. During these procedures, increased thrombosis and activation of the complement system occurs. Risk factors for thromboembolic events include: length of procedure, catheter and syringe material, underlying disease state, and concomitant medications.
To minimize thromboembolic events, use meticulous angiographic techniques, and minimize the length of the procedure. Avoid blood remaining in contact with syringes containing OMNIPAQUE, which increases the risk of clotting. Avoid angiocardiography in patients with homocystinuria because of the risk of inducing thrombosis and embolism.
5.7 Extravasation and Injection Site Reactions
Extravasation of OMNIPAQUE during intravenous or intra-arterial injection may cause tissue necrosis and/or compartment syndrome, particularly in patients with severe arterial or venous disease. Ensure intravenous or intra-arterial placement of catheters prior to injection. Monitor patients for extravasation and advise patients to seek medical care for progression of symptoms.
5.8 Thyroid Storm in Patients with Hyperthyroidism
Thyroid storm has occurred after the intravenous or intra-arterial use of iodinated contrast agents in patients with hyperthyroidism, or with an autonomously functioning thyroid nodule. Evaluate the risk in such patients before use of OMNIPAQUE.
5.9 Thyroid Dysfunction in Pediatric Patients 0 to 3 Years of Age
Thyroid dysfunction characterized by hypothyroidism or transient thyroid suppression has been reported after both single exposure and multiple exposures to iodinated contrast media (ICM) in pediatric patients 0 to 3 years of age.
Younger age, very low birth weight, prematurity, underlying medical conditions affecting thyroid function, admission to neonatal or pediatric intensive care units, and congenital cardiac conditions are associated with an increased risk of hypothyroidism after ICM exposure. Pediatric patients with congenital cardiac conditions may be at the greatest risk given that they often require high doses of contrast during invasive cardiac procedures.
An underactive thyroid during early life may be harmful for cognitive and neurological development and may require thyroid hormone replacement therapy. After exposure to ICM, individualize thyroid function monitoring based on underlying risk factors, especially in term and preterm neonates.
5.10 Hypertensive Crisis in Patients with Pheochromocytoma
Hypertensive crisis has occurred after the use of iodinated contrast agents in patient with pheochromocytoma. Monitor patients when administering OMNIPAQUE intravenously or intra-arterially if pheochromocytoma or catecholamine-secreting paragangliomas are suspected. Inject the minimum amount of contrast necessary, assess the blood pressure throughout the procedure, and have measures for treatment of a hypertensive crisis readily available.
5.11 Sickle Cell Crisis in Patients with Sickle Cell Disease
Iodinated contrast agents when administered intravenously or intra-arterially may promote sickling in individuals who are homozygous for sickle cell disease. Hydrate patients prior to and following OMNIPAQUE administration and use OMNIPAQUE only if the necessary imaging information cannot be obtained with alternative imaging modalities.
5.12 Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR) may develop from 1 hour to several weeks after intravenous or intra-arterial contrast agent administration. These reactions include Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN), acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS). Reaction severity may increase and time to onset may decrease with repeat administration of contrast agents; prophylactic medications may not prevent or mitigate severe cutaneous adverse reactions. Avoid administering OMNIPAQUE to patients with a history of a severe cutaneous adverse reaction to OMNIPAQUE.
5.13 Interference with Laboratory Test
OMNIPAQUE can interfere with protein-bound iodine test [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
5.14 Increased Risk of Seizures with Intrathecal Procedures
Focal and generalized motor seizures have been reported after intrathecal use of iodinated contrast agents. In several of the cases, higher than recommended doses were administered.
Use of medications that may lower the seizure threshold (phenothiazine derivatives, including those used for their antihistaminic properties; tricyclic antidepressants; MAO inhibitors; CNS stimulants; analeptics; antipsychotic agents) should be carefully evaluated. Consider discontinuing these agents at least 48 hours before and for at least 24 hours following intrathecal administration of OMNIPAQUE.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Risks Associated with Intrathecal Administration of OMNIPAQUE Injection 140 mg Iodine/mL and 350 mg Iodine/mL [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Risks Associated with Parenteral Administration of OMNIPAQUE Oral Solution [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Acute Kidney Injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Thromboembolic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Thyroid Dysfunction in Pediatric Patients 0 to 3 Years of Age [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Intrathecal Administration
Adults
Adverse reactions (≥1%) in 1,531 adult patients following intrathecal administration of OMNIPAQUE in clinical trials are presented in Table 16.
| System Organ Class | Adverse Reaction | Incidence N=1,531 |
|---|---|---|
| Nervous system disorders | Headaches | 18% |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | Pain including backache, neckache, stiffness, neuralgia | 8% |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Nausea | 6% |
| Vomiting | 3% | |
| Nervous System disorders | Dizziness | 2% |
Other adverse reactions (<1%) were:
Ear and labyrinth disorders: tinnitus, vertigo
Eye disorders: photophobia
General disorders and administration site conditions: sensation of heat
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: loss of appetite
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: feeling of heaviness
Nervous system disorders: drowsiness, hypertonia, neuralgia, neurological changes, paresthesia, syncope
Renal and urinary disorders: difficulty in micturition
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: sweating
Vascular disorders: hypertension, hypotension
Pediatric Patients
The adverse reactions reported in pediatric patients following intrathecal administration of OMNIPAQUE were generally similar to those reported in adults. A total of 152 pediatric patients were administered OMNIPAQUE 180 mg iodine/mL intrathecally by lumbar puncture for pediatric myelography in clinical trials. Adverse reactions (≥1%) are presented in Table 17.
| System Organ Class | Adverse Reaction | Incidence N=152 |
|---|---|---|
| Nervous system disorders | Headache | 9% |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Vomiting | 6% |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | Backache | 1.3% |
Other adverse reactions (<1%) were:
Gastrointestinal disorders: stomachache
General disorders and administration site conditions: fever
Nervous system disorders: neurological changes
Psychiatric disorders: visual hallucination
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: hives
Intra-arterial or Intravenous Administration
Adults
Adverse reactions (≥1%) in 1,485 adult patients following intra-arterial or intravenous administration of OMNIPAQUE in clinical trials are presented in Table 18.
| System Organ Class | Adverse Reaction | Incidence (N=1,485) |
|---|---|---|
| Cardiac disorders | Arrhythmias including PVCs and PACs | 2% |
| Nervous system disorders | Pain | 3% |
| Vision abnormalities including blurred vision and photomas | 2% | |
| Taste perversion | 1% | |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Nausea | 2% |
Other adverse reactions (<1%) were:
Cardiac disorders: hypotension, cardiac failure, asystole, bradycardia, tachycardia, vasovagal reaction
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: dyspnea, rhinitis, coughing, laryngitis
Gastrointestinal disorders: vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, cramp, dry mouth
General disorders and administration site conditions: fever, shivering
Nervous system disorders: cerebral infarction, convulsion, hemiparesis, motor and speech dysfunction, nystagmus, paresthesia, somnolence, transient ischemic attack, vertigo including dizziness and lightheadedness
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: still neck
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: urticaria, abscess, pruritus, purpura
Psychiatric disorders: anxiety, syncope
Pediatric Patients
Adverse reactions reported in pediatric patients following intra-arterial or intravenous administration of OMNIPAQUE were generally similar in quality and frequency to those reported in adults. A total of 391 pediatric patients in clinical trials were administered OMNIPAQUE 240 mg iodine/mL, 300 mg iodine/mL, or 350 mg iodine/mL by intra-arterial or intravenous injection for pediatric cardiac ventriculography, excretory urography, and CT head imaging.
Adverse reactions (≥1%) were vomiting (2%) and nausea (1%).
Other adverse reactions (<1%) were:
Cardiac disorders: Ventricular tachycardia, 2:1 heart block, hypertension, anemia
General disorders and administration site conditions: Pain, fever
Nervous system disorders: Convulsion, taste abnormality
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Congestion, apnea
Endocrine disorders: Hypoglycemia
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Rash
Oral or Rectal Administration for Examination of the Gastrointestinal Tract
Adults
A total of 54 adult patients were administered undiluted OMNIPAQUE 350 mg iodine/mL by oral route for radiographic examination of the gastrointestinal tract in clinical trials. Adverse reactions (≥1%) are presented in Table 19.
| System Organ Class | Adverse Reaction | Incidence N=54 |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Diarrhea | 42% |
| Nausea | 15% | |
| Vomiting | 11% | |
| Abdominal Pain | 7% | |
| Flatulence | 2% | |
| Nervous system disorders | Headache | 2% |
Pediatrics Patients
A total of 58 pediatric patients were administered OMNIPAQUE by oral or rectal administration in clinical trials. Adverse reactions (≥1%) are presented in Table 20.
| System Organ Class | Adverse Reaction | Incidence N=58 |
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Diarrhea | 36% |
| Vomiting | 9% | |
| Nausea | 5% | |
| Abdominal pain | 2% | |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | Fever | 5% |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Urticaria | 2% |
| Vascular disorders | Hypotension | 2% |
Oral Administration for CT of the Abdomen in Conjunction with Intravenous Administration
Adults
A total of 44 adult patients received diluted OMNIPAQUE (4-9 mg iodine/mL) by oral route in conjunction with intravenously injected OMNIPAQUE 300 mg iodine/mL for CT examination of the abdomen in clinical trials. Adverse reactions (≥1%) were limited to a single report of vomiting (2.3%).
Pediatric Patients
A total of 69 pediatric patients received diluted OMNIPAQUE (9-29 mg iodine/mL) by oral route in conjunction with intravenously administered OMNIPAQUE 240 mg iodine/mL or OMNIPAQUE 300 mg iodine/mL for CT examination of the abdomen in clinical trials. Adverse reactions (≥1%) were limited to a single report of vomiting (1.4%).
Intraarticular Administration
Arthrography in Adults
A total of 285 adult patients received OMNIPAQUE 240 mg iodine/mL, 300 mg iodine/mL, or 350 mg iodine/mL for various body cavity examinations in clinical trials. The most frequent adverse reactions (≥1%) were administration site pain (26%) and swelling (22%) in arthrography. Patients also experienced heat (7%).
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of OMNIPAQUE. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
General
Intrathecal Administration
Nervous system disorders: Meningism, aseptic meningitis, seizures or status epilepticus, disorientation, coma, depressed or loss of consciousness, transient contrast-induced toxic encephalopathy (including amnesia, hallucination, paralysis, paresis, speech disorder, aphasia, dysarthria), restlessness, tremors, hypoesthesia
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Pain, muscle spasms or spasticity
Psychiatric disorders: Confusional state, agitation, anxiety
Eye disorders: Transient visual impairment including cortical blindness
Renal and urinary disorders: Acute kidney injury
Intra-arterial or Intravenous Administration
Cardiac disorders: Severe cardiac complications (including cardiac arrest, cardiopulmonary arrest), shock, peripheral vasodilatation, palpitations, vasospasm including spasm of coronary arteries, myocardial infarction, syncope, cyanosis, pallor, flushing, chest pain
Vascular disorders: Vasospasm and thrombophlebitis following intravenous injection
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Neutropenia
Nervous system disorders: Disorientation, coma, depressed or loss of consciousness, transient contrast-induced toxic encephalopathy (including amnesia, hallucination, paralysis, paresis, speech disorder, aphasia, dysarthria), restlessness, tremors, hypoesthesia
Psychiatric disorders: Confusional state, agitation
Eye disorders: Eye irritation or itchiness, periorbital edema, ocular or conjunctival hyperemia, lacrimation
Renal and urinary disorders: Acute kidney injury, toxic nephropathy (CIN), transient proteinuria, oliguria or anuria, increased serum creatinine
Gastrointestinal disorders: Abdominal pain, pancreatitis aggravated, salivary gland enlargement
Endocrine disorders: Hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Respiratory distress, respiratory failure, pulmonary edema, bronchospasm, laryngospasm, throat irritation, throat tightness, laryngeal edema, wheezing, chest discomfort, asthmatic attack
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Contrast media reactions range from mild (e.g., pleomorphic rashes, drug eruption, erythema and skin discoloration, blisters, hyperhidrosis, angioedema, localized areas of edema) to severe (e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis [SJS/TEN], bullous or exfoliative dermatitis, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis [AGEP] and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms [DRESS])
Body Cavity Administration
Gastrointestinal disorders: Pancreatitis
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Arthritis (arthrography)
Hysterosalpingography: Injection of OMNIPAQUE for hysterosalpingography is associated with immediate, transient pain. Monitor injection pressure and volume instilled to minimize pain and to avoid disruptive distention of the uterus and fallopian tubes. Fluoroscopic monitoring is recommended.
Nervous system disorders: Pain (49%), somnolence and fever each with an individual incidence of 3%
Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea (3%)
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Drug-Drug Interactions
Metformin
In patients with renal impairment, metformin can cause lactic acidosis. Iodinated contrast agents appear to increase the risk of metformin-induced lactic acidosis, possibly as a result of worsening renal function. Stop metformin at the time of, or prior to, OMNIPAQUE administration in patients with an eGFR between 30 and 60 mL/min/1.73 m2; in patients with a history of hepatic impairment, alcoholism or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast. Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hours after the imaging procedure, and reinstitute metformin only after renal function is stable.
7.2 Drug-Laboratory Test Interactions
Protein-Bound Iodine Test
Iodinated contrast agents, including OMNIPAQUE, will temporarily increase protein-bound iodine in blood. Do not perform protein-bound iodine test for at least 16 days following administration of OMNIPAQUE. However, thyroid function tests that do not depend on iodine estimation, e.g., T3 resin uptake or direct thyroxine assays, are not affected.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Hysterosalpingography is contraindicated in pregnant women due to the potential risk to the fetus from an intrauterine procedure [see Contraindications (4)]. There are no data with iohexol use in pregnant women to inform any drug-associated risks. Iohexol crosses the placenta and reaches fetal tissues in small amounts (see Data). In animal reproduction studies, no developmental toxicity occurred with intravenous iohexol administration to rats and rabbits at doses up to 0.4 (rat) and 0.5 (rabbit) times the maximum recommended human intravenous dose (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
Literature reports show that intravenously administered iohexol crosses the placenta and is visualized in the digestive tract of exposed infants after birth.
Animal Data
Iohexol was neither embryotoxic nor teratogenic in either rats or rabbits at the following dose levels tested: 1.0, 2.0, 4.0 g iodine/kg in rats, administered intravenously to 3 groups of 25 dams once daily during days 6 through 15 of pregnancy; 0.3, 1.0, 2.5 g iodine/kg in rabbits, administered intravenously to 3 groups of 18 rabbits dosed once a day during days 6 through 18 of pregnancy.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Published literature reports that breast feeding after intravenous iohexol administration to the mother would result in the infant receiving an oral dose of approximately 0.7% of the maternal intravenous dose; however, lactation studies have not been conducted with oral, intrathecal, or intracavity administration of iohexol. There is no information on the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant or on milk production. Iodinated contrast agents are excreted unchanged in human milk in very low amounts with poor absorption from the gastrointestinal tract of a breastfed infant. Exposure to iohexol to a breastfed infant can be minimized by temporary discontinuation of breastfeeding (see Clinical Considerations). The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for OMNIPAQUE and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from OMNIPAQUE or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
Interruption of breastfeeding after exposure to iodinated contrast agents is not necessary because the potential exposure of the breastfed infant to iodine is small. However, a lactating woman may consider interrupting breastfeeding and pumping and discarding breast milk for 10 hours (approximately 5 elimination half-lives) after OMNIPAQUE administration to minimize drug exposure to a breastfed infant.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Intrathecal Use
The safety and effectiveness of OMNIPAQUE have been established in pediatric patients aged 2 weeks and older for myelography and CT myelography (lumbar, thoracic, cervical, total columnar) and for CT cisternography. Use of OMNIPAQUE is supported by controlled clinical studies in adults for myelography, in addition to clinical studies in pediatric patients undergoing myelography.
The safety and effectiveness of OMNIPAQUE have not been established for intrathecal use in pediatric patients less than 2 weeks of age.
The safety and effectiveness of OMNIPAQUE for CT cerebral ventriculography have not been established in pediatric patients.
Intra-arterial or Intravenous Use
Cardiac Ventriculography, Aortography, and Pulmonary Angiography
The safety and effectiveness of OMNIPAQUE have been established in pediatric patients from birth to 17 years of age for cardiac ventriculography, aortography, and pulmonary angiography. Use of OMNIPAQUE is supported by controlled clinical studies in adults for cardiac ventriculography and aortography, in addition to controlled clinical studies in pediatric patients undergoing cardiac ventriculography, including aortography.
Excretory Urography
The safety and effectiveness of OMNIPQUE have been established in pediatric patients from birth to 17 years of age for excretory urography. Use of OMNIPAQUE is supported by controlled clinical studies in adults for urography, in addition to controlled clinical studies in pediatric patients undergoing urography and clinical safety data in pediatric patients down to birth.
CT of the Head and Body
The safety and effectiveness of OMNIPAQUE have been established in pediatric patients from birth to 17 years of age for CT imaging of the head and body. Use of OMNIPAQUE is supported by controlled clinical studies in adults for head and body CT, in addition to clinical studies in pediatric patients undergoing head CT and in 69 pediatric patients undergoing CT of the abdomen after oral administration of diluted OMNIPAQUE plus intravenous administration of OMNIPAQUE.
Selective Coronary Arteriography, Cerebral and Peripheral Arteriography, Intra-arterial Digital Subtraction Angiography, Peripheral Venography, and Intravenous Digital Subtraction Angiography
The safety and effectiveness of OMNIPAQUE have not been established in pediatric patients for selective coronary arteriography, cerebral or peripheral arteriography, intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography, peripheral venography, and intravenous digital subtraction angiography.
Oral or Rectal Use
Examination of the GI Tract
The safety and effectiveness of OMNIPAQUE have been established in pediatric patients, from birth to 17 years of age for examination of the GI tract. Use of OMNIPAQUE is supported by controlled studies in adults for examination of the GI tract, in addition to clinical studies in pediatric patients undergoing examination of the GI tract.
CT of the Abdomen and Pelvis in Conjunction with Intravenous Use
The safety and effectiveness of OMNIPAQUE for CT of the abdomen and pelvis have been established in pediatric patients from birth to 17 years of age. Use is supported by clinical trials in adults, in addition to clinical studies in 69 pediatric patients undergoing CT of the abdomen.
Intraarticular Use
The safety and effectiveness of OMNIPAQUE have not been established in pediatric patients for arthrography.
Body Cavity Use
Voiding Cystourethrography
OMNIPAQUE is indicated for use in pediatric patients from birth to 17 years of age for voiding cystourethrography (VCU). Use for voiding cystourethrography is supported by clinical studies in 51 pediatric patients undergoing VCU.
ERCP, Herniography, and Hysterosalpingography
The safety and effectiveness of OMNIPAQUE have not been established in pediatric patients for ERCP, herniography, or hysterosalpingography.
In general, the frequency of adverse reactions in pediatric patients was similar to that seen in adults [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Pediatric patients at higher risk of experiencing adverse events during contrast-medium administration may include those having asthma, a sensitivity to medication and/or allergens, congestive heart failure, a serum creatinine greater than 1.5 mg/dL or those less than 12 months of age.
Thyroid function tests indicative of thyroid dysfunction, characterized by hypothyroidism or transient thyroid suppression have been reported following iodinated contrast media administration in pediatric patients, including term and preterm neonates. Some patients were treated for hypothyroidism. After exposure to iodinated contrast media, individualize thyroid function monitoring in pediatric patients 0 to 3 years of age based on underlying risk factors, especially in term and preterm neonates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
In clinical studies of OMNIPAQUE for CT of the head and body, 52 (17%) of patients were 70 and over. No overall differences in safety were observed between these patients and younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in safety and effectiveness between the elderly and younger patients.
Iohexol is substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to iohexol may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The clearance of iohexol decreases with increasing degree of renal impairment and results in delayed opacification of the urinary system. In addition, preexisting renal impairment increases the risk for acute kidney injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Iohexol can be removed by dialysis.
10. Overdosage
The adverse effects of overdosage in intra-arterial or intravenous administration are life-threatening and affect mainly the pulmonary and cardiovascular systems. The symptoms include: cyanosis, bradycardia, acidosis, pulmonary hemorrhage, convulsions, coma, and cardiac arrest. Treatment of an overdosage is directed toward the support of all vital functions, and prompt institution of symptomatic therapy. Iohexol can be dialyzed.
11. Omnipaque Injection Description
Iohexol is a nonionic radiographic contrast agent available as:
- OMNIPAQUE (iohexol) injection for intrathecal, intra-arterial, intravenous, oral, rectal, intraarticular, and body cavity use
- OMNIPAQUE (iohexol) oral solution for oral use
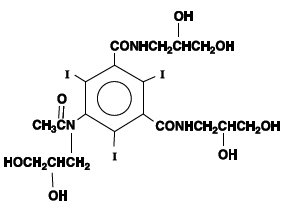
The chemical name of iohexol is Bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-5-[N-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-acetamido]-2,4,6- triiodoisophthalamide with a molecular weight of 821.14 (iodine content 46.36%). Iohexol has the following structural formula:
OMNIPAQUE injection is a sterile, pyrogen-free, colorless to pale yellow solution available in five concentrations of iodine:
- OMNIPAQUE 140 mg iodine/mL: Each mL contains 302 mg iohexol (providing 140 mg organically bound iodine) and the following inactive ingredients: 0.1 mg edetate calcium disodium and 1.21 mg tromethamine.
- OMNIPAQUE 180 mg iodine/mL: Each mL contains 388 mg iohexol (providing 180 mg organically bound iodine) and the following inactive ingredients: 0.1 mg edetate calcium disodium and 1.21 mg tromethamine.
- OMNIPAQUE 240 mg iodine/mL: Each mL contains 518 mg iohexol (providing 240 mg organically bound iodine) and the following inactive ingredients: 0.1 mg edetate calcium disodium and 1.21 mg tromethamine.
- OMNIPAQUE 300 mg iodine/mL: Each mL contains 647 mg iohexol (providing 300 mg organically bound iodine) and the following inactive ingredients: 0.1 mg edetate calcium disodium and 1.21 mg tromethamine.
- OMNIPAQUE 350 mg iodine/mL: Each mL contains 755 mg iohexol (providing 350 mg organically bound iodine) and the following inactive ingredients: 0.1 mg edetate calcium disodium and 1.21 mg tromethamine.
OMNIPAQUE oral solution is a sterile, pyrogen-free, colorless to pale yellow solution available in two concentrations of iodine:
- OMNIPAQUE oral solution 9 mg iodine/mL: Each mL contains 19 mg iohexol (providing 9 mg organically bound iodine) and the following inactive ingredients: 0.1 mg edetate calcium disodium and 1.21 mg tromethamine.
- OMNIPAQUE oral solution 12 mg iodine/mL: Each mL contains 26 mg iohexol (providing 12 mg organically bound iodine) and the following inactive ingredients: 0.1 mg edetate calcium disodium and 1.21 mg tromethamine.
The pH is adjusted between 6.8 and 7.7 with hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide. OMNIPAQUE injection and OMNIPAQUE oral solution contain no preservatives and no ingredient made from a gluten-containing grain (wheat, barley, or rye).
OMNIPAQUE injection and OMNIPAQUE oral solution have the following physical properties:
| Dosage Form | Concentration (mg iodine/mL) | Osmolality*
(mOsmol/kg water) | Absolute Viscosity (cP) | Specific Gravity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20°C | 37°C | 37°C | |||
|
|||||
| Injection | 140 | 322 | 2.3 | 1.5 | 1.164 |
| 180 | 408 | 3.1 | 2.0 | 1.209 | |
| 240 | 520 | 5.8 | 3.4 | 1.280 | |
| 300 | 672 | 11.8 | 6.3 | 1.349 | |
| 350 | 844 | 20.4 | 10.4 | 1.406 | |
| Oral solution | 9 | 38 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 1.011 |
| 12 | 45 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 1.014 | |
OMNIPAQUE injection has osmolalities from approximately 1.1 to 3 times that of plasma (285 mOsmol/kg water) or cerebrospinal fluid (301 mOsmol/kg water) as shown in the above table and are hypertonic .
OMNIPAQUE oral solution is hypotonic.
12. Omnipaque Injection - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The iodine atoms in iohexol provide attenuation of X-rays in direct proportion to the concentration of iohexol. Since concentration changes over time, iohexol provides time-dependent image contrast which may assist in visualizing body structures.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Intrathecal Administration
The initial concentration and volume of the contrast medium, in conjunction with patient manipulation and the volume of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) into which the contrast medium is placed, will determine the extent of the contrast that can be achieved. Following intrathecal injection in conventional radiography, OMNIPAQUE 180 mg iodine/mL, 240 mg iodine/mL, and 300 mg iodine/mL will continue to provide contrast for at least 30 minutes. Slow diffusion of iohexol takes place throughout the CSF with subsequent absorption into the bloodstream. At approximately 1 hour following injection, contrast will no longer be sufficient for conventional myelography.
After administration into the lumbar subarachnoid space, computerized tomography shows the presence of contrast medium in the thoracic region in about 1 hour, in the cervical region in about 2 hours, and in the basal cisterns in 3 to 4 hours.
Intravenous or Intra-arterial Administration
Following intravenous or intra-arterial administration of OMNIPAQUE, the degree of contrast enhancement is directly related to the iodine concentration of an administered dose; peak iodine blood concentrations occur immediately (15 seconds to 120 seconds) following rapid intravenous injection. The time to maximum contrast enhancement can vary, depending on the organ, from the time that peak blood iodine concentrations are reached to one hour after intravenous bolus administration. When a delay between peak blood iodine concentrations and peak contrast is present, it suggests that radiographic contrast enhancement is at least in part dependent on the accumulation of iodine containing agent within the lesion and outside the blood pool.
Oral Administration
Orally administered OMNIPAQUE produces visualization of the gastrointestinal tract. Less than 1% of orally administered iohexol is recovered in the urine, suggesting minimal amounts are absorbed from the normal gastrointestinal tract. This amount may increase in the presence of bowel perforation or bowel obstruction.
Intraarticular Administration
Visualization of the joint spaces can be accomplished by direct injection of contrast medium. For intraarticular cavities, the injected iohexol is absorbed into the surrounding tissue and subsequently absorbed into systemic circulation.
Body Cavity Administration
For most body cavities, the injected iohexol is absorbed into the surrounding tissue and subsequently absorbed into systemic circulation. Examinations of the uterus (hysterosalpingography) and bladder (voiding cystourethrography) involve the almost immediate drainage of contrast medium from the cavity upon conclusion of the radiographic procedure.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following the intravenous administration of iohexol (between 500 mg iodine/kg to 1,500 mg iodine/kg) to 16 adult subjects, apparent first-order terminal elimination half-life was 12.6 hours and total body clearance was 131 (98 to 165) mL/min. Clearance was not dose dependent.
Absorption
As evidenced by the amount recovered in urine, <1% of orally administered iohexol is absorbed from the normal gastrointestinal tract. This amount may increase in the presence of bowel perforation or bowel obstruction.
Distribution
In 16 adult subjects (receiving between 500 mg iodine/kg to 1,500 mg iodine/kg intravenous iohexol) the plasma volume of distribution was165 (108 to 219) mL/kg.
In five adult patients receiving 16 mL to 18 mL of OMNIPAQUE (180 mg iodine/mL) by lumbar intrathecal injection the plasma volume of distribution was 559 (350 to 849) mL/kg.
Elimination
Excretion
Following intravenous, intra-arterial or intrathecal administration, iohexol is excreted unchanged by glomerular filtration. Approximately 90% of the intravenously injected iohexol dose is excreted within the first 24 hours. Following intravenous or intraarterial administration, peak urine concentration occurs in the first hour after injection.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies have not been performed with iohexol to evaluate carcinogenic potential. Iohexol was not genotoxic in a series of studies, including the Ames test, the mouse lymphoma TK locus forward mutation assay, and a mouse micronucleus assay. Iohexol did not impair the fertility of male or female rats when repeatedly administered at intravenous dosages up to 4 g iodine/kg.
14. Clinical Studies
The safety and effectiveness of OMNIPAQUE for CT of the head were evaluated in three clinical studies. Each study also used an ionic high-osmolar iodinated contrast agent as a comparator. A total of 280 patients were randomized to administration of either OMNIPAQUE (n=142) or the comparator (n=138). OMNIPAQUE patients had a mean age of 52 years (range 16 to 85), 41% were women, and were administered a mean of 692 mg iodine/kg (range 337 to 1,250 mg iodine/kg) by intravenous injection with OMNIPAQUE 240 mg iodine/mL (1 study) or 300 mg iodine/mL (2 studies).
Efficacy was determined from investigator ratings of quality of contrast enhancement (none, poor, good, or excellent; only scans rated as good or excellent were considered diagnostic).
The percentage of OMNIPAQUE-enhanced scans rated as good or excellent was 100% in the two studies using OMNIPAQUE 300 mg iodine/mL, and 79% in the third study using OMNIPAQUE 240 mg iodine/mL.
16. How is Omnipaque Injection supplied
How Supplied
OMNIPAQUE (iohexol) injection and OMNIPAQUE (iohexol) oral solution are colorless to pale yellow solutions available in the following presentations:
| Dosage Form | Concentration (mg iodine/mL) | Package Size | Package Type & Material | Sale Unit | NDC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||
| Injection | 140 | 50 mL | Single-Dose Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1401-52 |
| 180 | 10 mL | Single-Dose Glass Vials | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1411-10 | |
| 240 | 10 mL | Single-Dose Glass Vials | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1412-10 | |
| 20 mL | Single-Dose Glass Vials | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1412-20 | ||
| 50 mL | Single-Dose Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1412-30 | ||
| 100 mL | Single-Dose Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1412-33 | ||
| 300 | 10 mL | Single-Dose Glass Vials | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1413-10 | |
| 30 mL | Single-Dose Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1413-59 | ||
| 50 mL | Single-Dose Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1413-61 | ||
| 100 mL | Single-Dose Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1413-63 | ||
| 125 mL | Single-Dose Glass Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1413-53 | ||
| 150 mL | Single-Dose Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1413-65 | ||
| 500 mL* | Imaging or Pharmacy Bulk Package Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1413-72 | ||
| 350 | 50 mL | Single-Dose Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1414-89 | |
| 75 mL | Single-Dose Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1414-90 | ||
| 100 mL | Single-Dose Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1414-91 | ||
| 125 mL | Single-Dose Glass Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1414-76 | ||
| 150 mL | Single-Dose Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1414-93 | ||
| 200 mL | Single-Dose Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1414-94 | ||
| 500 mL* | Imaging or Pharmacy Bulk Package Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1414-72 | ||
| Oral Solution | 9 | 500 mL | Single-Dose Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1415-09 |
| 12 | 500 mL | Single-Dose Polymer Bottles | Boxes of 10 | 0407-1416-12 | |
The container closure system components (bottle, vial, stopper, and cap) of OMNIPAQUE injection and OMNIPAQUE oral solution are not made with natural rubber latex.
Storage and Handling
- OMNIPAQUE Injection: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. May be stored in a contrast media warmer for up to one month, not to exceed 37°C (98.6°F).
- OMNIPAQUE Oral Solution: Store between 0°C and 30°C (32°F to 86°F).
Protect from light. Do not freeze. Discard any product that is inadvertently frozen, as freezing may compromise the closure integrity of the immediate container.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise the patient concerning the risk of hypersensitivity reactions that can occur both during and after OMNIPAQUE administration. Advise the patient to report any signs or symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions during the procedure and to seek immediate medical attention for any signs or symptoms experienced after discharge [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Advise patients to inform their physician if they develop a rash after receiving OMNIPAQUE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Acute Kidney Injury
Advise the patient concerning appropriate hydration to decrease the risk of contrast-induced acute kidney injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Extravasation
If extravasation occurs during injection, advise patients to seek medical care for progression of symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Lactation
Advise a lactating woman that interruption of breastfeeding is not necessary. However, to avoid any exposure, a lactating woman may consider pumping and discarding breast milk for 10 hours after OMNIPAQUE administration [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Thyroid Dysfunction
Advise parents/caregivers about the risk of developing thyroid dysfunction after OMNIPAQUE administration. Advise parents/caregivers about when to seek medical care for their child to monitor for thyroid function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Distributed by GE Healthcare Inc., Marlborough, MA 01752 U.S.A.
OMNIPAQUE is a trademark of GE HealthCare or one of its subsidiaries.
GE is a trademark of General Electric Company used under trademark license.
© 2024 GE HealthCare
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 300 mg Bottle Box Label
GE Healthcare
Y-538I
Contains
10 x 500 mL
Bottles
NDC 0407-1413-72
OMNIPAQUE™
(iohexol) Injection
300 mg Iodine/mL
This container can be used either as:
IMAGING BULK PACKAGE
For Intravenous Use Only
or
PHARMACY BULK PACKAGE
Not for Direct Infusion
For Intrathecal, Intra-arterial,
Intravenous, Oral, Rectal,
Intraarticular, or Body Cavity Use
Rx ONLY
See prescribing information for dosage and administration.
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C
(59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. May be stored in a
contrast media warmer for up to one month, not to exceed 37°C (98.6°F).
Protect from light. Do not freeze. Discard unused OMNIPAQUE 8 hours
after initial puncture.
Each mL contains 647 mg of iohexol (300 mg organically bound iodine),
0.1 mg edetate calcium disodium, and 1.21 mg tromethamine.
The pH is adjusted between 6.8 and 7.7 with hydrochloric acid or sodium
hydroxide. No preservative added.
+PLUSPAK™ (polymer bottle)
Distributed by GE Healthcare Inc.,
Marlborough, MA 01752 U.S.A.
For inquiries call 1-800-654-0118
Exp.: DD MMM YYYY
Lot: 12345678
0000000 USA

PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 350 mg Bottle Box Label
GE Healthcare
Y-548I
Contains
10 x 500 mL
Bottles
NDC 0407-1414-72
OMNIPAQUE™
(iohexol) Injection
350 mg Iodine/mL
This container can be used either as:
IMAGING BULK PACKAGE
For Intravenous Use Only
or
PHARMACY BULK PACKAGE
Not for Direct Infusion
For Intra-arterial,
Intravenous, Oral, Rectal,
Intraarticular, or Body Cavity Use
NOT FOR INTRATHECAL USE
Rx ONLY
See prescribing information for dosage and administration.
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C
(59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. May be stored in a
contrast media warmer for up to one month, not to exceed 37°C (98.6°F).
Protect from light. Do not freeze. Discard unused OMNIPAQUE 8 hours
after initial puncture.
Each mL contains 755 mg of iohexol (350 mg organically bound iodine),
0.1 mg edetate calcium disodium, and 1.21 mg tromethamine.
The pH is adjusted between 6.8 and 7.7 with hydrochloric acid or sodium
hydroxide. No preservative added.
+PLUSPAK™ (polymer bottle)
Distributed by GE Healthcare Inc.,
Marlborough, MA 01752 U.S.A.
For inquiries call 1-800-654-0118
Exp.: DD MMM YYYY
Lot: 12345678
0000000 USA

| OMNIPAQUE
iohexol injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| OMNIPAQUE
iohexol injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - GE Healthcare (053046579) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| GE Healthcare Ireland Limited | 988006565 | MANUFACTURE(0407-1413, 0407-1414) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| GE Healthcare Lindesnes | 518890970 | API MANUFACTURE(0407-1413, 0407-1414) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| GE Healthcare Shanghai Co., Ltd. | 545292716 | MANUFACTURE(0407-1413, 0407-1414) | |
More about iohexol
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Reviews (11)
- Latest FDA alerts (2)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: non-ionic iodinated contrast media
- Breastfeeding
Patient resources
- Iohexol (Injection, Intrathecal, Intravenous) advanced reading
- Iohexol (Oral) (Advanced Reading)
- Iohexol
