Liver cancer
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Apr 24, 2025.
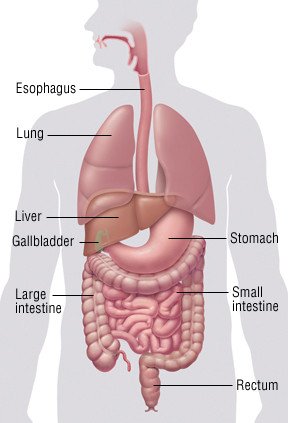
What is Liver cancer?

Liver cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the liver. It is also called hepatoma or hepatocellular carcinoma.
The liver:
- helps blood to clot
- removes or neutralizes poisons, drugs, and alcohol
- helps the body process fats and cholesterol
- helps to maintain normal blood sugar levels
- regulates hormones.
Most liver tumors in the United States spread to the liver from other places in the body. This is referred to as secondary liver cancer or metastatic cancer. For example, cancer that has spread to the liver from the lungs is called metastatic lung cancer.
The liver is the most common place for cancer to spread. In patients with secondary liver cancer, doctors treat patients at the original site of the cancer. So, metastatic lung cancer that has spread to the liver would be treated as lung cancer, not liver cancer.
On the other hand, primary liver cancer starts in the liver, as opposed to a cancer that originates in another part of the body and spreads to the liver. Primary liver cancer is treated as liver cancer.
|
|
Risk factors
Factors that increase your risk of developing primary liver cancer include:
- Persistent hepatitis B and C. People who never completely recover from infection with either the hepatitis B or C viruses have persistent inflammation in the liver.
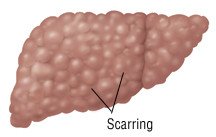
- Cirrhosis, which is the scarring of liver cells. In the United States, the most common causes of cirrhosis are drinking too much alcohol and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), which was formerly called non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Cirrhosis due to hepatitis C has decreased dramatically since the discovery and availability of very successful antiviral therapy to eradicate the infection.
|
|
- Direct contact with vinyl chloride (polyvinyl chloride or PVC). This chemical is used in manufacturing some types of plastics.
- Exposure to arsenic. This chemical is used as a wood preservative, herbicide and insecticide. It is used in some glass and metal manufacturing. Some drinking water is contaminated by arsenic. It also exists in natural mineral deposits.
- Anabolic steroids, which are male hormones used to treat certain conditions. They are sometimes used illegally by athletes to enhance performance.
- Tobacco use, which makes you more likely to develop other cancers that can spread to the liver.
Symptoms
Symptoms usually do not appear until the disease is advanced. Symptoms can include:
- unexplained weight loss
- loss of appetite
- feeling full after a small meal
- pain or swelling, especially in the upper-right abdomen
- a yellow tint in the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- liver enlargement or a mass in the area of the liver
- low blood sugar.
Liver cancer can lead to high pressure in blood vessels that feed into the liver. This can cause veins in the esophagus and stomach to swell with significant risk of bleeding and vomiting blood.
Diagnosis
Liver cancer is usually diagnosed in later stages of the disease because symptoms do not appear until then.
Once your doctor suspects you might have liver cancer, he or she will use one or more of the following methods to diagnose the disease:
- Physical examination. To check for weight loss, malnutrition, weakness, enlargement of the liver, and associated diseases such as hepatitis and cirrhosis.
- Blood tests. To detect elevated levels of a protein associated with primary liver cancer.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan. An imaging test using x-rays to detect and locate tumors.
- Ultrasound. An imaging test using sound waves that can determine if a spot on the liver is a tumor (solid growth) or a cyst (a fluid-filled cavity).
- Hepatic artery angiogram. A test that examines the blood vessels that supply blood to liver cancer. It also helps determine whether the tumor can be removed surgically.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). An imaging test using magnetic fields that produces more detailed images than CT or ultrasound.
- Biopsy. Removal of a small amount of tissue from a growth in the liver that is examined in a laboratory to determine if it is cancerous.
- Laparoscopy. Insertion of a thin, lighted tube through a small incision in the abdomen to view the liver and surrounding organs and lymph nodes.
Expected duration
Without treatment, liver cancer will continue to grow.
Prevention
Most primary liver cancer can be prevented. Here are some things you can do.
To minimize the risk of being infected with a hepatitis virus:
- Get vaccinated against hepatitis B.
- Do not have unprotected sex. Use a latex or polyurethane condom.
- Wear latex gloves when handling items that have been in contact with someone else's blood or bodily fluids.
- Don't share personal items such as razors, toothbrushes, or earrings.
- Make sure needles used for body piercing or tattoos are properly sterilized.
Other healthy lifestyle choices may also decrease your risk of developing liver cancer:
- Maintain a healthy body weight.
- Eat a diet that is rich in fruits and vegetables.
- Exercise regularly.
- Limit the amount of alcohol you drink to no more than one drink per day to decrease your risk of cirrhosis.
Treating chronic hepatitis B or C with antiviral drugs helps prevent cirrhosis and decreases the chance of developing primary liver cancer.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Treatment
The type of treatment depends on a number of factors, including the stage of the cancer, your age and your general health. Surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy are potential treatment options. Often, a combination of all three is used.
A primary liver cancer that has not spread to lymph nodes or other organs can often be surgically removed. However, only a small percentage of liver cancers are found in this early stage.
For most cases of liver cancer, it is not possible to remove the entire tumor, or the cancer has spread throughout much of the liver or to distant sites. There are no standard treatments for liver cancer in these stages. In a few cases, a liver transplant may be considered.
Newer therapies have improved the outlook for some patients with liver cancer. For example, in some cases of primary liver cancer, targeted therapies can be used. These drugs block the chemical pathways that stimulate growth and spread of cancer cells.
Other drugs, which decrease the blood supply that tumors need to grow, have also been shown to be helpful. In some cases, chemotherapy can be delivered directly into blood vessels that feed the tumor. Or materials can be injected into blood vessels that act as a clot and shut off the blood supply to the liver. Without blood supply, the tumor shrinks.
In many cases, liver cancer cannot be cured. Instead, treatment focuses on relieving the symptoms of the cancer or keeping the cancer from growing, spreading, or returning.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
When to call a professional
Most symptoms of liver cancer are not specific, such as fatigue, decreased appetite, and weight loss. Liver problems of any kind, including liver cancer, also may cause:
- a yellowing of skin and eyes
- dark colored urine
- abdominal pain, especially in the upper right part of the abdomen.
Prognosis
The outlook for people with liver cancer depends on how far the cancer has spread and whether it can be entirely removed with surgery.
Additional info
American Cancer Society (ACS)
https://www.cancer.org/
Cancer Research Institute
https://www.cancerresearch.org/
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
https://www.cdc.gov/
National Cancer Institute (NCI)
https://www.nci.nih.gov/
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN)
https://www.nccn.org/
Learn more about Liver cancer
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.