Athlete's foot (tinea pedis)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 18, 2025.
What is athlete's foot?

Athlete's foot, also known as tinea pedis, is a common foot infection caused by fungi called dermatophytes. Found in many different places indoors and outdoors, dermatophytes are especially common in the warm, moist environments of pools, showers, locker rooms and other sports facilities, where people walk with bare feet. Once dermatophytes contaminate the skin of a foot, the warm, moist environment of sweaty socks and shoes encourages them to grow.
Symptoms of athlete's foot
Symptoms of athlete's foot include:
- Intense itching of the feet
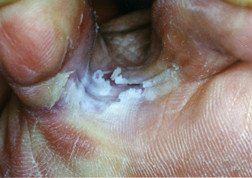
- Cracked, blistered or peeling areas of skin, especially between the toes
|
|
-
Redness and scaling on the soles.
In most people, signs of infection are seen on the webbed skin between the toes. In some people, the infection spreads to one or more toenails, causing the nail to appear unusually thick and cloudy yellow.
Diagnosing athlete's foot
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and about factors that make you more likely to develop athlete's foot, such as your use of public sports facilities, clubs or showers. Your doctor will ask about the type of shoes and socks you wear, what kind of work you do and what you wear on your feet to work.
Your doctor usually can diagnose athlete's foot simply by looking at your feet. To confirm the diagnosis, your doctor can gently scrape some flakes of skin from a scaly portion of your foot onto a slide. The dermatophytes that cause the infection often show up under a microscope.
Expected duration of athlete's foot
It usually takes several weeks to months for the infection to respond to treatment. Even after proper medical treatment, the infection can return easily if your feet are exposed again to fungi and sweaty, warm conditions. For this reason, many people have athlete's foot infection that lasts or keeps returning for many years. Successfully curing the infection often requires changes in how you care for your feet and what you wear on your feet.
Preventing athlete's foot
You can help to prevent athlete's foot by keeping your feet clean and dry. More specifically, you can try the following:
- Wash your feet thoroughly every day and wear a clean pair of socks after your bath or shower.
- Take time to dry your feet, including each toe, thoroughly (especially the webbed area between the toes) after you bathe, shower or swim.
- If you use public pools or showers, wear thongs or sandals to prevent your bare feet from touching floors contaminated with fungi.
- Choose leather shoes rather than vinyl, since leather lets feet "breathe" so they are more likely to stay dry.
- Wear cotton socks to absorb sweat.
- If possible, don't wear the same pair of shoes two days in a row. Give shoes a 24-hour break between wearing to air out and dry out.
- Don't share shoes.
Drugs used to treat this and similar conditions
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Treating athlete's foot
There are many effective topical medications, including ciclopirox (Loprox), clotrimazole (Lotrimin, Mycelex), econazole (Spectazole), ketoconazole (Nizoral), miconazole (Micatin), naftifine (Naftin), oxiconazole (Oxistat), sulconazole (Exelderm), terbinafine (Lamisil), terconazole (Terazol), and tolnaftate (Desenex, Tinactin and others). Some are available without a prescription. Many weeks of treatment may be necessary. For people with long-standing or recurring athlete's foot, topical antifungal drugs may relieve symptoms without actually curing the infection.
Medications by mouth can be more successful at curing an infection. However, you still can be susceptible to recurrences, and oral medications may be more likely to cause side effects. These require a prescription and include griseofulvin (Fulvicin, Grifulvin, Grisactin), itraconazole (Sporanox) and terbinafine (Lamisil).
When to call a professional
If you think you have athlete's foot, try a nonprescription antifungal ointment, cream or powder. Keep your feet as dry and clean as possible. If these measures do not help, make an appointment to see your doctor. Call your doctor for a more urgent evaluation and treatment if you see spreading redness or have fevers.
If you have diabetes and any foot problems, see your doctor right away. People with diabetes easily get skin infections, so they should see a doctor as soon as anything unusual appears on their feet.
Prognosis
Several weeks of treatment with a medication applied to the feet can usually cure athlete's feet in people with new or short-term symptoms. Chronic or recurring athlete's foot infections also can be cured this way, but may require significant changes in foot care and several weeks of treatment. More severe cases may call for an oral medication. Even after successful treatment, people remain at risk of re-infection if they do not follow prevention guidelines. Relapses are common.
Additional info
American Podiatric Medical Association (APMA)
https://www.apma.org/
Learn more about Athlete's foot
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.