Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a condition that increases blood pressure in your pulmonary artery. The pulmonary artery is the large blood vessel that brings blood from your heart to your lungs.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have chest pain or heart palpitations (strong, fast heartbeats).
- You have shortness of breath at rest, especially when you lie down.
- Your lips or fingers turn blue.
Return to the emergency department if:
- You are confused or feel like you are going to faint.
- Your legs or ankles are swollen.
- You cough up blood.
Call your doctor if:
- You have a fever.
- Your symptoms keep you from doing your daily activities.
- Your fingers or toes are clubbed (the ends are round and thick).
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Blood thinners help prevent blood clots. Clots can cause strokes, heart attacks, and death. Many types of blood thinners are available. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions for the type you are given. The following are general safety guidelines to follow while you are taking a blood thinner:
- Watch for bleeding and bruising. Watch for bleeding from your gums or nose. Watch for blood in your urine and bowel movements. Use a soft washcloth on your skin, and a soft toothbrush to brush your teeth. This can keep your skin and gums from bleeding. If you shave, use an electric shaver. Do not play contact sports.
- Tell your dentist and other healthcare providers that you take a blood thinner. Wear a bracelet or necklace that says you take this medicine.
- Do not start or stop any other medicines or supplements unless your healthcare provider tells you to. Many medicines and supplements cannot be used with blood thinners.
- Take your blood thinner exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not skip a dose or take less than prescribed. Tell your provider right away if you forget to take your blood thinner, or if you take too much.
- Diuretics help your body get rid of extra fluid and protect your heart from more damage. You may urinate more often while you are taking diuretics.
- Vasodilators improve blood flow by making the vessels in your heart and lungs wider.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Manage PAH:
- Check your blood pressure (BP) at home. Sit and rest for 5 minutes before you take your BP. Extend your arm and support it on a flat surface. Your arm should be at the same level as your heart. Follow the directions that came with your BP monitor. If possible, take at least 2 BP readings each time. Take your BP at least twice a day at the same times each day, such as morning and evening. Keep a record of your BP readings and bring it to your follow-up visits. Ask your healthcare provider what your BP should be.

- Limit sodium (salt) as directed. Too much sodium can affect your fluid balance. Check labels to find low-sodium or no-salt-added foods. Some low-sodium foods use potassium salts for flavor. Too much potassium can also cause health problems. Your provider will tell you how much sodium and potassium are okay for you to have in a day. Your provider may recommend that you limit sodium to 2,300 mg a day.
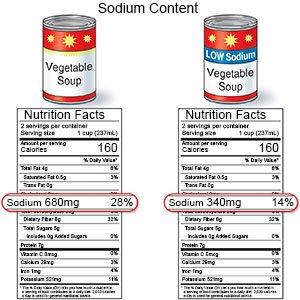
- Follow the meal plan recommended by your provider. A dietitian or your provider can give you more information on low-sodium plans or the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) eating plan. The DASH plan is low in sodium, unhealthy fats, and total fat. It is high in potassium, calcium, and fiber.
- Limit liquids as directed. You may need to drink less liquid to help balance your fluid level. Ask how much liquid you should drink each day. Your provider will give you an exact amount of liquid to drink each day. You may be limited to less than 2 liters a day.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine and other chemicals in cigarettes and cigars can increase your BP and also cause lung damage. Ask your provider for information if you currently smoke and need help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to your provider before you use these products.
- Limit or avoid alcohol. Alcohol can make it hard for you to control your BP. Limit alcohol to 1 drink within 24 hours if you are female. Limit alcohol to 2 drinks within 24 hours if you are male. A drink of alcohol is 12 ounces of beer, 5 ounces of wine, or 1½ ounces of liquor.
- Be physically active, as directed. Physical activity, such as exercise, may help decrease your symptoms and improve your heart function. Physical activity also helps with weight control. Do not start a physical activity program before you talk with your provider.
- Avoid activities that raise your body temperature. Do not sit in a sauna, hot tub, or hot bath. This can lower your blood pressure and cause you to faint.
- Talk to your provider about pregnancy if you are female. Pregnancy may not be safe for you. You may need to change your birth control method if you currently use birth control pills. Birth control pills may increase your risk for blood clots. Your provider can help you choose other methods that work for you.
- Manage health conditions affecting PAH. You may need treatment for sleep apnea, hypertension, or other medical conditions. Ask your provider for more information.
- Do not travel to high altitudes unless your provider says it is okay. You may need to bring extra oxygen if you are traveling to a high altitude or are flying.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Follow up with your doctor or specialist as directed:
You may need regular testing to monitor your symptoms. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Treatment options
Care guides
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
