Parathyroid Adenoma
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is a parathyroid adenoma?
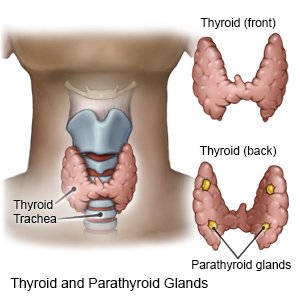
A parathyroid adenoma is a benign (not cancerous) tumor on one or more of your parathyroid glands. The parathyroid glands are 4 small glands located near the thyroid gland in your neck. The parathyroid gland produces parathyroid hormone (PTH). PTH keeps the level of calcium balanced in your blood. A parathyroid adenoma can cause extra PTH to be produced. This condition is called hyperparathyroidism. Hyperparathyroidism can cause blood calcium levels to increase, and lead to health problems such as osteoporosis (weak, brittle bones). The cause of parathyroid adenomas is usually not known.
 |
What are the signs and symptoms of a parathyroid adenoma?
You may not have any signs or symptoms. You may have symptoms of increased blood calcium if your parathyroid adenoma has caused hyperparathyroidism. You may have any of the following:
- Muscle weakness
- Fatigue
- Nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain
- Constipation
- Depression or anxiety
- General body aches and pains
- Bone and joint pain
- Loss of appetite
- Confusion or forgetfulness
- Increased thirst and urination
Related medications
How is a parathyroid adenoma diagnosed and treated?
Blood tests may show increased levels of parathyroid hormone and calcium. An ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may be done. You may be given contrast liquid to help the adenoma show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the healthcare provider if you have any metal in or on your body. Surgery may be done to remove the adenoma or parathyroid gland.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You heart beats faster or slower than normal, or it feels like fluttering in your chest.
- You have nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- You cannot think clearly.
When should I contact my healthcare provider?
- You have bone and joint pain.
- You have pain in your lower back, side, or stomach.
- You have pain or burning when you urinate or your urine is pink or red.
- You have increased thirst or you are urinating more often than usual.
- You have a loss of appetite.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
