Hyperthyroidism in Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
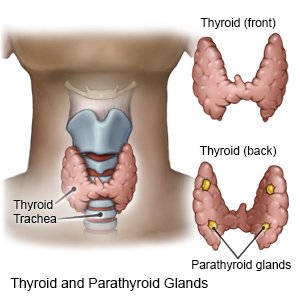
Hyperthyroidism is a condition that develops when the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. Thyroid hormones help control body temperature, heart rate, growth, and weight.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Rest:
You may need to rest in bed until your heart rate is under control. Your healthcare provider will tell you when it is okay to get out of bed. Call your healthcare provider before you get up for the first time. Sit or lie down right away if you feel weak or dizzy.
IV:
An IV is a small tube placed in your vein that is used to give you medicine or liquids.
Nutrition:
You may need to eat more to give your body the extra energy it needs. Foods high in protein and calories will help prevent weight loss.
Related medications
Medicines:
- Antianxiety medicine may be given to decrease anxiety and help you feel calm and relaxed.
- Antithyroid medicine decreases the amount of thyroid hormone made by your thyroid gland.
- Heart medicines help slow down your heart rate.
Tests:
- A biopsy is a procedure which uses a small needle to get a sample of your thyroid gland. The sample is sent to the lab for tests. Your healthcare provider may use numbing medicine so that you will not feel pain during the procedure.
- Blood tests will be done to check your thyroid hormone level.
- A contraction stress test test shows your baby's heart rate during a contraction. This helps healthcare providers see how your baby is doing.
- External fetal heart monitoring may be used to monitor your baby's heartbeat and the contractions of your uterus. A small metal disk is placed on your abdomen. A belt will be fastened around your waist to hold the disk in place. The disk may need to be moved as your baby moves inside you. The disk is attached to a monitor or a printer. The monitor or print out shows your uterus contracting and the baby's heartbeat.
- A fetal ultrasound test uses sound waves to show pictures of your baby on a monitor. Healthcare providers check your baby's movement, heart rate, and position.
- An EKG test records your heart rhythm and how fast your heart beats.
- An echocardiogram is a type of ultrasound. Sound waves are used to show the structure, movement, and blood vessels of your heart.
Treatment:
- Surgery may be done to remove all or part of the thyroid gland. Your healthcare provider may do surgery during your pregnancy if he or she feels that it will be safe for you and your baby. You may be given antithyroid medicine for several months before surgery. This medicine will decrease your symptoms and make the thyroid gland smaller before surgery.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
RISKS:
- Treatment for hyperthyroidism during pregnancy may carry certain risks for you and your child. Medicines for hyperthyroidism may cause itching and redness of skin, fever, sore throat, and joint pain. Medicines or surgery may damage too many thyroid gland cells and cause hypothyroidism (too little thyroid hormone). You may need treatment for hypothyroidism. Medicines may cause birth defects or be life-threatening to your baby. During surgery you may bleed more than usual or get an infection. Nerves in your thyroid gland may get nicked or cut and give you a hoarse voice. Even after successful treatment, you may still have signs and symptoms or they may return.
- If not treated, your signs and symptoms may get worse. You may lose too much weight and become weak. Your heart may be affected and this can be life-threatening. You may also have a thyroid storm. Your temperature may go very high, your heart may beat very fast, and you may have problems thinking. You may go into a coma, which can be life-threatening if you do not get medical care quickly. You may have increased blood pressure, vomiting, blurred vision, and bleeding in your womb. Your child may be born with birth defects, have a low birth weight, or be stillborn. You may also give birth earlier than expected.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Hyperthyroidism
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
