Hematemesis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is hematemesis?
Hematemesis is the vomiting of blood. This is caused by bleeding in your upper gastrointestinal (GI) system. The blood may be bright red, or it may look like coffee grounds. Hematemesis is a medical emergency that needs immediate treatment.
What causes hematemesis?
- Tears in the lining of your stomach from retching
- Irritation or loss of the lining of your stomach or esophagus
- Bleeding from varices in your stomach or intestine
- A tumor in your stomach or esophagus
- Radiation or a procedure such as endoscopy that damages your upper GI
- A viral infection, hepatitis, or an H pylori infection
- A condition such as gastroenteritis, gastritis, or a stomach ulcer
- Use of medicines such as NSAIDs, aspirin, or blood thinners
How is the cause of hematemesis diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms. Tell your provider when the vomiting started and how long it lasted. Describe the amount of blood you vomited, and if it was bright red or looked like coffee grounds. Your provider may ask about any recent illness you had, or if you have a chronic medical condition. Tell your provider if you recently took NSAIDs or aspirin, and how much you took. Your provider may also ask if you drink alcohol regularly.
- Blood tests may be used to check your oxygen and iron levels. The tests can also show how well your blood clots.
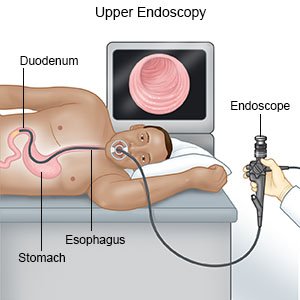
- Endoscopy is a procedure used to examine your upper GI. Your healthcare provider will use a scope (thin, bendable tube with a light on the end). The provider will move the scope down your throat and into your stomach. A tissue sample may be taken to be tested.
- A bowel movement sample may be tested for blood.
- CT or x-ray pictures may show the source of the bleeding. The pictures may show a tear, obstruction, or tumor that is causing you to vomit blood.
How is hematemesis treated?
Treatment will depend on what is causing you to vomit blood. You may need any of the following:
- Medicine may be given to reduce the amount of acid your stomach produces. This may help if your hematemesis is caused by an ulcer. You may also need medicine to prevent blood flow to an injury or tear.
- Endoscopy may be used to treat the cause of your bleeding. Your healthcare provider may use heat to close a tear. Tissue may be clipped together so it can heal.
- A blood transfusion may be needed if you lose a large amount of blood.
- An angiogram is done to look for and stop bleeding from an artery. Contrast liquid is injected into an artery and x-rays of your blood flow are taken. Tell a healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
- Surgery may be needed if you have severe bleeding or other treatments do not work. Surgery may be used to fix a tear in the lining of your stomach or intestine. You may need surgery to remove an obstruction or a tumor.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Related medications
What can I do to manage my symptoms?
- Do not take NSAIDs or aspirin. These medicines can cause stomach bleeding. Talk to your healthcare provider about other medicines that are safe for you to take.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine can damage blood vessels. Talk to your healthcare provider if you need help quitting. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Ask your healthcare provider for information before you use these products.
- Do not drink alcohol or caffeine. Alcohol and caffeine can irritate your stomach. The lining of your stomach or intestine may also be damaged. Talk to your healthcare provider if you need help to quit drinking alcohol.
- Eat a variety of healthy foods. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy products, lean meats, fish, and legumes such as lentils. Healthy foods can help you heal and improve your energy.
- Drink extra liquids as directed. You may need to drink extra liquids to prevent dehydration from vomiting. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid to drink each day and which liquids are best for you.
Call 911 for any of the following:
- You have signs of shock from blood loss, such as the following:
- Feeling dizzy or faint, or breathing faster than usual
- Pale, cool, clammy skin
- A fast pulse, large pupils, or feeling anxious or agitated
- Nausea or weakness
When should I seek immediate care?
- You are vomiting large amounts of blood, or you vomit several times in a row.
- You have severe pain in your abdomen.
When should I contact my healthcare provider?
- You have new or worsening symptoms.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Hematemesis
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
