Vasopressin: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Dosage form: injection
Drug class: Antidiuretic hormones
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Sep 3, 2025.
On This Page
- Indications and Usage
- Dosage and Administration
- Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Contraindications
- Warnings and Precautions
- Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Drug Interactions
- Use In Specific Populations
- Overdosage
- Description
- Clinical Pharmacology
- Nonclinical Toxicology
- Clinical Studies
- How Supplied/Storage and Handling
Highlights of Prescribing Information
VASOPRESSIN injection, for intravenous use.
VASOPRESSIN in dextrose injection for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2014
Indications and Usage for Vasopressin
• Vasopressin Injection is indicated to increase blood pressure in adults with vasodilatory shock who remain hypotensive despite fluids and catecholamines. (1)
Vasopressin Dosage and Administration
- Dilute 20 units/mL single dose vial contents with normal saline (0.9% sodium chloride) or 5% dextrose in water (D5W) to either 0.1 units/mL or 1 unit/mL for intravenous administration. Discard unused diluted solution after 18 hours at room temperature or 24 hours under refrigeration. (2.1)
- The 40 units/100 mL single dose vials do not require further dilution prior to administration. (2.1)
- Post-cardiotomy shock: 0.03 to 0.1 units/minute (2.2)
- Septic shock: 0.01 to 0.07 units/minute (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
• Injection:
o 20 units/mL in a single dose vial. To be used after dilution.
o 40 units/100 mL (0.4 units/mL) premixed in dextrose in a single dose vial. Ready to use. (3)
Contraindications
- The 1 mL single dose vial and 100 mL pre-mixed single dose vial does not contain chlorobutanol and is therefore contraindicated only in patients with a known allergy or hypersensitivity to 8-L-arginine vasopressin. (4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions include decreased cardiac output, bradycardia, tachyarrhythmias, hyponatremia and ischemia (coronary, mesenteric, skin, digital). (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Gland Pharma at 609-250-7990 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Pressor effects of catecholamines and Vasopressin Injection are expected to be additive. (7.1)
- Indomethacin may prolong effects of Vasopressin Injection. (7.2)
- Co-administration of ganglionic blockers or drugs causing SIADH may increase the pressor response. (7.3, 7.4)
- Co-administration of drugs causing diabetes insipidus may decrease the pressor response. (7.5)
Use In Specific Populations
Revised: 7/2025
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Vasopressin
Vasopressin Injection is indicated to increase blood pressure in adults with vasodilatory shock who remain hypotensive despite fluids and catecholamines.
2. Vasopressin Dosage and Administration
2.1 Preparation of Solution
Inspect parenteral drug products for particulate matter and discoloration prior to use, whenever solution and container permit.
Vasopressin Injection Solution for Dilution, 20 units/mL
Dilute vasopressin injection in normal saline (0.9% sodium chloride) or 5% dextrose in water (D5W) prior to use for intravenous administration. Discard unused diluted solution after 18 hours at room temperature or 24 hours under refrigeration.
Table 1 Preparation of diluted solutions
| Fluid restriction? | Final concentration | Mix |
|
| Vasopressin Injection | Diluent |
||
| No | 0.1 units/mL | 2.5 mL (50 units) | 500 mL |
| Yes | 1 unit/mL | 5 mL (100 units) | 100 mL |
Vasopressin Injection Premixed Solution, 40 units/100 mL (0.4 units/mL)
This product does not require further dilution prior to administration.
2.2 Administration
In general, titrate to the lowest dose compatible with a clinically acceptable response.
The recommended starting dose is:
Post-cardiotomy shock: 0.03 units/minute
Septic Shock: 0.01 units/minute
Titrate up by 0.005 units/minute at 10-to 15-minute intervals until the target blood pressure is reached. There are limited data for doses above 0.1 units/minute for post-cardiotomy shock and 0.07 units/minute for septic shock. Adverse reactions are expected to increase with higher doses.
After target blood pressure has been maintained for 8 hours without the use of catecholamines, taper vasopressin injection by 0.005 units/minute every hour as tolerated to maintain target blood pressure.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: vasopressin injection, USP is a clear practically, colorless solution available as:
o 20 units/mL in a single dose vial. To be used after dilution.
o 40 units/100 mL (0.4 units/mL) premixed in dextrose in a single dose vial. Ready to use.
4. Contraindications
The 1 mL single dose vial, 100 mL pre-mixed single dose vial does not contain chlorobutanol and is therefore contraindicated only in patients
with a known allergy or hypersensitivity to 8-L-arginine vasopressin.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Worsening Cardiac Function
A decrease in cardiac index may be observed with the use of vasopressin.
5.2 Reversible Diabetes Insipidus
Patients may experience reversible diabetes insipidus, manifested by the development of polyuria, a dilute urine, and hypernatremia, after cessation of treatment with vasopressin. Monitor serum electrolytes, fluid status and urine output after vasopressin discontinuation. Some patients may require readministration of vasopressin or administration of desmopressin to correct fluid and electrolyte shifts.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of vasopressin were identified in the literature. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to estimate their frequency reliably or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Bleeding/lymphatic system disorders: Hemorrhagic shock, decreased platelets, intractable bleeding
Cardiac disorders: Right heart failure, atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, myocardial ischemia
Gastrointestinal disorders: Mesenteric ischemia
Hepatobiliary: Increased bilirubin levels
Renal/urinary disorders: Acute renal insufficiency
Vascular disorders: Distal limb ischemia
Metabolic: Hyponatremia
Skin: Ischemic lesions
Postmarketing Experience
Reversible diabetes insipidus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Related/similar drugs
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Catecholamines
Use with catecholamines is expected to result in an additive effect on mean arterial blood pressure and other hemodynamic parameters. Hemodynamic monitoring is recommended; adjust the dose of vasopressin as needed.
7.2 Indomethacin
Use with indomethacin may prolong the effect of vasopressin injection on cardiac index and systemic vascular resistance. Hemodynamic monitoring is recommended; adjust the dose of vasopressin as needed [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Ganglionic Blocking Agents
Use with ganglionic blocking agents may increase the effect of vasopressin injection, on mean arterial blood pressure. Hemodynamic monitoring is recommended; adjust the dose of vasopressin as needed [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.4 Drugs Suspected of Causing SIADH
Use with drugs suspected of causing SIADH (e.g., SSRIs, tricyclic antidepressants, haloperidol, chlorpropamide, enalapril, methyldopa, pentamidine, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, felbamate) may increase the pressor effect in addition to the antidiuretic effect of vasopressin injection. Hemodynamic monitoring is recommended; adjust the dose of vasopressin as needed.
7.5 Drugs Suspected of Causing Diabetes Insipidus
Use with drugs suspected of causing diabetes insipidus (e.g., demeclocycline, lithium, foscarnet, clozapine) may decrease the pressor effect in addition to the antidiuretic effect of vasopressin injection. Hemodynamic monitoring is recommended; adjust the dose of vasopressin as needed.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on vasopressin injection use in pregnant women to inform a drug associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with vasopressin.
Clinical Considerations
Dose adjustments during pregnancy and the postpartum period: Because of increased clearance of vasopressin in the second and third trimester, the dose of vasopressin injection may need to be increased [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Maternal adverse reactions: Vasopressin injection may produce tonic uterine contractions that could threaten the continuation of pregnancy.
8.2 Lactation
There are no data on the presence of vasopressin injection in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of vasopressin injection in pediatric patients with vasodilatory shock have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of vasopressin did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5), Adverse Reactions (6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
Overdosage with vasopressin injection can be expected to manifest as consequences of vasoconstriction of various vascular beds (peripheral, mesenteric, and coronary) and as hyponatremia. In addition, overdosage may lead less commonly to ventricular tachyarrhythmias (including Torsade de Pointes), rhabdomyolysis, and non-specific gastrointestinal symptoms.
Direct effects will resolve within minutes of withdrawal of treatment.
11. Vasopressin Description
Vasopressin is a polypeptide hormone. Vasopressin injection, USP is a sterile, aqueous solution of synthetic arginine vasopressin for intravenous administration.
The 1 mL solution contains vasopressin 20 units/mL, 1.36 mg sodium acetate buffer and Water for Injection, USP. Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid are included to adjust to a pH of 3.3 to 3.6.
The 100 mL solution contains vasopressin 0.4 units/mL. Each mL of the 0.4 unit/mL strength also contains dextrose anhydrous, 0.0546 mg glacial acetic acid, 0.012 mg sodium acetate and Water for Injection, USP. Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid are included to adjust to a pH of 3.3 to 3.6.
Each vial of the vasopressin injection premixed solutions contains 5% Dextrose in approximately 100 mL Water for Injection. The chemical name of vasopressin is Cyclo (1-6) L-Cysteinyl-L-Tyrosyl-L-Phenylalanyl-L-Glutaminyl-L-Asparaginyl-L-Cysteinyl-L-Prolyl-L-Arginyl-L-Glycinamide. It is a white to off-white powder or flakes, very soluble in water. The structural formula is:
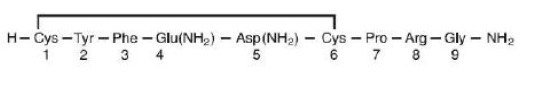
Molecular Formula: C46H65N15O12S2 Molecular Weight: 1084.24
One mg is equivalent to 530 units.
12. Vasopressin - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Vasopressin causes vasoconstriction by binding to V1 receptors on vascular smooth muscle coupled to the Gq/11-phospholipase C-phosphatidyl-inositol-triphosphate pathway, resulting in the release of intracellular calcium. In addition, vasopressin stimulates antidiuresis via stimulation of V2 receptors which are coupled to adenyl cyclase.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
At therapeutic doses exogenous vasopressin elicits a vasoconstrictive effect in most vascular beds including the splanchnic, renal and cutaneous circulation. In addition, vasopressin at pressor doses triggers contractions of smooth muscles in the gastrointestinal tract mediated by muscular V1-receptors and release of prolactin and ACTH via V3 receptors. At lower concentrations typical for the antidiuretic hormone vasopressin inhibits water diuresis via renal V2 receptors. In addition, vasopressin has been demonstrated to cause vasodilation in numerous vascular beds that are mediated by V2, V3, oxytocin and purinergic P2 receptors.
In patients with vasodilatory shock vasopressin in therapeutic doses increases systemic vascular resistance and mean arterial blood pressure and reduces the dose requirements for norepinephrine. Vasopressin tends to decrease heart rate and cardiac output. The pressor effect is proportional to the infusion rate of exogenous vasopressin. The pressor effect reaches its peak within 15 minutes. After stopping the infusion the pressor effect fades within 20 minutes. There is no evidence for tachyphylaxis or tolerance to the pressor effect of vasopressin in patients.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Vasopressin plasma concentrations increase linearly with increasing infusion rates from 10 to 200 μU/kg/min. Steady state plasma concentrations are achieved after 30 minutes of continuous intravenous infusion.
Distribution
Vasopressin does not appear to bind plasma protein. The volume of distribution is 140 mL/kg.
Elimination
At infusion rates used in vasodilatory shock (0.01 to 0.1 units/minute), the clearance of vasopressin is 9 to 25 mL/min/kg in patients with vasodilatory shock. The apparent t1/2 of vasopressin at these levels is ≤10 minutes.
Metabolism
Serine protease, carboxipeptidase and disulfide oxido-reductase cleave vasopressin at sites relevant for the pharmacological activity of the hormone. Thus, the generated metabolites are not expected to retain important pharmacological activity.
Excretion
Vasopressin is predominantly metabolized and only about 6% of the dose is excreted unchanged into urine.
Specific Populations
Pregnancy: Because of a spillover into blood of placental vasopressinase, the clearance of exogenous and endogenous vasopressin increases gradually over the course of a pregnancy. During the first trimester of pregnancy, the clearance is only slightly increased. However, by the third trimester the clearance of vasopressin is increased about 4-fold and at term up to 5-fold. After delivery, the clearance of vasopressin returns to preconception baseline within two weeks.
Drug Interactions Indomethacin more than doubles the time to offset for vasopressin’s effect on peripheral vascular resistance and cardiac output in healthy subjects [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
The ganglionic blocking agent tetra-ethylammonium increases the pressor effect of vasopressin by 20% in healthy subjects [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
Halothane, morphine, fentanyl, alfentanyl and sufentanyl do not impact exposure to endogenous vasopressin.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No formal carcinogenicity or fertility studies with vasopressin have been conducted in animals. Vasopressin was found to be negative in the in vitro bacterial mutagenicity (Ames) test and the in vitro Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell chromosome aberration test. In mice, vasopressin has been reported to have an effect on function and fertilizing ability of spermatozoa.
14. Clinical Studies
Increases in systolic and mean blood pressure following administration of vasopressin were observed in 7 studies in septic shock and 8 in post-cardiotomy vasodilatory shock.
16. How is Vasopressin supplied
Vasopressin Injection, USP is a clear, practically colorless solution for intravenous administration available as:
NDC 68083-520-10: A carton of 10 single dose vials. Each vial contains vasopressin 1 mL at 20 units/mL.
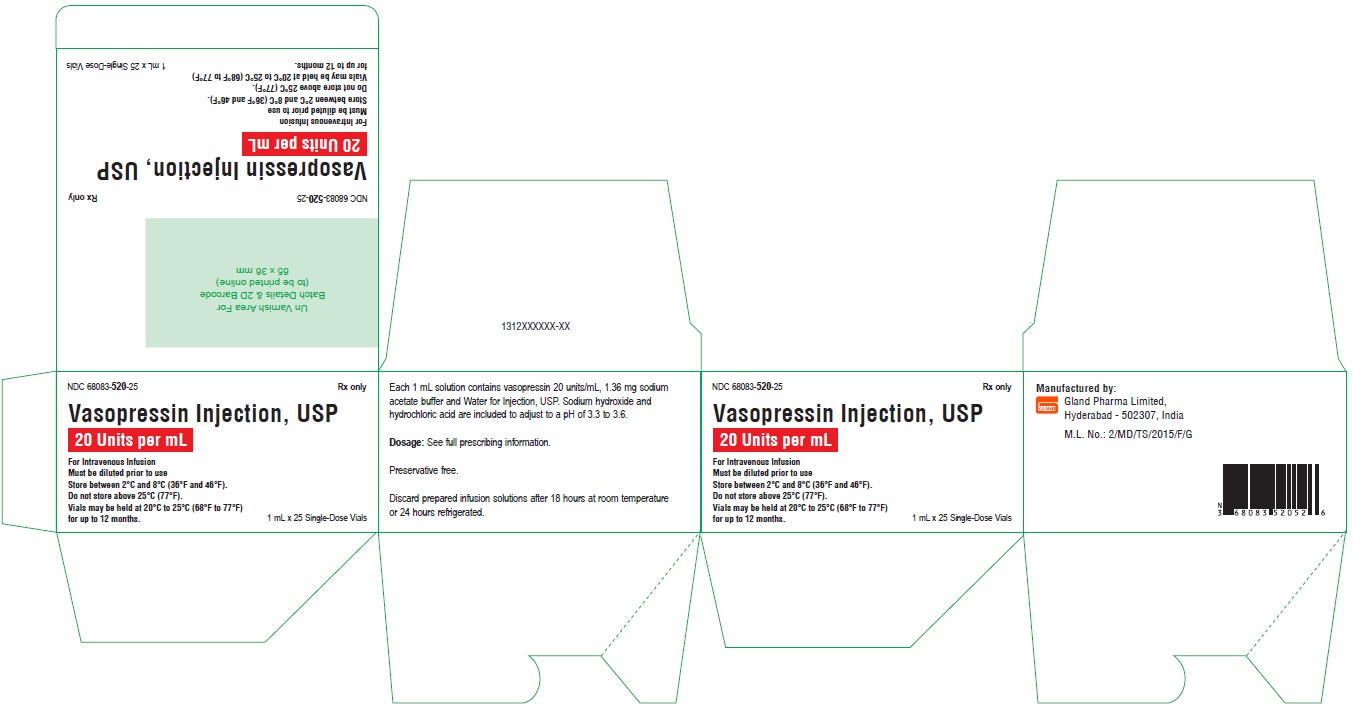
NDC 68083-520-25: A carton of 25 single dose vials. Each vial contains vasopressin 1 mL at 20 units/mL.
NDC 68083-663-10: A carton of 10 single dose vials. Each vial contains vasopressin premixed in dextrose 100 mL at 40 units/100 mL (0.4 units/mL).
Store between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F). Do not freeze.
Vials may be held up to 12 months upon removal from refrigeration to room temperature storage conditions (20°C to 25°C [68°F to 77°F], USP Controlled Room Temperature), anytime within the labeled shelf life. Once removed from refrigeration, unopened vial should be marked to indicate the revised 12 month expiration date. If the manufacturer’s original expiration date is shorter than the revised expiration date, then the shorter date must be used. Do not use vasopressin injection, USP beyond the manufacturer’s expiration date stamped on the vial.
The storage conditions and expiration periods are summarized in the following table.
| | Unopened Refrigerated 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) | Unopened Room Temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) Do not store above 25°C (77°F) | Opened (After First Puncture) |
| 1 mL Vial | Until manufacturer expiration date | 12 months or until manufacturer expiration date, whichever is earlier | N/A |
| 100 mL Vial | Until manufacturer expiration date | 12 months or until manufacturer expiration date, whichever is earlier | N/A |
Manufactured by:
Gland Pharma Limited
Hyderabad-502307, India
July, 2025
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Carton Label - 10's Pack
NDC 68083-520-10 Rx only
Vasopressin Injection, USP
20 Units per mL
For Intravenous Infusion
Must be diluted prior to use
Store between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F).
Do not store above 25°C (77°F).
Vials may be held at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for up to 12 months.
1 mL x 10 Single-Dose Vials
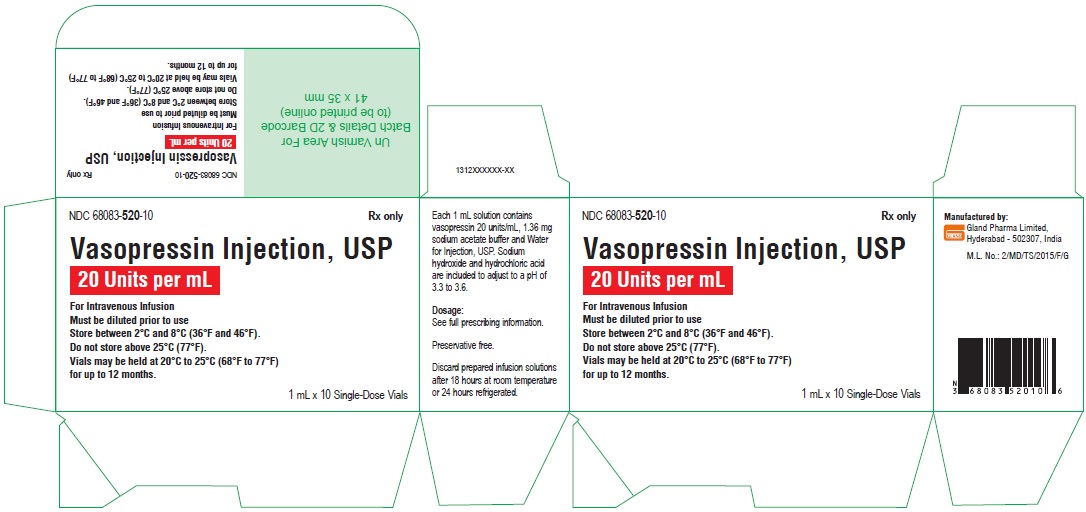
Carton Label-25's Pack
NDC 68083-520-25 Rx only
Vasopressin Injection, USP
20 Units per mL
For Intravenous Infusion
Must be diluted prior to use
Store between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F).
Do not store above 25°C (77°F).
Vials may be held at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for up to 12 months.
1 mL x 25 Single-Dose Vials
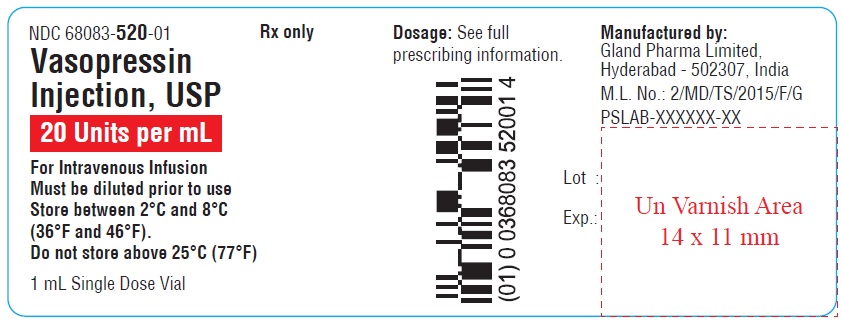
Container Label
NDC 68083-520-01 Rx only
Vasopressin Injection, USP
20 Units per mL
For Intravenous Infusion
Must be diluted prior to use
Store between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F).
Do not store above 25°C (77°F).
1 mL Single Dose Vial
Carton Label:
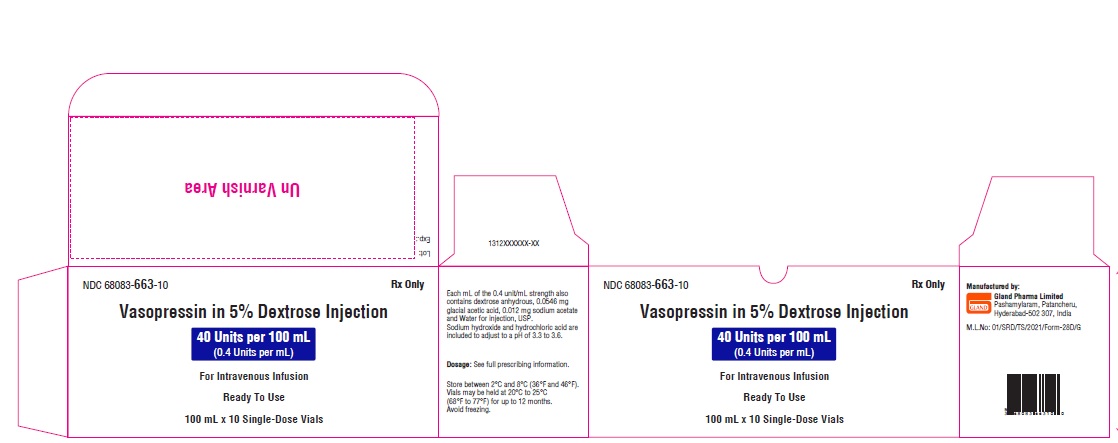
NDC 68083-663-10
Vasopressin in 5% Dextrose Injection
40 Units per 100 mL (0.4 Units per mL)
For Intravenous Infusion
Ready To Use
100 mL x 10 Single-Dose Vials
Container Label:
NDC 68083-663-01
Vasopressin in 5% Dextrose Injection
40 Units per 100 mL (0.4 Units per mL)
For Intravenous Infusion
Ready To Use
100 mL Single-Dose Vial

| VASOPRESSIN
vasopressin injection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VASOPRESSIN
vasopressin injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Gland Pharma Limited (918601238) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLAND PHARMA LIMITED | 858971074 | ANALYSIS(68083-520, 68083-663) , LABEL(68083-520, 68083-663) , MANUFACTURE(68083-520, 68083-663) , PACK(68083-520, 68083-663) | |
More about vasopressin
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (1)
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: antidiuretic hormones
- Breastfeeding
- En español
