Methylergonovine Maleate Tablets: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Dosage form: tablet
Drug class: Uterotonic agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jul 7, 2025.
On This Page
Methylergonovine Maleate Tablets Description
Methylergonovine Maleate Tablets, USP is a semi-synthetic ergot alkaloid used for the prevention and control of postpartum hemorrhage.
Methylergonovine Maleate Tablets, USP is available in tablets for oral ingestion containing 0.2 mg methylergonovine maleate.
Tablets
Active ingredient: Methylergonovine maleate, USP, 0.2 mg.
Inactive ingredients: acacia, corn starch, gelatin, lactose monohydrate, methylparaben, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, propylparaben, stearic acid, and tartaric acid.
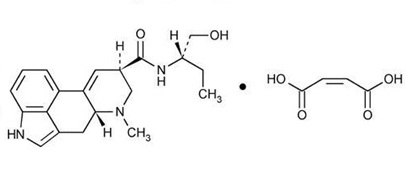
Chemically, methylergonovine maleate is designated as ergoline-8-carboxamide, 9,10-didehydro- N-[1-(hydroxy-methyl)propyl]-6-methyl-, [8 β( S)]-, ( Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1) (salt). Its structural formula is:
C 20H 25N 3O 2•C 4H 4O 4 Mol Wt: 455.51
Methylergonovine Maleate Tablets - Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Methylergonovine maleate acts directly on the smooth muscle of the uterus and increases the tone, rate, and amplitude of rhythmic contractions. Thus, it induces a rapid and sustained tetanic uterotonic effect which shortens the third stage of labor and reduces blood loss.
Pharmacodynamics
The onset of action after IV administration is immediate; after I.M. administration, 2 to 5 minutes, and after oral administration, 5 to 10 minutes.
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic studies following an IV injection have shown that methylergonovine is rapidly distributed from plasma to peripheral tissues within 2 to 3 minutes or less. The bioavailability after oral administration was reported to be about 60% with no accumulation after repeated doses. During delivery, with intramuscular injection, bioavailability increased to 78%. Ergot alkaloids are mostly eliminated by hepatic metabolism and excretion, and the decrease in bioavailability following oral administration is probably a result of first-pass metabolism in the liver.
Bioavailability studies conducted in fasting healthy female volunteers have shown that oral absorption of a 0.2 mg methylergonovine tablet was fairly rapid with a mean peak plasma concentration of 3243 ± 1308 pg/mL observed at 1.12 ± 0.82 hours. A delayed gastrointestinal absorption (T max about 3 hours) of methylergonovine maleate tablet might be observed in postpartum women during continuous treatment with this oxytocic agent.
For a 0.2 mg intramuscular (IM) injection, a mean peak plasma concentration of 5918 ± 1952 pg/mL was observed at 0.41 ± 0.21 hours. The extent of absorption of the tablet, based upon methylergonovine plasma concentrations, was found to be equivalent to that of the IM solution given orally, and the extent of oral absorption of the IM solution was proportional to the dose following administration of 0.1, 0.2, and 0.4 mg. When given intramuscularly, the extent of absorption of methylergonovine maleate solution was about 25% greater than the tablet. The volume of distribution (Vd ss/F) of intramuscularly administered methylergonovine was calculated to be 56.1 ± 17 liters, and the plasma clearance (CLp/F) was calculated to be 14.4 ± 4.5 liters per hour.
The decline of plasma level of intramuscularly administered methylergonovine was biphasic with a mean elimination half-life of 3.39 hours (range 1.5 to 12.7 hours).
Indications and Usage for Methylergonovine Maleate Tablets
Following delivery of the placenta, for routine management of uterine atony, hemorrhage and subinvolution of the uterus. For control of uterine hemorrhage in the second stage of labor following delivery of the anterior shoulder.
Warnings
General
This drug should not be administered I.V. routinely because of the possibility of inducing sudden hypertensive and cerebrovascular accidents. If I.V. administration is considered essential as a lifesaving measure, methylergonovine maleate should be given slowly over a period of no less than 60 seconds with careful monitoring of blood pressure. Intra-arterial or periarterial injection should be strictly avoided.
Caution should be exercised in the presence of impaired hepatic or renal function.
Coronary artery disease
Patients with coronary artery disease or risk factors for coronary artery disease (e.g., smoking, obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol) may be more susceptible to developing myocardial ischemia and infarction associated with methylergonovine-induced vasospasm.
Risk of Adverse Reactions or Reduced Therapeutic Effect Due to Drug Interactions
The concomitant use of Methylergonovine Maleate and certain drugs may result in potentially significant drug interactions, some of which may lead to adverse reactions or reduced therapeutic effect of Methylergonovine Maleate or the concomitant drug. (see CONTRAINDICATION and DRUG INTERACTION)
Medication errors
Inadvertent administration of methylergonovine maleate to newborn infants has been reported. In these cases of inadvertent neonatal exposure, symptoms such as respiratory depression, convulsions, cyanosis and oliguria have been reported. Usual treatment is symptomatic. However, in severe cases, respiratory and cardiovascular support is required.
Methylergonovine maleate has been administered instead of vitamin K and Hepatitis B vaccine, medications which are routinely administered to the newborn. Due to the potential for accidental neonatal exposure, methylergonovine maleate injection should be stored separately from medications intended for neonatal administration.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Caution should be exercised in the presence of sepsis, obliterative vascular disease. Also use with caution during the second stage of labor. The necessity for manual removal of a retained placenta should occur only rarely with proper technique and adequate allowance of time for its spontaneous separation.
Drug Interactions
CYP 3A4 Inhibitors (e.g., Macrolide Antibiotics and Protease Inhibitors)
There have been rare reports of serious adverse events in connection with the coadministration of certain ergot alkaloid drugs (e.g., dihydroergotamine and ergotamine) and potent CYP 3A4 inhibitors, resulting in vasospasm leading to cerebral ischemia and/or ischemia of the extremities. Although there have been no reports of such interactions with methylergonovine alone, strong and moderate CYP 3A4 inhibitors should not be co-administered with methylergonovine. Examples of some of the strong CYP 3A4 inhibitors include saquinavir, grapefruit juice, nefazodone, macrolide antibiotics (e.g., troleandomycin, clarithromycin), HIV protease or reverse transcriptase inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, indinavir, nelfinavir) or azole antifungals (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole). Moderate inhibitors include fluconazole, fluvoxamine and clotrimazole. Weak CYP 3A4 inhibitors should be administered with caution. Weak inhibitors include chlorzoxazone, cilostazol, and ranitidine. These lists are not exhaustive, and the prescriber should consider the effects on CYP 3A4 of other agents being considered for concomitant use with methylergonovine.
CYP3A4 inducers
Drugs (e.g. nevirapine, rifampin) that are strong inducers of CYP3A4 are likely to decrease the pharmacological action of methylergonovine maleate.
Beta-blockers
Caution should be exercised when methylergonovine maleate is used concurrently with beta-blockers. Concomitant administration with beta-blockers may enhance the vasoconstrictive action of ergot alkaloids.
Anesthetics
Anesthetics like halothane and methoxyflurane may reduce the oxytocic potency of methylergonovine maleate.
Glyceryl trinitrate and other antianginal drugs
Methylergonovine maleate produces vasoconstriction and can be expected to reduce the effect of glyceryl trinitrate and other antianginal drugs.
No pharmacokinetic interactions involving other cytochrome P450 isoenzymes are known.
Caution should be exercised when methylergonovine maleate is used concurrently with other vasoconstrictors, ergot alkaloids, or prostaglandins.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long-term studies have been performed in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential. The effect of the drug on mutagenesis or fertility has not been determined.
Pregnancy
Use of Methylergonovine Maleate is contraindicated during pregnancy because of its uterotonic effects. (See INDICATIONS AND USAGE) Animal reproductive studies have not been conducted with Methylergonovine Maleate. It is not known whether Methylergonovine Maleate can cause fetal harm or can affect reproductive capacity.
Labor and Delivery
The uterotonic effect of methylergonovine maleate is utilized after delivery to assist involution and decrease hemorrhage, shortening the third stage of labor. Caution should be exercised during the second stage of labor. The necessity for manual removal of a retained placenta should occur only rarely with proper technique and adequate allowance of time for its spontaneous separation.
Nursing Mothers
Mothers should not breast-feed during treatment with methylergonovine maleate and at least 12 hours after administration of the last dose. Milk secreted during this period should be discarded. Methylergonovine Maleate may produce adverse effects in the breast-feeding infant. Methylergonovine Maleate may also reduce the yield of breast milk
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of methylergonovine maleate did not include sufficient number of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in response between the elderly and younger patients. In general dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Clinical trials experience
Common Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reaction is hypertension associated in several cases with seizure and/or headache. Hypotension has also been reported. Abdominal pain (caused by uterine contractions), nausea and vomiting have occurred occasionally.
Rare Adverse Reactions
Rarely observed reactions have included: acute myocardial infarction, transient chest pains, vasoconstriction, vasospasm, coronary arterial spasm, bradycardia, tachycardia, dyspnea, hematuria, thrombophlebitis, water intoxication, hallucinations, leg cramps, dizziness, tinnitus, nasal congestion, diarrhea, diaphoresis, palpitation, rash, and foul taste.
There have been rare isolated reports of anaphylaxis, without a proven causal relationship to the drug product.
Post marketing Experience
The following adverse drug reactions have been derived from post-marketing experience with methylergonovine maleate via spontaneous case reports. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency which is therefore categorized as not known.
Nervous system disorders
Cerebrovascular accident, paraesthesia
Cardiac disorders
Ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, angina pectoris, atrioventricular block
Related/similar drugs
Drug Abuse and Dependence
Methylergonovine maleate has not been associated with drug abuse or dependence of either a physical or psychological nature.
Overdosage
Symptoms of acute overdose may include: nausea, vomiting, oliguria, abdominal pain, numbness, tingling of the extremities, rise in blood pressure, in severe cases followed by hypotension, respiratory depression, hypothermia, convulsions, and coma.
Because reports of overdosage with methylergonovine maleate are infrequent, the lethal dose in humans has not been established. The oral LD 50 (in mg/kg) for the mouse is 187, the rat 93, and the rabbit 4.5. Several cases of accidental methylergonovine maleate injection in newborn infants have been reported, and in such cases 0.2 mg represents an overdose of great magnitude. However, recovery occurred in all but one case following a period of respiratory depression, hypothermia, hypertonicity with jerking movements, and convulsions.
Also, several children 1 to 3 years of age have accidentally ingested up to 10 tablets (2 mg) with no apparent ill effects. A postpartum patient took 4 tablets at one time in error and reported paresthesias and clamminess as her only symptoms.
Treatment of acute overdosage is symptomatic and includes the usual procedures of:
1. removal of offending drug by inducing emesis, gastric lavage, catharsis, and supportive diuresis.
2. maintenance of adequate pulmonary ventilation, especially if convulsions or coma develop.
3. correction of hypotension with pressor drugs as needed.
4. control of convulsions with standard anticonvulsant agents.
5. control of peripheral vasospasm with warmth to the extremities if needed.
Methylergonovine Maleate Tablets Dosage and Administration
Orally
The recommended dosage of Methylergonovine Maleate is One tablet, 0.2 mg, orally 3 or 4 times daily in the puerperium for a maximum of 1 week.
How is Methylergonovine Maleate Tablets supplied
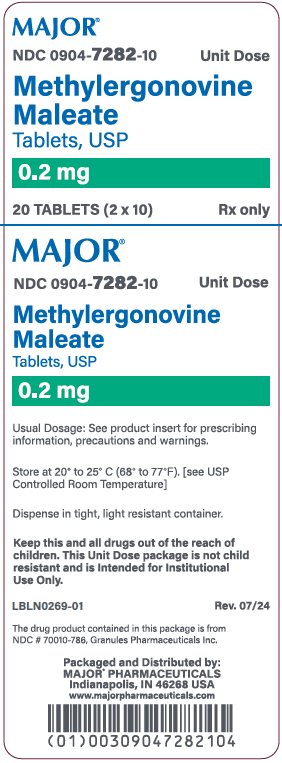
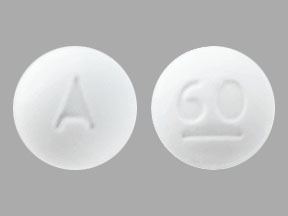
White, round, biconvex compressed tablets debossed with “G 786” on one side and plain on the other side.
Cartons of 20 tablets (10 tablets each blister pack x 2), NDC 0904-7282-10
WARNING: This Unit Dose package is not child resistant and is Intended for Institutional Use Only. Keep this and all drugs out of the reach of children.
Store and Dispense
Tablets: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted to 15ºC to 30ºC (59ºF to 86ºF).
Dispense in tight, light-resistant container.
Manufactured by:
Granules Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Chantilly VA 20151
Packaged and Distributed by:
MAJOR® PHARMACEUTICALS
Indianapolis, IN 46268 USA
Refer to package label for Distributor's NDC Number
Rev: 06/2025
| METHYLERGONOVINE MALEATE
methylergonovine maleate tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Major Pharmaceuticals (191427277) |
More about methylergonovine
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Reviews (10)
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: uterotonic agents
- Breastfeeding
- En español