Kaposi's Sarcoma
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is Kaposi sarcoma?
Kaposi sarcoma (KS) is a type of skin cancer. KS may appear on any part of your skin. It can also be found in your lymph nodes, stomach, intestines, liver, spleen, lungs, and bones. KS may start in one area and spread to other areas of your body.
What increases my risk for KS?
You may be at risk if you have HIV, AIDS, or a human herpes virus-8 (HHV-8) infection. Medicines used during cancer treatment and organ transplants or steroids may also increase your risk for KS.
What are the signs and symptoms of KS?
The most common sign is red, purple, blue, or dark spots or sores on your skin. They may be located anywhere on your body, including in your mouth. You may have other symptoms depending on where KS is in your body.
How is KS diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine your skin. Your provider will take a sample of skin from one of your sores and send it to a lab for tests. A chest x-ray, CT scan, or MRI may show if KS is in other areas or organs of your body. You may be given contrast liquid to help KS show up better in the pictures. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
How is KS treated?
- Medicines are given to stop cancer cells from growing and to kill new cancer cells. Medicines may also help strengthen your immune system. If you have HIV or AIDS, you will be given medicine to treat the viral infection.
- Radiation therapy uses x-rays or gamma rays to treat cancer. Radiation kills cancer cells and may stop the cancer from spreading. It may be given alone or with chemotherapy.
- Cryotherapy is a treatment to freeze and remove areas of KS from your skin.
- Surgery may be done to remove KS if it is in an organ or other area that causes severe symptoms.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
How can I manage my symptoms?
- Care for your mouth. Brush your teeth 2 times each day. Floss your teeth regularly, and use mouthwash. This may decrease your risk for mouth pain and trouble eating and swallowing.
- Eat healthy foods. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meats, and fish. Ask if you need to be on a special diet.

- Wear support stockings and elevate your legs to decrease swelling. Support stockings are also called compression garments. Support stockings are often worn during the day and removed at night.
- Go to physical therapy as directed. A physical therapist teaches you exercises to help improve movement and strength, and to decrease pain.
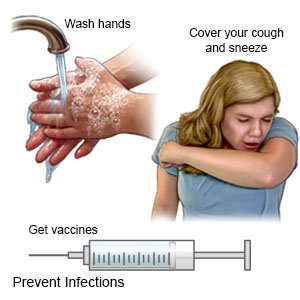
What can I do to prevent the spread of germs?
- Wash your hands often. Wash your hands several times each day. Wash after you use the bathroom, change a child's diaper, and before you prepare or eat food. Use soap and water every time. Rub your soapy hands together, lacing your fingers. Wash the front and back of your hands, and in between your fingers. Use the fingers of one hand to scrub under the fingernails of the other hand. Wash for at least 20 seconds. Rinse with warm, running water. Then dry your hands with a clean towel or paper towel. Use hand sanitizer that contains alcohol if soap and water are not available.

- Cover a sneeze or cough. Use a tissue that covers your mouth and nose. Throw the tissue away in a trash can right away. Use the bend of your arm if a tissue is not available. Wash your hands well with soap and water or use a hand sanitizer.
- Stay away from others while you are sick. Avoid crowds as much as possible.
- Ask about vaccines you may need. Your healthcare provider can tell you if you should also get vaccines not listed below:
- Ask your healthcare provider about the flu and pneumonia vaccines. All adults should get the flu (influenza) vaccine as soon as recommended each year, usually in September or October. The pneumonia vaccine is recommended for all adults aged 50 or older to prevent pneumococcal disease, such as pneumonia. Adults aged 19 to 49 years who are at high risk for pneumococcal disease should also receive the vaccine. You may need 1 dose or 2. The number depends on the vaccine used and your risk factors.
- COVID-19 vaccines are given to adults as a shot. At least 1 dose of an updated vaccine is recommended for all adults. COVID-19 vaccines are updated throughout the year. Adults 65 or older need a second dose of updated vaccine at least 4 months after the first dose. Your healthcare provider can help you schedule all needed doses as updated vaccines become available.
 |
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) if:
- You have trouble breathing or cough up blood.
When should I call my doctor?
- You have a fever.
- You get more sores on your skin, or they are more painful or itch.
- You have increased fatigue or weakness.
- Your hands and feet are itchy, swollen, or painful.
- You have numbness or tingling in your hand or foot.
- You have trouble eating or swallowing.
- You have nausea or vomiting that will not stop.
- You have diarrhea or constipation, or blood in your bowel movement.
- Your leg is swollen and painful and makes it difficult to walk.
- You have bone pain or increased headaches.
- You cannot control when you urinate.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Kaposi's Sarcoma
Treatment options
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
