Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumors
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
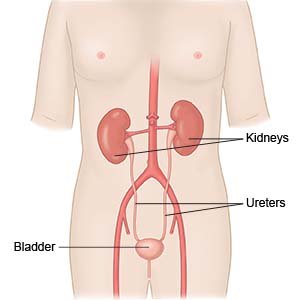
Transurethral resection of bladder tumors (TURBT) is surgery to remove one or more tumors from your bladder.
 |
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Seek care immediately if:
- You have heavy bleeding from your urethra.
- You start to urinate less often, very little, or not at all.
- You have severe pain in your abdomen or pelvis.
Call your doctor or surgeon if:
- You have a fever or chills.
- You have new or more blood in your urine.
- You have nausea or are vomiting.
- You have new or more pain when you urinate.
- You are unable to control when you urinate.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Related medications
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Antibiotics help prevent or treat a bacterial infection.
- Prescription pain medicine may be given. Ask your healthcare provider how to take this medicine safely. Some prescription pain medicines contain acetaminophen. Do not take other medicines that contain acetaminophen without talking to your healthcare provider. Too much acetaminophen may cause liver damage. Prescription pain medicine may cause constipation. Ask your healthcare provider how to prevent or treat constipation.
- Take your medicine as directed. Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Care for your Foley catheter:
Keep the bag below your waist. This will prevent urine from flowing back into your bladder and causing an infection or other problems. Keep the tube free of kinks so the urine will drain properly. Do not pull on the catheter. This can cause pain and bleeding and may cause the catheter to come out. Empty your urine drainage bag when it is ½ to ⅔ full, or every 8 hours. If you have a smaller leg bag, empty it every 3 to 4 hours.
Follow up with your doctor or surgeon as directed:
Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
