Myocarditis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
Myocarditis is inflammation of the heart muscle (myocardium). The myocardium pumps blood through the heart and to other parts of the body. Myocarditis can damage the heart muscle. This weakens the heart and makes it work harder. Over time, this may cause your heart to enlarge, lead to heart failure, and become life-threatening.
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
Keep the head of your bed raised to help you breathe easier.
You can also raise your head and shoulders on pillows or rest in a reclining chair. If you feel short of breath, let healthcare providers know right away.
Heart-healthy nutrition:
Healthcare providers may recommend you eat foods low in cholesterol, saturated fat, and trans fats. You may also need to eat foods low in sodium (salt).
Intake and output
may be measured. Healthcare providers will keep track of the amount of liquid you are getting. They also may need to know how much you are urinating. Ask healthcare providers if they need to measure or collect your urine.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Antibiotics or antivirals may be given to help treat or prevent an infection.
- Blood pressure medicine helps lower your blood pressure to reduce the strain on your heart.
- Diuretics may be given to help decrease edema (excess fluid) that collects in a part of your body, such as your legs. Diuretics can also remove excess fluid from around your heart or lungs and decrease your blood pressure. You may urinate more often when you take diuretics.
- Heart medicine may be given to reduce the strain on your heart and regulate your heart rate.
- Aspirin helps thin the blood to keep clots from forming. If you are told to take aspirin, do not take acetaminophen or ibuprofen instead. This medicine makes it more likely for you to bleed or bruise.
- Blood thinners help prevent blood clots. Clots can cause strokes, heart attacks, and death. Many types of blood thinners are available. Your healthcare provider will give you specific instructions for the type you are given. The following are general safety guidelines to follow while you are taking a blood thinner:
- Watch for bleeding and bruising. Watch for bleeding from your gums or nose. Watch for blood in your urine and bowel movements. Use a soft washcloth on your skin, and a soft toothbrush to brush your teeth. This can keep your skin and gums from bleeding. If you shave, use an electric shaver. Do not play contact sports.
- Tell your dentist and other healthcare providers that you take a blood thinner. Wear a bracelet or necklace that says you take this medicine.
- Do not start or stop any other medicines or supplements unless your healthcare provider tells you to. Many medicines and supplements cannot be used with blood thinners.
- Take your blood thinner exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not skip a dose or take less than prescribed. Tell your provider right away if you forget to take your blood thinner, or if you take too much.
- Pain medicine may be given to decrease your pain. Do not wait until the pain is severe before you ask for more medicine.
- NSAIDs help decrease swelling and pain or fever. This medicine is available with or without a doctor's order. NSAIDs can cause stomach bleeding or kidney problems in certain people. If you take blood thinner medicine, always ask your healthcare provider if NSAIDs are safe for you. Always read the medicine label and follow directions.
- Immunoglobulin (IVIG) may help reduce inflammation and treat an infection.
- Immunosuppressants may be given to reduce inflammation and prevent the immune system from attacking your body.
Tests:
Contrast liquid may be used before certain tests. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
- Blood tests may show inflammation or damage to your heart muscle.
- An EKG records the electrical activity of your heart. It is used to check for abnormal heart rhythm.
- An echocardiogram is a type of ultrasound. Sound waves are used to show the structure and function of your heart.
- X-ray or MRI pictures will show the size of your heart and check for inflammation. These tests can also check if you have fluid around your heart or lungs. You may be given contrast liquid before the pictures are taken to help providers see the pictures clearly. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the provider if you have any metal in or on your body.
- Nuclear imaging may be used to check for inflammation and damage to your heart. Radioactive dye is injected into a blood vessel to help providers see the pictures clearly.
- Cardiac catheterization is a procedure that uses an x-ray and contrast liquid to check your heart and the blood flow in your arteries. A tube is threaded to your heart through a blood vessel in your leg or arm. Contrast liquid may be given to help arteries show up more clearly.
- A biopsy is a procedure used to remove a small piece of your heart muscle tissue. The muscle tissue is sent to a lab for tests.
Treatment:
In addition to medicines, your healthcare provider may recommend a procedure or surgery. You may need any of the following:
- Breathing support , such as extra oxygen or a ventilator, may help you breathe easier and increase oxygen levels in your blood.
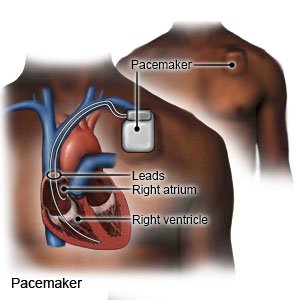
- A pacemaker is a device that helps your heart beat at a regular rate and rhythm. The pacemaker monitors your heart rhythm. If your heart does not beat as it should, the pacemaker sends small electric signals to your heart.
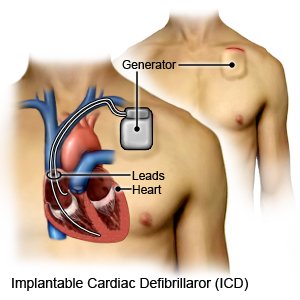
- An implanted cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is a small device that monitors your heart rate and rhythm. If your ICD senses that your heart is not beating correctly, it will give it a small electrical shock. This helps your heart to beat regularly again.
- Heart transplant surgery may be needed if your condition is severe. During a heart transplant, your damaged heart is removed and replaced with a healthy heart from a donor.
RISKS:
Myocarditis may weaken the heart muscle. This makes it hard to pump blood and may cause your heart to fail. You may have decreased blood flow and oxygen to organs, such as your brain and kidneys. This may cause fluid buildup in your lungs, and make it difficult to breathe. Inflammation from myocarditis can lead to blood clots and increase your risk for stroke or heart attack. Your condition may become life-threatening
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Myocarditis
- Atorvastatin (Lipitor): Top 12 Drug Facts You Need to Know
- Do blood pressure drugs interact with alcohol?
- Side Effects of Weight Loss Drugs
Treatment options
Care guides
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
