Intrauterine Growth Restriction
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)?
IUGR means your unborn baby is smaller or weighs less than expected during pregnancy or at birth. Healthcare providers may use other terms, such as small for gestational age or fetal growth restriction. IUGR can develop during the second or third trimester.
What increases the risk for IUGR?
- Weighing less than 100 pounds, or malnutrition during your pregnancy
- A health condition you have during pregnancy, such as diabetes, anemia, hypertension, or heart, lung, or kidney disease
- An infection such as rubella or cytomegalovirus during pregnancy
- A birth defect or problem with the placenta or umbilical cord
- Being pregnant with more than 1 baby
- Low amniotic fluid level
- Use of drugs, alcohol, or cigarettes during pregnancy
- Use of some medicines during pregnancy, such as cancer medicine, epilepsy medicine, or blood thinners
How is IUGR diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will ask about your medical history and past pregnancies. Tell him or her about your medicines. Your provider will combine this information with your body frame size and genetic background. These help determine how large your baby is expected to be. The following tests can help your provider find if your baby is the expected size for a certain trimester:
- Weight checks that show you are gaining less weight than expected can be a sign of IUGR.
- Ultrasound pictures are used to find the amount of amniotic fluid in your womb. The pictures may also show your baby's size. Moving ultrasound pictures are used to check blood flow through arteries in the umbilical cord and through the placenta.
- Fetal monitoring is used to measure your baby's heart rate and rhythm. Electrodes will be placed on your abdomen. The heart rate and rhythm will show up on a monitor or be printed.
- A biophysical profile checks your baby's breathing and movement. It also checks for the amount of amniotic fluid in your womb.
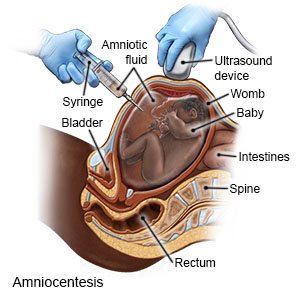
- Amniocentesis is used to take a sample of amniotic fluid to be tested for an infection or birth defect. This may be done if other tests show your baby may have IUGR. A needle will be put through your skin and into your uterus. The amniotic fluid is pulled out through the needle.
Related medications
How is IUGR treated?
- Labor may be induced (started) if you are at least 34 weeks along.
- Monitoring will be used if you are not yet at 34 weeks. Monitoring includes regular ultrasounds and nonstress testing.
- Treatment for a medical condition you have may be recommended. Examples include helping you gain a healthy amount of weight or controlling your blood pressure.
Manage IUGR:
Your healthcare provider may give you specific instructions to follow until you go into labor. The following are general guidelines:
- Do kick counts, if directed. Kick counts measure how much your baby is moving in your womb. A kick from can be felt as a twist, turn, swish, roll, or jab. Sit or lie on your left side. Place your hands on the largest part of your belly. Write down how much time it takes to count 10 kicks. It may take 30 minutes to 2 hours to count 10 kicks. It should not take more than 2 hours.
- Get more calories, if needed. Your healthcare provider or a dietitian can help you plan meals and snacks. More calories can help your baby gain weight before birth.
- Rest as directed. If possible, take naps during the day. Try to get at least 8 hours of sleep each night. Bed rest is sometimes recommended for IUGR. Bed rest means you limit the amount of walking around you do during the day.
How can I lower my risk for IUGR in a future pregnancy?
IUGR increases a baby's risk for conditions such as low blood sugar levels, seizures, and respiratory distress syndrome. IUGR also increases the risk for diseases as an adult, such as obesity, diabetes, and stroke. The following can help you prevent IUGR in a future pregnancy:
- Go to prenatal visits. Prenatal visits are used to check your health and your unborn baby's health. Your healthcare provider will tell you how often to have prenatal visits. He or she may recommend you have visits often to help prevent IUGR.
- Do not smoke. Nicotine in cigarettes increases the risk for problems with the placenta. Nicotine also causes low birth weight and other medical problems for the baby. Do not use e-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco in place of cigarettes or to help you quit. They still contain nicotine. Ask your healthcare provider for information if you currently smoke and need help quitting.
- Eat a variety of healthy foods. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy products, lean meats, and beans. Healthy foods can help you gain a healthy amount of weight during pregnancy, and prevent diabetes.

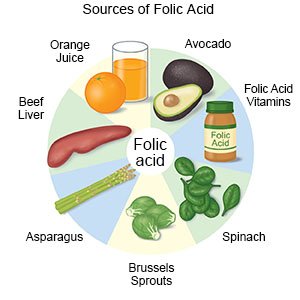
- Take prenatal vitamins as directed. The vitamins should contain at least 4,000 micrograms of folic acid. Folic acid helps prevent birth defects such as spina bifida. Your healthcare provider can help you choose a prenatal vitamin that is right for you.
- Drink liquids as directed. More liquid can help prevent dehydration and high blood pressure.
- Control diabetes or other medical conditions. Diabetes can cause problems for your baby, such as too much weight gain. If you have diabetes, work with your healthcare provider to manage your blood sugar levels before and during your next pregnancy.
When should I call my doctor or obstetrician?
- You think your baby is moving less than before.
- You are doing kick counts and feel a change in the number of kicks or movements of your baby.
- You feel fewer than 10 kicks within 2 hours.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
