Hepatitis B in Children
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
What is hepatitis B?
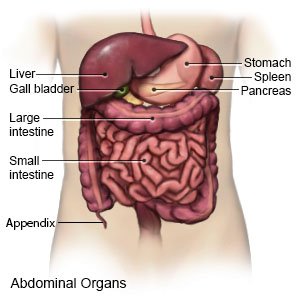
Hepatitis B is inflammation of the liver caused by hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. The infection is called acute when a person first becomes infected. The infection becomes chronic after 6 months. Chronic hepatitis B is less common in children than in adults.
 |
How is HBV spread?
HBV can spread from a mother to her baby during delivery. A baby who gets infected with HBV during birth has a high risk for developing chronic hepatitis B. HBV also spreads through contact with infected blood or body fluids. HBV can enter your child's body through a cut or scratch in his or her skin or through mucus membranes. HBV can live on objects and surfaces for 7 days or longer.
What increases my child's risk for hepatitis B?
- The following increase the risk for your adolescent:
- A stick from an infected needle, including for illegal drugs and for procedures such as tattooing
- Unprotected sex with an infected person, sex with more than one partner, or being a male who has sex with males
- The following increase the risk for your child or adolescent:
- An object with infected blood or body fluids on it touches a wound
- Close contact with an infected person
- Travel to areas in the world where HBV is common
- Living or working in a long-term care facility or correctional facility
- Rarely, a blood, organ, or tissue transplant from an infected donor
What are the signs and symptoms of hepatitis B?
Your child may have no signs or symptoms and may not know he or she has been infected. Symptoms may not develop for 1 to 6 months after your child is infected with HBV. He or she may have any of the following:
- Dark urine or pale bowel movements
- Fatigue and weakness
- Fever
- Loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting
- Jaundice (yellow skin or eyes), itchy skin, or skin rash
- Joint pain and body aches
- Pain in the right upper side of the abdomen
How is hepatitis B diagnosed?
Your child's healthcare provider will ask about his or her signs and symptoms and any health problems he or she has. Tell the provider if your child has other infections, such as HIV or hepatitis C. The provider may ask questions to check if your child is at increased risk for hepatitis B. Your child may also need any of the following tests:
- Blood tests are used to see if your child is infected with HBV and to check his or her liver function.
- An ultrasound may be done to check for signs of HBV and to look for other liver problems.
- Elastography is a test to check if your child's liver tissue is thick and stiff. This may mean your child is developing fibrosis or cirrhosis (liver scarring).
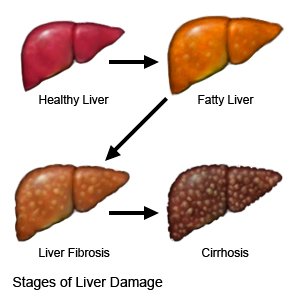
- A biopsy is used to test a sample of your child's liver for swelling, scarring, and other damage. A liver biopsy may help healthcare providers learn if your child needs treatment for HBV.
How is hepatitis B treated?
Hepatitis B may last a short time and go away on its own without treatment. Your child's healthcare provider will monitor him or her closely for signs of liver disease. If needed, treatment may help improve your child's liver function and decrease symptoms. He or she may need any of the following:
- Medicines may be given to help fight HBV and keep it from spreading in your child's body.
- A plasma or platelet transfusion may be needed if your child's blood is not clotting as it should. Plasma and platelets help blood clot. He or she will get the transfusion through an IV.
- A liver transplant is surgery to replace your child's diseased liver with a donor liver. Your child may need a liver transplant if he or she has severe liver disease or liver failure.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
What can I do to manage hepatitis B?
- Have your child eat a variety of healthy foods. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy products, beans, lean meats and fish, and whole-grain breads. Ask if your child needs to be on a special diet.

- Have your child drink more liquids. Liquids help your child's liver function properly. Ask your healthcare provider how much liquid your child should drink each day and which liquids are best for him or her.
- Talk to your adolescent about not drinking alcohol. Alcohol can increase liver damage. Talk to his or her healthcare provider if he or she drinks alcohol and needs help to stop.
- Talk to your adolescent about not smoking. Nicotine can damage blood vessels and make it more difficult to manage hepatitis B. Smoking can also lead to more liver damage. Ask your adolescent's healthcare provider for information if he or she currently smokes and needs help to quit. E-cigarettes or smokeless tobacco still contain nicotine. Talk to the provider before your adolescent uses these products.
What can I do to help prevent the spread of HBV?
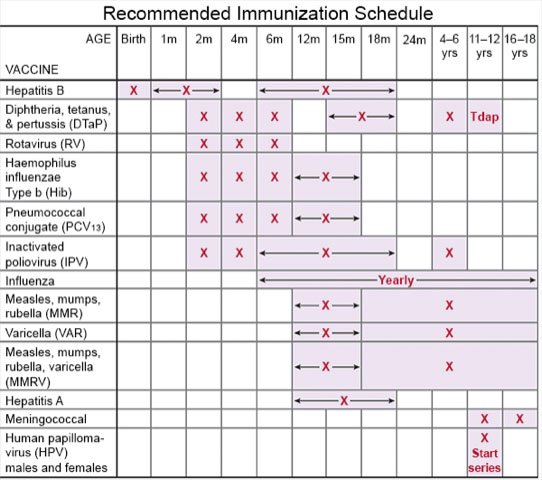
- Talk to your child's healthcare provider about the hepatitis B vaccine. The vaccine helps protect your child from the virus that causes hepatitis B. Babies are routinely given a hepatitis B vaccine dose 24 to 48 hours after birth. A second dose is given at 1 to 2 months, and a third dose at 6 to 18 months.
- Have your child cover any open cuts or scratches. If blood from a wound gets on a surface, clean the surface with bleach right away. Put on gloves before you clean. Throw away any items with blood or body fluids on them, as directed by your child's healthcare provider.
- Do not let your child share personal items. These items include toothbrushes, nail clippers, and razors. Tell him or her not to share needles.
- Talk to your adolescent about safe sex. If your male adolescent is sexually active, tell him or her to use a condom during sex. Sexually active girls should have their male partners wear a condom.
- Do not let your child donate blood. Donations are screened for HBV, but it is best not to donate at all.
- Protect your baby from hepatitis B. You will be checked for hepatitis B during each pregnancy. This is done even if you received the hepatitis B vaccine or were tested before. Your healthcare provider may recommend you get the hepatitis B vaccine if you never received it. You may need to have an HBV infection treated before you give birth. Your baby will need the hepatitis B vaccine at birth if you plan to breastfeed.
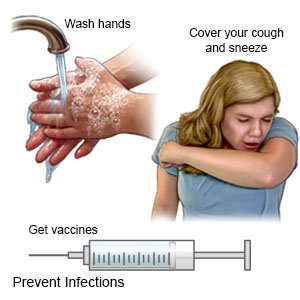
What can I do to prevent the spread of germs?
 |
- Keep your child away from other people while he or she is sick. This is especially important during the first 3 to 5 days of illness.
- Have your child wash his or her hands often. He or she should wash after using the bathroom and before preparing or eating food. Have your child use soap and water. Show him or her how to rub soapy hands together, lacing the fingers. Wash the front and back of the hands, and in between the fingers. The fingers of one hand can scrub under the fingernails of the other hand. Teach your child to wash for at least 20 seconds. Use a timer, or sing a song that is at least 20 seconds. An example is the happy birthday song 2 times. Have your child rinse with warm, running water for several seconds. Then dry with a clean towel or paper towel. Your older child can use hand sanitizer with alcohol if soap and water are not available.

- Remind your child to cover a sneeze or cough. Show your child how to use a tissue to cover his or her mouth and nose. Have your child throw the tissue away in a trash can right away. Then your child should wash his or her hands well or use a hand sanitizer. Show your child how to use the bend of his or her arm if a tissue is not available.
- Tell your child not to share items. Examples include toys, drinks, and food.
- Ask about other vaccines your child needs. Have your child get a yearly flu vaccine as soon as recommended, usually in September or October. Your child should also get at least 1 dose of an updated COVID-19 vaccine. Your child's healthcare provider can tell you other vaccines your child should get, and when to get them.
When should I seek immediate care?
- Your child has a sudden, severe headache and head pressure.
- Your child has new or increased bruising or red or purple dots on his or her skin. He or she may also have bleeding that does not stop easily.
- Your child's abdomen is swollen.
- Your child has severe nausea or cannot stop vomiting.
- You see blood in your child's urine or bowel movements, or he or she vomits blood.
- Your child has new or increased yellowing of the skin or the whites of the eyes.
- Your child has severe pain in his or her upper abdomen.
When should I call my child's doctor?
- The palms of your child's hands are red.
- Your child has a fever.
- Your child has new or increased swelling in his or her legs, ankles, or feet.
- Your child's muscles get smaller and weaker.
- You have questions or concerns about your child's condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your child's care. Learn about your child's health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your child's healthcare providers to decide what care you want for your child. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
Learn more about Hepatitis B
Treatment options
Care guides
- Gender Identity in your Adolescent
- Hemoglobin A1c
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis B Vaccine
- How to Childproof your Home
- Medication Safety for Children
- Promote Healthy Teeth and Gums in Young Children
Symptoms and treatments
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
