Deep Vein Thrombosis
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
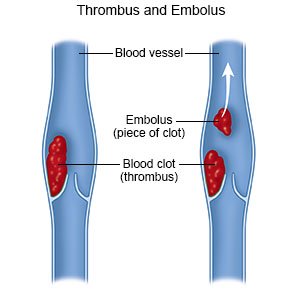
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot that forms in a deep vein of the body. The DVT can break into smaller pieces and travel to your lungs and cause a blockage called a pulmonary embolism. A PE can become life-threatening. It is important to go to all follow-up appointments and to take blood thinners as directed. This is especially important if you were discharged home from the emergency department.
 |
WHILE YOU ARE HERE:
Informed consent
is a legal document that explains the tests, treatments, or procedures that you may need. Informed consent means you understand what will be done and can make decisions about what you want. You give your permission when you sign the consent form. You can have someone sign this form for you if you are not able to sign it. You have the right to understand your medical care in words you know. Before you sign the consent form, understand the risks and benefits of what will be done. Make sure all your questions are answered.
An IV
is a small tube placed in your vein that is used to give you medicine or liquids.
Medicines:
- Blood thinners help prevent the DVT from getting bigger and prevent new clots from forming. While you are taking warfarin or other blood thinners, you may bleed or bruise more easily.
- Clot busters are emergency medicines that work to dissolve blood clots.
Related medications
Tests:
- A D-dimer blood test may be done to check for signs of a blood clot.
- An ultrasound uses sound waves to show pictures on a monitor. An ultrasound may be done to show a clot in your vein.
- A contrast venography is an x-ray of a vein. Contrast liquid is used to make the vein easier to see on the x-ray. Tell a healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast liquid.
Treatment:
- You may need extra oxygen if your blood oxygen level is lower than it should be. You may get oxygen through a mask placed over your nose and mouth or through small tubes placed in your nostrils. Ask your healthcare provider before you take off the mask or oxygen tubing.
- Intermittent pneumatic compression devices have cuffs that are wrapped around each limb. The air pump inflates the cuffs and squeezes your limbs. Then it deflates. The compression helps move blood through your veins towards your heart. The deflating allows blood to flow from your heart through arteries to your limbs.
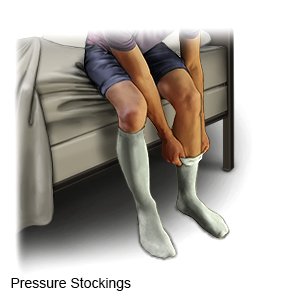
- Compression stockings or sleeves help blood move through your veins toward your heart.
- A vena cava filter may be placed inside your vena cava to treat your DVT. The vena cava is a large vein that brings blood from your lower body up to your heart. The filter may help trap pieces of a blood clot and prevent them from going into your lungs.
- Surgery called a thrombectomy may be done to remove the clot. A procedure called thrombolysis may instead be done to inject a clot buster that helps break the clot apart.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
RISKS:
The DVT can break into smaller pieces. Each piece is called an embolus. The embolus can travel to your lungs and cause a blockage called a pulmonary embolism (PE). A PE can become life-threatening. Increased pressure and decreased blood flow can damage the tissues around the DVT. The valves in the deep veins that allow your blood to flow back to your heart can be damaged. This can cause long-term pain and swelling.
CARE AGREEMENT:
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment.© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Deep Vein Thrombosis
Treatment options
Care guides
Symptoms and treatments
Medicine.com guides (external)
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
