Arginine Vasopressin Disorder
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 4, 2025.
Arginine vasopressin disorder (AVD) is a condition that causes frequent urination. The amount of urine you make is controlled by antidiuretic hormone (ADH). ADH is made in a part of the brain called the hypothalamus. ADH is stored and released by the pituitary gland. The 2 most common types of AVD are arginine vasopressin deficiency (AVP-D) and arginine vasopressin resistance (AVP-R).
DISCHARGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Call your local emergency number (911 in the US) or have someone call if:
- You feel weak and dizzy, or you have fainted.
- You are confused or have trouble staying awake.
- You have a seizure.
Seek care immediately if:
- You have a fast or irregular heartbeat.
- You are more thirsty than usual, and your thirst wakes you from sleep.
- You have muscle cramps or weakness.
- You have nausea or are vomiting.
- You urinate large amounts of light yellow or clear urine.
- You are losing weight daily without trying.
- You are dizzy, have headaches, or are easily irritated.
Call your doctor if:
- You have a dry mouth or cracked lips.
- You are more tired than usual.
- You have new headaches or vision changes.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Related medications
Treatment options
The following list of medications are related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
Medicines:
You may need any of the following:
- Vasopressin is a medicine that is similar to ADH. This will help decrease the amount you urinate.
- Certain diuretics, such as thiazide diuretics, can help your kidneys control the amount you urinate.
- NSAIDs can be used to decrease the amount you urinate.
Take your medicine as directed.
Contact your healthcare provider if you think your medicine is not helping or if you have side effects. Tell your provider if you are allergic to any medicine. Keep a list of the medicines, vitamins, and herbs you take. Include the amounts, and when and why you take them. Bring the list or the pill bottles to follow-up visits. Carry your medicine list with you in case of an emergency.
Manage your symptoms:
- Weigh yourself each day. Weigh yourself at the same time each day, on the same scale. Rapid weight loss can be a sign of fluid loss in your body.
- Drink liquids as directed. Keep track of how much liquids you drink and how often you urinate. This helps you stay hydrated and prevents too much water loss. Follow your healthcare provider's instructions about how much liquid to have each day and which liquids are best for you.
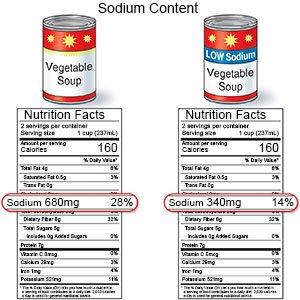
- Lower your sodium (salt) intake as directed. Too much sodium can affect your fluid balance. Reduced sodium will prevent your body from holding onto excess water. Check labels to find low-sodium or no-salt-added foods. Ask your provider how much sodium is safe for you to have in a day.
- Choose a variety of healthy foods. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain breads, low-fat dairy products, lean meats, and fish. Your provider or dietitian may recommend that you limit protein foods such as milk, fish, and meat. Protein makes your kidneys work harder.

- Limit or do not drink alcohol or caffeine. Alcohol and caffeine make you urinate more and increase your risk for dehydration.
Follow up with your doctor as directed:
You may need to return for more blood and urine tests to check if treatment is working. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
© Copyright Merative 2025 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.
The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.
Learn more about Arginine Vasopressin Disorder
Treatment options
Care guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
